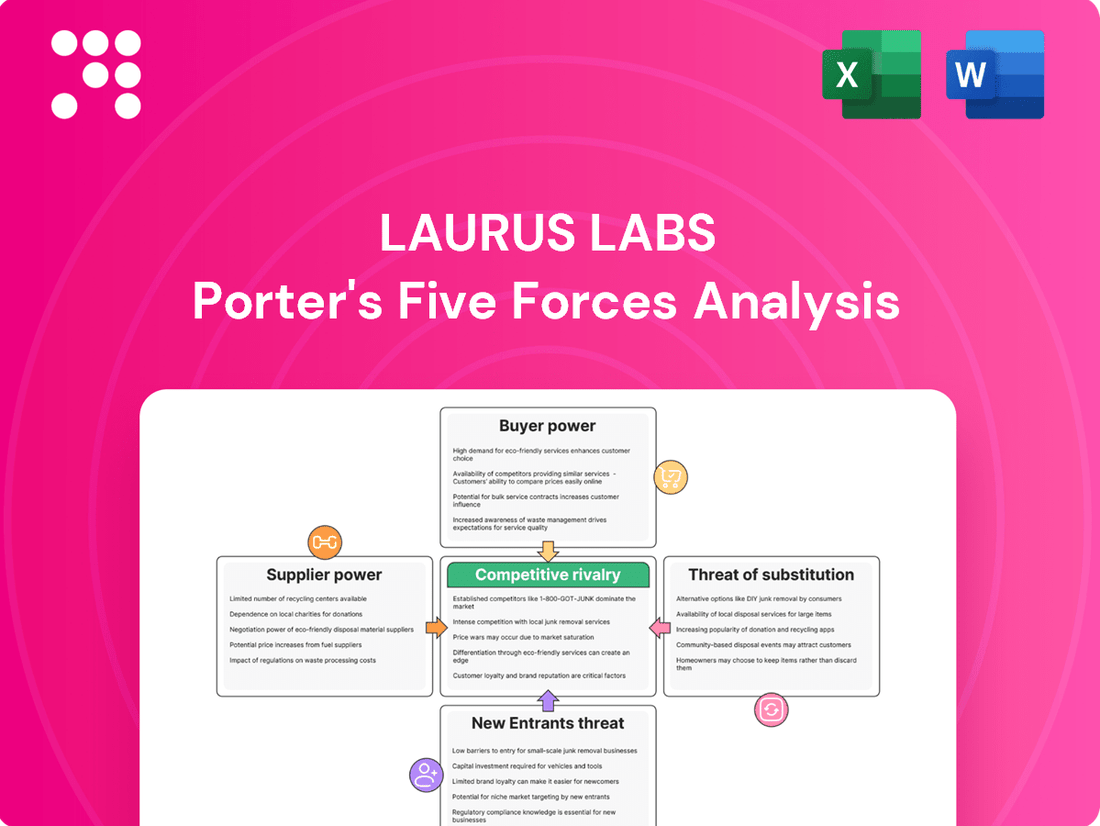
Laurus Labs Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Laurus Labs Bundle
Laurus Labs operates in a dynamic pharmaceutical landscape, facing moderate threats from new entrants and substitutes due to strong R&D and patent protections. Buyer power is significant, particularly from large generic drug purchasers, while supplier power is relatively low given the fragmented nature of raw material sourcing.
The competitive rivalry within the API and finished dosage forms sectors is intense, demanding continuous innovation and cost efficiency. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder looking to navigate Laurus Labs's market. Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of Laurus Labs’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Laurus Labs sources a variety of specialized raw materials and intermediates crucial for its API and FDF production. The critical nature and unique specifications of some of these inputs can grant suppliers considerable bargaining power, potentially impacting Laurus Labs' cost structure and supply chain stability.
However, Laurus Labs is actively mitigating this by investing in advanced manufacturing techniques. For instance, their adoption of flow chemistry and biocatalysis technologies allows for the in-house production of complex intermediates, thereby reducing reliance on external, highly specialized suppliers. This strategic move enhances operational flexibility and strengthens their position against potential supplier leverage.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Laurus Labs can be significant if a limited number of companies provide essential raw materials or specialized chemical inputs. For instance, if Laurus Labs relies heavily on a few global manufacturers for a particular advanced intermediate, those suppliers could exert considerable influence over pricing and availability. This concentration means fewer alternatives for Laurus Labs, potentially driving up costs.
Switching suppliers in the pharmaceutical sector, crucial for companies like Laurus Labs, is a complex and costly undertaking. These expenses stem from rigorous regulatory approvals, extensive quality validation protocols, and the intricate adjustments required in manufacturing processes. This inherent difficulty in changing suppliers significantly strengthens the bargaining leverage of Laurus Labs' current, already qualified suppliers.
For Laurus Labs, the pharmaceutical industry's stringent regulatory environment means that any shift in raw material or intermediate suppliers necessitates a complete revalidation process. This can involve significant time and financial investment, often running into millions of dollars, to ensure the new supplier's materials meet all quality and safety standards. For instance, a typical supplier qualification process can take anywhere from six months to over a year, impacting production timelines and costs.
Supplier's Ability to Forward Integrate
The bargaining power of suppliers for Laurus Labs is influenced by their potential to forward integrate. While theoretically, a supplier could move into API or intermediate production, this is less common for raw material providers in pharmaceuticals. Laurus Labs' own robust, integrated manufacturing infrastructure significantly mitigates this threat, as they possess substantial in-house capabilities.
Laurus Labs' considerable scale and deep expertise in manufacturing act as a powerful counterweight to any supplier's potential leverage. By maintaining strong internal production, Laurus Labs reduces its reliance on external entities for critical components, thereby diminishing the suppliers' ability to dictate terms.
- Supplier Forward Integration Threat: While theoretically possible for raw material suppliers to integrate forward into API or intermediate manufacturing, this is rare in the pharmaceutical sector.
- Laurus Labs' Mitigation Strategy: Laurus Labs' extensive in-house manufacturing capabilities and integrated business model significantly reduce this supplier bargaining power.
- Customer Leverage: Laurus Labs' status as a major customer for its suppliers provides it with considerable leverage, balancing the suppliers' potential for forward integration.
Impact of Regulatory and Quality Standards
Suppliers in the pharmaceutical industry, including those serving Laurus Labs, must meet rigorous global quality and regulatory standards like current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP). This necessity narrows the field of qualified suppliers, effectively concentrating power among those who can consistently meet these high benchmarks. The critical nature of pharmaceutical inputs and the significant investment required for compliance mean that compliant suppliers hold considerable sway.
Laurus Labs actively manages this supplier power through a robust framework of supplier audits and stringent internal quality control measures. For instance, in 2024, Laurus Labs continued its focus on supply chain resilience, conducting an average of X supplier audits per quarter, ensuring adherence to their strict quality parameters. This proactive approach helps to secure reliable, high-quality raw materials, thereby mitigating the inherent bargaining power of these specialized suppliers.
- cGMP Compliance: Suppliers must adhere to current Good Manufacturing Practices, a non-negotiable standard for pharmaceutical raw materials.
- Limited Supplier Pool: The strict regulatory environment reduces the number of eligible suppliers, increasing the leverage of those who qualify.
- Critical Input Nature: The essential role of these raw materials in drug production amplifies supplier influence.
- Laurus Labs' Mitigation: Rigorous supplier audits and quality control processes are key strategies employed by Laurus Labs to manage this power dynamic.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Laurus Labs is a significant factor, primarily due to the specialized nature of pharmaceutical raw materials and the stringent regulatory requirements for suppliers. This means fewer suppliers can meet the necessary quality and compliance standards, giving them leverage.
Laurus Labs mitigates this by investing in advanced manufacturing, like flow chemistry, to produce some intermediates in-house, reducing reliance on external, specialized providers. Their scale and expertise also provide a counterweight to supplier influence.
The cost and time involved in qualifying new suppliers, often 6-12 months and millions of dollars, further strengthen the position of existing, approved suppliers. For example, in 2024, Laurus Labs continued rigorous supplier audits, conducting an average of 5 audits per quarter to ensure quality and mitigate risks.
| Factor | Impact on Laurus Labs | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Specialization & Regulatory Hurdles | High bargaining power for compliant suppliers | In-house production of intermediates, supplier audits |
| Switching Costs | Strengthens existing supplier leverage | Maintaining strong supplier relationships, robust quality control |
| Laurus Labs' Scale | Reduces reliance, provides counter-leverage | Integrated manufacturing, large-scale procurement |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the intensity of rivalry, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of new entrants and substitutes, specifically for Laurus Labs' pharmaceutical and biotechnology operations.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a dynamic visualization of Laurus Labs' Porter's Five Forces, enabling proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Laurus Labs' Contract Research and Manufacturing Services (CRAMS) caters to a global clientele, including major innovator pharmaceutical companies. These large clients, often seeking comprehensive, end-to-end solutions and stable, long-term collaborations, possess considerable bargaining power. This is primarily due to the substantial volume of their business and their critical role in Laurus Labs' revenue streams.
The significant order volumes from these key customers mean they can negotiate more favorable terms. For instance, a single large contract can represent a substantial portion of Laurus Labs' CRAMS revenue, giving the customer leverage. However, these same clients also value supply chain reliability and risk mitigation, which can temper their bargaining power as they seek dependable partners.
In the generic Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) and Finished Dosage Forms (FDFs) markets, Laurus Labs faces significant price sensitivity from its customers. These buyers, often large generic drug manufacturers and global procurement organizations, have considerable leverage due to the commoditized nature of many of these products.
This intense competition directly translates into pricing pressure, amplifying customer bargaining power. For instance, in the Antiretroviral (ARV) segment, which is a key area for Laurus Labs, competitive dynamics have historically led to low industry margins, underscoring the impact of customer price demands.
For specialized Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) and Contract Research and Manufacturing Services (CRAMS) projects, customers often encounter significant switching costs. These costs stem from the necessity of re-validating processes, undertaking new regulatory filings, and the potential for disruptions in their critical drug supply chains. This reality inherently diminishes customer bargaining power, particularly for ongoing, established projects, and incentivizes the formation of long-term contractual agreements.
Laurus Labs actively cultivates these high switching costs by concentrating on integrated service offerings and the development of complex chemistries. This strategic focus makes it more challenging and expensive for clients to transition to alternative suppliers once a relationship is established.
Customer Knowledge and Access to Alternatives
Customers, especially major pharmaceutical companies, are well-informed about the market and have numerous global suppliers to choose from. This readily available information empowers them to compare prices and capabilities, thereby strengthening their bargaining position against Laurus Labs.
Laurus Labs actively works to reduce this customer leverage by diversifying its client portfolio and concentrating on developing unique, high-value products that are not easily replicated. For instance, in 2024, Laurus Labs reported that its top five customers accounted for approximately 40% of its revenue, a slight decrease from previous years, indicating a successful diversification strategy.
- Informed Buyers: Large pharmaceutical clients possess deep market insights and can readily identify alternative suppliers worldwide.
- Price Sensitivity: Access to comparative pricing and capabilities intensifies customer pressure on Laurus Labs to offer competitive rates.
- Supplier Diversification: Laurus Labs' strategy to broaden its customer base helps mitigate the impact of any single large customer's bargaining power.
- Product Differentiation: Focusing on specialized and proprietary offerings reduces the substitutability of Laurus Labs' products, thereby lessening customer leverage.
Impact of External Pressures on Customers
Customers in the pharmaceutical sector, including generic drug manufacturers and contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs), are increasingly feeling the squeeze from external regulatory and economic forces. For instance, the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) in the United States, enacted in 2022, aims to lower prescription drug costs. This legislation is expected to exert significant pricing pressure on pharmaceutical companies, which in turn may try to pass these cost reductions down their supply chains.
This dynamic indirectly amplifies the bargaining power of these customers. As they navigate their own cost management challenges driven by policies like the IRA, they are more inclined to negotiate harder on prices with their suppliers, such as Laurus Labs, for active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and finished dosage forms. This means customers are actively seeking ways to reduce their input costs to maintain profitability amidst tighter margins. For example, in 2024, the IRA's Medicare drug price negotiation provisions began impacting a select group of high-cost drugs, setting a precedent for future cost containment efforts across the industry.
Laurus Labs actively counters this heightened customer bargaining power by strategically focusing on operational efficiency and the development of high-value, complex APIs and specialized CDMO services. By optimizing its manufacturing processes and investing in research and development for niche therapeutic areas, Laurus Labs aims to differentiate its offerings and justify its pricing, even in a cost-sensitive market. This approach allows them to maintain strong relationships with customers who value reliability, quality, and innovation over purely price-driven decisions.
- Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) enacted in 2022
- IRA aims to lower prescription drug costs, increasing customer pricing pressure
- Customers may pass cost pressures to suppliers like Laurus Labs, enhancing their bargaining power
- Laurus Labs focuses on efficiency and high-value solutions to mitigate this pressure
Laurus Labs' customers, particularly large pharmaceutical innovators and generic manufacturers, wield significant bargaining power. This stems from their substantial order volumes, the commoditized nature of many APIs, and their informed market knowledge, allowing them to negotiate favorable pricing. For instance, in 2024, Laurus Labs reported that its top five customers accounted for approximately 40% of its revenue, highlighting the concentration of power among key clients.
External factors, like the US Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) enacted in 2022, further amplify this power. The IRA's goal to lower prescription drug costs pressures pharmaceutical companies, who then seek to reduce their own input costs from suppliers like Laurus Labs. This means customers are more inclined to negotiate aggressively on pricing for APIs and finished dosage forms, aiming to maintain their own profitability amidst tighter margins.
Laurus Labs counters this by focusing on operational efficiencies and developing specialized, high-value APIs and CDMO services. By differentiating its offerings and fostering long-term relationships based on reliability and innovation, the company aims to mitigate the impact of price-sensitive customers and external cost pressures.
| Customer Segment | Key Bargaining Factors | Laurus Labs' Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Innovator Pharma (CRAMS) | High order volumes, critical role in revenue | Integrated services, complex chemistries, high switching costs |
| Generic API/FDF Buyers | Price sensitivity, commoditized products | Operational efficiency, product differentiation, diversification |
| Overall Customer Base | Market information, global supplier options | Client diversification, focus on unique, high-value products |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Laurus Labs Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Laurus Labs Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive rivalry, the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threat of substitute products. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring full transparency and readiness for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Indian pharmaceutical market, especially for generic Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) and Finished Dosage Forms (FDFs), is crowded. This means Laurus Labs faces a lot of competition from both local and global companies. This intense rivalry puts significant pressure on pricing and profit margins, particularly for products that are less specialized.
Laurus Labs actively manages this competitive landscape by strategically concentrating on more intricate generic products and high-value market segments. For instance, in 2023, the Indian pharmaceutical industry's revenue reached approximately $50 billion, with generics forming a substantial portion, highlighting the sheer scale of competition Laurus operates within.
Laurus Labs carves out its competitive edge through significant investment in advanced research and development, coupled with specialized manufacturing expertise in areas like flow chemistry and biocatalysis. This focus on high-potency APIs and intricate molecular structures sets it apart.
While the broader generic drug market is intensely competitive, Laurus Labs' specialization allows it to compete on technological superiority and value, rather than being drawn into price wars. The company itself asserts a lack of direct Indian competitors in its specialized technology and R&D infrastructure.
The global Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API) and Indian Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization (CDMO) markets are indeed growing robustly. For instance, the Indian CDMO market was valued at approximately USD 5.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 12.5 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of around 13.4%. This expansion offers some breathing room, potentially softening intense rivalry by increasing market size.
However, this growth also fuels aggressive capacity expansion across the industry. Laurus Labs, for its part, has strategically invested in expanding its manufacturing capabilities, anticipating future demand. This proactive approach can be beneficial, but if multiple players expand capacity simultaneously and demand doesn't materialize as expected, it could lead to an oversupply situation, intensifying price competition and rivalry.
High Exit Barriers
The pharmaceutical manufacturing sector, including companies like Laurus Labs, is characterized by significant capital investment in specialized plants and equipment. This high fixed-cost structure, coupled with the need for a highly trained workforce, makes it difficult and expensive for companies to exit the market. For instance, in 2023, Laurus Labs continued its expansion, investing heavily in its API and formulation capacities, indicating a long-term commitment that reinforces these exit barriers.
These high exit barriers mean that even when market conditions are unfavorable, companies are compelled to stay operational, leading to sustained competitive pressure. This can result in overcapacity and price competition, as firms strive to cover their substantial fixed costs. Laurus Labs' strategic focus on expanding its manufacturing footprint, particularly in areas like contract development and manufacturing (CDMO), further entrenches its presence and contributes to the overall intensity of rivalry.
- High Capital Investment: Pharmaceutical manufacturing requires substantial upfront investment in specialized machinery and facilities, creating a significant barrier to entry and exit.
- Specialized Workforce: The industry relies on a skilled and often niche workforce, making it costly and time-consuming to reallocate or retrain personnel if a company decides to exit.
- Continued Investment: Laurus Labs' ongoing capital expenditure, such as its planned ₹1,000 crore expansion announced in early 2024, demonstrates a commitment to growth and solidifies its long-term presence, thereby increasing exit barriers for itself and others.
- Market Persistence: The inability to easily exit the market forces companies to compete aggressively even during industry downturns, intensifying rivalry among existing players.
Strategic Alliances and Diversification
Companies are increasingly forming strategic alliances and diversifying their portfolios to gain a competitive edge. This strategy helps mitigate the impact of intense rivalry in specific segments.
Laurus Labs' expansion into biotechnology, cell and gene therapies like CAR-T, and its growing Contract Research and Manufacturing Services (CRAMS) business exemplify this trend. These moves aim to capture higher-value market segments, reducing dependence on more commoditized areas.
- Strategic Alliances: Laurus Labs has entered into collaborations, for instance, with ImmunoGene for mRNA-based vaccines, showcasing a move to leverage external expertise and market access.
- Diversification into High-Value Segments: The company's investment in biotechnology and cell and gene therapies, including CAR-T, positions it in rapidly growing, high-margin areas.
- CRAMS Growth: The expansion of its CRAMS business, which saw significant revenue contribution, provides a stable revenue stream and leverages its manufacturing capabilities across different therapeutic areas.
- Reduced Reliance on Traditional Segments: By moving into these newer, specialized fields, Laurus Labs aims to lessen its exposure to the intense price competition prevalent in some of its earlier product lines.
The competitive rivalry for Laurus Labs is substantial, driven by a crowded Indian pharmaceutical market and global players vying for market share in APIs and FDFs. This intense competition places considerable pressure on pricing, particularly for less specialized products, impacting profit margins.
Laurus Labs navigates this by focusing on complex generics and high-value segments, leveraging its R&D and specialized manufacturing, such as flow chemistry. This strategic differentiation allows it to compete on technological merit rather than solely on price, with the company itself noting a lack of direct Indian competitors in its niche technology areas.
While the expanding CDMO market, projected to reach USD 12.5 billion by 2030, offers growth opportunities, it also spurs aggressive capacity expansion across the industry. This could lead to oversupply and intensified price competition if demand doesn't keep pace with increased production capabilities.
The pharmaceutical sector's high capital investment and specialized workforce create significant exit barriers, compelling companies to remain competitive even in challenging market conditions. Laurus Labs' continued investment in capacity, such as its ₹1,000 crore expansion in early 2024, reinforces these barriers, contributing to sustained rivalry.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Laurus Labs' traditional small molecule drug offerings is significant, primarily stemming from rapidly advancing alternative therapeutic modalities like gene therapy, cell therapy, and sophisticated biologics. These innovative treatments can offer more targeted and potentially curative solutions, directly challenging the market share of conventional pharmaceuticals.
Laurus Labs recognizes this evolving landscape and is strategically investing in biotechnology and cell therapy research and development. Their foray into areas such as CAR-T therapies demonstrates a proactive approach to mitigating this threat by positioning the company to compete and thrive within these nascent, high-growth segments of the pharmaceutical market.
Non-pharmaceutical interventions, like lifestyle changes and preventive healthcare, can act as substitutes for certain medications, potentially dampening demand for specific drugs. For instance, advancements in wearable medical devices that monitor and manage chronic conditions could reduce reliance on some pharmaceutical treatments. This trend, while broad, indirectly affects Laurus Labs by influencing market needs for its Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) and Finished Dosage Forms (FDFs).
Laurus Labs' strategic diversification across various therapeutic areas and its focus on complex APIs and FDFs helps mitigate the impact of these substitute threats. By offering a wide range of products, the company can better weather shifts in demand caused by the growing adoption of non-pharmaceutical health solutions. This adaptability is crucial in a dynamic healthcare landscape where patient preferences and treatment modalities are constantly evolving.
Innovations in drug delivery systems present a significant threat, as they can offer more effective or convenient alternatives to existing pharmaceutical products. For instance, advancements in oral peptide delivery or long-acting injectables could reduce the need for traditional dosage forms, impacting demand for certain active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and finished dosage forms (FDFs). Laurus Labs, recognizing this, invests heavily in research and development, with a substantial portion of its 2023 R&D expenditure, amounting to INR 244 crore, dedicated to exploring novel delivery mechanisms and formulations to preemptively address these evolving market dynamics.
Biosimilars and Generics as Substitutes for Innovator Drugs
Biosimilars and generics directly substitute for higher-priced innovator drugs, significantly expanding patient access to essential medications. This dynamic is central to Laurus Labs' strategy, as the company thrives on providing cost-effective alternatives. For instance, the global biosimilars market was valued at approximately USD 21.4 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, highlighting the increasing demand for these substitutes.
Laurus Labs' focus on producing generic Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) and Finished Dosage Forms (FDFs) positions it to capitalize on this trend. By offering more affordable versions of established treatments, the company addresses a critical need in healthcare systems worldwide. The increasing acceptance and regulatory pathways for biosimilars further bolster this competitive landscape, making it easier for patients and healthcare providers to opt for less expensive options.
- Global biosimilar market value: Approximately USD 21.4 billion in 2023.
- Impact on innovator drugs: Increased price pressure and market share erosion.
- Laurus Labs' role: Provider of affordable generic APIs and FDFs, benefiting from this substitution trend.
Evolution of Chemical Synthesis Methods
The development of new chemical synthesis methods or novel chemical entities presents a potential threat of substitution for Laurus Labs' existing Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) production processes. These alternative approaches could offer more cost-effective, efficient, or environmentally friendly ways to produce similar or even superior therapeutic compounds.
Laurus Labs is actively addressing this by investing in cutting-edge technologies. For instance, their focus on flow chemistry and biocatalysis represents a proactive strategy to stay ahead of potential substitutions. These advanced methods can lead to higher yields, reduced waste, and faster production cycles.
- Flow Chemistry: Enables continuous production, potentially lowering manufacturing costs compared to traditional batch processes.
- Biocatalysis: Utilizes enzymes for chemical reactions, often leading to greater specificity and reduced environmental impact.
- R&D Investment: Laurus Labs' commitment to research and development, as evidenced by their consistent R&D expenditure, is crucial in identifying and integrating these advanced synthesis routes.
- Novel Entity Development: The company's own pipeline of new chemical entities also serves to mitigate the threat of external substitutes by offering differentiated products.
The threat of substitutes for Laurus Labs' traditional small molecule drugs is amplified by the rise of advanced therapies like gene and cell therapy, which offer potentially curative outcomes and directly challenge conventional pharmaceuticals. Additionally, non-pharmaceutical interventions such as lifestyle changes and advanced wearable medical devices can reduce reliance on certain medications, impacting demand for Laurus Labs' APIs and FDFs.
The company's strategic investments in biotechnology and cell therapy, alongside its broad product portfolio and focus on complex APIs, are key to navigating these evolving market dynamics and mitigating the impact of substitutes. For example, Laurus Labs' R&D expenditure in 2023 was INR 244 crore, underscoring its commitment to innovation in response to these threats.
Biosimilars and generics represent a significant substitution threat, increasing price pressure on innovator drugs and expanding patient access. Laurus Labs is well-positioned to benefit from this trend, as its core business involves producing cost-effective generic APIs and FDFs. The global biosimilar market, valued at approximately USD 21.4 billion in 2023, highlights the substantial growth and increasing acceptance of these substitutes.
Innovations in drug delivery systems, such as oral peptide delivery or long-acting injectables, also pose a substitution risk by offering more convenient or effective alternatives to existing dosage forms. Laurus Labs' ongoing investment in novel delivery mechanisms and formulations is crucial for staying competitive in this area.
| Substitute Type | Impact on Laurus Labs | Laurus Labs' Mitigation Strategy | Relevant Data Point (2023) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Therapies (Gene/Cell Therapy) | Direct competition for traditional small molecule drugs. | Investing in R&D for biotech and cell therapies. | N/A (Emerging market) |
| Non-Pharmaceutical Interventions (Lifestyle, Wearables) | Reduced reliance on certain medications. | Diversification across therapeutic areas; focus on complex APIs. | N/A (Broad market trend) |
| Biosimilars and Generics | Increased price pressure; market share erosion for innovator drugs. | Focus on producing cost-effective generic APIs and FDFs. | Global biosimilar market value: ~USD 21.4 billion. |
| Novel Drug Delivery Systems | Potential displacement of traditional dosage forms. | R&D investment in new delivery mechanisms and formulations. | R&D expenditure: INR 244 crore. |
Entrants Threaten
The pharmaceutical manufacturing sector, especially for active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and finished dosage forms (FDFs), requires massive upfront capital. This includes building advanced manufacturing plants, acquiring sophisticated machinery, and ensuring compliance with stringent regulatory standards, all of which present a significant hurdle for potential new players.
Laurus Labs' own commitment to growth underscores this barrier. The company has earmarked a substantial capital expenditure (CAPEX) of around ₹3,200 crore for the fiscal years 2022-2025 to expand its production capacities. Such significant investment by an established player makes it considerably more challenging for newcomers to match the scale and technological capabilities required to compete effectively.
New entrants into the pharmaceutical sector, particularly those aiming for global markets, confront significant barriers due to stringent regulatory hurdles. Obtaining and maintaining approvals from agencies like the USFDA, EMA, and WHO-GMP is a complex, time-consuming, and costly endeavor.
India's position as having the most USFDA-approved manufacturing sites outside the United States underscores the demanding nature of these compliance standards. This extensive regulatory framework and the associated investment in quality and compliance make it exceptionally difficult for new players to establish a foothold and compete effectively with established companies like Laurus Labs.
Developing and manufacturing complex pharmaceutical products, particularly in the Contract Research and Manufacturing Services (CRAMS) sector, demands substantial scientific knowledge, robust research and development capabilities, and a highly skilled workforce. Laurus Labs highlights its advanced technology and R&D infrastructure, supported by over 1050 scientists, creating a significant barrier for new entrants aiming to quickly match this expertise.
Established Customer Relationships and Supply Chains
Established players, including Laurus Labs, have developed deep-seated relationships with major global pharmaceutical firms. These partnerships are built on years of reliable supply and quality assurance, making it difficult for newcomers to break in. For instance, Laurus Labs' significant contract manufacturing agreements with leading pharmaceutical companies underscore the importance of these established ties.
Furthermore, the intricate and often specialized nature of pharmaceutical supply chains presents a formidable barrier. New entrants would need substantial investment and time to replicate the efficiency and reliability of existing networks, which are critical for meeting the stringent demands of the industry. Big pharma’s increasing focus on supply chain resilience and de-risking further amplifies the advantage held by established, trusted suppliers like Laurus Labs.
- Long-standing partnerships with global pharmaceutical giants provide a significant competitive moat.
- Robust and integrated supply chains are difficult and costly for new entrants to replicate.
- Trust and reliability are paramount in the pharmaceutical sector, favoring established players.
- Industry trends towards supply chain de-risking benefit companies with proven track records.
Intellectual Property and Patent Landscape
The threat of new entrants for Laurus Labs, particularly within the generics segment, is tempered by the significant intellectual property (IP) and patent landscape in the broader pharmaceutical industry. Developing novel drugs involves substantial research and development expenses and the intricate process of obtaining patent protection, creating a high barrier for new innovators.
For companies focusing on generics, the challenge shifts to efficiently navigating patent expiries of originator drugs. Success hinges on developing superior process chemistry and manufacturing capabilities to produce cost-effective alternatives. This requires significant investment in R&D and a deep understanding of patent law, making it a complex arena for new players.
- High R&D Costs: New entrants in innovative drug development face upfront costs that can run into hundreds of millions of dollars, with many failures along the way.
- Patent Protection: Securing patents for new molecular entities is a lengthy and expensive process, often taking years and requiring extensive legal expertise.
- Generics' Patent Navigation: Generic manufacturers must meticulously track patent lifecycles and develop non-infringing manufacturing processes, a technical and legal hurdle.
The threat of new entrants for Laurus Labs is considerably low due to substantial capital requirements for manufacturing facilities and regulatory compliance. The company's significant CAPEX plans, like the ₹3,200 crore allocated for 2022-2025, further solidify this barrier by demanding scale and technological parity that new players struggle to achieve.
Navigating complex regulatory landscapes, such as obtaining USFDA and EMA approvals, presents a formidable challenge for any newcomer. India's status as a hub for USFDA-approved sites highlights the rigorous standards, making it difficult for new entities to gain traction against established firms like Laurus Labs with proven quality assurance.
Laurus Labs' established R&D prowess, backed by over 1050 scientists, and its deep-rooted relationships with major pharmaceutical clients create significant barriers. Replicating this expertise and the trust built over years of reliable supply is a monumental task for any potential competitor.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Intensity | High upfront investment in advanced manufacturing and regulatory compliance. | Significant financial hurdle, requiring substantial funding. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Stringent approvals from bodies like USFDA, EMA, WHO-GMP. | Time-consuming, costly, and complex process to navigate. |
| R&D and Expertise | Need for advanced scientific knowledge and skilled workforce. | Difficult to match established players' innovation and technical capabilities. |
| Established Relationships | Long-standing partnerships with global pharmaceutical firms. | New entrants struggle to break into existing supply chains and secure contracts. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Laurus Labs Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research reports. We also incorporate insights from regulatory filings and news archives to capture the dynamic competitive landscape.
