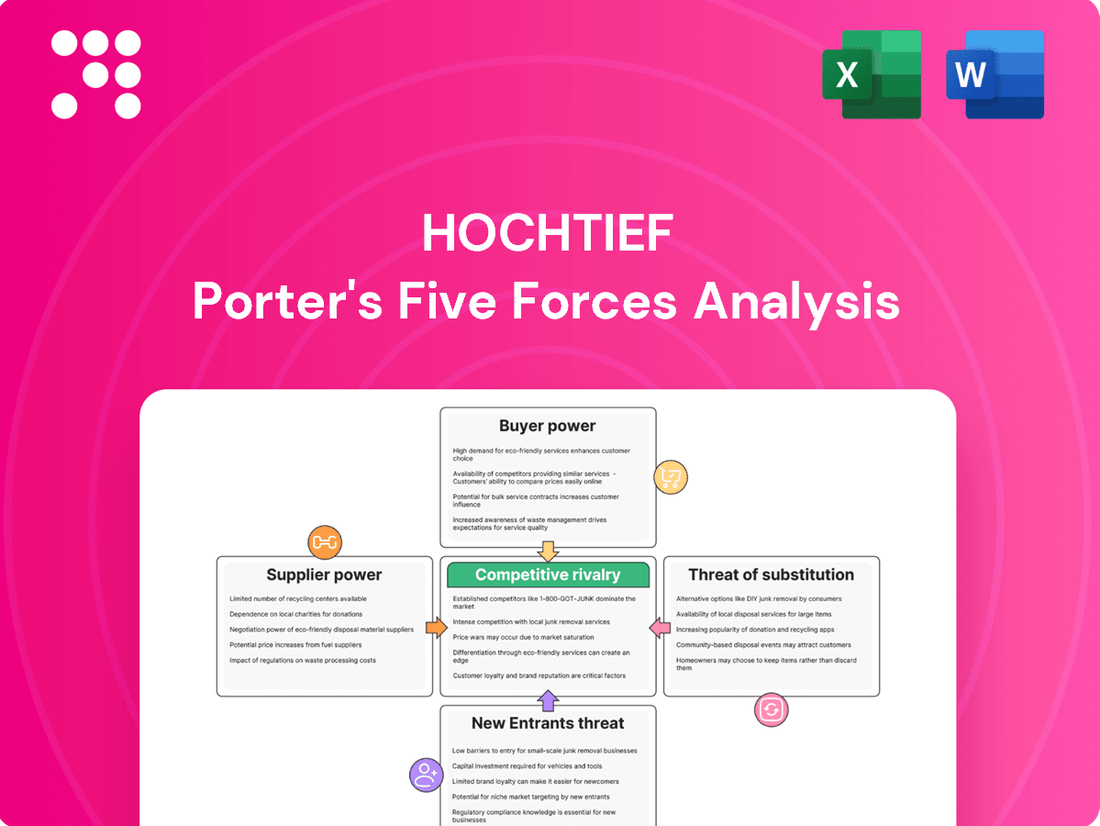
Hochtief Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Hochtief Bundle
Hochtief navigates a complex construction landscape shaped by powerful buyer bargaining, intense rivalry, and the constant threat of new entrants. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder. The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis offers a deep dive into these pressures, providing a strategic roadmap for success.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of Hochtief’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
HOCHTIEF's reliance on a small number of specialized suppliers for critical infrastructure project materials significantly strengthens supplier bargaining power. In 2024, the construction sector observed a concentrated market for essential materials such as aggregate, asphalt, and concrete, where a few dominant regional suppliers controlled substantial market share.
This limited availability of alternatives for crucial, often bespoke, components means these suppliers can exert considerable influence over HOCHTIEF. The scarcity of viable options for specialized materials directly translates into increased leverage for these suppliers in price negotiations and contract terms.
The construction sector, and by extension HOCHTIEF, is currently facing significant headwinds due to ongoing supply chain disruptions and dramatic fluctuations in material costs. Events worldwide have led to delays and price spikes for key inputs such as steel, cement, and timber, directly affecting project schedules and financial outcomes.
This environment of uncertainty regarding both the cost and availability of materials significantly bolsters the bargaining power of suppliers. Those who can guarantee consistent delivery and stable pricing, even amidst these global challenges, are in a much stronger position to dictate terms. For instance, in early 2024, steel prices saw an average increase of 15% compared to the previous year, a direct consequence of increased energy costs and limited production capacity in several key regions.
HOCHTIEF's significant involvement in large-scale infrastructure projects, including transportation and energy, inherently creates a dependence on specialized and often critical materials. This reliance means that suppliers of these unique inputs can wield substantial influence.
The booming data center construction sector exemplifies this, driving intense demand for specialized components such as advanced cooling systems and high-strength structural materials. This heightened demand for critical inputs directly translates into increased bargaining power for the suppliers of these specialized products.
Potential for Forward Integration by Suppliers
The potential for suppliers to integrate forward into construction activities, thereby increasing their bargaining power against HOCHTIEF, is a notable consideration. While raw material suppliers typically lack this capability, specialized component manufacturers might explore offering integrated solutions. This would directly reduce HOCHTIEF's leverage by creating a more direct competitor in certain project phases.
For instance, a major provider of advanced building management systems could potentially expand to offer installation and maintenance services, bypassing traditional contracting roles. This move would shift value towards the supplier and away from the general contractor like HOCHTIEF.
- Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers of specialized components or services could integrate forward into construction, offering end-to-end solutions.
- Impact on HOCHTIEF: This would diminish HOCHTIEF's negotiating power and potentially increase project costs.
- Mitigating Factors: The sheer complexity and global scale of HOCHTIEF's projects, involving diverse trades and logistics, may act as a significant barrier to widespread supplier forward integration.
Impact of Labor Shortages on Supplier Capacity
Ongoing skilled labor shortages in the construction sector are increasingly impacting supplier capacity, a critical factor in Hochtief's bargaining power of suppliers analysis. These shortages mean suppliers might struggle to produce or deliver materials efficiently. For instance, a report from the Bureau of Labor Statistics in early 2024 indicated a significant gap in skilled trades, directly affecting manufacturing and logistics within the supply chain.
This strain on suppliers translates to reduced availability of key construction materials and longer lead times. Consequently, suppliers facing these internal labor challenges gain leverage in their dealings with buyers like Hochtief. They can command higher prices and dictate terms more effectively, especially for specialized or in-demand components.
- Skilled Labor Gap: Persistent shortages in skilled trades, as highlighted by industry surveys in 2024, directly limit supplier production output.
- Increased Lead Times: Labor constraints lead to extended delivery schedules for essential construction materials, amplifying supplier negotiation power.
- Cost Pressures: Suppliers may pass on increased labor costs and operational inefficiencies to buyers, impacting project budgets.
- Supply Chain Resilience: The ongoing labor challenges are projected to continue into 2025, necessitating proactive supply chain management strategies for companies like Hochtief.
HOCHTIEF faces significant supplier bargaining power due to the concentrated nature of specialized material markets and ongoing supply chain volatility. In 2024, the construction industry saw price increases for key materials like steel, averaging 15% year-over-year, driven by energy costs and production limits. This environment, coupled with skilled labor shortages impacting supplier capacity, allows suppliers to dictate terms and command higher prices, particularly for critical components needed in large-scale infrastructure and data center projects.
| Factor | Impact on HOCHTIEF | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Limited alternatives increase supplier leverage. | Concentrated markets for aggregate, asphalt, concrete. |
| Material Price Volatility | Uncertainty in cost and availability of steel, cement, timber. | Steel prices up 15% in early 2024 due to energy costs. |
| Skilled Labor Shortages | Reduced supplier capacity, longer lead times, higher costs. | Bureau of Labor Statistics data shows significant skilled trades gap. |
| Demand for Specialized Materials | Heightened demand in sectors like data centers strengthens supplier power. | Increased demand for advanced cooling systems, high-strength materials. |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the competitive intensity within the construction industry for Hochtief, examining supplier power, buyer bargaining, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing firms.
Quickly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of Hochtief's industry landscape.
Customers Bargaining Power
HOCHTIEF's engagement with large-scale public clients, such as governments and municipalities, significantly influences its bargaining power. These entities often commission massive infrastructure projects, including transportation networks and urban developments, granting them considerable leverage. For instance, in 2024, major government infrastructure spending initiatives worldwide continued to shape contract negotiations, with public bodies often setting stringent terms and conditions.
The sheer scale and strategic importance of these public projects mean that HOCHTIEF faces a concentrated customer base where each client holds substantial sway. This dynamic is further amplified by competitive bidding processes, a common practice for public sector contracts, which inherently drives down margins and increases customer power. The ability of these clients to dictate project specifications, payment schedules, and risk allocation underscores their strong bargaining position in the market.
HOCHTIEF frequently engages in long-term infrastructure projects, which, while offering stability, also empower clients. These extended commitments can give customers significant leverage during negotiations and throughout the project's duration, influencing pricing and specifications.
The nature of these long-term contracts means that clients often have a vested interest in the project's success and may exert considerable influence. For example, many construction firms report average contract durations spanning several years, often with a high percentage of repeat business, highlighting the enduring relationships where customer power is a key factor.
While customers of large-scale infrastructure projects might seem powerful initially due to competitive bidding, their bargaining power significantly diminishes once a contract is awarded. HOCHTIEF's projects, often involving intricate engineering and system integration, create substantial switching costs for clients. For instance, the sheer scale and long-term commitment of projects like airport expansions or major road networks make changing contractors mid-stream incredibly disruptive and costly.
Client Sophistication and Specific Requirements
HOCHTIEF's clients in sectors like data centers and advanced technology are highly sophisticated, possessing deep technical knowledge and demanding precise operational outcomes. This informed client base actively seeks contractors capable of delivering specialized, high-quality solutions, thereby enhancing their bargaining power.
For instance, in 2024, the global data center construction market, a key area for HOCHTIEF, was valued at an estimated USD 225.5 billion, with significant growth driven by AI and cloud computing demands. These projects often involve intricate cooling systems, advanced power infrastructure, and stringent security protocols, requiring contractors with highly specialized expertise.
- Informed Decision-Making: Clients in these advanced sectors conduct thorough due diligence, comparing technical capabilities and past performance, which allows them to negotiate more effectively.
- Demand for Customization: The need for bespoke solutions, from unique structural designs to integrated IT infrastructure, means clients can leverage their specific requirements to influence contract terms and pricing.
- Risk Mitigation: Sophisticated clients understand the risks associated with complex projects and often seek partners with proven track records and the ability to offer comprehensive guarantees, further strengthening their negotiating position.
- Focus on Total Cost of Ownership: Beyond initial construction costs, these clients evaluate the long-term operational efficiency and reliability of the infrastructure, influencing their demands on the contractor.
Economic and Regulatory Influence of Public Clients
Public sector clients, a substantial segment of HOCHTIEF's clientele, are significantly shaped by prevailing economic conditions and governmental regulations. For instance, in 2024, global infrastructure spending, particularly in areas like renewable energy and digital connectivity, continued to be a key driver for construction firms. Government-backed programs aimed at modernizing infrastructure and promoting green building practices directly influence the demand for HOCHTIEF's services.
However, these public entities wield considerable bargaining power due to their ability to impose stringent requirements. In 2024, many governments continued to emphasize strict environmental standards, safety regulations, and detailed budget controls on public projects. These stipulations, coupled with competitive bidding processes, allow public clients to exert significant influence over project scope, pricing, and contractor selection, thereby impacting HOCHTIEF's profit margins and operational flexibility.
- Government Funding Initiatives: In 2024, initiatives like the European Union's NextGenerationEU plan continued to allocate substantial funds towards infrastructure renewal, creating significant opportunities but also setting specific project parameters.
- Regulatory Impact: Stricter building codes and environmental regulations introduced or reinforced in 2024, such as those related to carbon emissions in construction, empower public clients to demand more sustainable and compliant solutions.
- Budgetary Constraints: Public sector projects often operate under tight budgetary controls, allowing clients to negotiate fiercely on price and terms, a trend that remained prevalent throughout 2024.
While HOCHTIEF's sophisticated clients in sectors like data centers possess strong bargaining power due to their technical knowledge and demand for customization, this power often wanes once a contract is secured. The intricate nature of these projects, such as advanced cooling systems for data centers, creates substantial switching costs, making it difficult and expensive for clients to change contractors mid-project. This lock-in effect significantly reduces their leverage during the project's lifecycle.
Preview Before You Purchase
Hochtief Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Hochtief Porter's Five Forces analysis, detailing competitive rivalry, buyer power, supplier power, the threat of substitutes, and the threat of new entrants. The document displayed here is the part of the full version you’ll get—ready for download and use the moment you buy. You're looking at the actual document, providing an in-depth strategic overview of Hochtief's competitive landscape. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, enabling immediate strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
HOCHTIEF navigates a fiercely competitive global construction arena populated by many substantial domestic and international firms. Key rivals such as Grupo ACS, Pacific Construction Group, and Hyundai Engineering and Construction are prominent players, alongside engineering giants like AECOM and Shimizu.
The presence of companies like Bechtel, Bouygues SA, Fluor Corp, and Balfour Beatty Plc further diversifies the competitive set. This broad spectrum of organizations offering comparable services significantly heightens the intensity of market rivalry.
The construction industry, while showing steady growth in 2024, is particularly dynamic in complex infrastructure. HOCHTIEF's strategic direction towards energy, digitalization, and transportation projects places it in direct competition with other major players targeting these lucrative areas.
This intense rivalry is evident as companies like Vinci, Bouygues, and ACS all actively pursue large-scale infrastructure contracts. For instance, the global construction market was projected to grow by approximately 3.5% in 2024, with infrastructure spending, especially on renewable energy projects and digital networks, forming a substantial portion of this growth.
The construction sector, including giants like HOCHTIEF, is burdened by substantial fixed costs. These stem from significant investments in heavy machinery, specialized tooling, and the ongoing need for a highly skilled workforce and robust project management infrastructure. For instance, in 2024, major infrastructure projects often require upfront capital expenditures running into hundreds of millions of euros for equipment alone.
This high cost structure necessitates a continuous pipeline of large-scale projects to ensure operational efficiency and profitability. Companies must secure substantial contracts to spread these fixed expenses and achieve economies of scale. This creates a powerful incentive for aggressive bidding strategies, as firms aim to keep their expensive assets and teams fully utilized.
Consequently, the competition for these major contracts is fierce. HOCHTIEF and its peers are constantly vying for lucrative projects, leading to intensified rivalry. This dynamic is further amplified by the project-based nature of the industry, where each new bid represents a critical opportunity to offset considerable fixed outlays and maintain market position.
Importance of Reputation, Experience, and Technical Expertise
In the demanding world of complex infrastructure, a company's standing, depth of experience, and technical prowess are paramount. These qualities act as significant competitive advantages, influencing client trust and project acquisition.
For instance, HOCHTIEF's successful execution of large-scale projects, such as the development of a massive data center campus for Meta in the US, highlights the value of their established reputation and technical capabilities. Similarly, their work on major airport modernizations demonstrates a sustained ability to handle intricate and high-stakes undertakings.
This emphasis on qualitative factors creates a formidable barrier to entry for less established competitors. Consequently, the rivalry among established players intensifies, with competition frequently centering on these crucial differentiators rather than solely on price.
- Reputation: A strong track record builds client confidence, crucial for securing bids on high-value projects.
- Experience: Proven success in complex, large-scale projects demonstrates capability and reduces perceived risk for clients.
- Technical Expertise: Specialized skills are essential for navigating the technical challenges inherent in modern infrastructure development.
- Competitive Differentiation: These factors allow firms like HOCHTIEF to stand out in a market where project complexity is increasing.
Impact of Economic Conditions and Regulatory Environment
Economic stability, interest rates, and government infrastructure investments are critical drivers of competitive intensity within the construction sector. For instance, in 2024, a fluctuating global economic outlook and persistent inflation have put pressure on material costs, making project bidding more challenging. This environment can intensify rivalry as companies vie for a limited pool of profitable projects.
Lower interest rates, when present, can spur investment and activity, potentially easing competitive pressures by expanding the market. However, the current geopolitical landscape and supply chain disruptions, ongoing into 2024, continue to create volatility. These factors contribute to rising material costs and labor shortages, forcing firms to compete more fiercely for resources and skilled workers, thereby heightening rivalry.
- Economic Volatility: Persistent inflation and supply chain issues in 2024 have increased operating costs for construction firms.
- Interest Rate Sensitivity: Fluctuating interest rates impact the cost of capital for large infrastructure projects, influencing bidding strategies.
- Government Spending: Significant government infrastructure investment, such as the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law in the US, can create opportunities but also concentrate competition for awarded contracts.
- Labor and Material Costs: Shortages and rising prices for both labor and materials in 2024 directly escalate the cost of projects, intensifying competition among firms to secure profitable ventures.
Competitive rivalry within the global construction sector is exceptionally high, with HOCHTIEF facing numerous substantial domestic and international competitors like Grupo ACS, Pacific Construction Group, and Hyundai Engineering and Construction. The presence of other major engineering firms such as AECOM, Shimizu, Bechtel, Bouygues SA, Fluor Corp, and Balfour Beatty Plc further intensifies this competition, as they all offer comparable services and vie for the same lucrative projects. This dynamic is particularly pronounced in the infrastructure segment, a key focus for HOCHTIEF, where companies like Vinci and Bouygues are also aggressively pursuing large-scale contracts. The global construction market's projected growth of around 3.5% in 2024, driven by infrastructure spending, means more companies are targeting these opportunities, leading to a more crowded and competitive landscape.
The construction industry is characterized by substantial fixed costs, including significant investments in machinery, skilled labor, and project management. For instance, major infrastructure projects in 2024 often require upfront capital expenditures in the hundreds of millions of euros for equipment alone. This necessitates a continuous stream of large projects to maintain operational efficiency and profitability, driving aggressive bidding as firms aim to keep their assets and teams fully utilized. The project-based nature of the industry means each new bid is critical for offsetting these considerable fixed outlays and securing market position.
Qualitative factors such as reputation, experience, and technical expertise are crucial differentiators in securing complex infrastructure projects. HOCHTIEF's successful execution of projects like a large data center campus for Meta and airport modernizations underscores the importance of these strengths in building client trust and winning bids. These established capabilities create a significant barrier to entry for newer competitors, intensifying rivalry among existing players who increasingly compete on these core competencies rather than solely on price.
Economic factors significantly influence competitive intensity. In 2024, persistent inflation and supply chain disruptions have increased operating costs, making project bidding more challenging and forcing firms to compete more fiercely for profitable ventures. Fluctuating interest rates also impact the cost of capital for large projects, influencing bidding strategies. Government infrastructure investments, such as the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law in the US, can create concentrated opportunities, further intensifying competition among firms vying for these awarded contracts.
| Key Competitors | 2024 Market Focus | Competitive Differentiators |
|---|---|---|
| Grupo ACS | Infrastructure, Energy | Scale, Diversified Portfolio |
| Pacific Construction Group | Large-scale infrastructure, Buildings | Global Reach, Project Execution |
| Hyundai Engineering and Construction | Infrastructure, Industrial Plants | Technological Prowess, EPC Capabilities |
| AECOM | Design, Consulting, Project Management | Technical Expertise, Global Network |
| Bouygues SA | Construction, Media, Telecoms | Integrated Services, Financial Strength |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for HOCHTIEF's core construction services is growing as alternative project delivery methods gain traction. Modular construction and prefabrication, for instance, offer faster project completion and potentially lower costs through off-site assembly. In 2024, the global modular construction market was valued at approximately USD 160 billion, with projections indicating significant compound annual growth rates, highlighting its increasing viability as a substitute for traditional on-site builds.
Very large clients, especially those with substantial and continuous infrastructure demands, may choose to build or enhance their internal construction and project management teams. For instance, major public sector entities or large corporations with recurring projects could internalize certain construction functions.
While HOCHTIEF's expertise in highly complex and specialized projects makes direct substitution difficult, some clients might consider self-delivery for less intricate segments if they believe it offers better cost efficiency or tighter control. This could represent a partial threat, particularly in areas like routine maintenance or smaller-scale builds.
While HOCHTIEF's core business is physical infrastructure, a subtle but growing threat of substitution comes from advancements in non-physical or digital infrastructure solutions. These innovations aim to optimize existing physical assets and potentially reduce the need for entirely new large-scale construction projects in some sectors.
For instance, the increasing adoption of smart city technologies, which leverage data analytics and IoT devices to manage urban resources more efficiently, could lessen the demand for new road networks or expanded public transport systems. Similarly, the development of digital twins and AI-powered predictive maintenance for existing infrastructure can extend asset lifespans and improve performance, thereby delaying or obviating the need for new builds.
Consider the global smart cities market, which was projected to reach over $2.5 trillion by 2026, indicating a significant investment in digital solutions that could indirectly impact traditional infrastructure demand. This trend suggests that while physical infrastructure remains crucial, the strategic allocation of resources towards digital optimization presents an evolving substitute for some of HOCHTIEF's traditional project pipelines.
Renovation and Modernization vs. New Construction
Clients may increasingly favor renovating and modernizing existing structures over new construction projects. This trend, driven by sustainability mandates and cost-effectiveness, presents a significant threat of substitution for HOCHTIEF's core new-build business. For instance, in 2023, the global building renovation market was valued at approximately $1.3 trillion, with projections indicating continued growth, potentially diverting investment from new infrastructure development.
This shift impacts HOCHTIEF by potentially reducing demand for its large-scale new construction services. While the company does offer maintenance and operation, a substantial pivot towards refurbishment could necessitate strategic adjustments to its business model. The emphasis on circular economy principles and extending asset lifecycles further bolsters the attractiveness of renovation over new builds, a factor that will likely intensify in the coming years.
- Renovation Market Growth: The global building renovation market is projected to reach over $1.7 trillion by 2028, indicating a substantial alternative to new construction.
- Sustainability Drivers: Approximately 60% of construction industry professionals cite sustainability as a key driver for renovation projects in recent surveys.
- Cost Efficiency: Renovation projects can often be 20-40% cheaper than comparable new construction, making them an attractive option for budget-conscious clients.
- Asset Utilization: Companies are increasingly looking to maximize the value of existing assets, leading to greater investment in retrofitting and modernization.
Technological Advancements and Digitalization
Technological advancements like Building Information Modeling (BIM) and advanced robotics are significantly streamlining construction processes and boosting efficiency. While HOCHTIEF is actively investing in these areas, their broader industry adoption could empower smaller, more agile competitors to offer compelling alternatives. Clients may increasingly favor partners who are leaders in these innovations, potentially substituting traditional construction methods with more technologically integrated solutions.
The rapid pace of digitalization means that even specialized construction niches could see disruptive substitutes emerge. For instance, advancements in prefabrication and modular construction, enabled by new digital design and manufacturing tools, offer faster build times and potentially lower costs. This poses a threat as clients might opt for these off-site solutions, bypassing traditional on-site construction services offered by companies like HOCHTIEF. In 2024, the global construction technology market was valued at approximately $12.5 billion, with significant growth projected, indicating the increasing importance of these technological shifts.
- BIM adoption: Facilitates better project planning and execution, reducing waste and errors.
- Robotics and automation: Can perform tasks like bricklaying and welding with greater speed and precision.
- Prefabrication and modular construction: Offer faster project delivery and potential cost savings.
- Digital twins: Enable real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, enhancing lifecycle value.
The threat of substitutes for HOCHTIEF's core construction services is evolving, with clients increasingly considering renovations and modernizations over new builds. This trend, fueled by sustainability goals and cost efficiencies, diverts investment from new infrastructure. For example, the global building renovation market reached approximately $1.3 trillion in 2023, with continued growth expected.
Technological advancements in prefabrication and modular construction also present a substitute threat, offering faster project completion and potentially lower costs. The global modular construction market was valued around $160 billion in 2024, underscoring its growing viability. Furthermore, digital infrastructure solutions, like smart city technologies, can optimize existing assets, potentially reducing demand for new physical builds.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the global complex infrastructure construction market, where HOCHTIEF is a major player, demands enormous capital. Newcomers must secure substantial funding for heavy machinery, cutting-edge technology, specialized labor, and project financing. The global infrastructure construction market is expected to reach trillions of dollars in the coming years, underscoring the sheer scale of investment required.
The threat of new entrants in the infrastructure sector is significantly dampened by the sheer volume of experience and specialized knowledge required. HOCHTIEF's decades of successful project delivery, including complex undertakings like the expansion of Athens International Airport and the development of large data center facilities, showcase a level of expertise that new players struggle to replicate quickly. This deep-seated industry know-how and established credibility act as a formidable barrier.
The construction sector, particularly for major public works, faces significant regulatory barriers. New companies must contend with obtaining numerous permits, undergoing rigorous environmental impact studies, and complying with varying national and regional standards. For instance, in 2024, the European Union continued to emphasize stringent environmental regulations for construction projects, requiring extensive documentation and adherence to sustainability targets, which can deter smaller or less experienced entrants.
Established Client Relationships and Network Effects
HOCHTIEF's deeply entrenched client relationships are a significant barrier to new entrants. For instance, their long-standing partnerships with numerous public sector entities and private developers globally often translate into preferred bidder status and a steady stream of repeat business. This established trust, built over years of successful project delivery, makes it incredibly difficult for newcomers to break into the market and secure the substantial, high-risk infrastructure contracts that HOCHTIEF routinely wins.
Furthermore, network effects play a crucial role. As HOCHTIEF successfully completes projects, its reputation for reliability and expertise grows, strengthening its existing client networks and attracting new ones. This creates a virtuous cycle where past performance directly influences future opportunities, leaving new entrants with a considerable disadvantage in building the necessary credibility and market presence to compete effectively for major tenders.
Consider the impact on new entrants:
- Difficulty securing initial contracts: New firms struggle to gain the trust of clients who prioritize proven track records.
- Higher customer acquisition costs: Entrants must invest heavily in marketing and relationship-building to overcome HOCHTIEF's established presence.
- Limited access to high-value projects: The most lucrative infrastructure projects often require extensive pre-qualification and demonstrated experience, which new entrants lack.
- Slower market penetration: Without established networks, new companies face a much longer and more challenging path to market share.
Supply Chain Integration and Access to Resources
New entrants would find it difficult to establish robust and economical supply chains for the extensive range of materials and specialized components essential for large-scale infrastructure projects. For instance, in 2024, the global construction materials market, valued at over $1.2 trillion, is characterized by established supplier networks that new players would struggle to penetrate quickly or affordably.
Established firms such as HOCHTIEF typically possess deeply entrenched relationships with suppliers, often securing preferential pricing and guaranteed delivery schedules. They may also have integrated their own supply chain operations or secured long-term contracts for critical resources, creating a significant cost and logistical advantage that new entrants cannot easily replicate.
- Supply Chain Complexity: Infrastructure projects demand a diverse and consistent flow of materials, from concrete and steel to specialized electrical and mechanical components.
- Supplier Relationships: HOCHTIEF's established partnerships provide leverage in negotiations, ensuring better terms and reliability compared to new entrants.
- Resource Access: Existing players may have direct access or long-term agreements for key resources like aggregates or specialized equipment, limiting availability for newcomers.
- Cost Disadvantage: New entrants face higher initial procurement costs and potential delays due to their lack of established supply chain infrastructure and bargaining power.
The threat of new entrants in the global infrastructure construction sector is generally low due to the immense capital requirements and the need for extensive experience. New companies face significant hurdles in securing the vast funding necessary for machinery, technology, and specialized labor, especially given the market's multi-trillion-dollar valuation. Regulatory complexities, including permits and environmental compliance, further deter new players, as seen with the EU's stringent sustainability targets in 2024.
HOCHTIEF benefits from deeply ingrained client relationships and network effects, making it difficult for newcomers to secure high-value projects and build credibility. The established supply chains and preferential pricing enjoyed by incumbent firms also present a substantial cost and logistical disadvantage for new entrants attempting to penetrate the market.
| Barrier | Impact on New Entrants | HOCHTIEF Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Extremely high, requiring billions for projects. | Established financial capacity and access to capital markets. |
| Experience & Expertise | Lack of proven track record in complex projects. | Decades of successful, complex project delivery. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Navigating permits, environmental studies, and compliance. | Established processes and relationships for compliance. |
| Client Relationships | Difficulty in gaining trust and securing initial contracts. | Long-standing partnerships and preferred bidder status. |
| Supply Chain Access | Higher procurement costs and potential delays. | Preferential pricing and guaranteed delivery from established suppliers. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Hochtief Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, drawing from Hochtief's annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research. We also incorporate insights from construction sector trade publications and economic forecasts to provide a robust understanding of the competitive landscape.
