Textron Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Textron Bundle
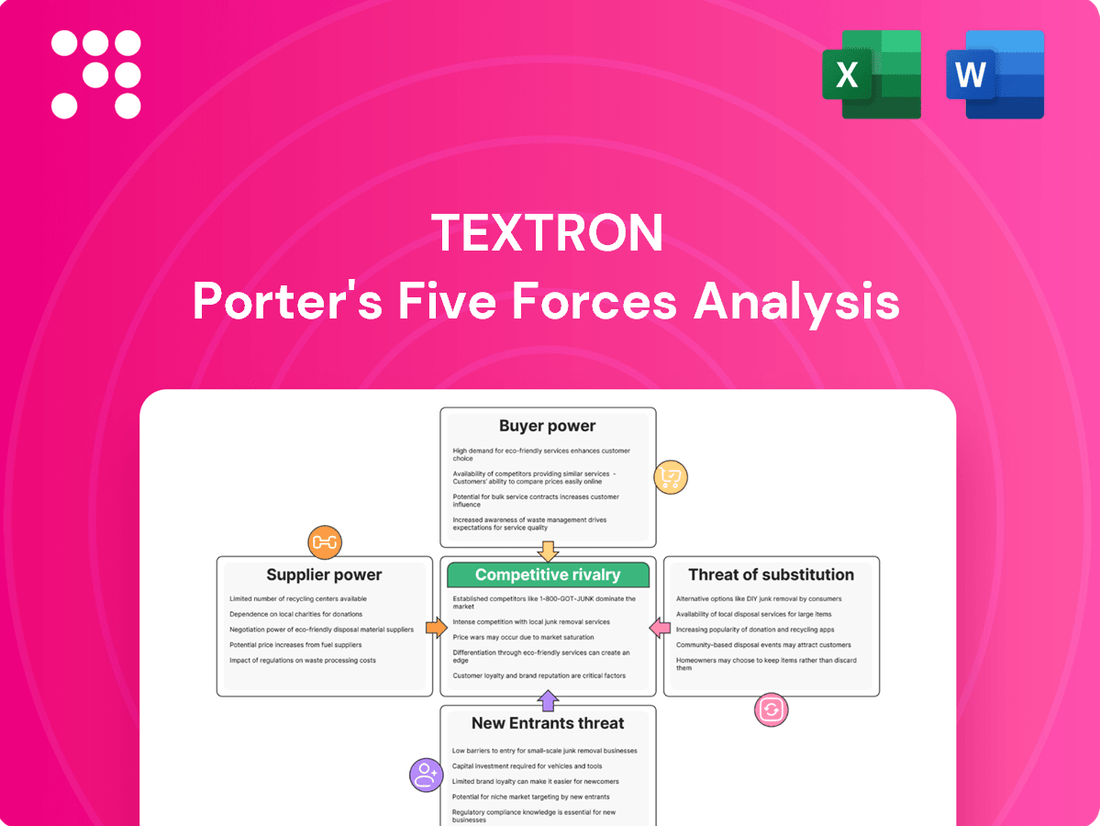
Textron's competitive landscape is shaped by the interplay of five key forces, revealing the intensity of rivalry and the bargaining power of suppliers and buyers. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating the aerospace and defense industry.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Textron’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Textron's reliance on a concentrated supplier base for specialized aerospace and defense components, such as engines and avionics, grants these suppliers considerable bargaining power. The high switching costs associated with re-qualifying new suppliers in this highly regulated industry further solidify this leverage, as seen in the complex certification processes for critical aircraft parts.
Recent supply chain disruptions, including events like the 2024 Boeing 737 MAX production issues stemming from supplier quality problems, underscore the vulnerability Textron faces. These disruptions can lead to production delays and increased costs, directly impacting Textron's operational efficiency and profitability.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Textron is significantly influenced by high switching costs, particularly within the aerospace and defense sectors. Many critical components are proprietary, meaning Textron would incur substantial expenses and face considerable complexity if it decided to change suppliers. These costs encompass re-engineering designs, re-tooling manufacturing processes, and undergoing rigorous re-certification procedures, all of which are both time-consuming and financially demanding.
Furthermore, Textron's dependence on suppliers who possess unique technologies or hold specific intellectual property rights strengthens the suppliers' leverage. This reliance means that alternative suppliers might not be readily available or capable of meeting the stringent quality and performance standards required in these industries. For instance, in 2024, the aerospace industry continued to grapple with supply chain disruptions, often leading to extended lead times and price increases for specialized parts, underscoring the power held by key component manufacturers.
Textron's reliance on suppliers for highly differentiated and technologically advanced components significantly influences supplier power. For instance, specialized propulsion systems or unique defense technologies, if not easily replicated by competitors, allow suppliers to dictate terms. This is especially relevant in the defense industry where performance is a critical factor.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
While the threat of suppliers integrating forward into manufacturing is generally low for a company like Textron, it's a factor that can't be entirely dismissed. Imagine a major supplier of a critical component for Textron's aircraft; if they see significant profit potential and possess the necessary manufacturing expertise, they might consider producing a sub-assembly or even a finished product themselves. This is particularly true if Textron's profit margins are seen as unusually high.
However, the sheer complexity and substantial capital investment required to manufacture aircraft and sophisticated defense systems act as significant deterrents. These barriers make it difficult for most suppliers to realistically pursue forward integration. For instance, developing the advanced engineering, testing facilities, and regulatory approvals needed for aerospace components is a monumental undertaking.
Even if the threat of direct forward integration is remote, its mere possibility can subtly influence Textron's negotiation leverage. Suppliers might be more inclined to offer competitive pricing or terms if they perceive that Textron could potentially bring certain manufacturing processes in-house or switch to alternative suppliers if negotiations falter. This dynamic plays a role in maintaining a balanced supplier relationship.
Consider the supplier landscape in 2024. For example, companies supplying advanced avionics or specialized composite materials might have the technical capabilities. However, the need for extensive certifications and the scale of operations required for defense contracts typically mean that suppliers focus on their core competencies rather than attempting to compete directly with prime contractors like Textron.
Importance of Supplier's Input to Textron's Product Quality and Performance
Textron's final products, particularly its sophisticated aircraft and defense systems, rely significantly on the quality of components sourced from its suppliers. The performance and reliability of these high-stakes items are directly tied to the materials and parts provided.
A failure in a critical supplier component can lead to disastrous outcomes for Textron, ranging from serious safety hazards for end-users to substantial damage to the company's reputation and expensive product recalls. For instance, in the aerospace sector, even minor component defects can ground fleets and incur millions in repair costs and lost revenue.
This deep reliance on specific, high-quality inputs grants considerable leverage to suppliers whose components are deemed essential for the performance and safety of Textron's offerings. In 2024, the aerospace and defense industry continued to face supply chain challenges, with lead times for specialized components often extending beyond 12 months, further amplifying supplier power.
- Critical Component Dependence: Textron's advanced products, such as Bell helicopters and Textron Aviation aircraft, require specialized components where quality is non-negotiable.
- Safety and Reputation Risks: Component failures can directly impact flight safety and Textron's brand image, making supplier reliability paramount.
- Supplier Leverage: Suppliers of unique or highly regulated components, especially those with limited alternative sources, hold significant bargaining power.
- 2024 Supply Chain Dynamics: Ongoing geopolitical factors and increased demand in 2024 have tightened supply chains for many critical aerospace materials, increasing supplier pricing power.
Textron's suppliers hold significant bargaining power due to the critical nature of their specialized components, particularly in the aerospace and defense sectors. High switching costs, proprietary technologies, and the essential role of these parts in ensuring product safety and performance amplify this leverage.
The 2024 supply chain environment, marked by extended lead times and increased demand for advanced materials, has further empowered key suppliers. For instance, lead times for specialized avionics and composite materials often exceeded 12 months, allowing suppliers to command higher prices and favorable terms.
Textron's reliance on a concentrated supplier base for unique components, such as advanced engine systems or proprietary defense electronics, means that alternative sourcing options are often limited. This dependence, coupled with the rigorous certification requirements for aerospace parts, solidifies supplier leverage.
| Supplier Characteristic | Impact on Textron | Example (2024 Context) |
|---|---|---|
| Critical Component Dependence | High reliance on specialized parts for product integrity and safety | Advanced avionics for Bell helicopters |
| Proprietary Technology/IP | Limited alternative suppliers, increasing supplier negotiation power | Unique composite materials for aircraft structures |
| High Switching Costs | Significant expense and time for re-qualification and re-tooling | Re-certification of engine components |
| Supplier Concentration | Fewer suppliers for specialized aerospace/defense parts | Limited manufacturers of specific turboprop engines |
| Safety & Reputation Risk | Component failure directly impacts end-user safety and Textron's brand | Potential grounding of aircraft due to faulty parts |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Textron, detailing the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and ultimately, Textron's strategic positioning.
Effortlessly identify and address competitive threats with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces model that visualizes industry power dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Textron's customer base is incredibly varied, encompassing commercial airlines, private jet owners, various branches of the military, and industrial businesses. Each of these groups has distinct needs and purchasing power, from individual aircraft buyers to large government entities. This broad spectrum of customers, while offering stability, also means that their collective bargaining power is generally diffused.
While some large government defense contracts can represent significant revenue, they are typically negotiated over extended periods and often involve specialized, high-value products. For the commercial and industrial sectors, Textron's diverse product lines mean that individual customers, even substantial ones, rarely command enough leverage to dictate terms across the entire company. This fragmentation limits the ability of any single customer segment to exert significant downward pressure on prices or demand highly customized terms that would impact Textron's overall profitability.
For many of Textron's complex products, like aircraft and defense systems, customers face substantial hurdles when considering a switch. These include the costs associated with pilot re-training, establishing new maintenance facilities, stocking a different range of spare parts, and ensuring integration with their current operational systems. These investments effectively lock customers in, significantly diminishing their ability to easily shift to a competitor.
Government entities, particularly the U.S. Army, represent a substantial customer base for Textron, especially for its Bell and Textron Systems divisions. For instance, programs like the Future Long-Range Assault Aircraft (FLRAA), where Textron is a contender, highlight the government's role as a major buyer.
These significant government contracts typically come with demanding specifications, competitive bidding processes, and the expectation of enduring partnerships. The government's leverage is evident in its ability to dictate precise requirements and manage program budgets, directly impacting suppliers.
Price Sensitivity and Standardization in Commercial Segments
In certain commercial industrial sectors, customers exhibit heightened price sensitivity, especially when dealing with standardized offerings. When product differentiation is minimal across manufacturers, buyers can readily compare pricing and shift to alternative suppliers if cost becomes the paramount consideration. This dynamic directly amplifies customer bargaining power.
For instance, in the aerospace components market where Textron operates, the demand for many off-the-shelf parts can be highly price elastic. A 2024 report indicated that for non-proprietary fasteners and standard structural elements, price differences of even 2-3% could influence purchasing decisions for large fleet operators. This highlights how standardization fuels customer leverage.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers in industrial segments often prioritize cost for standardized components.
- Low Differentiation: When products are similar across suppliers, price becomes a key differentiator.
- Switching Costs: For standardized parts, the ease of switching suppliers increases customer bargaining power.
- Market Data: In 2024, price differences as small as 2-3% could sway large buyers for common aerospace parts.
Aftermarket Services and Parts Demand
Textron's focus on aftermarket services and parts for its long-lived products, such as aircraft and industrial equipment, establishes a significant recurring revenue stream. This strategy inherently dampens customer bargaining power by fostering dependence on the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) for essential maintenance and certified components.
Customers often find themselves locked into using Textron's proprietary parts and specialized repair services. This reliance is particularly pronounced for complex machinery where deviations from OEM specifications could compromise performance, safety, or warranty validity. For instance, in the aviation sector, airlines depend on Textron for specific engine parts and maintenance protocols, limiting their ability to source from third parties.
- Aftermarket Revenue: Textron Aviation reported $3.2 billion in revenue from its Services segment in 2023, highlighting the importance of aftermarket parts and maintenance.
- Customer Lock-in: The specialized nature of Textron's products, particularly in aerospace, means that customers require OEM-certified parts and technicians, reducing their flexibility and bargaining leverage.
- Reduced Competition: By controlling the supply of critical parts and specialized knowledge, Textron mitigates the threat of lower-cost alternatives from independent providers in the aftermarket.
Textron's diverse customer base, ranging from individual aircraft buyers to large governmental defense agencies, generally limits the bargaining power of any single customer segment. While major defense contracts can be substantial, they are typically long-term and involve highly specialized products, preventing individual customers from dictating terms across Textron's broader operations.
The significant switching costs associated with Textron's complex products, such as aircraft and defense systems, further diminish customer leverage. These costs include retraining personnel, establishing new maintenance infrastructure, and integrating new parts, effectively locking customers into Textron's offerings and reducing their ability to easily switch to competitors.
While some industrial segments exhibit price sensitivity for standardized components, Textron's aftermarket services and proprietary parts create customer dependence. This reliance on OEM-certified parts and specialized maintenance for complex machinery significantly reduces customers' flexibility and bargaining power.
| Customer Segment | Impact on Bargaining Power | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Government Defense Agencies | Moderate to High (for specific programs) | Large contract values, ability to dictate specifications, competitive bidding |
| Commercial Airlines | Low to Moderate | High switching costs for aircraft, reliance on OEM for parts and maintenance |
| Private Jet Owners | Low | High cost of aircraft, reliance on Textron for service and parts |
| Industrial Businesses (Standardized Products) | Moderate | Price sensitivity, potential for switching if differentiation is low |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Textron Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Textron Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within the aviation industry. You're looking at the actual document, so you can be confident that the insights into buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, threat of substitutes, and industry rivalry are precisely what you'll receive. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file, ready for immediate use and strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The aerospace and defense sector is defined by immense fixed costs associated with research, development, and production. To achieve profitability through economies of scale, companies must maintain high production volumes. This economic reality naturally drives industry consolidation, concentrating market power among a limited number of substantial entities.
Textron operates within this landscape, facing formidable competition from global giants such as Airbus and Boeing. For instance, in 2023, Boeing reported revenues of $81.8 billion, highlighting the scale of operations and capital required to compete effectively. This intense rivalry among a few dominant players intensifies pressure on all participants to optimize efficiency and innovation.
The current geopolitical climate is significantly fueling global defense spending, creating a robust market for companies like Textron. This surge, with global military expenditure hitting $2.7 trillion in 2024, a 9.4% jump from the previous year, intensifies competition among defense contractors. Established players face both heightened rivalry for lucrative government contracts and substantial opportunities for expansion.
Competitive rivalry within Textron's diverse sectors heavily relies on product differentiation and continuous technological innovation. In the business jet market, for instance, advancements in fuel efficiency, cabin comfort, and avionics are key differentiators. Similarly, in military helicopters, capabilities like speed, payload, and survivability drive competition.
Textron's commitment to innovation is evident in projects like the Bell V-280 Valor, a tiltrotor aircraft designed for advanced military applications. This program, often referred to as the Future Long-Range Assault Aircraft (FLRAA) or MV-75, showcases Textron's focus on developing next-generation capabilities. The success of such innovative products is paramount for Textron to maintain its market position against formidable competitors.
Market Share and Backlogs in Aviation Segments
Textron Aviation navigates a competitive business jet landscape, with demand stabilizing at high levels and new jet deliveries projected to rise in 2025. While Textron holds a strong third position in business jet sales, trailing Gulfstream and Bombardier, it actively competes in both commercial and military helicopter sectors against major players like Airbus and Leonardo.
The company's robust backlogs underscore current market strength, with Textron Aviation reporting $7.85 billion and Bell holding $6.9 billion. However, efficient delivery execution is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in these markets.
- Business Jet Market Position: Textron is the third-largest seller of business jets.
- Helicopter Market Competition: Bell competes with Airbus and Leonardo in both commercial and military helicopter segments.
- Backlog Significance: Textron Aviation's $7.85 billion and Bell's $6.9 billion backlogs reflect strong demand but highlight the need for efficient delivery.
- Market Trend: Demand in the business jet market is normalizing at elevated levels, with increased deliveries anticipated in 2025.
Impact of Supply Chain and Labor Challenges
Ongoing supply chain disruptions, particularly extended lead times for essential components, continue to pressure manufacturers like Textron. For instance, in 2024, the aerospace sector experienced average component lead times that were still significantly higher than pre-pandemic levels, impacting production schedules and increasing costs.
Labor shortages, including a notable scarcity of skilled machinists and technicians, further exacerbate these production constraints. In 2024, several reports indicated that the aerospace and defense industry faced a deficit of tens of thousands of skilled workers, directly affecting output capacity.
These combined challenges intensify competitive rivalry. Companies struggling to secure parts and talent may lose market share to more agile competitors or be forced to accept lower profit margins to fulfill orders, potentially leading to lost opportunities if production cannot keep pace with market demand.
- Supply Chain Lead Times: In 2024, average lead times for critical aerospace components remained elevated, impacting operational efficiency.
- Skilled Labor Shortage: The aerospace and defense industry faced a significant deficit of skilled labor, with estimates suggesting a shortfall of over 50,000 workers in 2024.
- Production Capacity Impact: These challenges directly limit production capacity, intensifying competition among firms vying to meet demand.
Competitive rivalry within Textron's operating segments is intense, driven by a few dominant global players and the need for continuous innovation. Textron, as the third-largest business jet seller, faces strong competition from companies like Gulfstream and Bombardier. In the helicopter market, Bell competes directly with giants such as Airbus and Leonardo.
The aerospace and defense sector is characterized by high fixed costs and the pursuit of economies of scale, which naturally leads to consolidation and intense competition among established entities. For instance, in 2023, Boeing's $81.8 billion revenue demonstrates the sheer scale required to compete. The increasing global defense spending, reaching $2.7 trillion in 2024, further intensifies this rivalry as companies vie for lucrative government contracts.
| Company | 2023 Revenue (USD Billions) | Primary Segments |
|---|---|---|
| Textron | ~14.0 (2023) | Business Jets, Helicopters, Defense Systems |
| Boeing | 81.8 | Commercial Aircraft, Defense Systems |
| Airbus | 65.4 (approx. €60.1 billion in 2023) | Commercial Aircraft, Helicopters, Defense |
| Gulfstream (General Dynamics) | ~11.2 (2023 for Gulfstream segment) | Business Jets |
| Bombardier | ~8.4 (2023) | Business Jets, Regional Aircraft |
| Leonardo | ~15.7 (approx. €14.4 billion in 2023) | Helicopters, Aerospace, Defense |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For Textron's business jet and commercial turboprop segments, the threat of substitutes is significant. Commercial airline travel remains a primary substitute, especially for longer routes or when cost-efficiency is paramount. In 2024, the global airline industry is projected to carry over 4.7 billion passengers, highlighting the sheer volume of travelers opting for this mode.
High-speed rail also presents a viable alternative, particularly in regions with well-developed networks, offering a competitive travel time for medium distances. Furthermore, the increasing sophistication and adoption of virtual communication technologies, like video conferencing, can reduce the necessity for business travel altogether, impacting demand for private aviation services.
The increasing sophistication of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and drones presents a potential substitute threat, particularly in defense and specialized industrial sectors. These systems can perform tasks previously requiring manned aircraft or ground vehicles, potentially impacting demand for Textron's traditional offerings.
However, Textron Systems is actively engaged in the development and deployment of its own unmanned systems. This dual capability allows Textron to not only compete in the growing unmanned market but also to mitigate the threat of external substitutes by leveraging its internal expertise and product lines.
For instance, Textron's Aerosonde HQ program, a long-endurance UAV, demonstrates its commitment to this technology. In 2024, global defense spending on unmanned systems was projected to exceed $15 billion, highlighting the significant market shift Textron is positioned to address.
The emergence of new aviation technologies, like hybrid-electric engines and eVTOL aircraft, represents a significant long-term threat of substitutes for Textron's traditional aircraft and helicopter offerings. While Textron is actively investing in its eAviation segment to explore these innovations, swift technological progress by competitors could rapidly alter market dynamics and displace established products.
Shift in Industrial Processes
Advancements in industrial processes, particularly in automation and robotics, pose a threat of substitution for some of Textron's traditional industrial machinery. As factories increasingly adopt new manufacturing techniques, the demand for older equipment or components could decline. For instance, the rise of advanced additive manufacturing might reduce the need for certain types of conventional machining tools.
However, this shift also presents opportunities for Textron. The company's industrial segment can capitalize on the growing market for automated machinery and the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) in manufacturing. In 2024, the global industrial automation market was valued at approximately $500 billion, with significant growth projected due to Industry 4.0 initiatives.
- Automation and Robotics: Increased adoption of automated systems can displace demand for less sophisticated machinery.
- New Manufacturing Techniques: Innovations like 3D printing can substitute for traditional parts and production methods.
- IoT Integration: While a threat to older tech, IoT also drives demand for smart industrial equipment, a growth area for Textron.
- Market Growth: The industrial automation sector is expanding, offering Textron opportunities to supply advanced solutions.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Substitutes
The threat of substitutes for Textron's aviation segment, particularly Bell helicopters, is influenced by how well alternatives meet customer needs in terms of cost, efficiency, speed, and environmental impact. While advancements in electric and hybrid aircraft are emerging, their current limitations in range and payload capacity mean they aren't yet direct replacements for many of Bell's established helicopter applications. For instance, in 2024, the operational cost per flight hour for traditional turbine helicopters often remains more competitive for heavy-lift or long-duration missions compared to nascent electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) concepts still in development and certification phases.
The perceived value proposition of a substitute is key. For example, electric helicopters offer significant advantages in noise reduction and potentially lower operating costs due to fewer moving parts and cheaper energy sources. However, their current battery technology restricts flight duration and payload, making them less viable for critical missions requiring extended flight times or heavy cargo transport, which are core to many of Bell's current customer base.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Traditional helicopters often maintain a cost-per-flight-hour advantage for demanding missions in 2024.
- Performance Limitations: Electric and hybrid alternatives currently face challenges with range and payload capacity.
- Environmental Appeal: Growing demand for greener aviation solutions presents an opportunity for substitutes, but technological hurdles persist.
- Market Penetration: The slow pace of certification and infrastructure development for new aircraft types limits their immediate substitutive threat.
For Textron's aviation businesses, commercial air travel and high-speed rail serve as significant substitutes, particularly for business travel where cost and route length are key considerations. The global airline industry's projected 4.7 billion passengers in 2024 underscores the scale of this alternative. Additionally, advancements in virtual communication technologies are increasingly reducing the need for physical business travel, impacting demand for private jets and turboprops.
The threat of substitutes for Textron's helicopter division, Bell, is evolving with new aviation technologies. While electric and hybrid aircraft offer environmental benefits, their current limitations in range and payload capacity in 2024 prevent them from fully replacing traditional helicopters for many demanding missions. For instance, the cost per flight hour for turbine helicopters often remains more competitive for heavy-lift operations.
The industrial segment faces substitutes from automation and robotics, with the global industrial automation market valued at approximately $500 billion in 2024. While advanced manufacturing techniques like 3D printing can replace traditional parts, this also creates opportunities for Textron to supply advanced, IoT-integrated machinery, capitalizing on Industry 4.0 growth.
| Segment | Primary Substitutes | Key Factors Influencing Threat | 2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business Jets & Commercial Turboprops | Commercial Airlines, High-Speed Rail, Virtual Communication | Cost, Route Length, Travel Time, Necessity of Physical Presence | Over 4.7 billion global airline passengers |
| Bell Helicopters | Emerging Electric/Hybrid Aircraft (eVTOLs) | Range, Payload Capacity, Operational Cost, Environmental Impact | Traditional helicopters often more cost-effective for heavy-lift missions |
| Industrial Machinery | Automation, Robotics, Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) | Efficiency, Cost of Production, Technological Advancement | Global industrial automation market ~$500 billion |
Entrants Threaten
The aerospace and defense sectors, Textron's core operational areas, demand substantial upfront investment. Companies need significant capital for research and development, building advanced manufacturing plants, acquiring specialized machinery, and navigating rigorous testing and certification protocols. For instance, the development of a new aircraft program can easily run into billions of dollars, making it incredibly difficult for new, smaller companies to enter the market and compete.
Strict government regulations and the intricate certification processes for products like aircraft and defense systems present significant barriers for new companies looking to enter Textron's markets. These hurdles demand substantial time and financial resources to navigate.
For instance, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) certification for new aircraft models can take years and cost hundreds of millions of dollars, a daunting prospect for potential competitors. Similarly, defense contracts often require adherence to stringent military specifications, further complicating market entry.
Textron's threat of new entrants is significantly mitigated by its deeply entrenched brand reputation and strong customer relationships. Brands like Cessna and Bell are synonymous with quality and reliability in aviation, a sector where trust is paramount. Newcomers face a steep uphill battle to even approach this level of recognition.
Securing long-term contracts with commercial clients and government entities, crucial for Textron's revenue streams, hinges on a proven history of performance and dependability. For instance, Textron Aviation's backlog for business jets in early 2024 remained robust, reflecting the ongoing demand from established clients who value this track record. New entrants simply cannot replicate this accumulated trust and experience overnight, making it a formidable barrier.
Intellectual Property and Proprietary Technology
Textron's significant investment in research and development, resulting in a deep portfolio of intellectual property and proprietary technologies, acts as a substantial barrier to new entrants. For instance, in 2023, Textron reported R&D expenses of $1.1 billion, a testament to its ongoing commitment to innovation.
New companies would need to replicate this extensive technological foundation, a process that is both time-consuming and capital-intensive. Acquiring licenses for existing technologies could also prove prohibitively expensive, further deterring market entry.
- Extensive Intellectual Property: Textron holds numerous patents across its diverse business segments, including aerospace, defense, and industrial products.
- Proprietary Technologies: Decades of development have yielded unique manufacturing processes and product designs that are difficult for competitors to replicate.
- High Barrier to Entry: The cost and complexity of developing comparable technologies or licensing existing ones significantly raise the hurdle for new entrants.
- Competitive Advantage: This technological moat allows Textron to maintain a strong market position and command premium pricing.
Supply Chain Complexity and Economies of Scale
The aerospace and defense sector's supply chain is notoriously intricate, demanding specialized components and sophisticated manufacturing. Newcomers face a steep climb in establishing efficient, reliable supply networks and achieving the economies of scale that established firms like Textron leverage for competitive pricing.
For instance, Textron's extensive global network, built over decades, allows it to negotiate better terms for raw materials and components, a significant barrier for any new entrant aiming to match its cost structure. In 2024, the average lead time for critical aerospace components can extend to over 18 months, highlighting the established relationships and logistical expertise required.
- Supply Chain Specialization: The need for highly specialized parts, often with unique certifications, creates a high barrier to entry.
- Economies of Scale: Established players benefit from bulk purchasing and optimized production runs, reducing per-unit costs significantly.
- Logistical Hurdles: Managing a global, complex supply chain for aerospace requires immense capital investment and proven operational efficiency.
The threat of new entrants for Textron is generally low due to immense capital requirements, stringent regulations, and established brand loyalty in its core aerospace and defense markets. The cost of R&D, manufacturing, and certification, often running into billions for new aircraft programs, creates a significant financial barrier.
Furthermore, Textron benefits from deep customer relationships and a proven track record, making it difficult for newcomers to gain trust. For example, Textron Aviation's robust backlog in early 2024 underscores client confidence in its established performance. This, combined with substantial intellectual property and proprietary technologies, as evidenced by $1.1 billion in R&D spending in 2023, further deters potential competitors.
The complexity of the aerospace supply chain, requiring specialized components and long-term relationships, also presents a substantial hurdle. New entrants struggle to match the economies of scale and logistical expertise that Textron has cultivated over decades, with critical aerospace component lead times in 2024 averaging over 18 months.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment for R&D, manufacturing, and certification. | Significant deterrent due to massive upfront costs. | New aircraft program development: Billions of dollars. Textron's 2023 R&D: $1.1 billion. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex and lengthy certification processes (e.g., FAA). | Time-consuming and expensive to navigate, requiring specialized expertise. | FAA certification for new aircraft: Years and hundreds of millions of dollars. |
| Brand Reputation & Customer Loyalty | Established trust in brands like Cessna and Bell. | New entrants struggle to build credibility and secure clients. | Robust backlog for Textron Aviation in early 2024 reflects client trust. |
| Intellectual Property & Technology | Extensive patents and proprietary manufacturing processes. | High cost and complexity to replicate or license existing technologies. | Textron's commitment to innovation demonstrated by $1.1 billion R&D in 2023. |
| Supply Chain Complexity | Intricate network of specialized suppliers and long lead times. | Difficulty in establishing reliable supply chains and achieving economies of scale. | Average lead time for critical aerospace components in 2024: Over 18 months. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including company annual reports, industry-specific market research, and publicly available financial statements. This blend of primary and secondary sources allows for a comprehensive understanding of competitive intensity, buyer and supplier power, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
