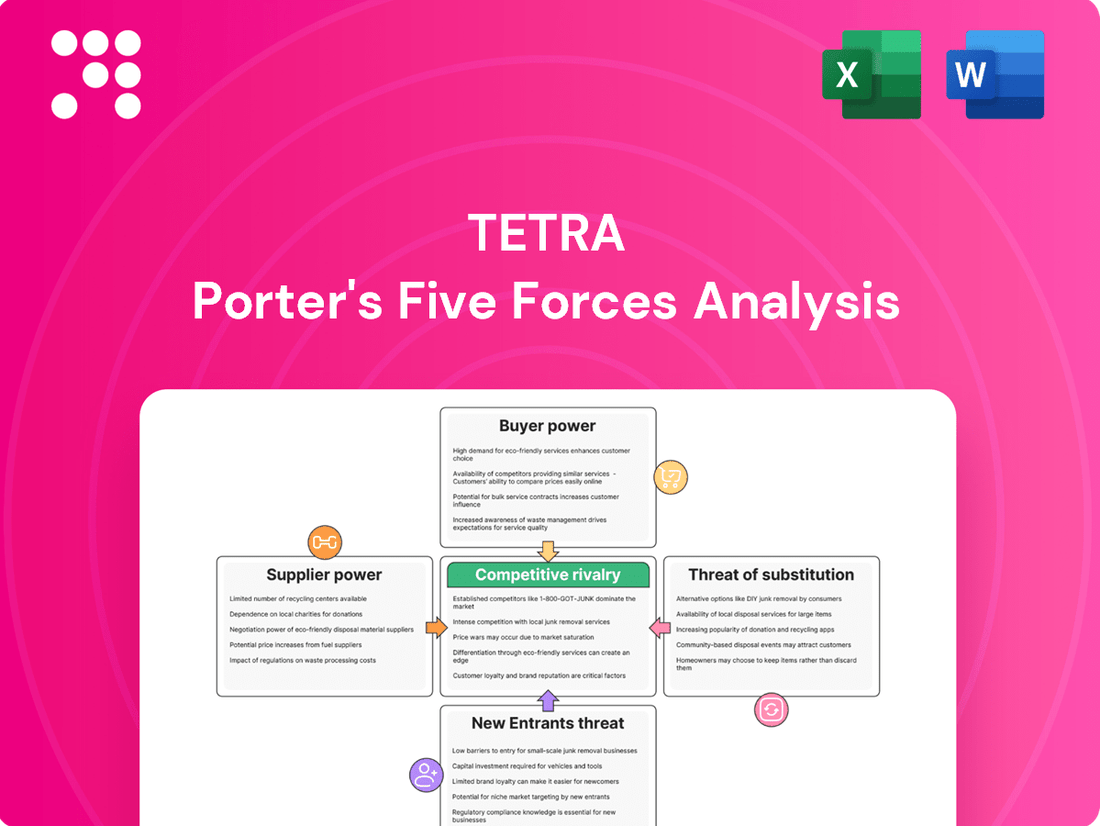
Tetra Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Tetra Bundle
Tetra's competitive landscape is shaped by the interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, threat of new entrants, substitutes, and industry rivalry. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating their market effectively.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Tetra’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
TETRA Technologies' reliance on specialized raw materials and chemicals, like calcium bromide and zinc bromide for its completion fluids, highlights the bargaining power of its suppliers. The limited availability and unique nature of certain high-purity chemicals, particularly for advanced products such as TETRA CS Neptune, can significantly shift leverage towards these suppliers.
For instance, if a key supplier of a critical component for TETRA's completion fluids experiences production issues or decides to increase prices, TETRA's operational costs could rise substantially. This was evident in the chemical industry in 2024, where supply chain disruptions and increased demand for certain industrial chemicals led to price hikes, impacting manufacturers across various sectors.
Suppliers offering proprietary equipment essential for water management solutions and production well testing can wield considerable bargaining power. For instance, if a key piece of technology used in TETRA's operations is patented or requires highly specialized manufacturing, TETRA's options for alternative suppliers become restricted.
This reliance on unique technologies can translate into higher costs for TETRA, as these specialized suppliers may command premium pricing. In 2023, the global market for oilfield services, which includes well testing, saw significant investment, with companies prioritizing advanced technologies to optimize production, potentially increasing the leverage of those holding such proprietary equipment.
The bargaining power of logistics and transportation suppliers for TETRA Technologies is significant due to the specialized nature of moving heavy fluids and equipment to often remote oil and gas locations. These suppliers are essential for TETRA's operational success, directly impacting its ability to meet client deadlines and maintain service continuity.
Factors like fluctuating fuel prices, the availability of skilled labor for specialized transport, and existing infrastructure constraints can empower these logistics providers. For instance, in 2024, global shipping costs saw continued volatility, directly affecting the overhead for companies like TETRA relying on these services. Shortages in qualified truck drivers, particularly those certified for hazardous materials, further amplify supplier leverage.
Skilled Labor and Specialized Expertise
The oil and gas services sector, which includes specialized areas like completion fluids and well testing, relies heavily on a workforce possessing advanced skills and significant experience. A scarcity of these specialized professionals, such as engineers and field technicians, directly amplifies the bargaining power held by employees and the recruitment agencies that source them.
This dynamic can translate into increased labor expenses and create considerable hurdles for companies like TETRA Technologies in attracting and keeping essential talent. For instance, in 2024, the demand for experienced petroleum engineers remained robust, with reports indicating a persistent shortage in key operational regions, potentially driving up compensation packages.
- High Demand for Specialized Skills: The complexity of completion fluids and well testing necessitates a niche skill set, making qualified personnel a valuable commodity.
- Impact on Labor Costs: A tight labor market for these skilled roles can force companies to offer higher wages and benefits, increasing operational expenditures.
- Talent Acquisition Challenges: Companies face difficulties in finding and securing the necessary expertise, impacting project timelines and operational efficiency.
- Supplier Power Amplification: Labor supply companies or agencies specializing in these fields gain leverage when demand outstrips the available pool of qualified workers.
Dependence on Energy Sector Trends
The bargaining power of suppliers for TETRA Technologies, Inc. is significantly influenced by the broader energy sector's health. During periods of high oil and gas activity, like the robust demand seen in early 2024, suppliers often experience increased demand for their inputs. This can translate into higher prices and potentially tighter availability for TETRA, especially for specialized chemicals and equipment critical to its operations. For instance, as of Q1 2024, the global oil and gas industry saw a notable uptick in drilling activity, which directly impacts the cost and supply of essential materials for companies like TETRA.
Conversely, a slowdown in energy exploration and production, which can occur with fluctuating commodity prices, might diminish supplier power. In such scenarios, suppliers may compete more aggressively for TETRA's business, potentially leading to more favorable pricing. However, TETRA's core business relies on specific, high-performance materials and technologies. This inherent need for specialized inputs means that even during downturns, suppliers of these niche products can retain considerable bargaining leverage due to the limited number of alternatives available to TETRA.
- Sector Dependence: TETRA's suppliers' pricing and availability are directly tied to the cyclical nature of the oil and gas industry.
- Demand Impact: High energy sector activity (e.g., Q1 2024 drilling increases) typically strengthens supplier pricing power.
- Specialty Needs: TETRA's reliance on high-performance, specialized materials limits its ability to switch suppliers, thus maintaining supplier leverage even in weaker market conditions.
The bargaining power of suppliers is a critical factor for TETRA Technologies, influencing its cost structure and operational flexibility. When suppliers control essential, specialized inputs or possess unique technologies, their ability to dictate terms increases significantly. This is particularly relevant in the oil and gas sector, where specialized chemicals and proprietary equipment are often required.
In 2024, the chemical industry continued to experience price volatility, impacting raw material costs for completion fluid manufacturers. For example, the price of key components like calcium bromide saw fluctuations driven by global supply and demand dynamics. Furthermore, the oilfield services market in 2023 saw substantial investment in advanced technologies, enhancing the leverage of suppliers offering patented or highly specialized equipment.
| Input Type | Supplier Leverage Factors | Impact on TETRA | 2024/2023 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specialized Chemicals (e.g., Bromides) | Limited suppliers, high purity requirements, supply chain disruptions | Increased raw material costs, potential supply shortages | Chemical price increases observed in 2024 due to supply chain issues. |
| Proprietary Equipment | Patents, unique manufacturing processes, high R&D investment | Higher equipment acquisition costs, limited alternative sourcing | Increased investment in advanced oilfield technologies in 2023. |
| Skilled Labor | Scarcity of specialized engineers and technicians, high demand | Increased labor costs, talent acquisition challenges | Persistent shortage of experienced petroleum engineers in 2024. |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Tetra, revealing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the influence of substitutes.
Visualize competitive intensity across all five forces with a dynamic, interactive dashboard, allowing for immediate identification of strategic vulnerabilities.
Customers Bargaining Power
TETRA's core clientele consists of major oil and gas exploration and production (E&P) companies. These entities, by virtue of their substantial size and the sheer volume of services they procure, wield considerable bargaining power. For instance, in 2023, the upstream segment of the oil and gas industry saw significant consolidation, with several large E&P companies merging, thereby increasing their collective purchasing might.
This trend towards larger, more consolidated customers directly translates into greater leverage for them when negotiating with service providers like TETRA. They can effectively demand more advantageous contract terms, competitive pricing, and the bundling of services to meet their operational needs more efficiently.
The oil and gas sector is known for its ups and downs, and this directly impacts how much customers care about price. When oil prices are high, customers might be a bit more forgiving, but when prices dip, they become very focused on saving money. This means companies like TETRA need to be sharp with their pricing to stay competitive.
In 2023, for instance, the volatility in crude oil prices, with Brent crude averaging around $82 per barrel for the year, put significant pressure on exploration and production (E&P) companies. This pressure naturally trickles down to their suppliers, like TETRA, forcing them to offer more competitive rates to win contracts and maintain market share.
TETRA's customers, primarily E&P companies, are constantly looking for ways to reduce their capital and operational expenditures. This drive for cost optimization means they will readily switch to a competitor if they can find a similar service at a lower price, making price a critical factor in TETRA's customer relationships.
For many standard oilfield services, like basic completion fluids or routine water management, customers often find it easy to switch providers. This is because the costs and effort involved in changing suppliers are usually quite low. For instance, a company needing a common completion fluid might only need to compare pricing sheets from a few vendors, with minimal disruption to their operations if they switch.
However, the situation changes dramatically when we look at specialized offerings. TETRA Technologies, for example, provides proprietary solutions such as TETRA CS Neptune fluids. For these advanced or custom-engineered products, switching costs for customers are significantly higher. This is due to the need for new training, potential equipment modifications, or the loss of performance benefits associated with the specialized service, thereby reducing customer bargaining power in these specific areas.
Customer's Ability to Self-Provide
When large integrated oil and gas companies can bring services in-house, like water management or well testing, it significantly boosts their bargaining power. This capability means they don't have to rely solely on external providers like TETRA Technologies, giving them leverage to negotiate better pricing and terms. For instance, many majors have invested in their own frac water treatment facilities, reducing their need for third-party services.
This potential for self-provision directly impacts TETRA's ability to dictate terms. Companies that can perform certain operations internally, or even produce some of their own completion fluids, have a strong incentive to do so if it's more cost-effective. This limits TETRA's pricing power and forces them to continuously demonstrate value.
- Reduced reliance on external vendors: Major oil companies often possess the capital and expertise to manage critical operational aspects internally.
- Cost-saving incentives: In-house capabilities can lead to direct cost reductions compared to outsourcing, especially for high-volume or repetitive services.
- Strategic control: Performing services internally allows companies greater control over quality, scheduling, and proprietary processes.
- Negotiating leverage: The mere possibility of self-provision strengthens a customer's hand in negotiations with service providers like TETRA.
Demand for Integrated Solutions
Customers are increasingly looking for complete packages of services instead of just individual parts. This helps them simplify their operations and have one company responsible for everything. For example, in the oilfield services sector, clients might prefer a single provider for drilling, completion, and production services.
This shift means customers can demand more from fewer suppliers, which naturally gives more leverage to bigger, more diversified companies. This consolidation trend puts pressure on specialized providers to either expand their offerings or face reduced bargaining power.
TETRA's capacity to bundle its services and introduce new, all-inclusive solutions is vital for keeping customers happy and lessening their influence. For instance, the introduction of integrated digital solutions like TETRA Oasis TDS, which combines various data management and analysis tools, directly addresses this customer demand for comprehensive offerings.
- Demand for Integrated Solutions: Customers are moving towards bundled service packages for operational efficiency and single-point accountability.
- Customer Leverage: This trend allows customers to consolidate suppliers, increasing their bargaining power with individual vendors.
- TETRA's Response: TETRA's ability to offer integrated solutions, such as TETRA Oasis TDS, is key to retaining customers and mitigating their bargaining power.
- Market Trend Impact: In 2024, the oilfield services market saw continued consolidation, with clients prioritizing providers capable of delivering end-to-end solutions, a trend observed in major project procurements.
Customers, primarily large oil and gas exploration and production (E&P) companies, hold significant bargaining power due to their substantial purchasing volume and the industry's cost-sensitive nature. This power is amplified by industry consolidation, as seen with mergers in 2023, which increases clients' collective leverage. When oil prices, like the 2023 average of around $82 per barrel for Brent crude, decline, customers intensify their focus on cost reduction, making price a critical negotiation point for service providers like TETRA.
The ease with which customers can switch suppliers for standard services, such as basic completion fluids, further enhances their bargaining power. However, for specialized offerings like TETRA CS Neptune fluids, switching costs are higher due to training and potential equipment needs, thereby diminishing customer leverage in these niche areas. Furthermore, the ability of major E&P companies to bring services in-house, such as water management, strengthens their negotiating position by reducing reliance on external vendors and providing strategic control.
Customers are increasingly demanding integrated, end-to-end solutions rather than individual services. This trend allows them to consolidate suppliers, thereby increasing their bargaining power with remaining vendors. TETRA's ability to offer comprehensive packages, exemplified by solutions like TETRA Oasis TDS, is crucial for retaining clients and mitigating their influence. The 2024 market trend continued to favor providers capable of delivering these consolidated offerings, impacting procurement strategies.
| Factor | Impact on TETRA | 2023/2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Size & Volume | High bargaining power due to large orders | Consolidation in upstream E&P increased client size. |
| Price Sensitivity | Customers demand competitive pricing, especially during price downturns | Brent crude averaged ~$82/barrel in 2023, increasing cost pressure. |
| Switching Costs (Standard Services) | Low switching costs empower customers to easily change providers | Minimal disruption for common fluids like basic completion fluids. |
| Switching Costs (Specialized Services) | Higher switching costs reduce customer leverage for proprietary solutions | TETRA CS Neptune fluids require new training, limiting easy switches. |
| In-house Capabilities | Potential for self-provision strengthens customer negotiation | Majors investing in own frac water treatment facilities. |
| Demand for Integrated Solutions | Customers consolidate suppliers, increasing leverage over individual vendors | Clients prioritize end-to-end providers in 2024 procurements. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Tetra Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Tetra Porter's Five Forces Analysis, presenting a detailed examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, offering a fully formatted and actionable strategic tool. No placeholders or sample content; you get the entire, ready-to-use analysis.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The oil and gas equipment and services sector, where TETRA Technologies operates, is characterized by a moderate level of fragmentation. This means there are several significant companies, but also a good number of smaller, niche providers.
TETRA faces formidable competition, particularly in its completion fluids segment, from industry giants such as Baker Hughes, Halliburton, and Schlumberger. These companies boast expansive global operations and a wide array of services, intensifying the battle for market share and client contracts.
For instance, in 2023, the global oilfield services market was valued at approximately $250 billion, with these major players holding substantial portions of that revenue, underscoring the competitive landscape TETRA navigates.
The oilfield services sector is characterized by substantial fixed costs, including investments in specialized machinery, operational facilities, and ongoing research. For example, a single offshore drilling rig can cost hundreds of millions of dollars, representing a significant upfront capital commitment.
This high fixed-cost structure compels companies like TETRA Technologies to prioritize high capacity utilization. To cover these costs, firms often engage in aggressive pricing, especially when demand softens, aiming to keep their expensive assets operational.
In 2023, TETRA Technologies reported revenue of $669.1 million, with operating expenses reflecting these fixed cost pressures. When demand falters, this can trigger price wars as competitors vie for market share, directly impacting TETRA's profitability and financial health.
When the oil and gas industry experiences slow growth in certain areas, competition naturally heats up. Companies have to fight harder for the available business, which can lead to more aggressive pricing and a focus on efficiency. This dynamic is particularly evident in segments like U.S. onshore completion services, where activity saw a noticeable dip in late 2024 and early 2025, impacting demand for essential services such as water management and flowback operations.
This slowdown in core onshore markets forces service providers to look for opportunities elsewhere. Some are doubling down on specialized niches, like the robust deepwater completion fluids market, to ensure revenue streams. Others are pursuing international expansion to tap into different growth cycles and diversify their customer base, aiming to mitigate the impact of regional downturns.
Product and Service Differentiation
Companies in the oil and gas services sector actively pursue product and service differentiation to stand out. This often involves investing heavily in technological innovation, enhancing service quality, and developing specialized solutions tailored to client needs. For instance, TETRA Technologies, a key player, differentiates itself through advanced completion fluids like its TETRA CS Neptune, designed for enhanced wellbore stability and production.
Furthermore, TETRA's commitment to innovation extends to its water treatment technologies, exemplified by the TETRA Oasis TDS system, which addresses critical water management challenges in the industry. These unique, high-value offerings allow TETRA to move beyond simple price competition, thereby solidifying its market position and creating a competitive moat.
- Technological Innovation: TETRA's development of specialized completion fluids and water treatment technologies showcases a focus on innovation.
- Service Quality: The emphasis on providing high-value solutions implies a commitment to superior service delivery.
- Specialized Solutions: Offering tailored products like TETRA CS Neptune and TETRA Oasis TDS addresses specific industry pain points.
- Mitigating Price Competition: Differentiation through technology and specialized services reduces the pressure of direct price wars.
Mergers, Acquisitions, and Strategic Alliances
Mergers, acquisitions, and strategic alliances are actively reshaping the competitive arena, with companies consolidating to boost market share, acquire new technologies, or broaden their service portfolios. This dynamic can foster the emergence of larger, more powerful competitors, compelling TETRA to constantly evaluate its strategic stance and consider similar moves.
For instance, in 2024, the global M&A market saw significant activity. The technology sector alone witnessed a surge in deals as companies sought to integrate AI capabilities and expand cloud services. This trend directly impacts TETRA by potentially creating more formidable rivals with greater resources and market influence.
- Increased Consolidation: M&A activity often leads to fewer, larger players in an industry, intensifying rivalry.
- Technology Acquisition: Companies acquire rivals to gain access to cutting-edge technologies, enhancing their competitive edge.
- Market Expansion: Alliances and acquisitions can facilitate entry into new geographic markets or customer segments.
- Enhanced Capabilities: Combined entities often possess greater financial strength, R&D capacity, and operational efficiencies.
Competitive rivalry in the oil and gas equipment and services sector is intense, driven by a few large, established players and numerous smaller firms. TETRA Technologies competes directly with giants like Baker Hughes and Halliburton, who possess significant market share and extensive service offerings.
The industry's high fixed costs necessitate high capacity utilization, often leading to aggressive pricing strategies, especially during periods of low demand. For example, in 2023, the global oilfield services market reached approximately $250 billion, with these major competitors holding substantial portions, highlighting the competitive pressures TETRA faces.
Differentiation through technological innovation and specialized services, such as TETRA's advanced completion fluids, is crucial for mitigating direct price competition. The sector also sees ongoing consolidation through mergers and acquisitions, creating larger, more formidable rivals that TETRA must continuously assess.
| Competitor | Key Offerings | Market Presence |
| Baker Hughes | Oilfield services, equipment, digital solutions | Global |
| Halliburton | Drilling, completion, production services | Global |
| Schlumberger | Reservoir characterization, drilling, production | Global |
| TETRA Technologies | Completion fluids, water management, offshore services | North America, International |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for clear brine fluids in well completion is moderate but growing. While clear brines are highly effective, alternative completion technologies are emerging. For instance, advancements in drilling efficiency and new completion designs could reduce the overall volume of fluids required, thereby lessening demand for traditional clear brines.
Unconventional drilling techniques, in particular, are a key area to watch. Some of these methods may utilize entirely different fluid systems or employ techniques that bypass the need for specific completion fluid properties that clear brines typically provide. This could lead to a gradual shift away from current fluid formulations.
In 2024, the global oilfield chemicals market, which includes completion fluids, was valued at approximately $30 billion. While clear brines represent a significant portion, the drive for cost reduction and operational efficiency in the upstream sector could accelerate the adoption of less brine-intensive or alternative fluid technologies if they prove economically viable and technically sound.
The threat of substitutes in water management is growing as Exploration and Production (E&P) companies enhance their in-house water recycling and reuse capabilities. This internal development can reduce reliance on external water management service providers.
Furthermore, the industry's focus on sustainability and cost efficiency fuels innovation in waterless or minimal-water extraction techniques. For instance, advancements in dry drilling technologies are being explored, which could significantly diminish the need for traditional water management services.
By 2024, the increasing investment in proprietary water infrastructure by major E&P firms signals a direct challenge to the market share of external water management companies. This trend is projected to continue as companies seek greater control over their operational costs and environmental footprint.
The threat of substitutes for traditional well testing methods is growing, driven by advancements in digital technologies. Companies like TETRA, which offer these services, need to consider how new approaches can fulfill similar needs.
Advanced digital technologies, including the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI), are emerging as viable substitutes. These technologies allow for continuous, real-time monitoring of reservoir performance, reducing the reliance on periodic, physical well tests. For instance, in 2024, the oil and gas industry saw increased investment in digital twin technologies for production optimization, which directly impacts the need for traditional testing.
The integration of real-time analytics provides deeper insights into reservoir characteristics and production efficiency. This capability can diminish the demand for conventional well testing services by offering a more dynamic and data-rich understanding of well performance, potentially leading to more efficient resource allocation and reduced operational costs for energy companies.
Shift to Non-Hydrocarbon Energy Sources
The global shift towards non-hydrocarbon energy sources presents a substantial threat of substitution for companies like TETRA Technologies, which primarily serves the oil and gas industry. As nations commit to decarbonization goals, investments in renewable energy are surging, directly impacting the long-term demand for fossil fuels and related services.
This transition is not a fleeting trend but a fundamental restructuring of the global energy landscape. For instance, by the end of 2023, global renewable energy capacity additions were projected to reach 510 gigawatts (GW), a significant increase from previous years, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA). This growing capacity directly displaces the need for traditional energy exploration and production.
- Growing Renewable Energy Investments: Global investment in clean energy is expected to exceed $2 trillion annually by 2030, according to BloombergNEF, diverting capital away from fossil fuel projects.
- Policy Support for Renewables: Governments worldwide are implementing policies and subsidies to accelerate the adoption of solar, wind, and other clean technologies, further diminishing reliance on oil and gas.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in battery storage and grid modernization are making renewable energy sources more reliable and cost-competitive, enhancing their appeal as substitutes.
Cost-Effectiveness of Substitutes
The attractiveness of substitutes for TETRA's offerings hinges significantly on their cost-effectiveness and performance relative to TETRA's specialized services. If alternative technologies or methods can achieve similar or better outcomes at a reduced price point, customers will naturally be drawn to switch.
For instance, while TETRA provides robust communication solutions, the increasing affordability and capability of certain commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) communication systems or even advanced private mobile networks could present a viable, lower-cost alternative for some clients by 2024. This cost-performance trade-off is a critical factor influencing customer adoption of substitutes.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Customers will weigh the total cost of ownership of TETRA solutions against emerging alternatives, considering factors like initial investment, maintenance, and operational expenses.
- Performance Benchmarking: The ability of substitutes to match or exceed TETRA's reliability, security, and features in specific use cases will determine their competitive threat.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in areas like 5G private networks or advanced satellite communication could offer compelling performance at potentially lower price points, challenging TETRA's market position.
The threat of substitutes for traditional well completion fluids, like clear brines, is moderate but escalating. Emerging technologies in drilling and completion designs are reducing the overall fluid volumes needed, impacting demand for clear brines.
Unconventional drilling methods, in particular, are a key driver, potentially employing different fluid systems or bypassing the need for specific clear brine properties.
In 2024, the global oilfield chemicals market, including completion fluids, was valued at approximately $30 billion, with clear brines being a significant segment. The industry's push for cost reduction could accelerate the adoption of less brine-intensive or alternative fluids if they prove economically and technically viable.
| Fluid Type | 2024 Market Value (USD Billion) | Threat of Substitution | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clear Brines | Estimated $5-7 Billion (of total $30B oilfield chemicals) | Moderate to Growing | Advancements in drilling efficiency, new completion designs, unconventional drilling techniques |
| Alternative Completion Fluids | N/A (Emerging Segment) | Low to Moderate | Cost-effectiveness, performance matching clear brines |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the oil and gas services sector, especially for specialized areas like completion fluids or well testing, requires a significant upfront investment. Companies need to fund advanced equipment, sophisticated manufacturing plants, and ongoing research and development. For instance, establishing a new well testing operation could easily require tens of millions of dollars for specialized vessels, diagnostic tools, and personnel training.
The services TETRA provides demand a high level of technological skill, particularly in creating intricate chemical formulations for clear brine fluids and in analyzing data from well testing. This expertise acts as a significant hurdle for potential new competitors.
Companies looking to enter this market would need to commit substantial resources to research and development to create comparable technologies or purchase existing ones. For instance, in 2023, the global oilfield services market, which includes services like those offered by TETRA, saw significant investment in technological advancements, with companies prioritizing digital solutions and advanced materials to enhance efficiency and safety.
TETRA's ongoing commitment to innovation, exemplified by its work on bromine and lithium projects, further elevates the entry barrier. These forward-looking initiatives require specialized knowledge and substantial capital, making it challenging for new players to match TETRA's technological capabilities and market position.
The oil and gas sector faces formidable barriers to entry due to stringent global environmental regulations and safety standards. New companies must contend with complex permitting procedures and invest heavily in compliant technologies, impacting their initial capital outlay and time-to-market.
For instance, in 2024, the average cost for obtaining environmental permits in the upstream oil and gas sector in the United States can range from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars, depending on the project's scope and location. This significant financial commitment and the lengthy approval timelines deter many potential new entrants.
Established Customer Relationships and Reputation
Tetra Technologies (TETRA) benefits from deeply entrenched customer relationships, particularly with major players in the oil and gas sector. These long-standing partnerships are built on a reputation for consistent reliability and high-quality service delivery, making it difficult for new entrants to gain traction.
Displacing established providers who have proven track records and secured supply chain agreements presents a significant hurdle for newcomers. This established network effect, where existing customers are unlikely to switch due to demonstrated performance and existing infrastructure, acts as a formidable barrier to entry.
- Established Trust: TETRA's decades-long relationships with key clients foster a high degree of trust, a critical factor in the capital-intensive oil and gas industry.
- Proven Performance: The company's history of successful project execution and reliable service delivery creates a strong incumbent advantage.
- Supply Chain Integration: Existing supply chain agreements and infrastructure further solidify TETRA's position, making it challenging for new entrants to match operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Access to Distribution Channels and Global Infrastructure
The threat of new entrants for TETRA, particularly concerning access to distribution channels and global infrastructure, is significantly mitigated by TETRA's established worldwide operations. TETRA's presence across six continents means it has already built and secured extensive distribution networks and logistics capabilities.
Replicating this global footprint would demand massive capital investment and considerable time for any new competitor. For instance, establishing a comparable infrastructure in 2024 would likely involve billions of dollars in upfront costs for warehousing, transportation, and local market penetration.
This high barrier to entry, especially in diverse and complex international markets, severely limits the ability of new players to gain a foothold and compete effectively on a global scale.
- Global Reach: TETRA operates across six continents, demonstrating a vast and integrated distribution and service network.
- Infrastructure Investment: Building a comparable global infrastructure in 2024 would require substantial capital outlay, likely in the billions of dollars.
- Time and Complexity: Establishing international distribution and logistics is a time-consuming and complex undertaking, posing a significant hurdle for new entrants.
The threat of new entrants into TETRA's specialized oil and gas services sector is considerably low. This is primarily due to the immense capital required for specialized equipment and advanced technologies, coupled with the need for highly skilled personnel. Furthermore, stringent environmental regulations and established customer relationships create significant hurdles for any potential new players aiming to compete.
| Barrier Type | Description | Estimated Cost/Impact (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Advanced equipment, manufacturing, R&D | Tens of millions USD for specialized operations |
| Technological Expertise | Intricate chemical formulations, data analysis | High barrier due to specialized knowledge |
| Regulatory Compliance | Environmental permits, safety standards | $10,000s - $100,000s+ for permits; lengthy approval |
| Customer Relationships | Established trust, proven performance | Difficult to displace incumbent providers |
| Global Infrastructure | Distribution networks, logistics capabilities | Billions USD to replicate global footprint |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from industry-specific market research reports, company financial statements, and expert analyst commentary to provide a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.
