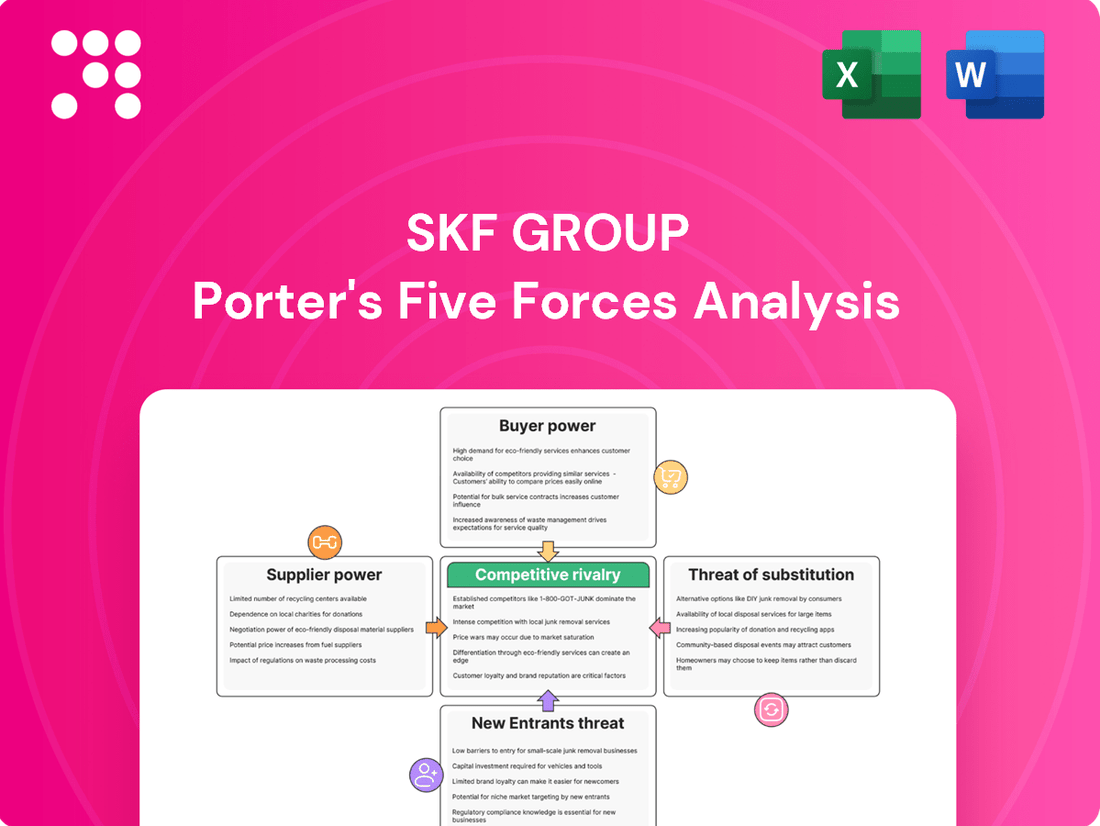
SKF Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
SKF Group Bundle
SKF Group operates in a competitive landscape shaped by moderate buyer and supplier power, with the threat of substitutes presenting a notable challenge. The intensity of rivalry within the bearing industry is significant, impacting SKF's pricing strategies and market share. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping SKF Group’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
SKF's reliance on specialized raw materials like steel, alloy steel, ceramics, and bronze means that a concentrated supplier base for these critical inputs can wield considerable bargaining power. If only a few companies produce these highly technical components, they can dictate terms and pricing, directly impacting SKF's cost of goods sold.
For instance, fluctuations in global steel prices, a primary input for SKF's bearings, can significantly affect the company's profitability. In early 2024, steel prices saw volatility due to geopolitical factors and supply chain disruptions, putting pressure on manufacturers like SKF to absorb or pass on these increased costs.
The intricate nature and high precision demanded for SKF's bearing components mean that changing suppliers for crucial materials or specialized parts can incur substantial costs. These expenses can encompass re-tooling machinery, the rigorous re-qualification process for new materials, and the potential for significant disruptions to ongoing production lines, all of which bolster the bargaining power of existing suppliers.
Suppliers offering unique or proprietary inputs, such as specialized alloys or advanced sensor technologies crucial for SKF's high-performance bearings, wield significant bargaining power. SKF's strategic direction towards smart bearings, incorporating predictive maintenance capabilities, further amplifies its reliance on suppliers with the technical prowess to meet these exacting specifications.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers, while not a prominent concern for SKF Group, represents a potential shift in industry dynamics. If key raw material suppliers were to develop the capabilities or express an intent to manufacture bearings themselves, their bargaining power would undoubtedly increase. This scenario is less probable in highly specialized sectors like bearing components, but it remains a theoretical risk.
The global bearing market is robust, with projections indicating continued growth. For instance, the market was valued at approximately USD 70 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5% through 2030. This substantial market size could theoretically incentivize some suppliers to explore vertical integration, aiming to capture a larger share of the value chain.
- Potential for Supplier Forward Integration: Suppliers developing bearing manufacturing capabilities would enhance their leverage.
- Industry Specialization: This threat is less common in specialized component industries like bearings.
- Market Size: The global bearing market's significant value, estimated at USD 70 billion in 2023, could theoretically drive supplier integration.
- Growth Projections: A projected CAGR of around 5% through 2030 indicates a healthy market that might attract such moves.
Importance of SKF to Suppliers
SKF's significant global presence and its role as a major customer for specialized bearing components mean that many suppliers rely heavily on SKF's business. If SKF constitutes a substantial percentage of a supplier's total revenue, that supplier's bargaining power against SKF would naturally be diminished. For instance, in 2023, SKF reported revenues of SEK 93.9 billion (approximately $8.9 billion USD), highlighting its scale as a buyer.
However, SKF's strategy of regionalizing its operations and building resilient regional value chains could also influence supplier relationships. This approach might involve diversifying its supplier base within specific regions, which could provide some suppliers with increased leverage if they become critical to a particular regional supply chain. SKF's commitment to innovation and advanced materials means it often partners with suppliers who possess unique technological capabilities, which can also grant those suppliers a degree of bargaining power.
- Supplier Dependence: A supplier's reliance on SKF for a large portion of its sales weakens its bargaining power.
- SKF's Scale: SKF's substantial revenue (SEK 93.9 billion in 2023) makes it a dominant customer for many specialized suppliers.
- Regionalization Strategy: SKF's focus on regional value chains can shift bargaining dynamics by creating dependencies within specific geographic areas.
- Technological Leverage: Suppliers with unique or critical technologies for SKF's advanced products may possess greater bargaining influence.
SKF's bargaining power with its suppliers is influenced by the concentration of suppliers for critical inputs like specialized steel and ceramics. When few suppliers can provide these high-precision materials, their pricing power increases. For example, in 2024, global steel price volatility, driven by supply chain issues, directly impacted SKF's input costs.
The high switching costs associated with re-tooling and re-qualifying new material suppliers for SKF's complex bearing components further solidify the power of existing suppliers. Suppliers offering proprietary materials or advanced technologies, essential for SKF's smart bearing initiatives, also command significant leverage.
| Factor | Impact on SKF | Example/Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High for specialized inputs | Few suppliers for high-grade alloys, ceramics |
| Switching Costs | Significant for SKF | Re-tooling, material re-qualification |
| Supplier Technology | Leverage for advanced materials | Proprietary alloys for smart bearings |
| SKF's Scale as Buyer | Reduces supplier power | 2023 Revenue: SEK 93.9 billion (~$8.9 billion USD) |
What is included in the product
SKF Group's Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the intense competition, significant buyer power, and moderate threat of new entrants in the bearing and sealing solutions market.
Instantly assess competitive pressures with a visual, color-coded breakdown of each of Porter's Five Forces for SKF Group.
Customers Bargaining Power
SKF's broad customer base across industrial, automotive, and aerospace sectors, supported by over 17,000 distributors globally, generally dilutes individual customer bargaining power. However, significant concentration exists with large Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) clients, especially in the automotive and industrial machinery segments.
These high-volume purchasers, by virtue of their substantial order sizes, wield considerable influence. For instance, in 2023, the automotive sector continued to be a major revenue driver for bearing manufacturers, and a few key automotive OEMs could represent a substantial portion of a single supplier's sales, thereby amplifying their negotiation leverage over pricing and terms.
For customers integrating SKF's bearings and solutions into their complex machinery, the costs associated with switching suppliers are substantial. These can include significant expenses for redesigning components, retooling manufacturing lines, conducting rigorous performance testing, and the inherent risk of encountering unforeseen operational issues with a new supplier's products. This makes it less likely for customers to switch away easily, thereby increasing their loyalty to SKF.
SKF's strategy of providing tailored solutions and integrated offerings further solidifies these customer switching costs. By embedding their products deeply within a customer's operational framework, SKF creates a dependency that makes a transition to a competitor a more complex and costly undertaking. This strategic approach directly diminishes the bargaining power of customers who might otherwise seek to leverage competition for better terms.
SKF's strong product differentiation significantly curtails customer bargaining power. By investing heavily in technological innovation, SKF offers advanced solutions like smart bearings and predictive maintenance, which are not easily replicated by competitors. This focus on unique value propositions means customers are less likely to switch based on price alone, as they perceive distinct benefits in SKF's offerings.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Large original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) in industries like automotive or heavy machinery possess the scale to consider backward integration, potentially producing their own bearings. This is particularly true for high-volume, standardized bearing types where the manufacturing process is more predictable and less specialized. For instance, a major truck manufacturer might evaluate the cost-effectiveness of producing standard wheel hub bearings in-house.
However, the significant capital expenditure for specialized machinery, the need for deep technical expertise in metallurgy and precision engineering, and achieving SKF's established economies of scale present substantial barriers. SKF's 2024 revenue of approximately €22.7 billion underscores the scale advantage they hold, making it difficult for most individual customers to replicate their production efficiency and cost structure for a broad range of bearing products. This high barrier limits the practical threat of backward integration for most of SKF's customer base, especially for their more complex or custom-engineered bearing solutions.
- High Capital Investment: Setting up bearing manufacturing facilities requires substantial upfront costs for specialized machinery and infrastructure.
- Technical Expertise: Producing high-quality bearings demands advanced knowledge in materials science, precision machining, and quality control.
- Economies of Scale: SKF's large production volumes allow for lower per-unit manufacturing costs, a benchmark difficult for individual customers to match.
- Product Complexity: The threat is less pronounced for customers requiring specialized or custom-designed bearings, where SKF's R&D and engineering capabilities are critical.
Price Sensitivity of Customers
SKF's ability to maintain margins, even with weaker market demand in certain areas, points to a degree of pricing power. This resilience is often achieved through strategic portfolio adjustments and well-timed pricing initiatives.
However, the bargaining power of customers is still a significant factor, particularly in industries where competition is fierce. For instance, in the automotive sector, customers are highly attuned to costs and will actively seek out more economical solutions.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers in competitive sectors like automotive are highly price-sensitive, influencing SKF's pricing strategies.
- Portfolio Management: SKF's ability to manage its product portfolio has helped mitigate the impact of price sensitivity in some markets.
- Margin Resilience: Despite market pressures, SKF has shown resilience in its profit margins, suggesting some success in passing on costs or offering higher-value solutions.
While SKF's vast customer base and high switching costs generally limit individual customer bargaining power, key Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs), particularly in automotive, wield significant influence due to their substantial order volumes. SKF's 2023 revenue, with automotive being a major contributor, highlights the leverage these large clients possess in price negotiations.
The threat of backward integration by customers is mitigated by SKF's significant economies of scale, as evidenced by its 2024 revenue of approximately €22.7 billion, and the high capital and technical expertise required for bearing manufacturing. This makes it challenging for most customers to produce bearings in-house, especially for specialized applications.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factors | SKF's Mitigating Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Large OEMs (Automotive, Industrial Machinery) | High volume purchases, potential for backward integration | Product differentiation, tailored solutions, high switching costs, economies of scale |
| General Industrial Customers | Price sensitivity in competitive markets | Portfolio management, margin resilience, value-added services |
| Aerospace Customers | Strict quality and performance requirements, long-term contracts | Technological innovation, R&D investment, customized solutions |
Same Document Delivered
SKF Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of the SKF Group, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, offering an in-depth examination of industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and substitute products. Rest assured, there are no surprises or placeholders; you're acquiring the complete, ready-to-use analysis for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global bearings market is a crowded arena with several formidable players, including Schaeffler Group, NSK Ltd., and NTN Corporation, alongside SKF Group itself. This intense competition means SKF must constantly innovate and refine its strategies to maintain its market standing.
In 2023, the global industrial bearings market was valued at approximately $75 billion, with these major companies holding significant market shares. SKF's revenue for 2023 was around $9.7 billion, showcasing its substantial presence but also the scale of the competitive challenge it faces.
The capabilities of these competitors are broad, encompassing advanced manufacturing techniques, extensive global distribution networks, and significant investment in research and development. For instance, Schaeffler Group, a key rival, reported revenues exceeding $17 billion in 2023, demonstrating its considerable scale and technological prowess.
The global bearings market is experiencing robust growth, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) between 6.39% and 9.2% from 2025 to 2037. This expansion is expected to push the market value to as high as $152.47 billion by 2037.
This significant market expansion, particularly in areas like electric vehicles and renewable energy, naturally fuels competitive rivalry. As the pie grows larger, existing players and new entrants alike are motivated to capture a greater share, leading to intensified competition for market dominance.
SKF's competitive rivalry is managed through a relentless focus on product differentiation and innovation. The company consistently invests in research and development, which is key to maintaining its edge. This commitment is evident in offerings like smart bearings, which provide predictive maintenance capabilities, and specialized high-performance bearings designed for demanding sectors such as aerospace and the rapidly growing electric vehicle market.
Exit Barriers
The bearing industry, including players like SKF Group, faces substantial exit barriers due to the immense capital investment required for manufacturing facilities, specialized machinery, and extensive global distribution networks. These high fixed costs make it economically challenging for companies to cease operations or divest assets. For instance, SKF's significant investments in advanced manufacturing technologies and its worldwide presence represent a considerable sunk cost.
These elevated exit barriers compel companies to remain in the market and continue competing, even when facing adverse economic conditions or declining profitability. This persistence can lead to intensified rivalry as firms strive to maintain market share and recover their investments. The sheer scale of operations and the specialized nature of the equipment mean that exiting the market is not a simple matter of shutting down operations; it often involves substantial write-offs and disposal challenges.
SKF's own strategic decisions, such as the previously announced separation of its Automotive business, underscore the complexity and difficulty associated with exiting or restructuring parts of the business. Such moves are often protracted and involve significant financial and operational considerations, reflecting the deep entrenchment of assets and capabilities within the industry.
- High Capital Intensity: The bearing industry demands massive investments in specialized manufacturing equipment and global logistics, creating significant financial hurdles for exiting firms.
- Specialized Assets: Machinery and facilities are often highly specific to bearing production, limiting their resale value and making divestment difficult.
- Global Distribution Networks: Maintaining and then dismantling worldwide supply chains and distribution channels represents a substantial cost and complexity, further discouraging exit.
- Persistence in Competition: Due to these barriers, companies are incentivized to stay operational and compete fiercely, even during downturns, to avoid incurring losses from premature asset disposal.
Market Concentration and Balance
The bearing market, while featuring significant global players, exhibits a relatively balanced competitive landscape. No single entity commands an overwhelming market share, which fosters an environment where strategic maneuvering is crucial for sustained success. This equilibrium means that factors like innovation, customer service, and cost management play pivotal roles in differentiating competitors.
SKF Group navigates this dynamic by emphasizing operational efficiency and disciplined pricing strategies. Their focus on optimizing production processes and maintaining competitive price points allows them to effectively counter rivals. Furthermore, SKF's ongoing portfolio management, which involves strategic acquisitions and divestitures, ensures they remain agile and responsive to market shifts.
- Balanced Market: Major players exist, but no single company dominates, creating a competitive equilibrium.
- SKF's Strategy: Operational efficiency and pricing discipline are key to SKF's competitive approach.
- Portfolio Management: SKF actively manages its business portfolio to adapt to market dynamics and maintain competitiveness.
SKF operates in a highly competitive bearing market, facing strong rivals like Schaeffler Group and NSK Ltd. This intense rivalry, fueled by a growing global market projected to reach over $152 billion by 2037, necessitates continuous innovation and strategic efficiency from SKF. The company's revenue of approximately $9.7 billion in 2023 highlights its significant position but also the scale of competition it must overcome.
| Competitor | 2023 Revenue (approx.) | Key Strengths |
|---|---|---|
| SKF Group | $9.7 billion | Innovation, operational efficiency, smart bearings |
| Schaeffler Group | >$17 billion | Advanced manufacturing, R&D investment, global reach |
| NSK Ltd. | Not specified | Global distribution, technological capabilities |
| NTN Corporation | Not specified | Market presence, product diversification |
SSubstitutes Threaten
While direct functional substitutes for bearings are scarce due to their core role in rotational mechanics, emerging technologies present potential long-term threats. Innovations in material science and concepts like magnetic levitation could offer alternative solutions in specific applications.
SKF is proactively addressing this by investing heavily in research and development. For instance, in 2023, SKF's R&D expenditure was €354 million, focusing on areas like advanced materials and digital solutions to maintain a competitive edge and adapt to evolving industry needs, such as the growing demand for specialized bearings in electric vehicles.
Any alternative technology would need to offer a demonstrably superior performance-to-cost ratio to truly displace traditional bearings on a widespread scale. For instance, while advanced composite materials might offer weight savings, their current production costs often outweigh the benefits compared to established steel alloys, limiting their adoption in cost-sensitive applications.
The highly optimized and mature nature of bearing technology presents a significant hurdle for potential substitutes. Innovations in materials science and manufacturing processes have continuously refined existing bearing designs, making it difficult for emerging alternatives to achieve a breakthrough performance advantage that justifies a higher price point or a less proven track record.
SKF's strategic emphasis on enhancing energy efficiency and extending the operational lifespan of its bearings directly addresses key customer value drivers. For example, SKF's hybrid bearings, incorporating ceramic rolling elements, can reduce friction by up to 50% in certain applications, leading to significant energy savings and reduced maintenance costs for end-users, thus strengthening their competitive position against potential substitutes.
Customers are often hesitant to switch from established bearing suppliers like SKF, especially for critical applications where performance and reliability are paramount. The potential for failure in a substitute product could lead to costly downtime and safety concerns, making the perceived risk of switching quite high.
The deep integration of SKF bearings into complex machinery and the long-standing trust built through consistent quality and support also act as significant deterrents to switching. For instance, in the automotive sector, a 2024 report indicated that over 70% of manufacturers prioritize supplier reliability and proven performance over marginal cost savings when selecting critical component suppliers.
Technological Advancements in the Bearing Industry
SKF's relentless pursuit of innovation in bearing design, materials science, and the integration of smart technologies like IoT and AI for predictive maintenance significantly reduces the threat of substitutes. By enhancing the performance, efficiency, and lifespan of its traditional bearings, SKF makes alternative solutions less appealing.
SKF's commitment to advancing bearing technology, including the development of advanced ceramic hybrid bearings and self-aligning spherical roller bearings, directly counters the allure of substitute products. For instance, their focus on reducing friction and increasing load capacity in their 2024 product lines offers superior performance compared to simpler or less engineered alternatives.
- SKF's R&D Investment: In 2023, SKF continued to invest heavily in research and development, focusing on areas like advanced lubrication systems and lightweight materials, further solidifying its position against substitutes.
- Smart Bearing Integration: The increasing adoption of SKF's smart bearings, which provide real-time data on operational status, offers a significant advantage over non-connected or less intelligent alternatives.
- Material Science Advancements: SKF's ongoing work with advanced alloys and composite materials aims to deliver bearings with enhanced durability and resistance to extreme conditions, diminishing the viability of less robust substitutes.
Regulatory and Standardization Hurdles
The bearing industry, particularly in demanding sectors like aerospace and automotive, operates under strict quality, safety, and performance regulations. For any substitute to gain traction, it must first clear these high regulatory and standardization hurdles, which can be a significant barrier to adoption. For example, in 2024, the automotive industry continued to emphasize advanced safety features, requiring components like bearings to meet evolving ISO standards for reliability and endurance.
These rigorous requirements mean that potential substitutes must demonstrate equivalent or superior performance and safety profiles to established bearing solutions. This process often involves extensive testing and certification, which can be time-consuming and costly, effectively limiting the threat from less rigorously developed alternatives. SKF, a leader in the sector, invests heavily in R&D to ensure its products consistently meet and exceed these global standards.
- Stringent Industry Standards: Aerospace and automotive sectors demand bearings that meet exacting quality and safety benchmarks.
- High Barrier to Entry: New substitute technologies must undergo rigorous testing and certification to prove compliance.
- Cost and Time Investment: Achieving regulatory approval for substitutes can be a lengthy and expensive process for manufacturers.
- SKF's Compliance Focus: SKF actively ensures its bearing solutions align with evolving global standards, maintaining a competitive edge.
The threat of substitutes for bearings is generally low due to their fundamental role in rotational machinery and the high switching costs for customers. However, advancements in material science and alternative motion technologies like magnetic levitation pose potential long-term challenges. SKF's significant investment in R&D, totaling €354 million in 2023, and focus on enhancing bearing performance and efficiency, such as with hybrid bearings offering up to 50% friction reduction, actively mitigates this threat.
Entrants Threaten
The bearing manufacturing industry demands significant upfront capital. New companies must invest heavily in sophisticated machinery, extensive research and development capabilities, and establishing global production facilities to compete effectively. For instance, SKF's ongoing investments, including plans for new plants in India, underscore the substantial financial commitment required.
Established players like SKF leverage substantial economies of scale, particularly in manufacturing, sourcing raw materials, and logistics. For instance, in 2023, SKF's net sales reached SEK 93.4 billion (approximately $8.9 billion USD), a scale that allows for considerable cost advantages.
Newcomers would find it exceptionally challenging to replicate these cost efficiencies without achieving comparable production volumes. This makes it difficult for them to compete effectively on price against incumbents who benefit from lower per-unit costs due to their established operational scale.
SKF's extensive portfolio of proprietary technologies and patents, including foundational innovations like the double-row self-aligning ball bearing, presents a significant hurdle for potential new entrants. This intellectual property requires substantial investment in research and development for any competitor seeking to match SKF's technological edge.
Access to Distribution Channels
SKF's formidable global distribution network, boasting over 17,000 distributors, presents a substantial barrier to entry. Establishing a comparable reach requires immense capital investment and years of relationship building, making it exceptionally difficult for newcomers to gain traction. This extensive network ensures product availability and customer service across diverse markets, a feat that new entrants would struggle to replicate quickly or cost-effectively.
The threat of new entrants is significantly mitigated by the sheer scale and established nature of SKF's distribution channels. For instance, in 2023, SKF reported continued strength in its distribution agreements, underscoring the loyalty and operational efficiency built over decades. Any new player would face the daunting task of not only matching this reach but also convincing distributors to carry their products over SKF's established offerings.
- SKF's global distribution network comprises over 17,000 distributors worldwide.
- Building a comparable network requires significant time, capital, and established relationships.
- New entrants face challenges in securing shelf space and customer access against SKF's entrenched presence.
Brand Loyalty and Reputation
SKF's formidable brand loyalty and reputation represent a significant barrier to new entrants. For over a century, SKF has cultivated a strong image centered on quality, unwavering reliability, and deep engineering expertise.
In demanding sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and industrial manufacturing, customers frequently place a premium on established performance and trusted suppliers. This inherent preference makes it exceptionally challenging for new, unproven companies to penetrate the market and win over established client bases.
- Brand Equity: SKF's brand is synonymous with high-performance bearings and sealing solutions, built over 115+ years.
- Customer Trust: In critical applications where failure is not an option, SKF's proven track record fosters deep customer trust and reduces perceived risk for buyers.
- Switching Costs: Beyond monetary costs, the effort and risk associated with qualifying and integrating new suppliers in sensitive industries deter many potential customers from switching away from SKF.
The threat of new entrants in the bearing industry is considerably low, largely due to the substantial capital investment required for manufacturing, research, and global operations. SKF's significant scale, evidenced by its 2023 net sales of SEK 93.4 billion, creates cost advantages that are difficult for newcomers to match.
Furthermore, SKF's extensive patent portfolio and established brand loyalty, built over more than a century, act as significant deterrents. Potential entrants face the challenge of replicating SKF's technological advancements and gaining customer trust in critical sectors.
The company's vast distribution network, comprising over 17,000 distributors worldwide, presents another formidable barrier. Building a comparable network requires immense time, capital, and established relationships, making it exceptionally difficult for new players to gain market access and compete effectively.
| Barrier Type | Description | SKF's Advantage | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment in machinery, R&D, and facilities. | SKF has established global production capabilities. | Significant hurdle for new companies to overcome. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs through high production volumes. | 2023 Net Sales: SEK 93.4 billion. | New entrants struggle to compete on price. |
| Intellectual Property | Proprietary technologies and patents. | Extensive patent portfolio, including foundational innovations. | Requires substantial R&D investment to match. |
| Distribution Network | Global reach for product availability and service. | Over 17,000 distributors worldwide. | Difficult and costly to replicate. |
| Brand Loyalty & Reputation | Customer trust in quality and reliability. | 115+ years of building trust and a strong brand image. | Challenging to penetrate established client bases. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our SKF Group Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, including SKF's official annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research from firms like IHS Markit and Mordor Intelligence.
