JSR Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
JSR Bundle
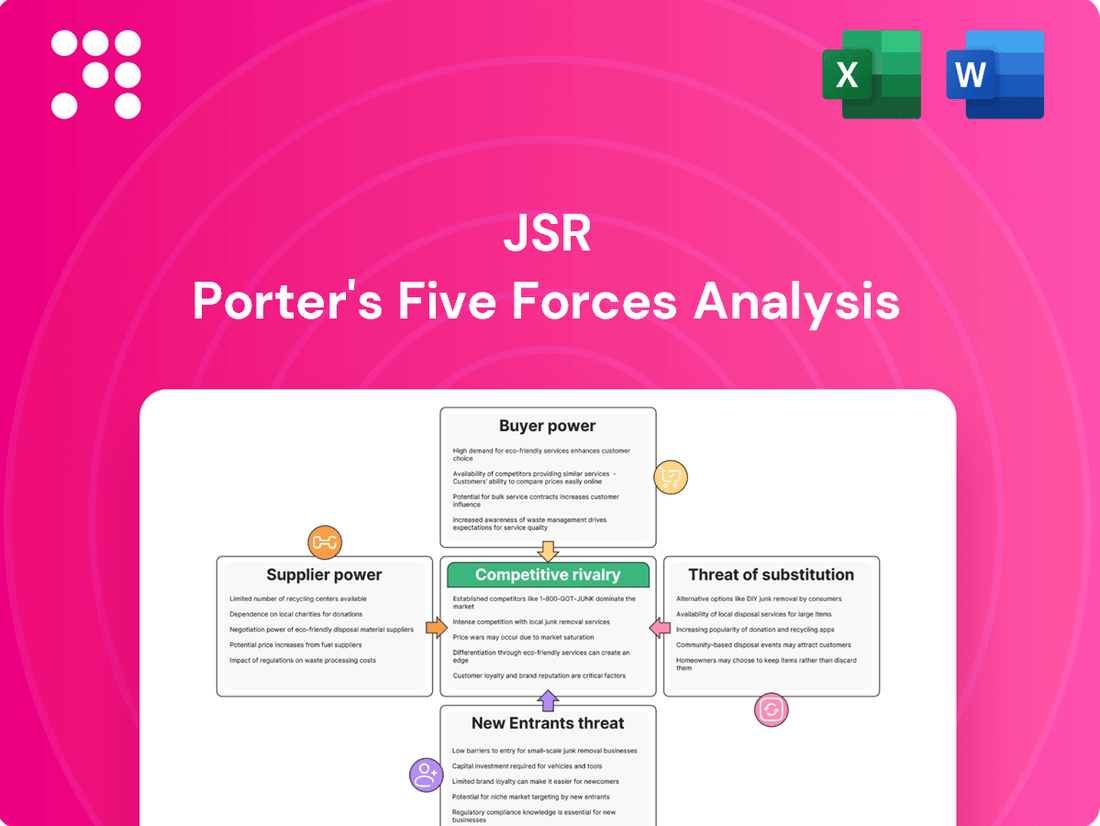
Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the competitive landscape for JSR, examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry. Understanding these forces is crucial for any business operating within or looking to enter JSR's market.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore JSR’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
JSR's reliance on highly specialized inputs in sectors like semiconductors and life sciences means supplier concentration is a key factor. If a limited number of firms provide critical, proprietary materials, their ability to dictate terms to JSR increases significantly.
For instance, in the semiconductor industry, the production of advanced photoresists, a core JSR product, often involves complex chemical formulations. A 2024 market analysis indicated that the top three global photoresist suppliers held approximately 70% of the market share, highlighting a concentrated supplier landscape.
This concentration translates to substantial bargaining power for these suppliers, especially when JSR faces high switching costs. These costs can arise from the need for extensive re-qualification processes, potential performance degradation with alternative materials, or the integration of specialized equipment tailored to a specific supplier's offerings.
The bargaining power of suppliers for JSR is significantly influenced by how critical their inputs are to JSR's final product quality and performance. For JSR, a leader in advanced materials, particularly for the semiconductor industry, the purity and specific characteristics of materials like photoresists are not just components but enablers of high-performance end products.
If a supplier offers unique or technologically superior materials that directly contribute to JSR's competitive edge in producing cutting-edge semiconductors, their negotiating leverage naturally grows. For example, in 2023, the semiconductor industry faced supply chain challenges, highlighting the dependence on specialized chemical suppliers for critical materials like advanced photoresists, where even minor variations can impact yield and device performance.
The threat of forward integration by suppliers significantly bolsters their bargaining power over JSR. If these suppliers possess the capability and motivation to move into JSR's market, perhaps by producing advanced materials or even the final products that utilize these materials, they gain a considerable advantage. This potential competition compels JSR to cultivate strong supplier relationships and consider offering competitive terms to prevent its suppliers from becoming direct rivals.
Switching Costs for JSR
Switching costs for JSR to change suppliers can significantly impact supplier bargaining power. If it's expensive or difficult for JSR to switch, suppliers gain leverage. These costs can involve substantial investments in re-tooling manufacturing lines, rigorous re-qualification of new materials, or the potential disruption of long-established supply chains, especially when dealing with highly specialized materials where performance validation is a lengthy and critical process.
JSR's strategic move to acquire Yamanaka Hutech, a supplier of high-purity chemicals, in August 2024 is a clear indicator of their efforts to strengthen their supply chain. This acquisition aims to secure access to critical inputs and potentially reduce JSR's dependence on external suppliers for these vital materials, thereby mitigating some of the supplier bargaining power.
- High Switching Costs: JSR faces elevated switching costs when changing suppliers, particularly for specialized materials requiring extensive re-tooling and validation, thus increasing supplier power.
- Strategic Acquisition: JSR's August 2024 acquisition of Yamanaka Hutech, a high-purity chemical supplier, signifies a move to enhance supply security and reduce reliance on external sources.
- Impact on Leverage: The ability of suppliers to command higher prices or favorable terms is amplified when JSR's costs and operational risks associated with switching are substantial.
Availability of Substitutes for Supplier's Products
When JSR faces few alternatives for the specialized materials it needs, suppliers hold significant sway. This is particularly true in advanced materials markets where unique properties are often required, limiting readily available substitutes. For instance, if JSR relies on a single supplier for a critical semiconductor precursor, that supplier's bargaining power is amplified.
Conversely, JSR's ability to source similar materials from multiple vendors or develop them in-house greatly reduces supplier leverage. The availability of comparable products from different manufacturers, or JSR's own capacity for backward integration, can shift the power dynamic favorably. In 2024, the semiconductor industry, a key market for advanced materials, continued to navigate supply chain complexities, with some niche components experiencing limited substitution options.
- Limited Substitutes Enhance Supplier Power: If JSR procures specialized materials with few direct alternatives, suppliers can command higher prices and dictate terms.
- Internal Development or Multiple Suppliers Mitigate Power: JSR's ability to develop materials internally or source from various suppliers significantly weakens supplier bargaining power.
- Niche Markets and Supplier Leverage: The advanced materials sector often contains specialized niches where substitute availability is inherently low, increasing supplier influence.
The bargaining power of suppliers for JSR is substantial due to the critical nature of their specialized inputs, particularly in the semiconductor and life sciences sectors. High switching costs, limited availability of substitutes, and the potential for supplier forward integration all contribute to this power. For example, the semiconductor industry, a key market for JSR, faced continued supply chain complexities in 2024, with niche component suppliers wielding significant influence.
| Factor | Impact on JSR | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increases supplier leverage | Top 3 photoresist suppliers held ~70% market share in 2024. |
| Switching Costs | Elevates supplier power | Re-tooling, re-qualification, and performance validation are costly. |
| Input Criticality | Strengthens supplier position | Unique material properties directly impact JSR's product performance. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Adds competitive pressure | Suppliers may enter JSR's markets, increasing JSR's need for favorable terms. |
| Limited Substitutes | Amplifies supplier leverage | Few alternatives for specialized materials empower suppliers. |
What is included in the product
JSR's Porter's Five Forces analysis dissects the competitive intensity within its operating industries, examining threat of new entrants, buyer power, supplier power, threat of substitutes, and existing rivalry.
Easily visualize the intensity of each competitive force with a clear, actionable spider chart, simplifying complex market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
JSR's bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by customer concentration. If a few major clients represent a substantial portion of JSR's revenue, these customers wield considerable influence. For instance, major semiconductor manufacturers, who are key buyers of JSR's advanced photoresists, can leverage their volume to negotiate more favorable pricing and terms. This concentration means that losing even one large customer could have a notable impact on JSR's financial performance.
Customers' threat of backward integration significantly amplifies their bargaining power. If customers can develop advanced materials in-house, they have less need to rely on JSR, giving them leverage to demand better pricing or terms.
This is especially true for major players in sectors like semiconductors, who often have the capital and technical know-how to explore in-house material production. For instance, in 2024, major semiconductor manufacturers continued to invest heavily in R&D for proprietary materials, demonstrating their potential capability to bypass external suppliers like JSR if cost or performance targets aren't met.
Customers are highly sensitive to price, especially when JSR's materials represent a substantial part of their total costs. This is particularly true in sectors like electronics and automotive, where companies often face intense competition and operate on tight margins. For instance, in 2024, the average profit margin for semiconductor manufacturers, a key customer segment for JSR's display materials, hovered around 20-25%, making them keenly aware of component pricing.
Availability of Substitute Materials for Customers
The availability of substitute materials significantly impacts JSR's customer bargaining power. If customers can readily find alternative materials with similar functionality and cost-effectiveness, their leverage to negotiate prices or demand better terms with JSR increases. This is particularly relevant in the advanced materials sector where innovation can quickly introduce new options.
While JSR operates in specialized markets, the dynamic nature of the materials industry means that potential substitutes are always on the horizon. For instance, in the semiconductor materials space, where JSR is a key player, advancements in lithography or new material compositions from competitors could present viable alternatives for chip manufacturers, thereby strengthening customer bargaining power.
- Increased Threat of Substitutes: The ease with which customers can switch to alternative materials directly correlates with their bargaining power.
- JSR's Market Position: JSR's strength in advanced, often proprietary materials can mitigate this, but ongoing R&D in the industry is crucial.
- Impact on Pricing: A higher availability of substitutes generally puts downward pressure on JSR's pricing power.
- Innovation as a Counterbalance: Continuous innovation by JSR to offer superior performance or unique properties in its materials is key to maintaining customer loyalty and reducing the threat of substitution.
Customer's Information Asymmetry
Customer information asymmetry significantly impacts JSR's bargaining power. If customers possess comprehensive data on JSR's production costs, pricing strategies, and the availability of competing suppliers, their ability to negotiate favorable terms intensifies. This transparency directly empowers them to seek better deals.
In the specialized realm of high-tech materials, customers often exhibit profound technical expertise. They conduct extensive testing and analysis, which inherently minimizes information asymmetry. This deep understanding of product performance and market alternatives strengthens their position to demand specific quality standards and competitive pricing from JSR.
- Reduced Information Gap: Customers in the high-tech materials sector, like those JSR serves, often possess detailed technical knowledge, reducing the information gap.
- Rigorous Testing: Extensive product testing by customers diminishes JSR's informational advantage, increasing customer leverage.
- Demand for Specifics: This knowledge empowers customers to dictate performance requirements and negotiate pricing more assertively.
JSR's customers possess significant bargaining power due to their ability to switch to alternative materials. In 2024, the semiconductor industry, a key market for JSR, saw continued investment in R&D for proprietary materials, indicating a growing potential for in-house production or alternative sourcing by manufacturers. This trend, coupled with the price sensitivity of customers operating on tighter margins, like those in the electronics sector with average profit margins around 20-25% in 2024, empowers them to negotiate more aggressively on pricing and terms.
| Factor | Impact on JSR's Customer Bargaining Power | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High if few large clients dominate revenue. | Major semiconductor firms, key JSR buyers, can leverage volume for better terms. |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Increases customer leverage. | Semiconductor giants invested in R&D for proprietary materials in 2024, signaling potential to bypass suppliers. |
| Price Sensitivity | High when JSR's materials are a significant cost. | Electronics sector customers, with 20-25% profit margins in 2024, are highly cost-aware. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Strengthens customer negotiation power. | Advancements in lithography or new material compositions can offer alternatives to chip manufacturers. |
Full Version Awaits
JSR Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the full JSR Porter's Five Forces Analysis, providing a comprehensive examination of the competitive landscape within JSR Corporation's industry. You are viewing the exact, professionally formatted document that will be delivered instantly upon purchase, ensuring complete transparency and immediate usability for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The advanced materials sector, encompassing semiconductor materials, life sciences, and synthetic rubbers, is characterized by a robust presence of established global competitors. JSR navigates this landscape alongside formidable rivals such as Shin-Etsu Chemical, Asahi Kasei, Tokyo Ohka Kogyo, AGC, and Sysmex.
This diverse array of competitors means JSR must continually innovate and differentiate its offerings. For instance, in the semiconductor materials segment, Shin-Etsu Chemical is a major player, and JSR's performance is directly impacted by their strategic moves and market share. As of early 2024, the global semiconductor materials market was valued at over $60 billion, highlighting the significant scale of competition.
The advanced materials market is anticipated to expand, but the intensity of competition can differ across its various segments. In areas experiencing slower growth, companies might engage in more aggressive tactics to capture market share. Conversely, segments with rapid expansion can enable companies to grow by increasing their own output rather than directly challenging competitors for existing business.
Looking ahead, the global advanced materials market is projected to experience a compound annual growth rate of 6.9% between 2025 and 2034. This indicates a market that is expanding, yet one where competition remains a significant factor for participants.
JSR's capacity to distinguish its offerings through advanced technology, enhanced performance, or distinctive characteristics is vital for softening the intensity of competitive rivalry. For instance, in the highly competitive semiconductor sector, JSR highlights its leading-edge EUV photoresists and innovative next-generation metal oxide photoresists as significant differentiators.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers can significantly amplify competitive rivalry within an industry. When companies face substantial costs or difficulties in leaving a market, they may be compelled to continue operations even when profitability dwindles, leading to prolonged and intense competition. For instance, in the advanced materials sector, the specialized nature of manufacturing equipment and the substantial capital investment required for research and development can create formidable exit barriers.
These barriers mean that companies are essentially locked into the market, contributing to sustained competitive pressure. Consider the semiconductor industry, a close cousin to advanced materials, where fab construction alone can cost billions of dollars. Companies that have made such investments are unlikely to simply shut down operations, instead opting to compete aggressively to recoup their capital, even in a saturated market.
- Specialized Assets: High costs associated with unique machinery or intellectual property make it difficult to repurpose or sell assets, trapping companies in the industry.
- Long-Term Contracts: Binding agreements with suppliers or customers can obligate companies to continue operations for extended periods, regardless of current market conditions.
- Capital Investments: Significant upfront investments in plant, property, and equipment, common in capital-intensive industries like advanced materials, create a strong disincentive to exit due to sunk costs.
- Government and Social Factors: Regulations or social pressure to maintain employment levels can also act as exit barriers, forcing companies to remain operational.
Strategic Stakes
The advanced materials sector is strategically vital for national economies and technological progress, fueling intense competition. Companies and governments alike pour significant resources into securing leadership in this arena. This high-stakes environment means that rivalry among existing players is often fierce, with innovation and market share being paramount.
JSR's privatization by JIC Capital in June 2024 underscores this strategic importance. The deal, valued at approximately $1.4 billion, was designed to bolster JSR's global competitiveness within the semiconductor industry. This move signals a commitment to long-term strategy and potential mergers and acquisitions to solidify its position.
- Strategic Importance: Advanced materials are critical for national economic growth and technological advancement, driving substantial investment and competition.
- JSR's Privatization: The June 2024 privatization of JSR by JIC Capital for roughly $1.4 billion aims to enhance its global standing in the semiconductor sector.
- Competitive Drivers: Intense rivalry stems from the pursuit of market leadership through innovation and strategic investments in R&D and capacity.
- Long-Term Vision: The privatization reflects a strategy focused on long-term growth and potential M&A activities to maintain a competitive edge.
Competitive rivalry in the advanced materials sector, where JSR operates, is intense due to the presence of established global players like Shin-Etsu Chemical and Asahi Kasei. This rivalry is amplified by high exit barriers, such as specialized assets and significant capital investments, which lock companies into the market. The strategic importance of advanced materials, particularly for semiconductor technology, further fuels this competition, with JSR's privatization in June 2024 for approximately $1.4 billion aimed at bolstering its global position.
| Competitor | Key Segments | 2024 Market Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Shin-Etsu Chemical | Semiconductor materials, PVC, silicones | Continued dominance in silicon wafers, expansion in advanced semiconductor chemicals |
| Asahi Kasei | Fibers, chemicals, electronics, housing | Growth in specialty chemicals and high-performance materials for automotive and electronics |
| Tokyo Ohka Kogyo (TOK) | Photoresists, fine chemicals | Innovation in EUV and next-generation lithography materials |
| AGC | Glass, chemicals, electronics | Focus on high-performance displays and semiconductor processing materials |
| Sysmex | In-vitro diagnostics, medical devices | Advancements in diagnostic reagents and automated systems |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for JSR's products is significant, particularly in its key markets like display materials. Alternative display technologies such as Quantum Dot LED (QLED) and Micro-LED are increasingly viable replacements for the Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) materials where JSR holds a strong position. These emerging technologies offer potential advantages in brightness, lifespan, and energy efficiency, directly challenging JSR's existing product lines.
The threat of substitutes is amplified when alternative materials provide comparable or superior performance at a more attractive price point. For JSR, this means that if competitors can offer similar functionality in areas like semiconductor materials or display components for less, it poses a significant challenge.
JSR's strategy centers on offering a distinct price-performance advantage. By focusing on highly specialized, high-performance materials, the company aims to create a value proposition that is inherently difficult for substitutes to replicate without compromising quality or incurring higher development costs.
In 2024, the semiconductor industry, a key market for JSR, continued to see intense competition. While advanced lithography materials are critical, the cost of these specialized inputs remains a significant factor for chip manufacturers, making the price-performance balance of substitutes a constant consideration.
The threat of substitutes for JSR's products is influenced by how easily and expensively customers can switch to alternative materials. For businesses deeply embedded in JSR's material supply chain, the cost of switching can be significant. These costs can include re-engineering products, undergoing new material qualification processes, and the potential for costly production interruptions during the transition. For example, in the semiconductor industry where JSR is a key supplier of photoresists, the rigorous qualification process for new materials can take months or even years, representing a substantial switching cost for chip manufacturers.
Technological Advancements in Substitute Industries
Rapid technological advancements in industries adjacent to JSR's core markets can introduce novel substitute materials or processes. For instance, breakthroughs in bio-based polymers or advanced composite materials could offer alternatives to JSR's existing product lines in areas like electronics or automotive components. JSR's commitment to research and development, with an R&D expenditure of approximately ¥100 billion in 2023, is crucial for identifying and mitigating these threats by developing next-generation solutions.
The emergence of new technologies can fundamentally alter value propositions, making existing offerings less attractive. Consider the rapid evolution of display technologies; advancements in microLED or quantum dot technologies could challenge the market position of traditional LCD materials. JSR's strategic focus on anticipating these shifts, as evidenced by its investments in emerging material science, aims to ensure its continued relevance and competitiveness.
- Technological Disruption: New materials or processes from other sectors can emerge as viable substitutes.
- R&D Investment: JSR's significant R&D spending, around ¥100 billion in 2023, is a proactive measure against this threat.
- Market Evolution: Shifts in technology, like display advancements, can quickly render current products obsolete.
- Strategic Adaptation: JSR's focus on innovation and anticipating market changes is key to maintaining its competitive edge.
Customer Propensity to Substitute
Customers' openness to switching to alternatives is a key factor. This willingness is often fueled by the allure of lower costs, a growing commitment to environmental responsibility, or the promise of superior performance. For instance, in the advanced materials sector, a significant push towards sustainable practices is actively encouraging the adoption of new, eco-friendly substitutes.
The increasing consumer demand for products with a smaller environmental footprint directly impacts the threat of substitutes. As of 2024, reports indicate that over 60% of consumers globally consider sustainability a crucial factor when making purchasing decisions, a trend that is likely to accelerate the adoption of greener alternatives across various industries.
- Customer Propensity to Substitute: A significant driver for substitution is the customer's willingness to embrace new technologies or materials.
- Key Drivers: This willingness is primarily influenced by potential cost savings, growing environmental consciousness, and perceived performance enhancements.
- Sustainability Trend: The ongoing shift towards sustainable practices in advanced materials is a notable catalyst, driving demand for novel, environmentally friendly substitutes.
- Market Data: In 2024, consumer surveys reveal that environmental impact is a primary consideration for a majority of buyers, directly increasing the appeal of substitute products.
The threat of substitutes for JSR's advanced materials, particularly in displays and semiconductors, remains a critical consideration. Emerging technologies in these sectors offer performance improvements and potential cost advantages, directly challenging JSR's established product lines.
In 2024, the semiconductor industry saw continued pressure on material costs, making the price-performance ratio of substitutes a key factor for manufacturers. Similarly, advancements in display technologies like Micro-LED continue to present viable alternatives to OLED materials, where JSR has a strong presence.
JSR's substantial R&D investment, around ¥100 billion in 2023, is a proactive strategy to counter this threat by developing next-generation materials that offer superior performance and value, thereby mitigating the incentive for customers to switch.
Customer willingness to adopt substitutes is driven by factors like cost savings and increasing demand for sustainable products. By 2024, over 60% of global consumers considered sustainability in purchasing decisions, highlighting the growing appeal of eco-friendly alternatives.
| Market Segment | JSR's Key Products | Potential Substitutes | Key Threat Factors | 2024 Market Trend Impact |
| Display Materials | OLED materials | Quantum Dot LED (QLED), Micro-LED | Performance (brightness, lifespan), Cost | Increased viability of QD and Micro-LED |
| Semiconductor Materials | Photoresists, lithography materials | Alternative chemical formulations, advanced manufacturing processes | Cost, performance equivalence, qualification time | Cost pressures driving evaluation of alternatives |
| General | Specialty polymers, coatings | Bio-based materials, advanced composites | Sustainability, performance, price | Growing consumer demand for eco-friendly options |
Entrants Threaten
The advanced materials sector, especially areas like semiconductor manufacturing, demands massive upfront investment. Companies need significant capital for cutting-edge research and development, building state-of-the-art production facilities, and acquiring highly specialized machinery.
These substantial capital requirements create a formidable barrier for potential new competitors. For instance, establishing a new semiconductor fabrication plant, or fab, can easily cost tens of billions of dollars, making it incredibly difficult for smaller or less-resourced companies to enter the market.
In 2024, the global semiconductor industry alone saw capital expenditures exceeding $200 billion, a clear indicator of the immense financial commitment necessary to compete. This high entry cost effectively deters many new players from challenging established giants.
Established players like JSR leverage significant economies of scale in production and procurement. For instance, JSR's extensive manufacturing capabilities allow for lower per-unit costs compared to a new entrant starting at a smaller scale. This cost advantage makes it difficult for newcomers to compete on price without substantial upfront investment.
Furthermore, JSR benefits from economies of scope through its diversified product portfolio and integrated supply chain. This allows for cost sharing across different business segments, a luxury not readily available to a new entrant focused on a single market. In 2024, JSR's revenue reached approximately ¥390 billion, underscoring its substantial operational footprint and the scale advantage it holds.
JSR's robust portfolio of proprietary technologies and patents in polymer chemistry and advanced materials acts as a significant barrier to new entrants. This deep R&D expertise, particularly in specialized areas like photoresists where JSR holds a substantial market share due to its intellectual property, makes it incredibly challenging for newcomers to replicate its product offerings and technological advantages.
Access to Distribution Channels
New entrants would find it difficult to secure essential distribution channels, especially in sectors like semiconductor materials and life sciences, which are heavily reliant on established relationships. JSR Corporation has cultivated extensive global networks and fostered robust customer ties, creating significant barriers to entry for newcomers seeking to replicate this reach.
For instance, in the advanced materials sector, securing shelf space or partnerships with major manufacturers often requires years of trust-building and proven performance. JSR's long-standing presence and deep integration into supply chains mean that new competitors would struggle to gain comparable access, impacting their ability to deliver products effectively.
- Distribution Channel Barriers: New players face significant hurdles in establishing and accessing critical distribution networks.
- Relationship-Driven Industries: Sectors like semiconductors and life sciences demand strong, pre-existing customer relationships that are hard for new entrants to build quickly.
- JSR's Advantage: JSR's established global distribution networks and proven customer loyalty create a competitive moat.
- Market Access Challenges: Without established channels and relationships, new entrants will find it difficult to reach their target markets and compete effectively.
Government Policy and Regulations
Government policies and regulations significantly impact the threat of new entrants in the chemical and advanced materials industries. Strict regulatory requirements, such as those mandated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States, can create substantial barriers. For instance, the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) requires extensive testing and review for new chemical substances, adding considerable time and expense for potential market entrants.
Environmental standards, including emissions controls and waste disposal regulations, also increase the cost and complexity of starting operations. Companies must invest in compliance technologies and processes, which can be prohibitive for smaller, new firms. In 2024, the ongoing focus on sustainability and circular economy principles is likely to lead to even more stringent environmental regulations, further deterring new entrants who lack established infrastructure and capital.
Trade policies, including tariffs and import/export restrictions, can also influence market entry. For example, geopolitical tensions and trade disputes can disrupt supply chains and increase the cost of raw materials or finished goods, making it harder for new domestic or international players to compete. The World Trade Organization (WTO) data indicates that trade barriers remain a concern for many sectors, including chemicals, impacting the global competitive landscape.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Compliance with agencies like the EPA under TSCA can cost millions of dollars and take years for new chemical substances.
- Environmental Compliance Costs: Investments in pollution control technology and waste management systems represent a significant capital expenditure for new chemical manufacturers.
- Trade Policy Impact: Tariffs on key chemical inputs, as seen in various trade disputes in recent years, can inflate operating costs for new entrants.
High capital requirements, estimated in the tens of billions for a new semiconductor fab, act as a substantial deterrent to new entrants in advanced materials. JSR's significant 2024 revenue of approximately ¥390 billion highlights its scale advantage, making it difficult for smaller, less-resourced companies to compete on cost.
JSR's proprietary technology and established global distribution networks, built over years of customer relationships, present formidable barriers. Newcomers struggle to replicate this deep R&D expertise and market access, especially in sectors reliant on trust and proven performance.
Stringent government regulations, like EPA oversight under TSCA, and evolving environmental standards further increase the cost and complexity of market entry. These factors, combined with potential trade policy impacts, significantly raise the barrier for new players in the chemical and advanced materials industries.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | JSR's Position |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Massive upfront investment for R&D, facilities, and machinery. | Prohibitive for smaller firms; semiconductor fabs can cost tens of billions. | Leverages scale and existing infrastructure. |
| Economies of Scale/Scope | Lower per-unit costs and cost sharing across diverse products. | New entrants starting smaller face higher unit costs. | Significant cost advantage due to large operational footprint. |
| Proprietary Technology & IP | Patented processes and deep R&D expertise. | Difficult to replicate; requires substantial R&D investment. | Holds substantial market share in key areas like photoresists. |
| Distribution Channels & Relationships | Established global networks and strong customer ties. | Challenging to gain comparable access and trust. | Extensive global reach and deep integration into supply chains. |
| Government Regulations & Trade Policies | Compliance costs, environmental standards, tariffs. | Adds significant time, expense, and complexity. | Established infrastructure for compliance and navigating trade. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, drawing from financial statements, industry-specific market research reports, and publicly available company filings to provide a comprehensive view of competitive dynamics.
