Hanes Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Hanes Bundle
Hanes's position in the apparel market is shaped by intense competition and the constant threat of substitutes. Understanding the power dynamics with suppliers and buyers is crucial for navigating this landscape.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Hanes’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for Hanesbrands is significantly influenced by the availability of specialized raw materials. For instance, the increasing demand for sustainably sourced cotton or recycled polyester means suppliers offering these niche materials hold considerable leverage. This is particularly relevant as Hanesbrands has publicly stated goals for increasing its use of sustainable materials, potentially leading to higher costs if these specialized suppliers are few and in high demand.
For basic materials like cotton and synthetic fibers, suppliers typically hold less bargaining power. This is because these materials are widely available from many sources around the world, and Hanesbrands, being a major buyer, can use its large purchase volumes to secure better pricing and terms, thereby limiting supplier leverage.
However, the global supply chain disruptions experienced in early 2025 demonstrated how quickly this balance can shift. For instance, a shortage of key cotton varieties due to adverse weather events in major producing regions could temporarily empower those few suppliers with available inventory, forcing larger buyers to accept less favorable conditions.
Vertical integration significantly curtails the bargaining power of suppliers. For instance, Hanesbrands, by owning a substantial portion of its global manufacturing facilities, lessens its dependence on contract manufacturers and certain raw material providers. This ownership structure grants Hanesbrands greater command over production expenses and quality standards, effectively diminishing the leverage external manufacturing suppliers might otherwise wield.
Switching costs
The costs Hanesbrands incurs when switching suppliers can significantly influence supplier bargaining power. These costs often include expenses related to retooling manufacturing equipment, implementing new quality control procedures, and the administrative burden of renegotiating contracts and establishing new logistical channels. For instance, a substantial investment in specialized machinery for a particular fabric or component means that switching to a new supplier who uses different specifications would necessitate further capital expenditure.
While Hanesbrands strives for supply chain agility, the transition from long-standing supplier relationships for critical inputs can be a complex and expensive undertaking. This complexity acts as a deterrent to frequent supplier changes, thereby granting existing suppliers a degree of leverage. In 2024, the global apparel industry continued to grapple with supply chain disruptions, making the stability offered by established supplier relationships particularly valuable, even if it means slightly higher costs.
These switching costs create a tangible barrier, discouraging rapid or frequent changes in the supplier base. This stability benefits incumbent suppliers by reducing the immediate threat of losing business to competitors, allowing them to maintain pricing power or favorable contract terms. For Hanesbrands, this means that any potential savings from switching suppliers must be weighed against these substantial transition expenses.
Consider these factors impacting switching costs for Hanesbrands:
- Retooling Expenses: Costs associated with adapting machinery for new materials or specifications.
- Quality Assurance Adjustments: Investments in testing and validation for new suppliers' outputs.
- Contractual Obligations: Potential penalties or exit clauses in existing supplier agreements.
- Logistical Integration: Time and resources needed to integrate new suppliers into existing distribution networks.
Supplier concentration
Supplier concentration significantly impacts bargaining power. When Hanesbrands relies on a limited number of large suppliers for critical raw materials or components, these suppliers gain leverage. For instance, if only a few major cotton producers or textile manufacturers exist, they can dictate terms more effectively.
Conversely, a broad and fragmented supplier base for a specific input dilutes individual supplier power. This allows Hanesbrands more flexibility in sourcing and negotiating prices. The apparel sector is increasingly favoring deeper, more strategic supplier partnerships, which can lead to fewer, but more concentrated and thus potentially more powerful, supplier relationships.
- Supplier Concentration: A few dominant suppliers for key inputs grant them greater bargaining power over Hanesbrands.
- Fragmented Supply Base: A wide array of suppliers for an input reduces the power of any single supplier.
- Industry Trend: The apparel industry's move towards deeper supplier relationships may consolidate power among fewer, larger suppliers.
- Impact on Hanesbrands: Increased supplier concentration can lead to higher input costs and less favorable terms for Hanesbrands.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Hanesbrands is influenced by the concentration of its supplier base. A limited number of suppliers for critical materials like specialized cotton or advanced synthetic fibers can give these suppliers significant leverage, potentially driving up costs for Hanesbrands. For instance, in 2024, disruptions in cotton supply chains due to climate events in key growing regions highlighted how a concentrated supplier base can dictate terms when demand outstrips limited availability.
Conversely, a broad and fragmented supplier market for inputs such as basic polyester or standard dyes allows Hanesbrands to play suppliers against each other, securing more favorable pricing and terms. This diversification of sourcing options is crucial for mitigating supplier power. The company's strategy often involves cultivating relationships with multiple suppliers to maintain this flexibility.
The trend towards deeper, more strategic supplier partnerships within the apparel industry, observed through 2024 and into early 2025, suggests a potential consolidation of power among fewer, larger suppliers. This shift could increase the bargaining power of these key partners for Hanesbrands, necessitating careful relationship management to avoid unfavorable cost increases.
| Factor | Impact on Hanesbrands | 2024/2025 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increased leverage for fewer suppliers, potentially higher costs | Climate impacts on cotton in 2024/2025 tightened supply for some varieties |
| Supplier Fragmentation | Greater negotiating power for Hanesbrands, competitive pricing | Hanesbrands actively diversifies sourcing for standard materials |
| Strategic Partnerships | Potential for increased supplier power with fewer, larger partners | Industry trend towards consolidation may shift balance in favor of key suppliers |
What is included in the product
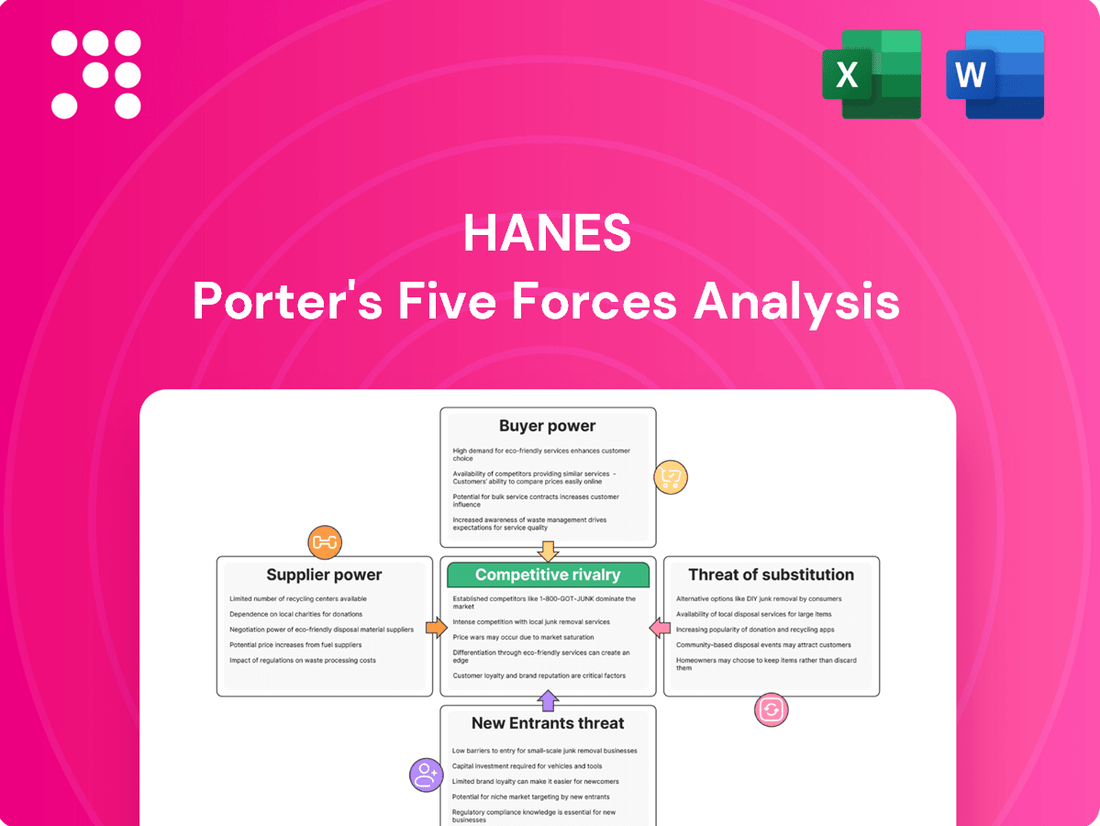
A Hanes-specific Porter's Five Forces analysis examines the competitive intensity and profitability of the apparel industry, evaluating threats from new entrants, buyers, suppliers, substitutes, and existing rivals.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of industry power dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Hanesbrands operates in the everyday basic apparel market, a sector where consumers are notably price-sensitive, prioritizing comfort and affordability. This sensitivity is a significant factor influencing their purchasing decisions, especially when economic pressures are high.
The availability of numerous alternatives in the apparel market further amplifies consumer price sensitivity. This competitive landscape forces Hanesbrands to maintain aggressive and competitive pricing strategies to retain market share. For instance, in 2024, the apparel industry continued to see consumers actively compare prices across various retailers and brands.
Consumers are increasingly demonstrating a willingness to switch brands if they perceive prices to be too high. This dynamic means that Hanesbrands must constantly monitor its pricing relative to competitors to avoid losing customers who are actively seeking the best value for their money.
The proliferation of e-commerce and digital marketplaces has dramatically shifted the balance of power towards consumers. Platforms like Amazon, Shein, and Temu allow shoppers to effortlessly compare prices, read reviews, and explore a global catalog of apparel, directly challenging Hanesbrands' pricing strategies. In 2023, global e-commerce sales reached an estimated $6.3 trillion, underscoring the vast reach and influence of online retail.
This readily available information empowers customers, enabling them to identify the most competitive offerings and readily switch brands if Hanesbrands fails to meet their price and value expectations. For instance, the ability to instantly see competitor pricing for similar items like basic t-shirts or underwear means brand loyalty alone is less of a moat against price sensitivity.
Hanesbrands benefits from established brands like Hanes and Bonds, which can foster customer loyalty. This loyalty means consumers are less likely to switch to competitors for basic apparel, thereby reducing their bargaining power. For instance, Hanes' long-standing reputation for comfort in the innerwear market provides a degree of insulation.
However, the apparel industry, particularly for basics, is highly competitive. Hanesbrands must continually invest in marketing and product innovation to reinforce brand preference and combat the ease with which consumers can find alternatives. Failure to do so could erode loyalty and increase customer bargaining power.
Volume of purchases by retailers
The sheer volume of purchases made by Hanesbrands' key retail partners, particularly large chains, significantly amplifies their bargaining power. These major buyers can negotiate more favorable pricing, extended payment terms, and preferential delivery schedules because they represent a substantial portion of Hanesbrands' revenue.
For instance, in 2023, Hanesbrands' top customers accounted for a significant percentage of their net sales, illustrating the leverage these entities hold. This concentration of purchasing power is a well-established dynamic within the apparel sector, where scale directly translates to influence.
- Significant Retailer Volume: Large retail chains, by consolidating their purchases, can demand better terms from suppliers like Hanesbrands.
- Pricing and Payment Leverage: High-volume buyers often secure discounts and more flexible payment schedules due to their substantial order sizes.
- Industry Norm: This buyer power is a common feature in the apparel industry, where major retailers are critical partners.
Growing demand for sustainable products
The increasing consumer focus on sustainability significantly bolsters customer bargaining power. As more individuals prioritize eco-friendly and ethically produced goods, they gain leverage by choosing brands that align with these values. Hanesbrands has been actively pursuing sustainability targets, like reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 50% by 2030 and decreasing waste to landfill by 50% by 2030, which can serve as a competitive advantage. However, this trend also means customers can more effectively pressure companies for enhanced environmental practices, potentially impacting pricing and production methods.
Brands that successfully integrate sustainability into their operations often see increased customer loyalty. Conversely, those perceived as lagging in environmental responsibility risk market share erosion. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that 65% of consumers are willing to pay more for products from sustainable brands. This willingness directly translates to customer power, allowing them to dictate terms by favoring more responsible manufacturers.
- Consumer Prioritization: A growing segment of the market actively seeks out and rewards brands demonstrating a commitment to environmental and social responsibility.
- Hanesbrands' Sustainability Efforts: The company's stated goals, such as significant reductions in emissions and waste by 2030, position it to meet this demand but also highlight areas where customer pressure can influence further action.
- Market Influence: Brands that align with consumer values regarding sustainability tend to capture greater market share, while those that do not face the risk of losing customers to more conscientious competitors.
The bargaining power of customers is a key force shaping Hanesbrands' operations. With a vast array of apparel choices available, consumers can easily switch brands if prices are not competitive or if they find better value elsewhere. This price sensitivity is amplified by the ease of online comparison shopping, a trend that saw global e-commerce sales exceed $6.3 trillion in 2023.
While strong brands like Hanes can foster loyalty, reducing customer leverage, the highly competitive nature of the basic apparel market means Hanesbrands must continuously innovate and maintain aggressive pricing. The increasing consumer demand for sustainability also empowers customers, as evidenced by a 2024 survey showing 65% of consumers willing to pay more for sustainable products, allowing them to influence corporate practices.
| Factor | Impact on Hanesbrands | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | High; consumers easily switch for better value | Continued consumer focus on affordability due to economic factors |
| Availability of Alternatives | Increases customer power due to easy comparison | Proliferation of online retailers and fast fashion brands |
| Brand Loyalty | Can mitigate bargaining power | Hanes brand equity provides some resilience, but requires ongoing investment |
| Sustainability Focus | Empowers consumers to choose ethically | 65% of consumers willing to pay more for sustainable products (2024 survey) |
Full Version Awaits
Hanes Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Hanes Porter's Five Forces Analysis, providing an in-depth examination of the competitive landscape within the apparel industry. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring full transparency and immediate access to this valuable strategic tool. You can trust that the professionally formatted analysis, detailing industry rivalry, buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, and threat of substitutes, is exactly what you'll download.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The basic apparel sector is incredibly crowded. Hanesbrands faces a multitude of competitors, from massive global players and well-known brands to store-specific private labels and agile direct-to-consumer startups. This intense fragmentation means Hanesbrands must constantly fight for market share through competitive pricing, fresh product designs, and impactful marketing campaigns.
The sheer size of the global apparel market, projected to reach $1.84 trillion by 2025, underscores the vastness of this competitive arena. Within this massive market, the basic apparel segment is particularly saturated, making it challenging for any single company to dominate. Hanesbrands' position is continually tested by this widespread competition.
Price competition is fierce in the apparel market, especially for basic items like those Hanesbrands produces. This often leads to frequent sales and discounts to attract customers. For instance, in 2023, many apparel retailers reported promotional activity as a key driver of sales volume, even as they grappled with rising input costs.
Hanesbrands has to balance offering competitive prices with maintaining healthy profit margins. The ongoing challenge of inflation in the apparel sector means that aggressive discounting can quickly erode profitability. Investors remain watchful, as excessive price wars can signal underlying demand issues and impact the company's bottom line.
Companies in the apparel sector, including Hanesbrands, invest significantly in marketing and advertising to stand out and grab consumer attention. For instance, in 2023, Hanesbrands reported marketing and advertising expenses of $298 million. This substantial outlay is crucial for differentiating brands in a crowded marketplace.
The recent sale of the Champion brand for $1.2 billion in late 2023 highlights Hanesbrands' strategic shift. This divestiture signals a move to streamline operations and enhance financial performance amidst a challenging market environment, allowing for a sharper focus on core brands.
Maintaining market share in the apparel industry hinges on effective brand messaging and continuous innovation. Brands that consistently deliver compelling narratives and introduce fresh products are better positioned to resonate with consumers and retain their competitive edge.
Global sourcing and production capabilities
Competitors frequently tap into global supply chains, particularly production hubs in Asia, to drive down costs. This widespread reliance on international manufacturing means many players can achieve similar cost efficiencies.
Hanesbrands' substantial owned manufacturing footprint offers a distinct edge, granting greater control over production and accelerating time-to-market. However, it's important to note that other industry participants also possess highly developed sourcing networks, enabling them to compete effectively on this front.
The apparel industry is currently experiencing a notable trend towards nearshoring, a strategic shift that could significantly reshape competitive dynamics. This move to bring production closer to home markets may alter cost structures and supply chain resilience for various companies.
- Global Production Reliance: Many competitors heavily depend on Asian manufacturing for cost advantages.
- Hanesbrands' Advantage: Owned facilities offer control and speed, though rivals also have strong sourcing.
- Nearshoring Trend: The industry's move towards localized production could change competitive landscapes.
Product differentiation and innovation
While basic apparel might seem like a commodity, companies like Hanesbrands actively pursue product differentiation. They focus on enhancing fabric technology, incorporating comfort features, and updating styles to capture consumer interest. This strategy is crucial for standing out in a highly competitive landscape.
Hanesbrands' commitment to comfort and affordability, coupled with strategic product introductions such as the HanesMoves activewear line, plays a vital role in customer acquisition and loyalty. For instance, in 2024, Hanesbrands continued to invest in product innovation, aiming to capture a larger share of the athleisure market, a segment that saw significant growth in recent years.
- Fabric Technology: Hanesbrands leverages advanced materials for improved breathability and durability.
- Comfort Features: Innovations like tag-free designs and softer waistbands enhance customer experience.
- Style Updates: Regular fashion-forward collections cater to evolving consumer tastes.
- New Product Launches: HanesMoves exemplifies the company's push into performance-oriented apparel.
Continuous innovation is not just a strategy but a necessity for Hanesbrands to maintain relevance and a competitive edge. The company understands that staying ahead requires consistent effort in developing products that meet and exceed customer expectations in a dynamic market.
The competitive rivalry in the basic apparel sector is intense, characterized by a multitude of players ranging from global giants to niche direct-to-consumer brands. This saturation necessitates constant efforts in pricing, design, and marketing to capture and retain market share.
Hanesbrands faces significant pressure from competitors who leverage global supply chains for cost efficiencies, a strategy that many players employ. For example, in 2023, the reliance on Asian manufacturing remained a key factor in cost management across the industry.
The company's own manufacturing capabilities provide an advantage in controlling production and speed, but rivals also possess robust sourcing networks. Furthermore, the emerging trend of nearshoring could alter the competitive cost landscape in the coming years.
Product differentiation through innovation in fabric technology, comfort features, and style updates is crucial for Hanesbrands to stand out. The company's investment in lines like HanesMoves in 2024 reflects this commitment to meeting evolving consumer demands in a dynamic market.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The burgeoning second-hand and resale market is a potent substitute for new apparel. This sector, valued at an estimated $260.24 billion in 2025, offers consumers a more budget-friendly and environmentally conscious way to acquire clothing. The increasing consumer adoption of thrift shopping directly challenges the demand for new garments, impacting brands like Hanesbrands.
Retailers frequently introduce their own private label basic apparel, often priced significantly lower than established brands like Hanes. For instance, a major US retailer might offer a multipack of plain t-shirts for 30-40% less than a comparable branded offering.
Furthermore, the market is saturated with unbranded or generic alternatives that fulfill the same basic function without the associated brand equity. These products are readily accessible through various channels, from discount stores to online marketplaces, directly competing for the attention of budget-conscious shoppers.
This availability of lower-cost, unbranded options poses a substantial threat, as it allows consumers to bypass brand loyalty for essential apparel items. In 2024, the demand for value-oriented apparel continued to grow, with private label sales in the apparel sector showing a notable increase, impacting the market share of traditional brands.
Improvements in apparel durability directly threaten Hanesbrands by reducing the need for frequent purchases of basic items like underwear and t-shirts. As clothing lasts longer, consumers will buy less often, directly substituting for new product sales. For example, advancements in fabric technology, like reinforced stitching or stain-resistant coatings, can significantly extend a garment's usable life, potentially impacting Hanes' sales volume for core products.
Consumers choosing to repair or upcycle
A growing emphasis on sustainability and economic prudence is leading consumers to repair, repurpose, or upcycle their existing clothing instead of purchasing new items. This trend, while potentially minor for everyday apparel, acts as a substitute by prolonging garment lifecycles and decreasing demand for new production.
This shift impacts brands like Hanes, as consumers increasingly view their wardrobes as resources to be maintained and creatively reused. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that over 60% of consumers surveyed are actively seeking ways to reduce their fashion consumption, with repair and second-hand purchasing being key strategies.
This growing inclination towards extending the life of apparel represents a tangible threat of substitution. It directly challenges the traditional model of continuous new purchases, forcing companies to consider circular economy principles.
- Consumer Behavior Shift: Increased focus on sustainability and frugality drives repair and upcycling.
- Reduced Demand: Extended garment lifecycles lessen the need for new apparel purchases.
- Market Impact: Brands face pressure to adapt to circular economy models.
- Data Point: Over 60% of consumers in a 2024 survey are reducing fashion consumption through methods like repair.
Shift in consumer priorities
Changing consumer priorities, often driven by economic uncertainty or evolving lifestyle choices, can significantly impact demand for apparel. For instance, during periods of high inflation, consumers might curb discretionary spending on clothing, opting instead for essential goods or services. This shift in spending habits means that consumers buying less clothing overall acts as a substitute for purchasing Hanesbrands' products.
This trend is evident in consumer behavior observed in 2024. A notable example is the 'wait and see' approach many consumers are adopting before making non-essential purchases, including apparel, due to persistent inflationary pressures. This cautiousness directly reduces the volume of new clothing bought, effectively substituting for the need to acquire new items from brands like Hanes.
- Reduced Discretionary Spending: Economic conditions can force consumers to prioritize essential purchases over apparel.
- Lifestyle Shifts: Changing priorities can lead consumers to allocate funds to experiences or other goods instead of clothing.
- The 'Wait and See' Approach: Inflationary concerns in 2024 have prompted many consumers to delay clothing purchases, acting as a substitute for immediate buying.
- Overall Consumption Reduction: Simply buying less clothing, regardless of the specific reason, directly substitutes for purchasing Hanesbrands' offerings.
The threat of substitutes for apparel brands like Hanes is multi-faceted, encompassing the growing resale market, private label offerings, and unbranded alternatives. These options often provide a lower price point, directly appealing to value-conscious consumers. In 2024, the resale market continued its upward trajectory, offering a sustainable and affordable alternative to new clothing, impacting overall demand for traditional apparel brands.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Hanesbrands | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Second-hand/Resale Market | Budget-friendly, sustainable | Reduces demand for new apparel | Estimated to reach $260.24 billion by 2025; growing consumer adoption |
| Private Label Brands | Lower price point, comparable quality | Erodes market share for branded basics | Notable increase in private label apparel sales in 2024 |
| Unbranded/Generic Alternatives | Functional, low cost | Bypasses brand loyalty for essential items | Readily available across various retail channels |
Entrants Threaten
Hanesbrands enjoys considerable brand recognition and customer loyalty, particularly with its well-known labels such as Hanes, Bonds, and Maidenform. This established trust makes it difficult for newcomers to gain traction.
A new entrant would require significant capital for marketing and brand development to even begin to challenge Hanesbrands' established consumer relationships. For instance, in 2023, Hanesbrands invested $597 million in selling, general, and administrative expenses, a substantial portion of which is dedicated to brand support.
This strong brand equity acts as a formidable barrier, deterring new companies from easily entering the market and competing for market share against these trusted names.
Hanesbrands leverages its status as a vertically integrated giant to unlock massive economies of scale across manufacturing, sourcing, and distribution. This allows them to produce goods at a lower cost per unit than smaller competitors. For instance, in 2023, Hanesbrands reported net sales of $5.5 billion, a testament to their operational volume.
Newcomers face a steep uphill battle trying to replicate these cost advantages. Without the upfront capital for extensive manufacturing facilities and a vast distribution network, it’s nearly impossible to match Hanesbrands' pricing power in the competitive basic apparel market. This scale is a significant barrier, making it tough for new players to gain traction on price alone.
Hanesbrands leverages its deeply entrenched relationships with major retailers worldwide, securing significant market access. For instance, in 2024, Hanesbrands continued its strong presence across thousands of brick-and-mortar stores, a testament to decades of partnership building.
New entrants would find it exceedingly difficult to replicate this level of access, facing substantial hurdles in securing prime shelf space or establishing comparable direct-to-consumer and e-commerce operations. The capital and time investment required to build such distribution networks are immense, creating a formidable barrier.
Capital requirements
Entering the apparel manufacturing and marketing space, especially to compete with established players like Hanesbrands, demands significant upfront investment. This includes building or acquiring manufacturing plants, stocking substantial inventory, launching extensive marketing campaigns, and developing robust supply chain networks. For instance, in 2024, the global apparel market is valued in the hundreds of billions, underscoring the scale of investment needed to capture even a small market share.
These high capital requirements act as a formidable barrier. Newcomers must secure substantial funding to establish operations and achieve economies of scale necessary to compete on price and reach. Without this financial muscle, aspiring entrants struggle to gain traction against incumbents who have already amortized these costs over years of operation.
- Substantial Investment: Establishing a competitive presence in the apparel industry requires significant capital for manufacturing, inventory, and distribution.
- Economies of Scale: High initial costs necessitate achieving large production volumes to lower per-unit expenses, a challenge for new entrants.
- Marketing and Brand Building: Competing with established brands like Hanesbrands necessitates considerable spending on marketing to build brand awareness and customer loyalty.
Supply chain complexity and ethical sourcing demands
The intricate nature of establishing and managing a global supply chain, especially one that adheres to ethical sourcing and transparency, presents a significant hurdle for new entrants. This complexity requires substantial investment in infrastructure, technology, and relationships, which can be prohibitive for startups.
Adding to this challenge are the escalating demands from consumers and regulators for sustainable and ethically produced goods. New companies must immediately confront these requirements, which often translate into higher operational costs and the need for rigorous auditing and compliance processes. For instance, in 2024, the global apparel market continued to see increased scrutiny on labor practices and environmental impact, with many brands facing pressure to improve supply chain transparency.
- Supply Chain Complexity: New entrants must navigate intricate logistics, supplier relationships, and quality control across multiple international locations.
- Ethical Sourcing Demands: Meeting consumer and regulatory expectations for fair labor and environmental sustainability adds significant cost and operational burden.
- Resource Intensity: Establishing robust ethical sourcing programs requires substantial investment in auditing, technology, and supplier development.
- Competitive Disadvantage: Incumbents with established, efficient, and ethically certified supply chains hold a distinct advantage over newcomers.
The threat of new entrants for Hanesbrands is relatively low due to several significant barriers. These include established brand loyalty, substantial capital requirements for market entry, and the difficulty in replicating existing economies of scale and distribution networks. For instance, Hanesbrands' 2023 net sales of $5.5 billion highlight their massive operational volume, which new entrants would struggle to match in terms of cost efficiency.
New companies face immense challenges in building brand recognition comparable to Hanesbrands' well-known labels like Hanes and Maidenform, requiring significant marketing investment. Furthermore, securing widespread retail distribution, as Hanesbrands has achieved through decades of partnership, is a formidable obstacle for any newcomer aiming to gain market access in 2024.
The complexity of global supply chains, coupled with increasing demands for ethical and sustainable sourcing, adds another layer of difficulty for potential entrants. Meeting these standards requires substantial upfront investment in infrastructure and compliance, a burden that established players like Hanesbrands have already managed.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Hanesbrands' Advantage (2023/2024 Data) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brand Loyalty | Established customer trust in brands like Hanes, Bonds, Maidenform. | Difficult for newcomers to gain traction. | Significant brand recognition and customer loyalty. |
| Capital Requirements | Need for substantial investment in manufacturing, marketing, and distribution. | Prohibitive for many aspiring entrants. | $597 million SG&A in 2023 indicates significant investment in brand support and operations. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to high production volumes. | New entrants cannot match pricing power. | $5.5 billion in net sales in 2023 demonstrates vast operational scale. |
| Distribution Networks | Entrenched relationships with major retailers and e-commerce presence. | Challenging to secure prime shelf space and market access. | Strong presence across thousands of brick-and-mortar stores in 2024. |
| Supply Chain Complexity & Ethics | Navigating global logistics, ethical sourcing, and sustainability demands. | High operational costs and compliance burden. | Established supply chains are more efficient and potentially better positioned for ethical compliance. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Hanes leverages data from industry-specific market research reports, financial statements of key competitors, and consumer trend surveys to understand the competitive landscape.
