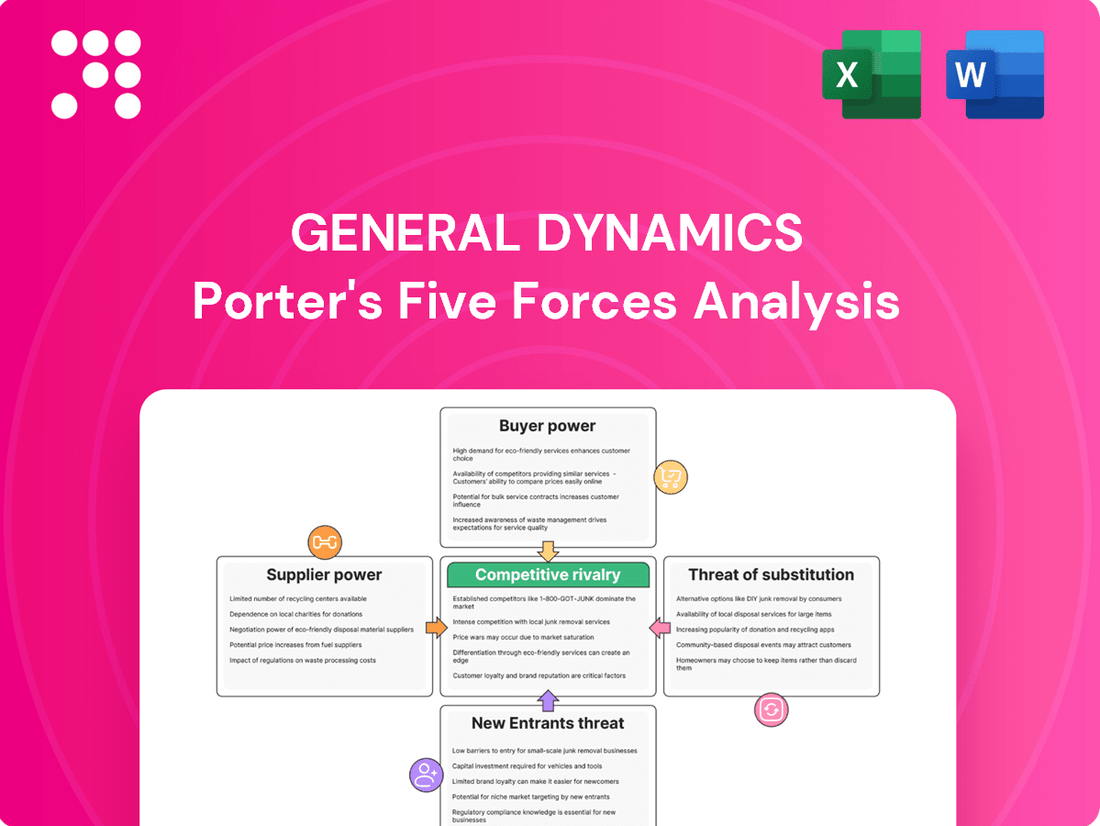
General Dynamics Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
General Dynamics Bundle
General Dynamics operates in a complex defense landscape, where the bargaining power of powerful government buyers significantly shapes pricing and contract terms. Understanding the intensity of rivalry among major defense contractors is crucial for identifying strategic advantages.
The threat of new entrants, while often mitigated by high barriers to entry in defense, still warrants careful consideration, especially with emerging technologies. Furthermore, the availability of substitute products and the power of suppliers are key forces impacting General Dynamics's profitability.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore General Dynamics’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
General Dynamics' reliance on highly specialized components and raw materials for its advanced aerospace and defense products grants considerable bargaining power to its suppliers. These specialized inputs are often critical and difficult to substitute, allowing suppliers to command higher prices or dictate terms.
The defense industry's intricate and heavily regulated supply chain amplifies supplier leverage. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Department of Defense reported significant delays in certain component deliveries due to geopolitical tensions and concentrated manufacturing capabilities, highlighting the vulnerability to supplier-side disruptions.
General Dynamics frequently secures long-term contracts with critical suppliers, often spanning 7 to 10 years. These agreements typically include provisions for fixed pricing and guaranteed purchase volumes, offering stability and predictability in its supply chain. For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of its key component procurement was locked in through such multi-year deals, mitigating price volatility.
The company actively cultivates strategic partnerships with technology and manufacturing suppliers. These collaborations are vital for ensuring consistent access to cutting-edge materials and advanced cybersecurity solutions, which are essential for its defense and aerospace products. In 2023, General Dynamics announced several new partnerships aimed at enhancing its capabilities in areas like advanced composite materials and secure communication systems.
The aerospace and defense sector, by its very nature, often features a restricted pool of suppliers capable of meeting stringent quality and technological demands. This scarcity, particularly for specialized components and advanced systems, inherently elevates the bargaining power of these suppliers. For instance, in 2024, the lead times for certain advanced composite materials, crucial for next-generation aircraft, remained extended due to limited production capacity among a few key manufacturers, allowing them to command premium pricing.
Switching Costs for General Dynamics
Switching suppliers in the defense and aerospace sector presents significant hurdles for General Dynamics, primarily due to the substantial costs and time involved in re-certifying and integrating new components into their sophisticated platforms. This complexity inherently strengthens the bargaining power of existing suppliers who have already met stringent qualification requirements.
The rigorous testing, validation, and regulatory approvals necessary for any component change in defense systems mean that even minor substitutions can lead to multi-year delays and millions in additional expenses. For instance, a change in a critical electronic component might necessitate a complete overhaul of system software and re-testing across the entire platform, a process that General Dynamics would actively seek to avoid.
- High Integration Costs: General Dynamics faces substantial costs to integrate new suppliers' components into existing, complex defense systems.
- Regulatory Hurdles: The defense sector's strict certification processes for parts and systems create significant barriers to switching suppliers.
- Long Qualification Times: The lengthy period required to qualify new suppliers and their products directly enhances the leverage of incumbent providers.
- Specialized Components: Many components are highly specialized and designed for specific platforms, making off-the-shelf replacements difficult or impossible without extensive re-engineering.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Geopolitical Factors
The aerospace and defense supply chain experienced considerable strain throughout 2024. Factors like labor unrest, persistent parts shortages, and escalating geopolitical tensions significantly impacted operations. These widespread disruptions served to bolster the bargaining power of suppliers.
With constrained capacity and increased demand, suppliers found themselves in a stronger position to dictate terms. This often translated into higher prices for components and materials, directly affecting companies like General Dynamics. For instance, reports in late 2024 indicated that lead times for critical aerospace components had extended by an average of 20% compared to the previous year, a direct consequence of these supply chain pressures.
- Labor Disruptions: Strikes and workforce shortages in key manufacturing sectors impacted production schedules.
- Parts Shortages: Ongoing issues with raw material availability and semiconductor supply continued to affect component production.
- Geopolitical Tensions: International conflicts and trade disputes created uncertainty and logistical hurdles, further limiting supply.
General Dynamics' suppliers hold significant bargaining power due to the specialized nature of components and the high costs associated with switching. The defense industry's complex regulatory environment and the need for rigorous qualification processes further solidify this power. In 2024, extended lead times for critical aerospace components, averaging a 20% increase, underscored supplier leverage stemming from constrained capacity and ongoing supply chain pressures.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | 2024 Data/Observation |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Components | High reliance on unique, difficult-to-substitute inputs | Critical for advanced aerospace and defense platforms |
| Switching Costs | Substantial expenses and time for re-certification and integration | Multi-year delays and millions in additional expenses for component changes |
| Regulatory Environment | Strict testing, validation, and approval processes | Lengthy qualification times enhance incumbent supplier leverage |
| Supply Chain Disruptions | Labor unrest, parts shortages, geopolitical tensions | Extended lead times for components by an average of 20% |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting General Dynamics, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry.
Effortlessly identify and address competitive threats by visualizing each force's intensity, allowing for targeted strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
The U.S. military and its allies represent a substantial portion of General Dynamics' customer base, driving significant revenue in areas like Marine Systems and Combat Systems. This reliance on government contracts means these entities wield considerable influence.
These government customers, placing massive orders, possess strong bargaining power. Their ability to shape contract terms and influence procurement regulations directly impacts General Dynamics' profitability and operational flexibility.
For instance, in 2024, defense spending by the U.S. alone was projected to exceed $886 billion, highlighting the sheer scale of government procurement and the leverage these buyers have over defense contractors.
General Dynamics benefits from long-term defense contracts, offering predictable revenue. However, these agreements also empower government customers, like the U.S. Department of Defense, to influence pricing and performance expectations over the contract's life. For instance, shifts in U.S. defense spending priorities, such as a reported 6.3% increase in the FY2024 defense budget proposal to $886 billion, directly shape demand for General Dynamics' offerings and provide leverage to the customer.
In the commercial aviation sector, particularly for high-value items like Gulfstream business jets, customer bargaining power can be significant. While demand for premium aircraft, especially larger cabin models, remains robust, buyers of these multi-million dollar assets often have the leverage to negotiate pricing and customization options. This is particularly true when market conditions favor buyers or when specific aircraft configurations are readily available.
For instance, in 2024, the business jet market experienced continued demand, but the ability for customers to negotiate was influenced by factors such as inventory levels and the lead times for new aircraft. Customers with substantial financial resources and the flexibility to choose from various manufacturers or even pre-owned aircraft can exert considerable influence on deal terms. This power is amplified when they can compare offerings across different brands and models.
Product Uniqueness and Customization
General Dynamics' strength in producing highly specialized and customized defense systems, like the Abrams main battle tank or Virginia-class submarines, significantly limits the bargaining power of its customers. These unique, technologically advanced products often have a limited number of qualified manufacturers, making it difficult for buyers, primarily government entities, to switch suppliers or negotiate aggressively on price for such critical assets.
While product uniqueness is a strong defense, government clients still wield influence. They can demand specific performance features and push for competitive bidding processes, even for highly specialized equipment. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. Department of Defense continued to emphasize cost-efficiency across its procurement programs, impacting contract negotiations for major defense platforms.
The bargaining power of customers is also shaped by the lifecycle of General Dynamics' products. For established platforms, customers might have more leverage due to mature supply chains and potential for upgrades from other vendors. However, for cutting-edge systems, the lack of alternatives typically keeps customer power in check.
Key factors influencing customer bargaining power for General Dynamics include:
- High switching costs for specialized defense platforms.
- Limited availability of alternative suppliers for advanced military technology.
- Government procurement processes that, while competitive, often prioritize unique capabilities.
Budgetary Constraints and Procurement Policies
General Dynamics' customers, particularly government agencies, are significantly influenced by budgetary limitations and strict procurement regulations. These factors shape their buying behavior and bargaining power. For example, the Fiscal Year 2025 National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) emphasizes domestic sourcing and aims to bolster the defense industrial base, which can affect contract awards and pricing for defense contractors like General Dynamics.
- Budgetary Constraints: Government spending is often tied to annual appropriations, creating predictable but also rigid budget cycles that can limit the scope and timing of purchases.
- Procurement Policies: Federal Acquisition Regulations (FAR) and agency-specific policies dictate competitive bidding processes, cost controls, and supplier qualifications, giving customers leverage.
- Domestic Preference: Provisions like those in the FY2025 NDAA favoring U.S.-made components and labor can influence sourcing decisions and potentially increase costs for suppliers.
- Supply Chain Strengthening: Initiatives to enhance the defense supply chain may lead to greater scrutiny of existing supplier relationships and encourage diversification or consolidation among buyers.
General Dynamics' customers, especially government entities, hold considerable bargaining power due to the sheer scale of their orders and their ability to influence contract terms and procurement regulations. This is evident in the U.S. defense budget, which in 2024 was projected to exceed $886 billion, underscoring the leverage these buyers possess. While General Dynamics' specialized products limit direct price negotiation, government clients can still impact pricing and performance expectations through long-term contracts and budget-driven demands, as seen with the FY2024 defense budget proposal's 6.3% increase.
| Customer Type | Key Influence Factor | Example Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| U.S. Military & Allies | Massive order volume, contract terms, procurement regulations | U.S. Defense Spending: Projected > $886 billion |
| Commercial Aviation Buyers | Negotiating pricing, customization, market conditions | Robust demand for premium business jets, influenced by inventory/lead times |
| Government Agencies | Budgetary constraints, procurement policies (FAR), domestic preference | FY2025 NDAA emphasis on domestic sourcing impacting contract awards |
What You See Is What You Get
General Dynamics Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see here is the complete, ready-to-use General Dynamics Porter's Five Forces Analysis. What you're previewing is exactly what you'll receive—a professionally formatted and insightful examination of the competitive landscape impacting General Dynamics. This detailed analysis will equip you with a thorough understanding of the industry's forces, allowing for strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The aerospace and defense sector is a battleground for a select group of formidable global corporations. General Dynamics faces intense rivalry from giants such as Boeing, Lockheed Martin, Airbus, Raytheon Technologies, and Northrop Grumman, each vying for lucrative contracts across various defense and aerospace domains.
This concentrated market means competition is fierce, with these major players constantly innovating and bidding aggressively for government and commercial projects. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. Department of Defense awarded significant contracts, highlighting the intense competition for these vital defense programs.
Competitive rivalry in the defense sector is intensely fueled by rapid technological advancements. Companies like General Dynamics pour significant resources into research and development, aiming to secure a leading edge through innovation. This constant push for new capabilities creates a dynamic and challenging competitive landscape where staying ahead technologically is paramount.
General Dynamics' competitive strength is significantly bolstered by its technological leadership. For instance, their advancements in integrating artificial intelligence into combat platforms and their robust cybersecurity solutions provide a distinct advantage. In 2023, the company reported substantial R&D spending, reflecting its commitment to maintaining this technological superiority amidst fierce competition.
The competition for government contracts is fierce, as securing these deals is vital for companies like General Dynamics. This intense rivalry drives innovation and efficiency as firms vie for major defense projects.
General Dynamics' substantial backlog, exceeding $90 billion as of early 2024, underscores its success in winning significant government contracts. This strong position reflects its ability to navigate the competitive landscape and secure long-term revenue streams.
Diversified Portfolio and Market Positioning
General Dynamics' broad diversification across aerospace, marine systems, combat systems, and technologies significantly dilutes the intensity of competitive rivalry. This multi-faceted approach allows the company to absorb shocks in one sector by leveraging strengths in others, creating a stable market presence. For instance, in 2023, General Dynamics reported total revenue of $42.3 billion, showcasing the scale and breadth of its operations.
Within its aerospace segment, the Gulfstream business jet division maintains a formidable market position, particularly when measured by dollar value. While not always leading in unit production, Gulfstream's focus on the premium segment means it captures a substantial portion of the market's financial value. This strategic positioning means that while direct unit-based competition exists, the overall financial impact of rivals in this specific niche is carefully managed by Gulfstream's brand and product offering.
The company's diverse portfolio means that competitors often focus on specific segments rather than challenging General Dynamics across its entire operational spectrum. This segmentation of the competitive landscape reduces direct, head-to-head battles across all business units simultaneously. For example, while Lockheed Martin might be a key competitor in combat systems, its presence in the business jet market is negligible, illustrating how rivalry is often siloed.
- Diversification as a Risk Mitigator: General Dynamics operates across aerospace, marine, combat systems, and technologies, reducing reliance on any single market.
- Gulfstream's Premium Positioning: The Gulfstream business jet segment leads in dollar value within its market, despite not always topping unit sales.
- Segmented Competition: Rivalry is often confined to specific business areas, preventing a unified competitive threat across the entire company.
- Financial Strength: A 2023 revenue of $42.3 billion underscores the company's scale and ability to withstand competitive pressures.
Global Defense Spending and Geopolitical Tensions
Global defense budgets are on the rise, with a projected increase to $2.2 trillion in 2024 according to some estimates, driven by ongoing geopolitical instability. This surge in spending creates a highly competitive environment as major players like General Dynamics compete for contracts related to military modernization and the development of advanced defense systems.
The focus on next-generation capabilities, including artificial intelligence, cyber warfare, and hypersonics, intensifies this rivalry. Companies are heavily investing in research and development to secure a competitive edge in these critical areas.
- Increased Defense Budgets: Global defense spending is expected to continue its upward trend, reaching new highs in 2024.
- Geopolitical Drivers: Persistent international tensions are a primary catalyst for this increased demand.
- Focus on Modernization: Companies are prioritizing investments in advanced technologies and next-generation military systems.
- Intensified Competition: The growing market fuels fierce competition among established defense contractors.
The competitive rivalry for General Dynamics is characterized by a concentrated market with a few dominant global players. Companies like Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and Northrop Grumman are direct competitors, constantly vying for lucrative aerospace and defense contracts. This intense competition is further amplified by rapid technological advancements, forcing significant investment in research and development to maintain a competitive edge.
General Dynamics' diversification across segments like aerospace, marine, and combat systems helps mitigate the intensity of rivalry, as competitors often specialize. For instance, while Gulfstream leads in the premium business jet market by dollar value, its direct competition is segmented, unlike broader defense contracts. The company's substantial backlog, exceeding $90 billion in early 2024, demonstrates its success in navigating this competitive landscape.
The global defense budget's projected increase to $2.2 trillion in 2024, driven by geopolitical factors, intensifies competition for modernization contracts. This environment necessitates continuous innovation in areas like AI and cyber warfare.
| Competitor | Key Segments | 2023 Revenue (Approximate, Billions USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Boeing | Aerospace, Defense | 77.8 |
| Lockheed Martin | Aerospace, Defense | 67.6 |
| Northrop Grumman | Aerospace, Defense | 39.0 |
| Raytheon Technologies | Aerospace, Defense | 67.0 |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For many of General Dynamics' specialized defense products, like submarines and advanced combat vehicles, direct substitutes are scarce. These systems are engineered for unique operational demands and national security, making off-the-shelf alternatives impractical. This scarcity significantly reduces the threat of substitution for these critical offerings.
While General Dynamics faces few direct substitutes for its core defense products like tanks and submarines, the threat of substitution can emerge from disruptive technologies. For instance, advancements in autonomous unmanned systems, whether aerial, ground, or maritime, could offer alternative solutions to traditional manned platforms, potentially reducing demand for some of General Dynamics' offerings.
The increasing sophistication of artificial intelligence in warfare and cyber capabilities also presents a form of substitution. These technologies can provide new methods for achieving strategic objectives, potentially bypassing the need for certain physical assets or platforms that General Dynamics specializes in, thereby altering defense spending priorities.
Consider the global defense market, which is projected to reach approximately $750 billion by 2024. Within this, the segment for unmanned systems is experiencing rapid growth, with some estimates suggesting it could reach over $30 billion by 2025. This indicates a tangible shift where technological innovation is creating viable alternatives to established defense solutions.
The evolving landscape of global security, marked by the rise of asymmetric threats and cyber warfare, presents a significant substitution risk for traditional defense contractors like General Dynamics. These new forms of conflict often favor less capital-intensive and more adaptable technologies, potentially diverting demand from large-scale platforms. For instance, the increasing reliance on drones and sophisticated cyber capabilities in modern conflicts, as seen in the ongoing geopolitical shifts of 2024, offers alternatives to traditional armored vehicles or naval vessels.
Commercial Aviation Alternatives
While Gulfstream's business jets offer distinct advantages, the threat of substitutes in commercial aviation is present. For instance, in 2024, the global business jet market, though robust, still sees travelers considering commercial flights for shorter distances or cost-sensitive trips. Fractional ownership and jet card programs also serve as alternatives, providing access to private aviation without full ownership, though often with less flexibility than a dedicated Gulfstream aircraft.
The unique value proposition of Gulfstream, particularly for long-range missions and specific operational requirements, mitigates some of this substitution threat. However, the availability of numerous commercial airlines and a growing array of fractional and charter options means that customers can often find viable, albeit different, solutions for their travel needs.
- Commercial Airlines: Offer extensive networks and potentially lower per-trip costs for standard travel.
- Fractional Ownership: Provides access to private jets with shared costs and management.
- Jet Card Programs: Allow for pre-purchased flight hours with guaranteed availability.
- Smaller Business Jets: Competitors offer less luxurious or shorter-range options at a lower price point.
Budgetary Reallocation by Governments
Governments, particularly in defense spending, can act as a significant force influencing demand for established products. If national budgets are reallocated, it directly impacts the market for companies like General Dynamics. For instance, a shift in strategic priorities could see a reduction in funding for traditional armored vehicles, a core product for General Dynamics, in favor of cybersecurity or drone technology.
This budgetary reallocation can function as a threat of substitutes. If governments decide that investing in advanced cyber defense systems or unmanned aerial vehicles offers a more cost-effective or strategically superior solution than procuring more traditional hardware, demand for General Dynamics' existing product lines could diminish. This is particularly relevant as nations increasingly focus on asymmetric warfare and digital security.
In 2023, global military spending reached an estimated $2.4 trillion, a 9% increase from 2022, marking the ninth consecutive year of growth. While this overall growth might seem positive, the *distribution* of this spending is crucial. For example, a significant portion of the 2024 US defense budget, which often sets trends, is allocated to emerging technologies and space-based assets, potentially diverting funds from traditional platforms.
- Budgetary Shifts: Governments may prioritize new technologies like AI-driven defense systems over traditional hardware, impacting demand for General Dynamics' established offerings.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Alternative solutions, such as advanced cybersecurity or drone capabilities, might be perceived as more efficient uses of defense funds.
- Strategic Advantage: A nation's evolving military doctrine could favor different types of defense capabilities, indirectly substituting demand for conventional military platforms.
- Market Impact: A reallocation of defense budgets, even with overall spending increases, can directly reduce the market size for specific product categories.
The threat of substitutes for General Dynamics is relatively low for its core, highly specialized defense products like submarines and advanced combat systems. These require immense technological expertise and significant capital investment, making direct, off-the-shelf alternatives scarce. However, disruptive technologies and evolving defense strategies can introduce indirect substitutes.
For instance, the rise of unmanned systems and advanced cyber warfare capabilities presents a form of substitution. These technologies can achieve strategic objectives, potentially diverting funds from traditional manned platforms. The global defense market's projected growth to around $750 billion by 2024, with a rapidly expanding unmanned systems segment, highlights this shift.
Government budgetary decisions are a key factor. A reallocation of defense spending towards areas like cybersecurity or drones, driven by evolving geopolitical threats and a focus on asymmetric warfare, can reduce demand for General Dynamics' established hardware. This is evident in 2024 defense budgets, where emerging technologies are receiving significant investment, potentially at the expense of traditional platforms.
| Substitution Threat Factor | Impact on General Dynamics | Supporting Data/Trend (as of 2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Technological Advancements (e.g., AI, Drones) | Moderate to High for certain platforms | Unmanned systems market projected to exceed $30 billion by 2025; AI integration in defense is a growing priority. |
| Evolving Warfare Doctrines (Cyber, Asymmetric) | Moderate | Increased global focus on cyber defense and drone warfare in recent conflicts. |
| Government Budgetary Reallocation | Moderate to High | Global military spending reached $2.4 trillion in 2023, with significant portions of 2024 budgets targeting new technologies. |
| Commercial Aviation Alternatives (for Gulfstream) | Moderate | Business jet market coexists with commercial airlines, fractional ownership, and jet cards. |
Entrants Threaten
The aerospace and defense sector demands colossal capital outlays. For instance, developing a new fighter jet or a sophisticated satellite system can easily run into billions of dollars, a sum prohibitive for most newcomers. General Dynamics, having invested heavily in advanced manufacturing and cutting-edge research, has established a formidable cost advantage.
The defense industry, where General Dynamics operates, is characterized by extensive regulatory hurdles and certifications. Navigating these complex requirements, including stringent security clearances and compliance mandates, presents a significant barrier for potential new entrants. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Department of Defense continued to emphasize cybersecurity compliance, with new regulations impacting supply chain security and data handling, making it harder for less established firms to meet these evolving standards.
The development and production of sophisticated defense and aerospace systems, like those General Dynamics specializes in, require immense technical expertise and a highly skilled workforce. This deep technological complexity, often built over decades, acts as a significant barrier, making it challenging for new entrants to quickly replicate the necessary capabilities.
Companies like General Dynamics invest heavily in research and development, fostering a culture of innovation that is difficult to match. For instance, in 2023, General Dynamics reported $3.1 billion in R&D spending, a figure that underscores the commitment required to stay at the forefront of the industry and deters potential new competitors who lack such established resources.
Established Customer Relationships and Contracts
Incumbent defense contractors like General Dynamics benefit from deeply entrenched customer relationships, particularly with government agencies. These long-standing ties, often spanning decades, foster a high degree of trust and familiarity, making it difficult for new entrants to penetrate the market and secure initial contracts. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. Department of Defense awarded over $700 billion in contracts, with a significant portion flowing to established prime contractors.
The nature of defense procurement often involves complex, multi-year contracts and extensive vetting processes. New companies face considerable hurdles in demonstrating the reliability, security, and performance necessary to compete for these substantial, long-term agreements. The defense industrial base has also experienced significant consolidation, further concentrating market power among a few large players and raising the barriers to entry.
- Deeply Rooted Government Relationships: General Dynamics leverages decades of experience and established trust with key government clients, a crucial advantage in securing new business.
- Contractual Lock-in and Pipeline: Existing, long-term contracts create a predictable revenue stream and make it challenging for new competitors to displace incumbents.
- Defense Industry Consolidation: Mergers and acquisitions have reduced the number of major players, increasing the competitive advantage of established firms.
- High Barriers to Entry: The specialized nature of defense products, stringent security requirements, and the need for proven track records present significant obstacles for new entrants.
Intellectual Property and Proprietary Technologies
General Dynamics and its rivals hold significant intellectual property and proprietary technologies vital for advanced defense and aerospace products. This technological moat makes it difficult for newcomers to compete effectively without substantial R&D investment or costly technology acquisitions.
For instance, in 2024, the global defense market saw continued high spending, with companies like General Dynamics investing heavily in innovation. New entrants would face the challenge of replicating or surpassing these established technological capabilities, requiring billions in upfront investment.
- High R&D Costs: Developing cutting-edge defense technology requires massive, sustained investment in research and development, often exceeding billions of dollars.
- Patented Technologies: Existing players have secured numerous patents on critical components and systems, creating legal and practical barriers for new entrants.
- Complex Manufacturing Processes: Proprietary manufacturing techniques and specialized facilities are often necessary, further increasing the capital required to enter the market.
The threat of new entrants for General Dynamics is considerably low due to the sector's immense capital requirements and deep technological complexities. Developing advanced aerospace and defense systems demands billions in investment, a hurdle most new companies cannot overcome. Furthermore, decades of R&D and established expertise create a formidable barrier.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our General Dynamics Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages a comprehensive array of data, including annual reports, investor presentations, and SEC filings, to meticulously examine competitive dynamics.
We incorporate insights from industry-specific market research reports, competitor news releases, and government defense spending databases to provide a robust assessment of the forces shaping the aerospace and defense sector.
