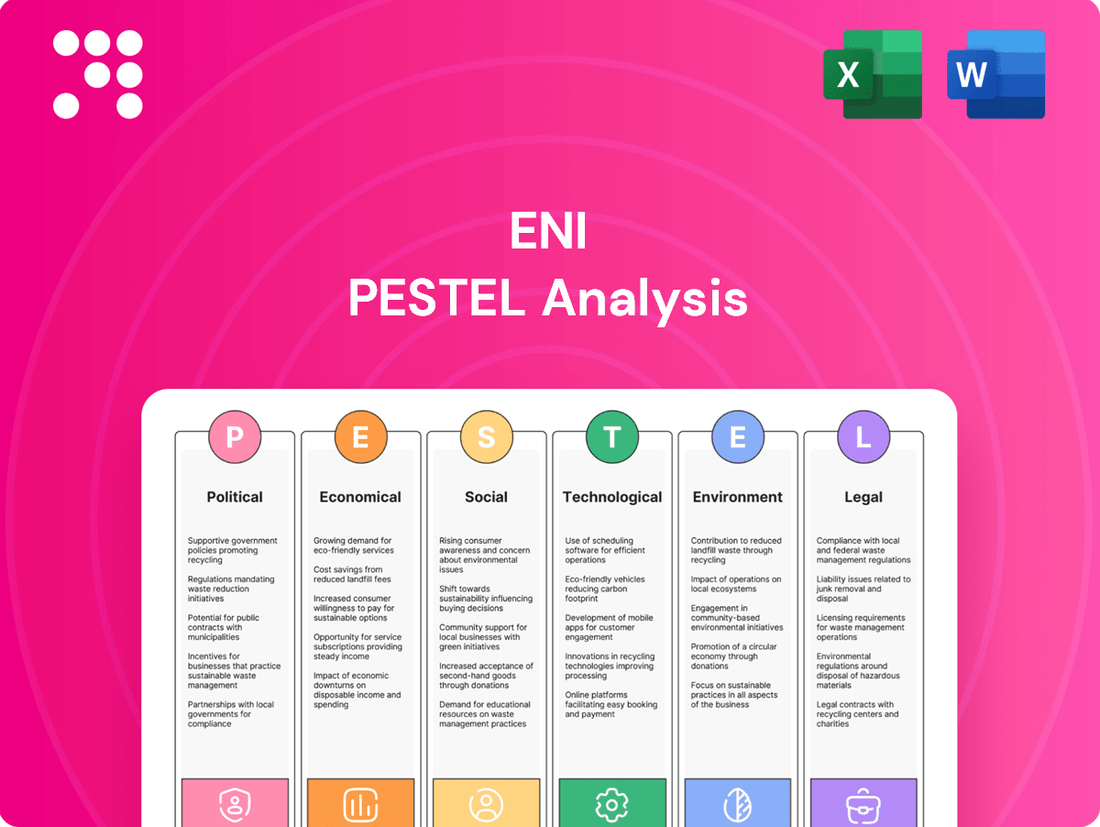
Eni PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Eni Bundle
Unlock critical insights into the external forces shaping Eni's future with our comprehensive PESTLE analysis. Understand the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors influencing this energy giant. Equip yourself with the knowledge to anticipate market shifts and make informed strategic decisions. Download the full analysis now and gain a significant competitive advantage.
Political factors
Eni's operations are deeply intertwined with global geopolitical stability, especially in regions like North Africa and the Eastern Mediterranean, which are critical for its exploration and production activities. For instance, ongoing tensions in these areas can disrupt supply chains and pose risks to Eni's physical assets, impacting its ability to deliver energy reliably.
The global push for energy security, accelerated by events in 2022 and continuing through 2024, directly shapes Eni's strategic direction. This has led to increased investment in Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) as a transitional fuel, with Eni aiming to boost its LNG portfolio significantly. By 2024, Eni projected a substantial increase in its LNG production capacity, reflecting this strategic pivot driven by national energy security concerns.
Political stability in countries where Eni has a significant presence, such as Libya and Egypt, is paramount. Instability can lead to project delays, increased operational costs, and even force the suspension of activities, directly affecting Eni's financial performance and long-term project viability.
Governments globally are intensifying efforts to drive the energy transition through measures like carbon pricing, renewable energy mandates, and subsidies for green technologies. For instance, the European Union's Fit for 55 package aims to cut emissions by 55% by 2030, directly impacting fossil fuel operations.
These policy shifts compel companies like Eni to significantly invest in renewable sources, biofuels, and carbon capture. Eni's strategic pivot towards carbon neutrality by 2050 is a direct response to these evolving political and regulatory frameworks, including national climate targets and international agreements.
Eni's global footprint makes it highly susceptible to shifts in international relations and trade pacts. For example, the European Union's energy diversification efforts, spurred by geopolitical events in 2022, significantly boosted demand for Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG), a key commodity for Eni. These agreements and diplomatic ties directly impact Eni's access to exploration blocks and the flow of its energy products.
Bilateral and multilateral trade agreements are crucial for Eni's operations, particularly those governing natural gas supply and infrastructure development. In 2024, the company continued to leverage its long-term LNG contracts, such as those with Qatar and Algeria, to secure stable supply chains and meet European energy needs. Such contracts are vital for mitigating risks associated with regional instability and diversifying energy sources.
Changes in diplomatic relations can create both opportunities and challenges for Eni. For instance, improved relations between Italy and North African countries in 2023-2024 have facilitated new exploration licenses and pipeline projects, enhancing Eni's upstream capabilities. Conversely, trade sanctions or political tensions can restrict market access and disrupt existing operational plans.
Regulatory Frameworks and Compliance
Eni must navigate a complex web of regulations across its global operations, impacting everything from environmental standards to labor practices and corporate governance. Compliance with directives like the European Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), which mandates detailed sustainability disclosures, is essential for maintaining its operational legitimacy and avoiding fines. For instance, in 2023, Eni reported €247 million in environmental provisions, highlighting the financial implications of environmental compliance.
Stricter environmental regulations, particularly concerning emissions and the transition to renewable energy, require substantial investments and operational shifts. The company's 2024-2027 strategy, for example, allocates significant capital to decarbonization efforts, reflecting the pressure to align with evolving climate policies. Failure to adapt to these evolving legal landscapes can lead to penalties and reputational damage.
- Environmental Regulations: Eni faces increasing scrutiny and compliance demands related to emissions reduction targets and the development of low-carbon energy sources.
- Labor Laws: Adherence to diverse national labor laws ensures fair treatment of employees and avoids potential disputes and legal challenges.
- Corporate Governance: Compliance with corporate governance codes, including those promoting transparency and accountability, is vital for investor confidence and market access.
- Sustainability Reporting: Mandates like the CSRD necessitate robust data collection and reporting on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance.
Nationalization Risks and Political Instability in Host Countries
Eni's operations in politically volatile regions, particularly those rich in natural resources, present a significant risk of asset nationalization or unfavorable alterations to existing contracts. For instance, in 2024, several African nations continued to explore increased state control over energy resources, impacting foreign investment sentiment. This political instability can directly hinder Eni's production, potentially leading to substantial financial setbacks and influencing strategic decisions regarding asset allocation and divestment.
The potential for political unrest, abrupt governmental changes, or internal conflicts in host countries poses a direct threat to Eni's operational continuity. Such disruptions can severely affect production levels and result in considerable financial losses. For example, ongoing geopolitical tensions in certain regions where Eni operates have led to supply chain disruptions and increased operational costs throughout 2024.
- Nationalization Risk: Countries like Venezuela have historically nationalized energy assets, a precedent that investors monitor closely in other resource-rich nations.
- Contractual Changes: Governments may seek to renegotiate terms on existing concessions, potentially increasing royalties or taxes, as seen in some Latin American countries in late 2024.
- Operational Disruption: Civil unrest in a key African operational area in early 2025 led to a temporary halt in exploration activities, impacting projected output.
- Portfolio Management: Eni's strategy involves diversifying its geographical footprint to mitigate the impact of localized political instability, a key consideration in its 2024-2025 investment planning.
Governmental policies and political stability are critical for Eni's global operations, influencing everything from exploration rights to energy transition strategies. For instance, the European Union's ambitious climate targets, like the Fit for 55 package aiming for a 55% emissions reduction by 2030, directly impact Eni's fossil fuel business and necessitate significant investment in renewables and decarbonization technologies. Eni's strategic plan for 2024-2027 reflects this, allocating substantial capital to green initiatives to align with these evolving regulatory landscapes.
Geopolitical events continue to shape energy security concerns, driving demand for fuels like LNG. Eni's commitment to bolstering its LNG portfolio, with projected capacity increases by 2024, is a direct response to this, as seen in its continued reliance on long-term contracts with suppliers like Qatar and Algeria to secure stable energy flows into Europe. These diplomatic and trade agreements are vital for navigating market volatility and ensuring supply chain resilience.
Political instability in key operational regions, such as North Africa and the Eastern Mediterranean, poses risks to Eni's assets and operational continuity. The potential for nationalization or renegotiation of contracts, a concern highlighted by trends in resource-rich nations in 2024, necessitates a diversified geographical footprint to mitigate localized political risks. This strategic diversification is a core element of Eni's investment planning for 2024-2025.
| Factor | Impact on Eni | Example/Data Point (2023-2025) |
| Energy Transition Policies | Drives investment in renewables and decarbonization, impacts fossil fuel operations. | EU's Fit for 55 package; Eni's 2024-2027 strategy allocates significant capital to decarbonization. |
| Geopolitical Stability & Energy Security | Influences LNG demand and supply chain strategies. | Eni's projected LNG capacity increase by 2024; reliance on contracts with Qatar and Algeria. |
| Political Instability in Host Countries | Risk of asset disruption, nationalization, or contract changes. | Monitoring trends in African nations for increased state control over resources (2024); Eni's geographical diversification strategy. |
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis provides a comprehensive examination of the external macro-environmental factors impacting Eni, covering Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal dimensions.
Offers a clear, actionable roadmap for navigating Eni's complex external environment, transforming potential challenges into strategic opportunities.
Economic factors
Global commodity price volatility significantly impacts Eni's financial performance, particularly its exploration and production segment. For instance, a notable decline in Brent crude oil prices, which saw fluctuations throughout late 2024 and into early 2025, directly reduced Eni's revenue streams and earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT).
This sensitivity means that while periods of stable or increasing commodity prices can bolster Eni's profitability, the inherent unpredictability of these markets presents a persistent hurdle for accurate financial planning and maintaining operational stability. For example, if Brent crude averaged $75 per barrel in Q4 2024 and fell to $60 per barrel in Q1 2025, Eni's upstream revenues would likely see a material decrease.
Eni, as a global energy company, is significantly exposed to currency exchange rate fluctuations, especially concerning the Euro (EUR) and the US Dollar (USD). Since many of its commodity sales and purchases are priced in USD, movements in the EUR/USD exchange rate directly influence its reported earnings and operational costs when translated back into Euros.
For instance, if the Euro strengthens against the US Dollar, Eni's USD-denominated revenues will translate into fewer Euros, potentially reducing its reported profitability. Conversely, a weaker Euro can boost reported earnings from USD-based activities. In early 2024, the EUR/USD hovered around 1.08, a level that can present both challenges and opportunities depending on Eni's specific hedging strategies and revenue/cost mix.
Managing these currency risks is a crucial element of Eni's financial strategy, often involving hedging instruments to mitigate volatility. The company's ability to navigate these fluctuations is vital for maintaining financial stability and achieving its investment and operational targets in a dynamic global market.
Eni is strategically shifting its economic focus, channeling significant capital into areas like renewable energy, liquefied natural gas (LNG), biofuels, and carbon capture. This pivot is essential for long-term viability and to meet global climate goals.
These ambitious investments, while vital, demand considerable upfront capital, which could put pressure on Eni's short-term financial performance. For instance, Eni's 2024-2027 strategic plan outlines €25 billion in investments, with a substantial portion dedicated to decarbonization and energy transition projects.
The ultimate economic resilience of Eni hinges on the successful development and profitability of these diversified energy ventures, ensuring a stable financial future amidst evolving market demands.
Market Demand for Traditional and New Energy Products
Global demand for Eni's traditional oil and gas products remains tied to economic expansion and industrial output, though a noticeable shift towards cleaner alternatives is underway. For instance, in 2024, while oil demand growth is projected to moderate, natural gas is expected to see continued demand, particularly in Asia.
Eni is experiencing a significant uplift in demand for its new energy offerings, such as biofuels and liquefied natural gas (LNG). This growth is fueled by global decarbonization mandates and a strategic pivot by many economies towards lower-carbon energy sources. Eni's investment in biomethane production, for example, has seen its capacity expand, meeting rising interest from industrial and transportation sectors seeking sustainable fuels.
The company's strategic focus on adapting to these evolving market dynamics is critical. By optimizing production of traditional energy sources while aggressively expanding its new energy portfolio, Eni aims to balance current market needs with future sustainability goals. This dual approach is essential for maintaining market share and capitalizing on emerging opportunities in the energy transition.
- Global Oil Demand Growth (2024): Projected to be around 1.2 million barrels per day, a slowdown from previous years, reflecting efficiency gains and the shift to alternatives.
- LNG Demand Growth: Expected to remain robust, with Asia continuing to be the primary driver, potentially seeing demand increase by over 5% year-on-year in 2024.
- Biofuel Market Expansion: The global biofuel market size was valued at approximately $120 billion in 2023 and is forecast to grow at a CAGR of over 6% through 2030, indicating strong market appetite for Eni's biofuel products.
Financial Discipline and Shareholder Returns
Eni demonstrates a commitment to financial discipline, even amidst economic headwinds, with a clear objective of bolstering its balance sheet and delivering reliable shareholder returns. This strategic focus is evident in its proactive management of leverage and its efforts to optimize cash flow generated from its operations.
The company actively pursues measures such as share buyback programs and dividend distributions to reward investors and solidify their confidence. These actions not only aim to enhance shareholder value but also provide Eni with the necessary financial agility to pursue key strategic investments, ensuring long-term growth and stability.
For instance, in 2023, Eni announced a dividend of €0.44 per share, reflecting its consistent approach to shareholder remuneration. Furthermore, the company continued its share buyback program, repurchasing approximately €1.3 billion worth of shares in the first nine months of 2023, demonstrating a tangible commitment to returning capital to its investors while maintaining financial strength.
- Financial Discipline: Eni prioritizes a robust balance sheet and consistent shareholder returns through careful management of debt and operational cash flow.
- Shareholder Returns: The company implements share buyback programs and dividend payments to enhance investor confidence and provide capital appreciation.
- Financial Flexibility: These prudent financial strategies equip Eni with the resources needed for strategic investments and to navigate economic uncertainties.
- 2023 Performance: Eni declared a dividend of €0.44 per share and repurchased around €1.3 billion in shares during the first nine months of 2023, underscoring its commitment to financial health and shareholder value.
Global economic growth directly influences Eni's demand for both traditional and new energy products. A robust economy typically translates to higher energy consumption, benefiting Eni's sales volumes. Conversely, economic slowdowns or recessions can dampen demand, impacting revenue and profitability.
What You See Is What You Get
Eni PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive Eni PESTLE analysis covers all critical external factors impacting the company's operations and strategic planning. You'll gain valuable insights into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental landscape affecting Eni.
Sociological factors
Public perception heavily shapes Eni's ability to operate, with societal expectations around environmental stewardship and ethical business practices being paramount. As climate activism intensifies, with organizations like Greenpeace actively scrutinizing energy companies, maintaining a positive social license is critical for Eni's long-term viability and access to capital.
Eni's commitment to sustainability, as detailed in its 2023 Integrated Report, highlights investments in renewable energy and emissions reduction targets, aiming to address public concerns. These efforts are crucial for navigating increasing climate litigation risks and fostering community trust, particularly in regions where Eni operates.
The global energy transition necessitates a significant evolution in Eni's workforce capabilities, with a growing demand for expertise in areas like renewable energy technologies, advanced digital solutions, and circular economy principles. This shift requires substantial investment in upskilling and reskilling existing employees to meet these new demands.
To navigate this transformation effectively, Eni must prioritize programs that retrain and redeploy personnel from its traditional fossil fuel sectors. This proactive approach is crucial for ensuring a 'just transition,' minimizing potential job displacement, and maintaining employee morale and engagement throughout the company's strategic pivot.
Eni's commitment to community engagement is crucial for its global operations. In 2023, Eni invested €140 million in social initiatives, focusing on energy access, education, and health in the countries where it operates. For instance, its "Eni for Life" program aims to improve living conditions and access to essential services, directly impacting local development and fostering goodwill.
These community-focused projects are not just philanthropic; they are strategic. By addressing local needs, such as providing access to clean water or supporting local businesses, Eni builds trust and secures its social license to operate. This proactive approach helps mitigate risks associated with social unrest or regulatory hurdles, ensuring smoother project execution and long-term operational stability.
Consumer Behavior and Energy Choices
Consumer preferences are increasingly leaning towards environmentally friendly energy. This shift directly affects companies like Eni, influencing demand for their traditional fossil fuels and driving interest in their newer, greener offerings. For instance, the growing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) means less demand for gasoline, while simultaneously boosting the need for charging infrastructure.
Eni's strategic moves, such as investing in EV charging networks and developing sustainable aviation fuel (SAF), directly respond to these evolving consumer desires. By 2024, global EV sales are projected to exceed 15 million units, highlighting the significant market opportunity in this sector. Furthermore, consumer surveys in 2025 indicate that over 60% of individuals are willing to pay a premium for sustainable products and services.
This evolving consumer landscape presents both challenges and opportunities for Eni:
- Shifting Demand: Growing consumer preference for low-carbon solutions directly impacts demand for Eni's fossil fuel products.
- EV Adoption: The rise of electric mobility creates new revenue streams for Eni in areas like EV charging infrastructure.
- Sustainability Focus: Consumer willingness to pay more for sustainable options, as evidenced by surveys, supports Eni's investments in SAF and other green initiatives.
Health, Safety, and Human Rights
Eni places significant emphasis on the health, safety, and human rights of its workforce and stakeholders. This commitment is woven into its operational fabric, aiming to foster secure environments and uphold ethical standards throughout its global activities and supply chains. The company actively works to prevent violence against women and champions safe working conditions, demonstrating a dedication to social responsibility that resonates with its sustainability objectives.
In 2023, Eni reported a Total Recordable Injury Frequency Rate (TRIFR) of 0.67 per million hours worked, a figure reflecting its ongoing efforts to minimize workplace accidents. Furthermore, the company's sustainability reports detail initiatives aimed at promoting diversity and inclusion, including programs specifically designed to support women in the workplace and combat gender-based violence. These actions are crucial for building trust and ensuring long-term social license to operate.
Key sociological considerations for Eni include:
- Employee and Contractor Well-being: Prioritizing a zero-harm culture through robust safety protocols and training programs.
- Human Rights Due Diligence: Implementing processes to identify, prevent, and mitigate adverse human rights impacts across its operations and supply chains.
- Community Engagement: Fostering positive relationships with local communities through dialogue and support for social development initiatives.
- Ethical Labor Practices: Ensuring fair wages, reasonable working hours, and freedom from forced or child labor throughout its value chain.
Societal expectations regarding environmental responsibility and ethical conduct are increasingly influencing Eni's operations and public image. As global awareness of climate change grows, so does scrutiny on energy companies, making a positive social license to operate essential for Eni's future access to capital and project approvals.
Eni's investments in renewable energy and emissions reduction, as highlighted in its 2023 reports, are strategic responses to these societal pressures. These initiatives are vital for managing climate litigation risks and building trust with communities, especially in regions where Eni has a significant presence.
The workforce must adapt to the energy transition, requiring new skills in renewables and digital technologies. Eni's focus on upskilling and reskilling its employees, particularly those from fossil fuel sectors, is critical for a just transition and maintaining workforce morale.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards sustainable energy solutions, impacting demand for traditional fossil fuels and boosting interest in Eni's green initiatives. By 2025, consumer surveys indicate a strong willingness to pay a premium for sustainable products, reinforcing Eni's strategic direction in areas like electric vehicle charging and sustainable aviation fuel.
Eni's commitment to employee and community well-being is a core aspect of its social strategy. The company's safety record, with a Total Recordable Injury Frequency Rate of 0.67 per million hours worked in 2023, and its social investments, totaling €140 million in 2023 for initiatives like energy access and education, underscore this dedication.
| Sociological Factor | Eni's Response/Initiative | Key Data/Impact |
| Environmental Stewardship & Climate Activism | Investments in renewables, emissions reduction targets | 2023 Integrated Report details sustainability efforts; critical for social license |
| Workforce Transformation & Just Transition | Upskilling/reskilling programs for renewable energy expertise | Focus on retraining fossil fuel sector employees |
| Evolving Consumer Preferences | Expansion into EV charging networks, SAF development | Global EV sales projected to exceed 15 million units by 2024; 60%+ consumers willing to pay premium for sustainable options (2025 surveys) |
| Health, Safety, and Human Rights | Zero-harm culture, human rights due diligence | TRIFR of 0.67 per million hours worked in 2023; diversity and inclusion programs |
| Community Engagement | Social initiatives, local development support | €140 million invested in social initiatives in 2023; "Eni for Life" program |
Technological factors
Continuous advancements in solar, wind, and other renewable energy technologies are fundamental to Eni's energy transition. These innovations directly support the company's strategy to shift towards cleaner energy sources.
Eni, through its Plenitude arm, is significantly boosting its renewable capacity. The company aims to reach 5.5 GW of installed capacity by the close of 2025, with an ambitious target of 15 GW by 2030, showcasing a strong commitment to this technological evolution.
Improvements in renewable technology directly translate to enhanced efficiency and lower production costs. This makes solar and wind power increasingly competitive, bolstering Eni's efforts to integrate these sources into its portfolio.
Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) technologies are pivotal for Eni's strategy to reduce emissions, especially in sectors that are difficult to decarbonize. Eni is making significant investments in this area, with projects like Ravenna CCS in Italy and HyNet North West in the UK demonstrating their commitment. These initiatives are essential for Eni to meet its ambitious carbon neutrality targets, with a new dedicated CCUS company slated for launch in 2025.
Eni is aggressively investing in advanced biofuels and biorefining, aiming to significantly boost its production of Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF). This strategic pivot includes transforming existing refineries, like the Livorno facility, into advanced biorefineries. By 2024, Eni projected its biorefining capacity to reach 3 million tonnes per year, with a target of 5 million tonnes by 2030, showcasing a substantial commitment to this technological frontier.
Digital Transformation and AI Integration
Eni is actively embracing digital transformation, notably through its advanced supercomputing capabilities. The company's HPC6 system, for instance, plays a crucial role in optimizing various aspects of its operations, from intricate reservoir modeling to the seamless integration of renewable energy sources. This digital push is designed to drive efficiency and foster innovation across its energy solutions.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is another key area of focus for Eni. The company is exploring AI's potential for a range of applications, including the possibility of supplying 'blue power' to data centers, leveraging its carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology. This strategic integration of AI aims to unlock new efficiencies and create novel energy service offerings.
The impact of this digital transformation is far-reaching. It significantly enhances operational efficiency, improves the accuracy of decision-making processes, and accelerates the development of next-generation energy solutions. Eni's commitment to these technological advancements underscores its strategy to remain competitive and sustainable in the evolving energy landscape.
- HPC6 Supercomputing: Eni's investment in advanced computing power like HPC6 is central to its digital strategy, enabling complex simulations for reservoir management and renewable energy integration.
- AI for Blue Power: The exploration of AI for supplying 'blue power' to data centers, coupled with CCS technology, highlights Eni's innovative approach to decarbonization and new market opportunities.
- Operational Efficiency Gains: Digital transformation initiatives are projected to yield substantial improvements in operational efficiency, reducing costs and streamlining processes across Eni's diverse business segments.
Exploration and Production Technologies
Eni remains committed to advancing its oil and gas exploration and production (E&P) technologies, even as it diversifies into new energy sectors. This strategic focus aims to extract maximum value from its current hydrocarbon assets.
The company is investing in sophisticated reservoir modeling and enhanced oil recovery techniques. These innovations are crucial for optimizing extraction efficiency, especially in projects with high potential and lower cost thresholds, ensuring continued hydrocarbon supply during the energy transition.
- Reservoir Modeling: Eni utilizes advanced seismic imaging and data analytics to create detailed 3D models of underground reservoirs, improving the understanding of geological structures and fluid flow. This allows for more precise well placement and production strategies.
- Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR): The company employs methods like waterflooding, gas injection, and chemical EOR to increase the amount of oil or gas that can be extracted from a reservoir beyond primary and secondary recovery methods.
- Digitalization: Eni is integrating digital technologies, including AI and machine learning, into its E&P operations. This enhances predictive maintenance, optimizes drilling operations, and improves overall operational efficiency and safety.
- Low-Breakeven Projects: A significant portion of Eni's investment is directed towards projects with inherently low production costs. For instance, in 2024, the company highlighted its focus on developing assets in regions like Egypt and Mozambique, which offer competitive breakeven prices, ensuring profitability even in volatile market conditions.
Technological advancements are central to Eni's strategic repositioning in the energy sector. The company is heavily investing in renewable energy technologies like solar and wind, aiming to significantly expand its installed capacity. For instance, Eni's Plenitude aims for 5.5 GW of renewable capacity by the end of 2025, a substantial increase from previous years.
Furthermore, Eni is prioritizing Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) technologies to address emissions from harder-to-abate sectors. The development of projects like Ravenna CCS in Italy and HyNet North West in the UK demonstrates this commitment, with a new dedicated CCUS company planned for launch in 2025.
Eni is also pushing the boundaries in advanced biofuels and biorefining, with a target to reach 3 million tonnes per year of biorefining capacity by 2024. This focus on sustainable fuels, like Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF), is a key technological driver for the company's decarbonization efforts.
Digital transformation, powered by advanced supercomputing like HPC6 and the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI), is enhancing Eni's operational efficiency and enabling new service offerings, such as supplying 'blue power' to data centers.
Legal factors
Eni operates under an increasingly strict environmental legal framework, encompassing emissions targets and detailed reporting obligations. Compliance with regulations such as the European Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) is a legal necessity, impacting how Eni discloses its environmental performance.
The company has committed to legally binding goals for reducing its Scope 1 and 2 emissions, alongside specific targets for methane emissions reduction, particularly crucial in the oil and gas sector.
Eni is increasingly exposed to climate litigation, with environmental groups filing lawsuits alleging the company's contribution to climate change. These legal challenges, such as those filed in Italy and other jurisdictions, could force Eni to expedite its emissions reduction targets and potentially incur substantial financial penalties or operational limitations.
The growing trend of climate-related lawsuits directly impacts Eni's strategic planning regarding decarbonization and the transparency of its climate-related disclosures. For instance, by mid-2024, several high-profile climate cases against energy majors were progressing, setting precedents for future legal actions and increasing the financial and reputational risks for companies like Eni.
Eni, as a global energy player, navigates a complex web of international sanctions and trade laws. These regulations, enacted by entities like the United Nations, the European Union, and individual nations, dictate where and how Eni can conduct business. For instance, sanctions can restrict access to specific markets or prohibit dealings with certain state-owned enterprises, impacting Eni's exploration, production, and sales activities.
The evolving geopolitical landscape significantly influences these legal frameworks. As of early 2024, the global energy sector continues to grapple with the implications of sanctions targeting major energy-producing nations, affecting supply chains and commodity flows. Eni's ability to adapt its operations and financial transactions to comply with these ever-changing international trade laws is crucial for maintaining market access and operational continuity.
Corporate Governance and Transparency Requirements
Eni operates under stringent corporate laws and regulations that define its governance framework, shareholder protections, and reporting transparency. In 2023, Eni published its Corporate Governance Report, detailing its compliance with Italian legislative decrees and the Corporate Governance Code. This commitment to transparency is vital for maintaining investor trust and securing necessary regulatory approvals for its operations and strategic initiatives.
Key aspects of Eni's corporate governance and transparency include:
- Board Structure and Independence: Eni's board composition adheres to legal requirements, emphasizing independent directors to ensure objective oversight and decision-making.
- Shareholder Rights: The company upholds shareholder rights, including voting at general meetings and receiving timely, accurate information about the company's performance and strategy.
- Disclosure and Reporting: Eni provides comprehensive financial and non-financial disclosures, including annual reports and sustainability reports, to meet regulatory obligations and inform stakeholders.
- Compliance Mechanisms: Robust internal controls and compliance programs are in place to ensure adherence to all applicable laws and ethical standards.
Contractual Obligations and Licensing Agreements
Eni's extensive operations rely heavily on a complex web of long-term contracts. These agreements cover everything from exploring for new energy sources to producing and supplying oil, natural gas, and increasingly, renewable energy. Adhering strictly to the terms of these contractual obligations and the various licensing agreements established with host governments and its many partners is absolutely critical for Eni to maintain its business operations and ensure consistent revenue streams.
The legal framework surrounding these contracts is a significant factor. For instance, in 2024, Eni continued to navigate complex regulatory environments in countries like Egypt and Mozambique, where its major projects are governed by production sharing agreements and specific exploration licenses. Any disputes arising from these agreements, or any attempts to renegotiate terms, can lead to substantial legal challenges and considerable financial repercussions, impacting Eni's profitability and operational stability.
Key legal considerations for Eni include:
- Compliance with International and National Laws: Ensuring all exploration, production, and supply activities adhere to the legal frameworks of the countries where Eni operates.
- Contractual Dispute Resolution: Managing and resolving potential disagreements with governments or partners over contract terms, royalties, or production quotas.
- License Renewal and Compliance: Meeting all legal requirements for maintaining and renewing exploration and production licenses, which are vital for ongoing operations.
Eni faces increasing legal scrutiny regarding its environmental impact, with regulations like the EU's Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) mandating detailed disclosures. The company is also subject to legally binding emission reduction targets, including specific goals for methane, which are critical for its oil and gas operations.
Climate litigation represents a growing legal risk for Eni, with lawsuits alleging the company's contribution to climate change potentially leading to stricter emissions targets and financial penalties. For example, by mid-2024, several high-profile climate cases against energy majors were advancing, establishing precedents that could impact companies like Eni.
Environmental factors
Eni is under significant pressure to decarbonize, aiming for net-zero emissions by 2050. This commitment involves substantial investments in renewable energy sources and carbon capture technologies to slash Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions. For instance, Eni's 2023-2026 strategy outlines €7 billion in investments for decarbonization and circular economy initiatives.
The physical effects of climate change, such as increasingly severe weather, pose direct risks to Eni's operational infrastructure and supply chains. This necessitates adaptive strategies to mitigate potential disruptions and ensure business continuity in a changing climate.
Eni is actively working to lessen its footprint on biodiversity and ecosystems within its operating regions. This commitment translates into efficient natural resource management, pollution reduction, and responsible waste handling, all aimed at safeguarding natural habitats.
The company adheres to international standards and performs thorough environmental impact assessments to ensure its operations align with environmental protection goals. For instance, Eni's 2023 sustainability report highlighted a 10% reduction in flaring intensity compared to 2022, a key metric for minimizing ecosystem disruption.
Water scarcity and quality are significant environmental challenges, especially in regions where Eni has operations. Eni is committed to responsible water management, targeting water positivity at a substantial portion of its sites by 2035. This initiative focuses on minimizing freshwater withdrawals and safeguarding aquatic ecosystems.
In 2023, Eni reported a 10% reduction in freshwater withdrawal intensity compared to its 2018 baseline, demonstrating progress towards its stewardship goals. The company's strategy includes implementing advanced water treatment technologies and promoting circular economy principles within its water usage.
Waste Management and Circular Economy Principles
Eni's extensive operations, from exploration to refining, naturally produce diverse waste streams, necessitating sophisticated management systems. The company is actively integrating circular economy principles, aiming to transform waste into valuable resources and minimize its environmental footprint. This strategic shift involves redesigning processes to prioritize material reuse and recovery, a key component of their sustainability roadmap.
In 2023, Eni reported a significant focus on waste reduction and valorization, with initiatives targeting the reuse of materials in its industrial processes. For instance, their efforts in the circular economy contributed to a reduction in the volume of waste requiring disposal. The company is exploring innovative technologies to further enhance the circularity of its operations, aligning with global trends towards resource efficiency.
- Waste Reduction Targets: Eni has set ambitious targets for reducing waste generation across its value chain, aiming for a substantial decrease by 2030 compared to 2019 levels.
- Circular Economy Investments: The company is investing in projects that promote the reuse and recycling of materials, particularly in its refining and petrochemical segments, to create closed-loop systems.
- Resource Optimization: Eni's strategy includes optimizing the use of raw materials and by-products, thereby minimizing waste and enhancing overall operational efficiency.
- New Business Models: The adoption of circular economy principles is also driving the development of new business models focused on product longevity, repair, and remanufacturing.
Methane Emissions Reduction
Eni is placing a significant emphasis on cutting methane emissions, recognizing its potent impact as a greenhouse gas. The company has committed to achieving near-zero methane emissions by 2030, a goal that extends their environmental focus beyond just carbon dioxide. This ambitious target necessitates the deployment of sophisticated technologies for measuring and reducing methane leaks throughout their natural gas operations.
To achieve this, Eni is actively implementing advanced monitoring systems and mitigation strategies. For instance, by the end of 2023, Eni reported a 10% reduction in methane emissions intensity compared to 2019 levels across its upstream operations. Their strategy includes regular aerial surveys using specialized sensors and ground-based leak detection equipment, particularly in their exploration and production sites. This proactive approach aims to identify and repair fugitive emissions efficiently.
- Methane Emissions Target: Aiming for near-zero methane emissions by 2030.
- Progress: Achieved a 10% reduction in methane emissions intensity by the end of 2023 compared to 2019.
- Technology Deployment: Utilizing advanced measurement (aerial surveys, sensors) and mitigation technologies in gas operations.
Eni's environmental strategy is deeply intertwined with climate change mitigation, targeting net-zero emissions by 2050 through significant investments in renewables and carbon capture. The company is also focused on reducing its impact on biodiversity and improving water management practices, aiming for water positivity at many sites by 2035.
Waste reduction and the adoption of circular economy principles are key priorities, with ambitious targets set for 2030. Furthermore, Eni is aggressively addressing methane emissions, aiming for near-zero by 2030, having already achieved a 10% reduction in intensity by the end of 2023 compared to 2019.
| Environmental Factor | Eni's Commitment/Action | Key Data/Target |
| Decarbonization | Net-zero emissions by 2050; Investment in renewables & carbon capture | €7 billion investment in decarbonization (2023-2026 strategy) |
| Climate Change Impact | Adaptive strategies for operational resilience | Focus on mitigating risks from severe weather events |
| Biodiversity | Efficient resource management, pollution reduction | 10% reduction in flaring intensity (2023 vs 2022) |
| Water Management | Responsible water usage, wastewater treatment | Water positivity at substantial portion of sites by 2035; 10% reduction in freshwater withdrawal intensity (2023 vs 2018) |
| Waste Management & Circularity | Waste reduction, material reuse, resource optimization | Substantial decrease in waste generation by 2030 (vs 2019); Investing in reuse and recycling projects |
| Methane Emissions | Near-zero methane emissions by 2030 | 10% reduction in methane emissions intensity by end of 2023 (vs 2019) |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our Eni PESTLE Analysis is meticulously constructed using data from reputable sources including the International Energy Agency (IEA), national energy ministries, and leading financial institutions. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors impacting Eni.
