Barloworld Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Barloworld Bundle
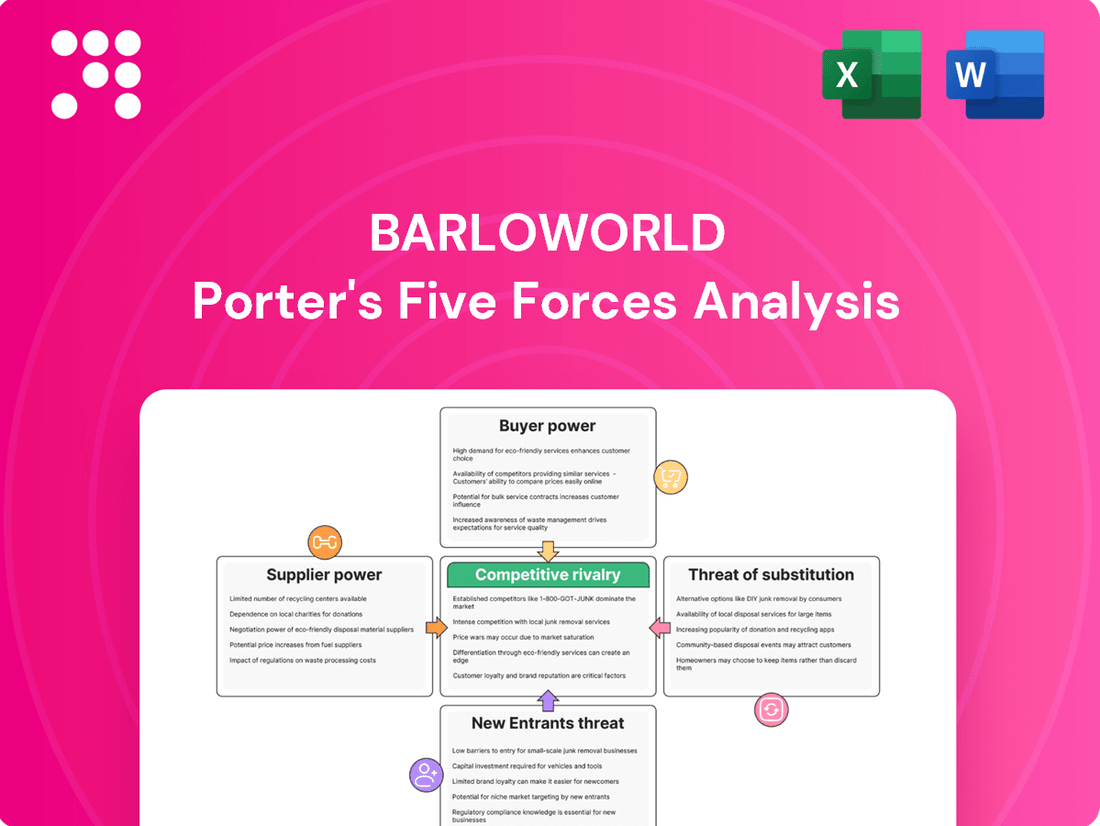
Barloworld faces significant competitive pressures, with moderate bargaining power from both buyers and suppliers, and a notable threat from substitutes. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for strategic advantage.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Barloworld’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Barloworld's dependence on a few dominant global manufacturers, such as Caterpillar for its essential earthmoving and power systems, highlights a significant concentration of key suppliers. This limited supplier base means these major players wield considerable influence.
The specialized nature of the equipment supplied by these manufacturers further amplifies their bargaining power. Barloworld's product portfolio is intrinsically linked to these brands through official dealership agreements, reinforcing the suppliers' leverage.
Barloworld faces significant supplier power due to high switching costs. Transitioning to alternative equipment manufacturers or parts suppliers would necessitate substantial investments in retooling service centers, retraining technicians, and potentially jeopardizing brand loyalty built with current partners.
The established and extensive network for parts and service support, particularly for brands like Caterpillar, makes a change a complex and financially burdensome undertaking for Barloworld, thereby reinforcing the bargaining strength of its existing suppliers.
The equipment and parts Barloworld sources, particularly from giants like Caterpillar, are often the benchmark for quality, dependability, and technological advancement in demanding sectors such as mining and construction. This means Barloworld has few easily accessible alternatives that can match the perceived value and essential function these components provide to its customers.
The highly specialized nature of heavy machinery, including diesel engines and excavators, further solidifies the uniqueness of these supplier offerings. This specialization means that switching suppliers for critical components is not a simple or cost-effective process for Barloworld.
Potential for Supplier Forward Integration
The potential for supplier forward integration, where a manufacturer like Caterpillar might enter Barloworld's distribution and service markets, presents a theoretical threat. However, Barloworld's substantial investment in its extensive distribution and support infrastructure makes this a challenging proposition for major equipment manufacturers to fully replicate across all its operating regions.
While direct, full-scale forward integration by a primary supplier like Caterpillar into Barloworld's established territories is unlikely given the significant capital and logistical hurdles, suppliers do exert power. This leverage is primarily maintained through stringent dealership agreements and their control over the supply of essential original equipment manufacturer (OEM) parts and new equipment.
For instance, Caterpillar, a key supplier to Barloworld, reported revenues of approximately $67.1 billion in 2023. This financial strength underscores their capacity to influence terms, though the operational complexity of replacing Barloworld's existing network limits their incentive for direct market takeover.
Barloworld's strategic advantage lies in its deeply entrenched customer relationships and localized service capabilities, which are difficult and costly for an OEM to build from scratch. This makes Barloworld's existing distribution and after-sales service network a significant barrier to entry for potential supplier forward integration.
Barloworld's Limited Backward Integration Capability
Barloworld, operating mainly as an industrial equipment distributor, possesses minimal capacity and no current strategic drive to integrate backward into manufacturing the heavy machinery it sells. This inability to produce its own equipment directly increases its dependence on its suppliers, thereby strengthening their bargaining power.
The significant complexity and substantial capital investment required to manufacture heavy machinery render backward integration an impractical and unfeasible strategy for Barloworld. For instance, in 2024, the capital expenditure for establishing a new heavy equipment manufacturing plant can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars, a barrier Barloworld has not sought to overcome.
- Limited Backward Integration: Barloworld's business model as a distributor restricts its ability to manufacture heavy equipment.
- Supplier Dependence: This lack of in-house manufacturing capability forces reliance on external suppliers for its product range.
- Supplier Bargaining Power: Consequently, suppliers hold considerable leverage due to Barloworld's need for their products.
- High Entry Barriers for Manufacturing: The immense capital and technical expertise needed for heavy equipment production make backward integration an unviable option.
Barloworld's bargaining power with suppliers is constrained by its reliance on a few dominant global manufacturers, such as Caterpillar, for its core product lines. The specialized nature of heavy machinery and the significant capital investment required for manufacturing mean Barloworld cannot easily produce its own equipment, thereby increasing supplier leverage.
High switching costs further empower suppliers. Barloworld faces substantial expenses and operational disruptions when considering alternative equipment or parts, including retooling service centers and retraining technicians. This makes Barloworld's dependence on current suppliers, like Caterpillar, a significant factor in their strong bargaining position.
For example, Caterpillar, a key supplier, reported revenues of approximately $67.1 billion in 2023, showcasing its financial strength and ability to influence terms. The immense capital required for heavy equipment manufacturing, potentially hundreds of millions of dollars in 2024, makes backward integration by Barloworld unfeasible, reinforcing supplier power.
| Supplier Characteristic | Impact on Barloworld | Barloworld's Position |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration (e.g., Caterpillar) | High dependence on a few key players | Limited supplier choice |
| Uniqueness of Product/Service | Specialized heavy machinery, few direct substitutes | Low ability to switch |
| Switching Costs | High costs for retooling, training, and logistics | Reinforces supplier leverage |
| Lack of Backward Integration | Inability to manufacture own equipment | Increased reliance on external suppliers |
What is included in the product
Analyzes how supplier power, buyer bargaining, new entrants, substitutes, and existing rivalry shape Barloworld's operating environment and profitability.
Quickly identify and address competitive threats by visualizing Barloworld's market position with an intuitive five forces dashboard.
Customers Bargaining Power
Barloworld's customer base spans diverse sectors like mining, construction, and industrial equipment, offering broad market reach. However, the bargaining power of customers can be amplified in segments where a few major players dominate, such as large mining operations. For instance, in 2024, major mining contracts often involve substantial equipment orders, giving these large customers significant leverage in price negotiations with suppliers like Barloworld.
Customers who have invested significantly in a fleet of specialized equipment, such as those from Caterpillar, and have existing maintenance agreements with Barloworld often face moderate to high costs when considering a switch to a competitor. These expenses can include the outright purchase of new machinery, the cost of retraining their operational staff on different systems, and the effort required to adapt their established maintenance procedures.
Customers in cyclical industries, such as mining and construction, often exhibit significant price sensitivity. This is particularly true when economic conditions weaken or commodity prices fall. For instance, Barloworld's 2024 financial performance indicated a revenue decrease, with challenges in its Equipment Southern Africa segment highlighting this customer behavior and tough market conditions.
This heightened price sensitivity can compel Barloworld to engage in price competition, potentially eroding its profit margins. The company's reported revenue decline in 2024, influenced by softer trading in key sectors, underscores the direct impact of customer price demands on its financial results.
Availability of Alternative Equipment and Service Providers
The bargaining power of Barloworld's customers is significantly influenced by the availability of alternative equipment and service providers. Customers can readily source similar machinery and support from a wide array of competitors. This includes other authorized dealers representing different equipment brands, independent service and parts suppliers, and even rental companies offering short-term solutions.
This abundance of choices empowers customers, as they can easily switch suppliers if Barloworld's pricing or service levels are not competitive. For instance, in the construction equipment sector, a customer needing a specific type of excavator might find comparable models from Caterpillar, Komatsu, or Volvo, each with its own network of dealers and service centers. This competitive landscape means customers can often negotiate better terms or find more favorable pricing elsewhere.
- Increased Customer Leverage: A broad market with multiple equipment manufacturers and service providers grants customers greater negotiation power.
- Price Sensitivity: The presence of alternatives often leads to increased price sensitivity among buyers, forcing suppliers like Barloworld to remain competitive.
- Switching Costs: While some switching costs exist, the availability of compatible equipment and services from various providers can mitigate these for customers.
- Market Dynamics: In 2024, the global construction equipment market, a key segment for Barloworld, continued to see robust activity, with numerous players vying for market share, further amplifying customer choice.
Customer's Potential for Backward Integration (Limited)
While some very large customers, such as major mining operations, might undertake a degree of in-house maintenance or direct parts sourcing, this is generally limited. The significant capital investment and specialized expertise required for heavy equipment distribution, rental, or manufacturing make full backward integration by most of Barloworld's clientele impractical. Their primary focus remains on their core operations, not on becoming equipment providers themselves.
This limitation on backward integration significantly curtails the bargaining power of Barloworld's customers. For instance, in 2023, Barloworld’s Equipment Southern Africa division reported revenue of R35.7 billion, serving diverse sectors like mining and construction. The specialized nature of these industries means customers are unlikely to replicate Barloworld's extensive supply chain and service networks.
- Limited Scope of In-House Capabilities: Most customers lack the infrastructure and technical know-how to handle complex equipment distribution and manufacturing.
- High Barrier to Entry: Establishing a competing equipment supply or rental business requires substantial capital and specialized knowledge, deterring most customers.
- Focus on Core Competencies: Customers prioritize their own industry operations, such as mining or infrastructure development, over venturing into equipment provision.
- Barloworld's Integrated Offering: Barloworld provides a comprehensive solution including sales, rentals, parts, and service, which is difficult for individual customers to replicate cost-effectively.
Barloworld's customers, particularly large entities in mining and construction, possess considerable bargaining power due to the significant volume of equipment and services they procure. This leverage is amplified when these customers can easily switch between suppliers or when market conditions favor buyers, as seen in 2024 with increased price sensitivity in certain sectors. For example, Barloworld's Equipment Southern Africa revenue saw a decrease in 2024, reflecting these pressures.
The availability of numerous alternative equipment manufacturers and service providers further strengthens customer negotiating positions. Customers can often find comparable machinery and support from competitors, allowing them to demand better pricing or service terms. This competitive landscape means Barloworld must remain highly competitive to retain its customer base.
While some customers might perform limited in-house maintenance, the complexity and capital investment required for full equipment distribution or manufacturing prevent most from backward integration. This limitation significantly caps their ability to exert extreme bargaining power, as they rely on Barloworld's specialized infrastructure and extensive networks for their operational needs.
| Customer Type | Bargaining Power Drivers | Impact on Barloworld | 2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Large Mining Operations | High order volumes, potential for switching suppliers | Price pressure, contract negotiation leverage | Significant equipment orders in 2024 mining sector drove price discussions. |
| Construction Companies | Availability of alternative equipment brands, cyclical demand | Price sensitivity, focus on cost-effectiveness | Revenue challenges in Equipment Southern Africa in 2024 linked to market conditions. |
| Industrial Equipment Users | Moderate switching costs, diverse service providers | Negotiation on service packages and parts pricing | Continued competition from independent service providers in 2024. |
Full Version Awaits
Barloworld Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Barloworld Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering an in-depth examination of the competitive landscape. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing information. You can trust that this professionally formatted analysis is ready for your immediate use and strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Barloworld operates in highly competitive markets, facing pressure from a diverse range of players. This includes large, diversified conglomerates like Bidvest, which often have significant financial resources and broad market reach.
Specialized equipment dealers, such as Toromont Cat and Bell Equipment Co., also present a strong competitive front by focusing on specific product lines and customer segments. These companies often possess deep technical expertise and established customer relationships.
Furthermore, the presence of equipment rental service providers, like Boels, adds another layer of competition by offering flexible, short-term solutions that can appeal to customers seeking to avoid large capital outlays. This broad competitive landscape necessitates continuous innovation and strategic positioning for Barloworld to maintain its market share.
The industrial equipment and services sector, where Barloworld operates, is inherently tied to economic cycles, especially in mining and construction. This cyclicality means that demand can fluctuate significantly, impacting competitive dynamics.
Barloworld's performance in its 2024 financial year illustrates this. The company reported a revenue decline in certain key segments, a direct reflection of a challenging and volatile trading environment. Such periods often see intensified competition as businesses fight for a larger piece of a shrinking market pie.
Barloworld stands out by offering more than just equipment; they provide integrated solutions. This includes comprehensive product support and genuine parts for brands like Caterpillar, ensuring quality and reliability for their customers. This focus on minimizing downtime through superior service is a key differentiator.
Their strategy of emphasizing value-added services and a robust aftermarket business significantly reduces the pressure from direct price competition. For instance, Barloworld's commitment to genuine parts and expert servicing directly addresses customer needs for operational continuity, which is often more critical than initial purchase price.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
Barloworld's heavy machinery distribution and logistics operations are characterized by significant fixed costs. These include substantial investments in inventory, extensive service infrastructure, and the need for highly skilled labor. For instance, maintaining a broad network of dealerships and service centers for brands like Caterpillar requires considerable upfront and ongoing capital expenditure.
The specialized nature of the assets involved, such as large-scale equipment and dedicated logistics fleets, also contributes to high exit barriers. Companies find it difficult and costly to divest these assets, which can lead to prolonged periods of intense competition. This dynamic often compels players to remain in the market and compete aggressively, even when facing economic headwinds, in an effort to cover their fixed cost base.
- High Fixed Costs: Barloworld's business model necessitates significant investment in physical assets like machinery inventory and service facilities.
- Specialized Assets: The equipment and infrastructure are highly specialized, making them difficult to repurpose or sell quickly.
- Exit Barriers: The combination of high fixed costs and specialized assets creates substantial barriers to exiting the market.
- Intense Rivalry: These factors encourage companies to stay and compete, even during economic downturns, to cover operating expenses.
Geographical and Segment Diversification
Barloworld's strategic approach involves spreading its operations across different regions and business segments. This geographical diversification includes a presence in Southern Africa, Russia through Vostochnaya Technica, and Mongolia. The company also diversifies across equipment, power systems, and logistics solutions.
This multi-faceted strategy is designed to lessen the pressure from intense competition within any single market or industry. For instance, strong performance in one area, such as Mongolia's robust showing in 2024, can effectively counterbalance weaker results in other regions or segments.
- Geographic Spread: Barloworld operates in Southern Africa, Russia (Vostochnaya Technica), and Mongolia.
- Segment Diversity: Key segments include equipment, power systems, and logistics solutions.
- Risk Mitigation: Diversification helps buffer against intense rivalry in specific markets or sectors.
- Performance Offset: Strong regional performance, like Mongolia's in 2024, can offset challenges elsewhere.
Barloworld faces intense competition from diversified conglomerates like Bidvest and specialized dealers such as Toromont Cat, who leverage deep expertise and customer relationships. The presence of rental service providers like Boels further intensifies rivalry by offering flexible alternatives.
High fixed costs associated with specialized assets and extensive infrastructure create significant exit barriers, compelling companies to compete aggressively even during economic downturns to cover their cost base.
Barloworld's 2024 financial year saw revenue declines in some segments, highlighting the impact of cyclicality and intensified competition during challenging periods.
The company differentiates itself through integrated solutions, including comprehensive product support and genuine parts, which reduce direct price competition by emphasizing operational continuity and reliability.
| Competitor Type | Examples | Competitive Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Diversified Conglomerates | Bidvest | Financial resources, broad market reach |
| Specialized Dealers | Toromont Cat, Bell Equipment Co. | Technical expertise, established customer relationships |
| Rental Service Providers | Boels | Flexible, short-term solutions |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for new heavy equipment is significant, with equipment rental services presenting a primary alternative. Companies often choose to rent rather than buy for short-term projects or to manage capital expenditure, directly impacting the demand for new equipment sales. Barloworld itself is a provider of these rental solutions, highlighting the internal availability of this substitute.
The market for used and remanufactured equipment and parts represents a significant threat of substitutes for new sales. Barloworld itself acknowledges this by engaging in the sale of used equipment and offering remanufactured components. This strategy directly addresses customers seeking more budget-friendly options or requiring rapid replacements, thereby diverting demand from new product purchases.
Customers for Barloworld's logistics solutions face a significant threat from substitutes, primarily the option to manage their supply chains in-house. This internal capability allows companies to maintain direct control over operations, potentially reducing reliance on external providers and associated costs. For example, many large manufacturing firms have developed sophisticated internal logistics departments to optimize their specific needs.
Furthermore, the market is flooded with alternative third-party logistics (3PL) providers, each offering specialized or generalist services that can directly compete with Barloworld. This broad competitive landscape, featuring numerous firms with similar service offerings, intensifies the threat of substitution. The global 3PL market was valued at approximately $1.1 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating ample choice for customers seeking logistics support.
Technological Advancements and Efficiency Gains
Technological advancements are a significant threat of substitutes for Barloworld. For instance, the increasing efficiency of electric vehicles and autonomous mining equipment could reduce the demand for traditional internal combustion engine machinery, a core part of Barloworld's equipment rental and sales business. In 2024, the global market for electric construction equipment was projected to grow substantially, indicating a clear shift that substitutes can capitalize on.
Furthermore, digital solutions for fleet management, predictive maintenance, and remote operation offer alternatives that can optimize asset utilization and reduce the need for physical equipment ownership or extensive service contracts. Companies investing heavily in these digital innovations can present compelling value propositions that rival Barloworld's traditional offerings. For example, advancements in AI-powered diagnostics can preemptively address equipment issues, thereby lowering the overall cost of ownership and maintenance for customers.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations like electric and autonomous machinery directly challenge traditional equipment offerings.
- Digital Solutions: Advanced fleet management and predictive maintenance software can reduce reliance on physical assets and services.
- Market Impact: The growing electric construction equipment market, with significant projected growth in 2024, highlights the increasing viability of substitutes.
- Competitive Landscape: Rapid innovation by competitors in digital and sustainable technologies creates new and potentially more attractive alternatives for customers.
Customer's Operational Adjustments
Customers can adapt by optimizing their existing equipment, extending its lifespan through better maintenance, or shifting to less equipment-intensive processes. For instance, a construction company might invest in advanced fleet management software to maximize the utilization of its current machinery, thereby reducing the need for new rentals or purchases from suppliers like Barloworld.
These customer-driven operational adjustments directly dampen demand for new equipment and services. In 2024, the global construction equipment market saw increased emphasis on rental and used equipment sales, reflecting a trend towards cost optimization and extended asset life, which can impact original equipment manufacturers and their service divisions.
This shift poses a significant threat as it lessens the overall volume of business available. Companies might also explore alternative technologies or methods that require fewer specialized machines, further eroding the market share for traditional equipment providers.
Consider these customer operational adjustments:
- Fleet Optimization: Implementing telematics and data analytics to ensure maximum uptime and efficiency of existing equipment.
- Extended Equipment Lifecycles: Investing in comprehensive maintenance and repair programs to prolong the operational life of machinery.
- Adoption of Alternative Methods: Exploring construction techniques that require less heavy machinery, such as prefabrication or modular construction.
- Increased Rental and Used Equipment: Favoring rental agreements or purchasing refurbished equipment over new acquisitions to manage capital expenditure.
The threat of substitutes for Barloworld's offerings is substantial, encompassing equipment rental, used and remanufactured products, in-house logistics management, and alternative technologies. These substitutes directly impact demand for new equipment and services by providing cost-effective or more specialized alternatives.
Technological advancements, such as electric and autonomous machinery, along with digital fleet management solutions, represent a growing threat. The electric construction equipment market, projected for significant growth in 2024, exemplifies this trend. Furthermore, customers are increasingly optimizing existing fleets and extending equipment lifecycles, reducing the need for new purchases.
| Substitute Category | Key Examples | Impact on Barloworld | Supporting Data (2023/2024 Estimates) |
| Equipment Rental | Short-term project needs | Reduces new equipment sales volume | Global equipment rental market valued at over $100 billion |
| Used/Remanufactured Equipment | Budget-conscious buyers, rapid replacement | Diverts demand from new products | Significant market share in certain equipment segments |
| In-house Logistics | Direct control, cost optimization | Reduces demand for outsourced logistics | Many large manufacturers manage their own supply chains |
| Alternative Technologies | Electric vehicles, autonomous machinery, digital solutions | Challenges traditional internal combustion engine equipment | Electric construction equipment market projected for substantial growth in 2024 |
| Customer Operational Adjustments | Fleet optimization, extended lifecycles | Lowers overall demand for new equipment and services | Increased focus on cost optimization in the construction sector |
Entrants Threaten
The industrial equipment sector, where Barloworld operates, presents a formidable barrier to entry due to incredibly high capital requirements. New players need vast sums to acquire and maintain extensive fleets of heavy machinery, establish widespread service and support networks, and develop sophisticated IT systems for operations and logistics. For instance, acquiring even a modest fleet of mining or construction equipment can easily run into tens or hundreds of millions of dollars.
Established players like Barloworld benefit from significant economies of scale in procurement, inventory management, and operational efficiency across their diverse divisions. For instance, Barloworld's extensive dealership network for heavy machinery allows for bulk purchasing discounts, reducing per-unit costs.
New entrants would struggle to achieve similar cost advantages without considerable initial investment and time, making it difficult to compete on price or service delivery. The experience curve also plays a crucial role; Barloworld's long operational history translates into optimized processes and reduced waste, further solidifying its cost leadership.
New companies face significant hurdles in accessing established distribution channels and dealership networks, particularly for high-value products like heavy equipment. Securing exclusive rights for major brands, such as Caterpillar, is exceptionally difficult due to existing long-term relationships and the substantial investment required to build comparable infrastructure.
Barloworld's extensive network of dealerships and service centers, built over decades, represents a significant competitive advantage. For instance, in 2023, Barloworld Equipment Southern Africa reported revenue of R36.5 billion, underscoring the scale and reach of its distribution capabilities, which new entrants would struggle to replicate quickly.
Strong Brand Loyalty and Reputation
Barloworld benefits significantly from its established brand loyalty, particularly its long-standing 96-year track record in the equipment sector. This deep-rooted trust, especially its association with Caterpillar, makes it difficult for new entrants to replicate the same level of customer commitment and reliability perception.
The substantial investment and time required to build comparable brand loyalty and a reputation for quality service present a formidable barrier. New competitors would need to overcome decades of established customer relationships and proven performance, which is a considerable challenge.
- Established Brand Equity: Barloworld's decades-long presence has cultivated strong brand recognition and trust, making it a preferred choice over newer, unproven alternatives.
- Caterpillar Association: The partnership with Caterpillar, a globally recognized leader, further enhances Barloworld's credibility and customer confidence, a difficult reputation to build from scratch.
- High Switching Costs: For many customers, switching from Barloworld involves not just changing suppliers but also potentially retraining staff, altering maintenance protocols, and risking disruptions to operations, all of which deter new entrants.
Regulatory Hurdles and Specialized Knowledge
The industrial equipment and logistics industries, where Barloworld operates, are heavily burdened by complex regulations. These include stringent safety standards and environmental compliance mandates. For instance, in 2024, the global industrial automation market faced increasing regulatory scrutiny, with new data privacy laws and emissions standards impacting operations. New companies must invest heavily in understanding and adhering to these intricate legal frameworks.
Acquiring the necessary specialized technical and industry knowledge is another significant barrier to entry. This expertise is crucial for efficient operations, equipment maintenance, and supply chain management. In 2024, the demand for skilled technicians in areas like advanced machinery repair and digital logistics solutions remained high, indicating a persistent need for specialized training and experience.
- Regulatory Complexity: Navigating safety, environmental, and data privacy laws in industrial equipment and logistics requires substantial legal and compliance resources.
- Specialized Knowledge: A deep understanding of machinery, maintenance, and complex supply chain logistics is essential, demanding significant investment in training and expertise.
- Capital Investment: Meeting regulatory standards and acquiring specialized knowledge often necessitates significant upfront capital, deterring smaller players.
The threat of new entrants for Barloworld is considerably low, primarily due to the immense capital required to enter the industrial equipment and logistics sectors. These industries demand substantial investments in machinery, infrastructure, and skilled personnel, creating high barriers to entry. For example, acquiring a fleet of heavy-duty mining trucks alone can cost tens of millions of dollars, a prohibitive sum for most new businesses.
Furthermore, Barloworld benefits from strong economies of scale and established brand loyalty, particularly through its long-standing partnership with Caterpillar. Replicating Barloworld's extensive dealership network and its 96-year reputation for reliability and service would require decades and massive financial commitment, making it exceedingly difficult for newcomers to compete effectively.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Acquiring heavy machinery fleets, service infrastructure, and IT systems demands hundreds of millions of dollars. | Extremely high, deterring most potential entrants. |
| Economies of Scale | Barloworld's bulk procurement and operational efficiencies lower per-unit costs. | New entrants struggle to match cost advantages without significant scale. |
| Brand Loyalty & Reputation | 96 years of association with Caterpillar builds deep customer trust. | Difficult for new players to gain customer confidence and loyalty. |
| Distribution Channels | Exclusive dealership rights and extensive service networks are hard to secure. | New entrants face challenges accessing markets and providing support. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to stringent safety and environmental standards requires significant investment. | Adds to the upfront costs and operational complexity for new companies. |
| Specialized Knowledge | Expertise in machinery, maintenance, and logistics is crucial. | Requires substantial investment in training and experienced personnel. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Barloworld is built upon a foundation of diverse and credible data sources, including Barloworld's official annual reports and investor presentations, alongside industry-specific market research reports from firms like Frost & Sullivan and IHS Markit.
