Koninklijke Ahold Delhaize Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Koninklijke Ahold Delhaize Bundle
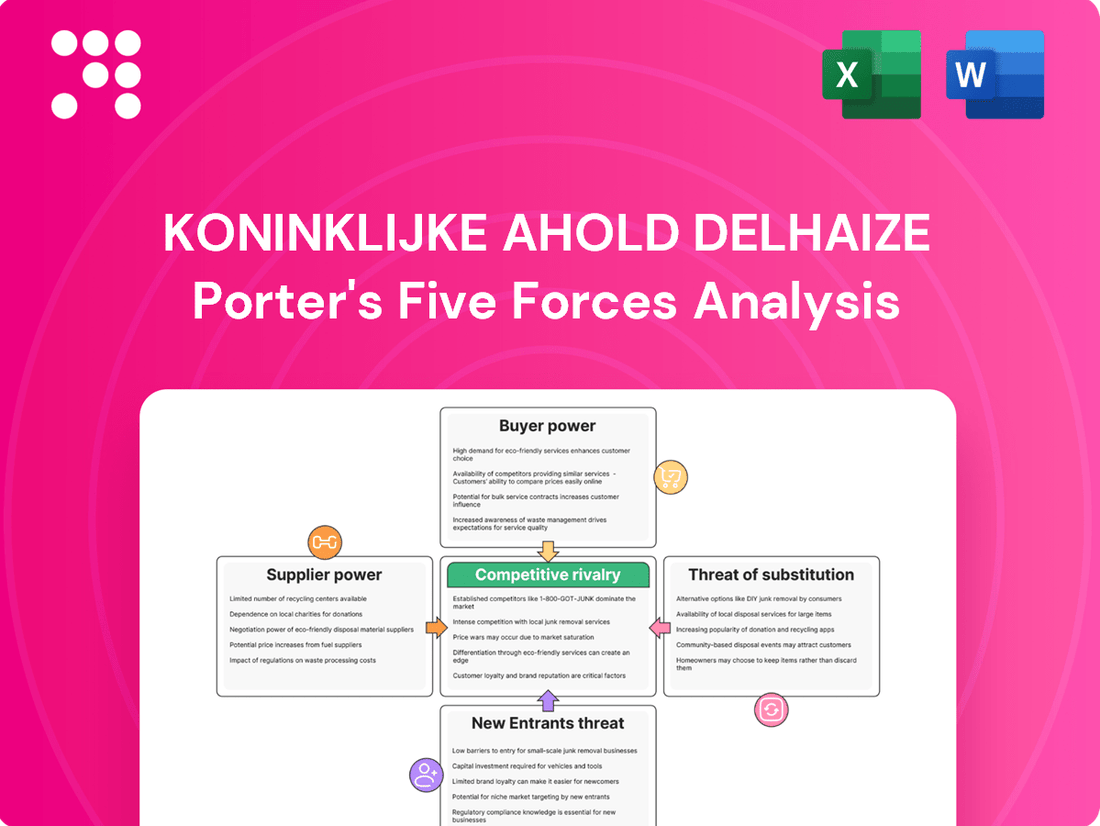
Koninklijke Ahold Delhaize navigates a dynamic retail landscape shaped by intense buyer power and the constant threat of new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder looking to grasp their competitive position.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Koninklijke Ahold Delhaize’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Supplier concentration within the grocery retail sector, particularly for a large player like Koninklijke Ahold Delhaize, generally leans towards fragmentation. This means that for many product categories, Ahold Delhaize deals with a vast number of suppliers, from local farmers providing fresh produce to large manufacturers of packaged goods. For instance, in 2024, the European food retail market saw continued consolidation among retailers, but the supplier side often remained diverse for staple items.
This broad supplier base significantly dilutes the bargaining power of any individual supplier. When a retailer can easily switch to an alternative supplier for a specific product, the supplier’s ability to dictate terms, such as price increases or unfavorable payment schedules, is considerably weakened. This dynamic is a key factor in managing procurement costs for Ahold Delhaize.
Koninklijke Ahold Delhaize's substantial market share in the US and Europe makes it an indispensable partner for numerous food producers. For many suppliers, securing shelf space with Ahold Delhaize is a significant revenue driver, with some estimating that losing such a large customer could impact their sales by over 10% in the short term.
The scale of Ahold Delhaize's operations translates into considerable purchasing power, allowing the company to negotiate favorable terms. Suppliers who rely heavily on Ahold Delhaize for a significant portion of their sales, potentially exceeding 20% of their total revenue, find themselves with less leverage to dictate pricing or supply conditions.
For many product categories, especially common goods and ingredients for Ahold Delhaize's own brands, the company can easily switch between various suppliers. This flexibility in sourcing and the ability to conduct competitive bidding significantly reduces the bargaining power of any single supplier.
In 2024, Ahold Delhaize's extensive private label program, which accounted for a substantial portion of its sales, further amplified its ability to leverage multiple suppliers for key ingredients. This strategy allows them to negotiate favorable terms, as suppliers are aware that alternative sourcing options exist, thereby limiting price increases.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Ahold Delhaize's retail operations is generally low. While some major food and beverage producers have explored direct-to-consumer models, replicating Ahold Delhaize's vast retail footprint, including its extensive store network and sophisticated logistics, demands significant capital investment and operational expertise that most suppliers lack.
For instance, operating a large supermarket chain like Ahold Delhaize requires substantial investment in real estate, supply chain management, and marketing. In 2024, Ahold Delhaize operated over 20,000 stores across its various brands, a scale that presents a formidable barrier to entry for most suppliers.
- Limited Supplier Capabilities: Most suppliers focus on production and lack the retail infrastructure, brand recognition, and customer loyalty necessary to compete directly with established retailers.
- High Capital Requirements: Establishing and maintaining a nationwide retail presence, as Ahold Delhaize does, involves billions in capital expenditure for store development, technology, and distribution centers.
- Focus on Core Competencies: Suppliers generally prioritize their manufacturing and brand-building efforts rather than diverting resources to the complex and capital-intensive retail sector.
Ahold Delhaize's Private Label Strategy
Ahold Delhaize's robust focus on and expansion of its private label brands significantly enhances its leverage with national brand suppliers. For instance, in 2023, private label penetration across its European operations reached approximately 30%, demonstrating a substantial shift towards its own offerings.
Should national brand product pricing become unfavorable, Ahold Delhaize can effectively steer consumers towards its private label alternatives. These house brands are typically priced more competitively and offer higher profit margins, directly strengthening the company's negotiating stance.
- Private Label Growth: Ahold Delhaize aims to increase its private label sales share, which stood at 30% in Europe as of 2023.
- Margin Enhancement: Private label products generally offer better margins compared to national brands, providing Ahold Delhaize with greater flexibility.
- Consumer Choice: The availability of attractive private label options allows Ahold Delhaize to mitigate the impact of rising national brand costs.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Koninklijke Ahold Delhaize is generally low due to the company's immense scale and the fragmented nature of many supplier markets. With a vast network of over 20,000 stores across Europe and the US as of 2024, Ahold Delhaize represents a significant customer for a wide array of producers, making it difficult for individual suppliers to exert substantial leverage.
This low supplier bargaining power is further reinforced by Ahold Delhaize's strategic emphasis on its private label brands, which in 2023 reached approximately 30% penetration in its European operations. This allows the retailer to readily substitute national brands with its own offerings, which typically provide better margins and pricing flexibility, thereby limiting suppliers' ability to dictate terms.
Furthermore, the threat of suppliers integrating forward into retail is minimal, as replicating Ahold Delhaize's extensive infrastructure and brand recognition would require prohibitively high capital investment and operational expertise. Consequently, suppliers often depend on Ahold Delhaize for a significant portion of their sales, diminishing their negotiating power.
| Factor | Impact on Ahold Delhaize | Supporting Data (2023/2024 Estimates) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Low | Fragmented supplier base for many product categories. |
| Volume of Purchases | High | Ahold Delhaize's substantial market share in key regions. |
| Switching Costs for Retailer | Low | Ability to source from multiple suppliers, especially for private labels. |
| Supplier Dependence on Retailer | High for some | Losing Ahold Delhaize could impact some suppliers' sales by over 10%. |
| Private Label Penetration | Enhances leverage | Approx. 30% in Europe (2023), with plans for growth. |
What is included in the product
This analysis delves into the competitive forces shaping Koninklijke Ahold Delhaize's market, examining the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes on its strategic positioning.
Ahold Delhaize's Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a clear, actionable roadmap to navigate competitive pressures, transforming complex market dynamics into manageable strategic insights.
Customers Bargaining Power
Consumers in 2024 and 2025 demonstrate significant price sensitivity, a trend amplified by persistent inflation and economic unpredictability. This makes them more inclined to hunt for deals and cheaper alternatives, directly impacting retailers like Ahold Delhaize.
This elevated price consciousness grants customers greater bargaining power. They are more willing to switch to competitors offering better prices, forcing Ahold Delhaize to carefully manage its pricing strategies to retain market share.
Customers face very low switching costs when moving between grocery retailers. This means a shopper can easily shift their spending from one supermarket to another, or even to a discount store or online grocery service, without incurring significant expenses or hassle. In 2024, the proliferation of online grocery options and the continued strength of discount retailers further lowered these barriers, giving consumers more power to seek out the best prices and convenience.
Consumers today have an incredible amount of information at their fingertips. With countless websites, mobile apps, and review platforms, shoppers can easily compare prices, read about product quality, and find out about ongoing sales. This makes it much harder for companies to charge premium prices without justification.
For instance, in 2024, the average consumer spends over 2 hours per day online researching purchases, a significant increase from previous years. This readily available data means customers are more aware of alternatives and can readily switch to competitors offering better value, directly impacting Ahold Delhaize's pricing power.
Growth and Acceptance of Private Labels
The growing quality and wider selection of private label goods from Ahold Delhaize and its competitors give shoppers appealing, often more affordable, options compared to established brands. This trend significantly boosts the bargaining power of customers.
Consumers are increasingly comfortable buying private label products, even as their own purchasing power increases, which further strengthens their leverage. This shift means customers have more choices and can more easily switch if prices or quality don't meet expectations.
- Increased Private Label Penetration: In 2023, private label sales represented a significant portion of grocery sales, with some categories seeing over 30% market share, demonstrating strong consumer acceptance.
- Price Sensitivity: Consumers often perceive private labels as offering better value, leading them to favor these options, especially during periods of economic uncertainty.
- Retailer Investment in Quality: Retailers like Ahold Delhaize are investing heavily in improving the quality and innovation of their private label offerings, making them more competitive with national brands.
Diversified Shopping Habits
Consumers are increasingly spreading their grocery purchases across multiple retailers, seeking the best deals and specific products at each. This trend is amplified by the widespread use of loyalty programs and the constant pursuit of promotions, enabling shoppers to efficiently compare prices and offers.
This diversified shopping behavior significantly bolsters customer bargaining power, as shoppers can easily switch to competitors if they perceive better value elsewhere. For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of grocery shoppers reported visiting at least three different stores weekly to fulfill their needs, driven by price comparison and promotional availability.
- Diversified Shopping: Consumers actively visit multiple retailers for different product categories or to capitalize on specific sales.
- Loyalty Programs & Promotions: Shoppers leverage loyalty schemes and ongoing promotions across various channels to secure better pricing.
- Enhanced Bargaining Power: This behavior allows customers to easily switch to competitors, putting pressure on retailers to offer competitive pricing and value.
- Consumer Behavior Data (2024): Reports indicated that over 60% of consumers surveyed in early 2024 regularly shopped at more than two grocery outlets per week.
The bargaining power of customers for Ahold Delhaize remains substantial in 2024 and 2025, driven by heightened price sensitivity and easy access to information. Consumers are actively comparing prices across numerous retailers and private label options, which are increasingly competitive in both quality and value. This environment forces Ahold Delhaize to maintain aggressive pricing and promotional strategies to retain its customer base.
| Factor | Impact on Ahold Delhaize | Supporting Data (2024/2025 Trends) |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | High pressure on margins; need for competitive pricing. | Consumers report spending over 2 hours daily researching purchases. Inflation continues to drive demand for value. |
| Low Switching Costs | Easy customer churn; requires strong loyalty initiatives. | Proliferation of online grocery and discount retailers lowers barriers to entry for competitors. |
| Information Availability | Reduces pricing power; necessitates transparency. | Over 60% of consumers shop at multiple grocery outlets weekly to compare prices and promotions. |
| Private Label Growth | Offers value but competes with national brands; opportunity for margin. | Private label sales exceeded 30% in some grocery categories in 2023, indicating strong consumer acceptance and trust. |
Same Document Delivered
Koninklijke Ahold Delhaize Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Koninklijke Ahold Delhaize Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering an in-depth examination of competitive forces within the retail sector. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring full transparency and no hidden content. You're looking at the actual, professionally formatted analysis, ready for your immediate use and strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The grocery retail sector is incredibly competitive, with Ahold Delhaize facing rivals from global giants to local players. This includes established chains, discounters like Aldi and Lidl, and even online grocers, all vying for market share. For instance, in 2024, the European grocery market continued to see intense price wars, particularly in discount segments.
Retailers like Ahold Delhaize often face intense price competition, especially with inflation impacting consumer spending. In 2024, many grocery chains are employing aggressive pricing, with promotions and loyalty programs becoming crucial for customer retention. This pressure directly affects profit margins, necessitating stringent cost control measures for companies like Ahold Delhaize.
The grocery sector is deep in an omnichannel and digital innovation race, significantly intensifying competitive rivalry. Consumers increasingly expect seamless transitions between online and in-store shopping, pushing retailers like Ahold Delhaize to invest heavily in digital capabilities. This digital arms race involves sophisticated e-commerce platforms, rapid delivery networks, and AI for personalized customer experiences, all crucial for capturing market share.
By 2024, online grocery sales have become a substantial portion of the overall market, with companies like Ahold Delhaize reporting significant growth in their digital channels. For instance, Ahold Delhaize's online sales saw robust increases, demonstrating the critical nature of these investments. This ongoing digital transformation means that continuous innovation in technology, logistics, and customer engagement is no longer optional but a necessity for survival and growth.
Differentiation Through Private Labels
Competitive rivalry in the grocery sector, including for Koninklijke Ahold Delhaize, is significantly shaped by the strategic development and promotion of private label brands. Retailers are actively cultivating these own-brand products, presenting them as superior, distinct options compared to established national brands. This approach aims to foster stronger customer allegiance and secure better profit margins.
By offering high-quality private labels, grocers like Ahold Delhaize can differentiate themselves beyond simple price competition. This strategy allows them to build unique value propositions that resonate with consumers seeking both quality and affordability. For example, in 2024, many leading retailers reported substantial growth in their private label sales, often outpacing the growth of national brands.
- Private Label Growth: Many retailers saw private label sales increase by over 5% in the first half of 2024, capturing a larger share of the overall market.
- Margin Enhancement: Private label products typically offer higher gross margins, often 10-20% more than comparable national brands, directly impacting profitability.
- Customer Loyalty: Successful private label programs are credited with increasing customer basket size and visit frequency, as seen in loyalty program data from major chains.
- Brand Perception: Retailers are investing heavily in marketing to position their private labels as premium, innovative, and trustworthy alternatives, blurring the lines with national brand quality.
Market Share Defense and Expansion
Koninklijke Ahold Delhaize is intensely focused on protecting its established market share, particularly with its flagship brand, Albert Heijn, which holds a commanding position in the Netherlands. Simultaneously, the company is actively pursuing growth by acquiring market share in both the United States and Europe. This dual strategy means Ahold Delhaize is in direct competition with formidable global retailers and robust local players across its operating territories.
The competitive landscape is fierce, with Ahold Delhaize consistently vying for customer loyalty and sales volume. For instance, in the U.S., its Food Lion banner competes head-to-head with giants like Walmart and Kroger, while in Europe, Albert Heijn faces strong national chains. This dynamic rivalry necessitates continuous innovation in pricing, product assortment, and customer experience to maintain and expand its market presence.
- Market Share Defense: Albert Heijn's leading position in the Netherlands, a key market for Ahold Delhaize, is a primary focus for defense.
- Market Share Expansion: The company actively seeks to increase its share in the competitive U.S. market through banners like Food Lion and Stop & Shop.
- Global and Local Competition: Ahold Delhaize contends with multinational corporations and strong regional grocery chains in both its European and American operations.
- Strategic Initiatives: Investments in online grocery capabilities and store modernization are crucial for fending off rivals and capturing new customers.
Competitive rivalry is a defining characteristic of the grocery sector, impacting Koninklijke Ahold Delhaize significantly. The company faces intense pressure from a wide range of competitors, from global behemoths to nimble local operators, all vying for consumer spending. This dynamic environment necessitates continuous adaptation and strategic maneuvering.
Price wars remain a constant threat, particularly as inflation influences consumer purchasing power, a trend evident throughout 2024. Retailers are increasingly relying on promotions and loyalty programs to retain customers, which directly squeezes profit margins and demands efficient cost management. The digital race further intensifies this rivalry, with significant investments required in e-commerce and omnichannel capabilities to meet evolving consumer expectations.
Private label brands are a key battleground, with retailers like Ahold Delhaize focusing on developing high-quality own-brand offerings to foster customer loyalty and improve profitability. In 2024, private label sales have shown robust growth, often outperforming national brands and providing a crucial differentiator beyond price alone.
| Competitor Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Ahold Delhaize |
|---|---|---|
| Global Giants | Vast scale, extensive supply chains, strong brand recognition | Intense price competition, need for efficient operations |
| Discounters (e.g., Aldi, Lidl) | Aggressive pricing, limited assortment, operational efficiency | Pressure on Ahold Delhaize's pricing strategies, particularly in value segments |
| Online Grocers | Convenience, rapid delivery, personalized digital experiences | Requires significant investment in e-commerce and logistics capabilities |
| Local/Regional Players | Deep understanding of local markets, strong community ties | Can capture niche markets and challenge Ahold Delhaize's market share in specific regions |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The rise of quick-service restaurants and meal kits presents a significant threat to traditional grocery sales. Consumers increasingly seek convenience, and these options offer ready-to-eat meals, bypassing the need for grocery shopping and meal preparation.
Even within grocery stores, prepared food sections and hot bars are becoming more sophisticated. While overall foodservice traffic saw a dip in Q2 2024, these in-store offerings are directly competing with external restaurants, diverting spending that might have otherwise gone towards grocery ingredients.
The threat of substitutes for Koninklijke Ahold Delhaize is amplified by the growing direct-to-consumer (DTC) food brand movement. Consumers increasingly bypass traditional supermarkets for specialized, niche, or farm-to-table food items, seeking personalized experiences and direct brand connections.
This shift is evident in the expanding market for artisanal foods and subscription boxes, which offer convenience and unique product selections. For instance, the global online food delivery market, a related substitute channel, was projected to reach over $300 billion by 2024, indicating a significant consumer willingness to explore alternative purchasing avenues for food.
The rise of farmers' markets and local food systems presents a notable threat of substitution for large grocery retailers like Ahold Delhaize. Consumers are increasingly drawn to the perceived freshness, quality, and traceability of products purchased directly from local producers. This shift is fueled by a growing emphasis on health consciousness and sustainability, with many shoppers actively seeking out organic and locally sourced options.
In 2024, the demand for local food continues to surge. For instance, the USDA reported that local food sales reached $11.7 billion in 2022, and this trend is expected to maintain its upward trajectory. Farmers' markets, in particular, offer a direct-to-consumer channel that bypasses traditional retail infrastructure, providing a compelling alternative for consumers who prioritize community connection and a more direct relationship with their food sources.
Specialty Food Stores and Niche Retailers
Specialty food stores and niche retailers present a significant threat of substitutes for broad-range supermarkets like Ahold Delhaize. Consumers increasingly seek unique, gourmet, or specific dietary products, finding these curated selections at specialized outlets. For instance, a consumer looking for artisanal cheeses or specific gluten-free baked goods might bypass a traditional supermarket for a dedicated delicatessen or health food store. This trend is supported by the growth in the specialty food sector, which saw continued expansion through 2024 as consumers prioritized quality and provenance.
These niche players effectively cater to distinct consumer preferences and shopping missions, offering an alternative to the one-stop-shop approach of larger chains. The ability of these stores to provide a highly targeted product assortment can draw away specific customer segments, impacting overall market share for supermarkets.
- Specialty food market growth: The global specialty food market continued its upward trajectory in 2024, driven by consumer demand for unique and health-conscious options.
- Targeted consumer segments: Niche retailers excel at capturing consumers focused on specific dietary needs (e.g., vegan, organic) or culinary interests (e.g., international cuisine).
- Customer loyalty: The curated experience and product expertise offered by specialty stores can foster strong customer loyalty, making them a compelling alternative for certain purchases.
Subscription-Based Food Services
The rise of subscription-based food services presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional grocery retailers like Ahold Delhaize. These services offer convenience and curated experiences, delivering items like snacks, coffee, and meal kits directly to consumers' doors. For instance, services catering to specific dietary needs or offering ready-to-eat meals bypass the need for traditional grocery shopping entirely.
This trend is amplified by the increasing consumer preference for convenience and personalized consumption. In 2024, the global meal kit delivery market alone was projected to reach a substantial value, indicating a strong consumer adoption of these alternative food sourcing methods. Ahold Delhaize must consider how these services directly compete for consumer spending on food and groceries.
- Convenience Factor: Subscription services eliminate the need for consumers to plan, shop, and prepare meals from scratch, offering a significant time-saving benefit.
- Curation and Specialization: Many services focus on niche markets, such as organic, vegan, or gourmet options, catering to specific consumer preferences that might be harder to fulfill through a general grocery store.
- Direct-to-Consumer Model: These businesses often operate with a direct-to-consumer approach, potentially offering competitive pricing or unique value propositions that traditional retailers need to counter.
- Market Growth: The continued expansion and investment in the subscription food sector indicate a growing consumer base and a persistent threat to established grocery players.
The competitive landscape for Koninklijke Ahold Delhaize is increasingly shaped by substitutes that offer convenience and specialized experiences. Quick-service restaurants and meal kit services directly compete by providing ready-to-eat or easily prepared meals, bypassing traditional grocery shopping and preparation entirely. This trend is supported by the projected over $300 billion valuation of the global online food delivery market by 2024, highlighting a significant consumer shift towards alternative food sourcing channels.
Furthermore, the growing direct-to-consumer (DTC) food brand movement and the expansion of farmers' markets and local food systems present distinct alternatives. Consumers are drawn to the perceived freshness, quality, and direct connection offered by these channels. For instance, local food sales reached $11.7 billion in 2022, demonstrating a robust consumer preference for locally sourced products.
Specialty food stores and subscription-based services also pose a considerable threat by catering to niche dietary needs and offering curated selections. The continued growth in the specialty food sector through 2024 underscores consumers' willingness to seek out unique and health-conscious options outside of traditional supermarkets.
| Substitute Category | Key Offering | Consumer Appeal | 2024 Market Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quick-Service Restaurants & Meal Kits | Convenience, ready-to-eat meals | Time-saving, reduced effort | Global online food delivery market projected >$300 billion |
| Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Brands | Specialized, niche products, direct connection | Personalization, unique offerings | Growing market for artisanal foods and subscription boxes |
| Farmers' Markets & Local Foods | Freshness, quality, traceability, community connection | Health consciousness, sustainability, local support | Local food sales reached $11.7 billion in 2022 (USDA) |
| Specialty Food Stores & Subscription Services | Curated selections, niche dietary options | Targeted needs, unique experiences | Continued expansion of specialty food sector |
Entrants Threaten
The sheer scale of investment needed to compete in the food retail sector, particularly for a player like Ahold Delhaize, presents a formidable hurdle for newcomers. Establishing a robust physical presence, complete with numerous stores and efficient distribution networks, demands billions. For instance, major supermarket chains often spend hundreds of millions annually on store openings and renovations alone.
Established players like Ahold Delhaize leverage significant economies of scale in purchasing, distribution, and marketing, which translates into lower per-unit costs. For instance, Ahold Delhaize's vast network of stores and efficient supply chain management in 2024 allow for bulk purchasing discounts, a hurdle for new entrants.
Newcomers face the daunting task of matching these cost efficiencies. Without the same purchasing power and established operational expertise, they often struggle to compete on price, a critical factor in the grocery sector.
Koninklijke Ahold Delhaize benefits immensely from its portfolio of strong local brands, each possessing deep roots and established customer loyalty in their respective markets. For instance, Albert Heijn in the Netherlands consistently holds a leading market share, demonstrating significant brand stickiness. This deep-seated trust and recognition make it incredibly difficult for new entrants to gain traction.
Building comparable brand recognition and trust, alongside an extensive physical and online network, is a formidable challenge for any new competitor. Ahold Delhaize's vast store footprint and sophisticated omnichannel operations, like those seen with Stop & Shop in the US, represent significant capital investments and logistical hurdles that new players must overcome. In 2024, the company continued to invest heavily in its digital infrastructure and store modernization, further solidifying these advantages.
Complex Regulatory Environment and Local Knowledge
The food retail sector is heavily regulated, with complex rules covering everything from food safety and labeling to labor practices and land use. These regulations differ significantly across countries and even within regions, creating substantial barriers for newcomers. For instance, in 2024, navigating the specific requirements for sourcing and selling fresh produce in the Netherlands, where Ahold Delhaize has a strong presence, demands intricate knowledge of local agricultural standards and import/export laws.
New entrants must invest heavily in understanding and complying with these diverse regulatory landscapes. This includes obtaining necessary licenses, adhering to stringent hygiene standards, and managing labor relations in accordance with local laws. Ahold Delhaize's established presence means they have already built the infrastructure and expertise to manage these complexities efficiently, a significant advantage over any potential new competitor attempting to enter the market without this ingrained knowledge.
Acquiring deep local market knowledge is equally critical. This encompasses understanding consumer preferences, supply chain intricacies, and competitive dynamics specific to each operating territory. For example, a new entrant in Belgium would need to grasp the nuances of regional consumer demand for specific types of baked goods or dairy products, information Ahold Delhaize has cultivated over years of operation. This localized expertise is a formidable barrier.
- Regulatory Complexity: Food safety, labor, and zoning laws create significant compliance burdens for new entrants in the food retail sector.
- Regional Variation: Regulations and market demands differ substantially across countries and even within specific regions, requiring tailored approaches.
- Knowledge Barrier: Deep local market understanding, including consumer preferences and supply chain specifics, is essential and difficult for new players to acquire quickly.
- Operational Challenges: Navigating these regulatory and knowledge hurdles presents substantial operational and financial challenges for potential new entrants.
Intense Digital Investment and Omnichannel Demands
The threat of new entrants in the grocery sector, particularly concerning digital and omnichannel capabilities, is significant. New players must invest heavily in sophisticated e-commerce infrastructure, efficient last-mile logistics, and cutting-edge data analytics, including AI, to even begin competing. For instance, in 2024, the average cost for developing a robust online grocery platform with integrated inventory management and personalized customer experiences can range from hundreds of thousands to millions of dollars, depending on the scale and features. This high initial capital outlay acts as a considerable barrier.
Furthermore, the expectation for a seamless omnichannel experience, where online and in-store operations are perfectly integrated, presents a substantial technological hurdle. Customers demand the ability to browse online, pick up in-store, or have items delivered with consistent pricing and promotions across all channels. Companies like Instacart, which expanded its partnership with Kroger in 2024, demonstrate the ongoing investment in technology to meet these evolving customer expectations, further raising the bar for new entrants aiming to replicate such integrated services.
- High Capital Investment: Significant upfront costs for e-commerce platforms and logistics.
- Technological Sophistication: Need for advanced data analytics, AI, and seamless omnichannel integration.
- Operational Complexity: Managing both online and offline operations efficiently is a major challenge.
- Customer Expectations: Meeting demands for consistent, convenient, and personalized shopping experiences across all touchpoints.
The threat of new entrants for Koninklijke Ahold Delhaize remains moderate due to substantial barriers to entry. The immense capital required for establishing physical store networks and sophisticated omnichannel operations, including advanced logistics and e-commerce platforms, deters many potential competitors. For instance, in 2024, building a comprehensive online grocery presence with efficient last-mile delivery can easily cost millions, a significant hurdle for startups.
Ahold Delhaize's established brand loyalty, particularly with brands like Albert Heijn, and its deep-rooted local market knowledge in regions like the Netherlands and Belgium, create a strong competitive moat. New entrants would struggle to replicate this customer trust and understanding of nuanced regional preferences. Furthermore, navigating the complex web of food safety, labor, and land use regulations across different markets demands significant expertise and investment, further solidifying the position of incumbents.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Ahold Delhaize Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High costs for physical stores, distribution, and e-commerce infrastructure. | Significant deterrent. | Leverages existing scale and investment capacity. |
| Brand Loyalty & Market Knowledge | Established customer trust and understanding of local consumer preferences. | Difficult to penetrate established markets. | Strong portfolio of trusted local brands. |
| Regulatory Landscape | Complex and varying regulations across geographies (food safety, labor, etc.). | Requires extensive compliance investment and expertise. | Existing infrastructure and knowledge for efficient compliance. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to large-scale purchasing and operations. | Price competition challenges. | Bulk purchasing power and optimized supply chains. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our analysis of Koninklijke Ahold Delhaize's competitive landscape is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research from reputable firms. We also incorporate data from regulatory filings and news archives to capture evolving market dynamics and competitive pressures.
