3M Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
3M Bundle
3M navigates a complex landscape shaped by intense rivalry, the threat of new entrants, and the bargaining power of both buyers and suppliers. Understanding these forces is crucial for any business operating within or looking to enter its diverse markets.
This snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore 3M’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
3M relies on a select group of suppliers for highly specialized raw materials critical to its vast product range. This concentration of suppliers can grant them significant leverage. For instance, in 2024, 3M's advanced materials segment, which includes products requiring unique chemical compounds, saw a 5% increase in the cost of certain specialized inputs, directly impacting margins.
Supplier switching costs represent a significant factor in the bargaining power of suppliers for a company like 3M. If it is expensive and time-consuming for 3M to switch from one supplier to another for critical components or raw materials, then suppliers gain leverage. These costs can include the expense of qualifying new materials, retooling production lines, and the potential for disruptions to 3M's manufacturing processes during the transition. For example, in 2023, companies across various manufacturing sectors reported an average of 15-20% increase in costs associated with qualifying new suppliers for specialized chemicals or advanced materials, directly impacting their ability to switch easily.
Some suppliers possess proprietary technologies or patents that are critical for 3M's manufacturing processes and product innovation. This intellectual property grants these suppliers considerable bargaining power, as 3M faces significant hurdles in finding alternative sources or developing comparable technologies independently without substantial investment or legal challenges.
For instance, in 3M's advanced materials division, which contributes significantly to its revenue streams, reliance on specialized chemical compounds or unique manufacturing techniques developed by a few key suppliers can create a dependency. In 2024, the global market for advanced materials, a sector where such dependencies are common, was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, highlighting the value and exclusivity of these proprietary inputs.
Supplier's Ability to Forward Integrate
If suppliers can effectively integrate forward into 3M's business, their leverage grows. This means a supplier might start manufacturing their own finished goods that directly compete with 3M's offerings, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
While raw material suppliers typically don't possess the capability or incentive for this, a supplier that develops competing end products presents a tangible threat to 3M. For instance, a specialized adhesive manufacturer could begin producing its own branded tapes or sealants.
3M's extensive and diverse product portfolio, spanning areas like healthcare, consumer goods, and industrial materials, makes assessing this threat complex. The potential for forward integration varies significantly across the many industries 3M operates within.
- Supplier Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers developing competing finished products can significantly enhance their bargaining power against 3M.
- Complexity for 3M: The wide range of 3M's products means this threat must be evaluated across numerous distinct markets.
- Industry Variation: The likelihood of suppliers forward integrating differs greatly depending on the specific industry and the supplier's strategic capabilities.
Importance of 3M to the Supplier's Business
3M's immense global purchasing power significantly influences its suppliers. Despite the specialized nature of some materials, 3M's sheer volume makes it a critical customer for many, potentially mitigating supplier leverage.
For instance, in 2023, 3M reported total revenues of approximately $32.7 billion. This vast scale means that a considerable portion of many suppliers' output is directed to 3M, creating an incentive for them to maintain favorable terms and pricing to secure this substantial business.
- Significant Customer: 3M's global operations translate into substantial purchasing volumes across a wide array of inputs.
- Volume Leverage: This large scale can counterbalance supplier power, as suppliers value 3M's consistent and high-volume orders.
- Supplier Dependence: Many suppliers may rely on 3M for a significant percentage of their revenue, fostering a desire to maintain a strong relationship.
The bargaining power of suppliers for 3M is a key consideration, particularly for specialized materials. In 2024, the increasing cost of certain advanced chemical compounds, crucial for 3M's high-performance products, demonstrated this leverage, impacting the company's profit margins.
High switching costs for 3M, stemming from the need to qualify new materials and retool production lines, further empower suppliers. For example, industry data from 2023 indicated that qualifying new specialized chemical suppliers could add 15-20% to a company's costs, making it difficult for 3M to change suppliers easily.
Suppliers holding critical patents or proprietary technologies also wield significant power, as 3M faces substantial hurdles in finding alternatives or developing comparable technologies independently.
| Factor | Impact on 3M | 2023/2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Materials Dependence | Increases supplier leverage | 5% cost increase for specific advanced materials in 2024 |
| Switching Costs | Limits 3M's ability to change suppliers | 15-20% cost increase for supplier qualification (industry average 2023) |
| Proprietary Technology/Patents | Creates supplier dependency | Critical for advanced materials and product innovation |
What is included in the product
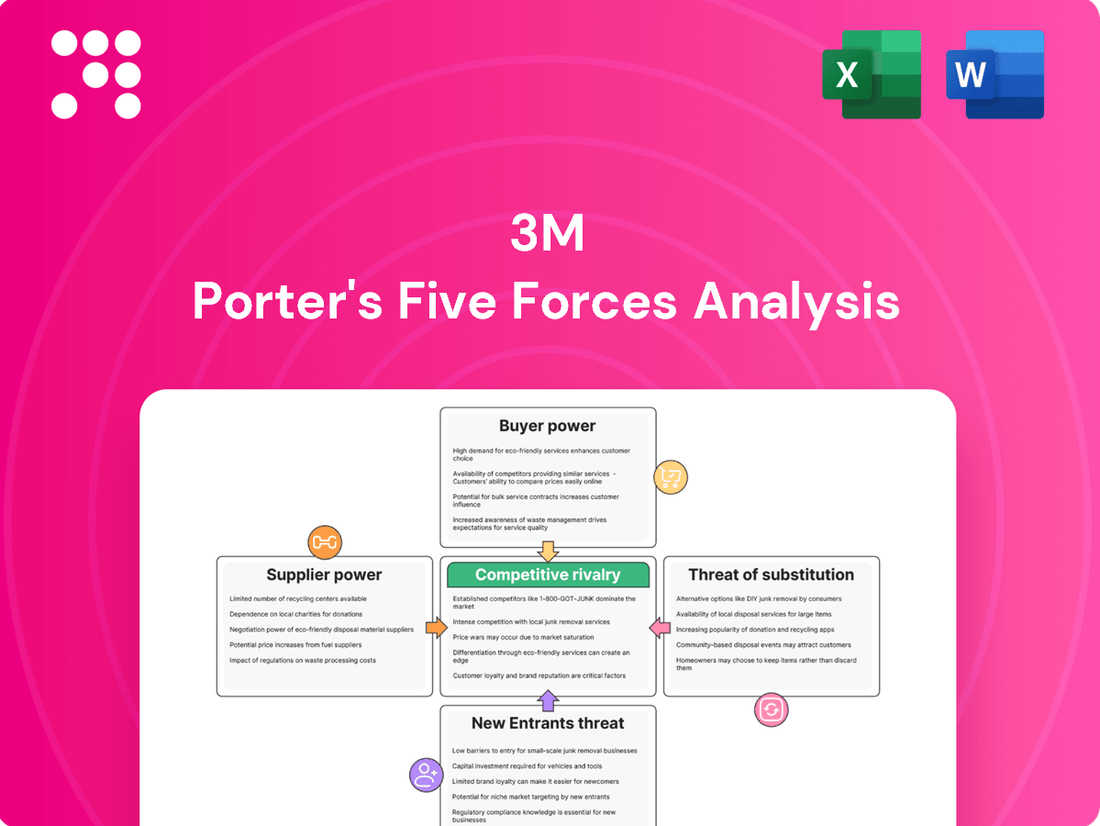
This analysis of 3M's competitive landscape examines the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces, allowing for targeted strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
3M's customer base is incredibly diverse, spanning over 70 different industries. This includes major sectors like healthcare, industrial manufacturing, consumer goods, and electronics. Such widespread reach significantly dilutes the bargaining power of any single customer or industry segment.
No individual customer represents a dominant portion of 3M's overall revenue. For instance, in 2023, 3M reported total sales of $32.7 billion. This broad revenue stream means that losing one customer, even a large one, would not cripple the company, thus limiting their leverage.
3M's robust brand portfolio, featuring household names like Post-it, Scotch, and Command, cultivates deep customer loyalty. This strong brand recognition, built on a reputation for consistent quality and innovation, significantly diminishes the ease with which customers can switch to rival products. For instance, in 2023, 3M's consumer segment continued to demonstrate resilience, with these trusted brands acting as a buffer against price sensitivity, thereby limiting customer bargaining power across various markets.
In highly commoditized areas, like certain industrial adhesives or basic cleaning supplies, customers are often very focused on price. This means if 3M's prices aren't in line with competitors, buyers can easily switch to another supplier. For example, in the global industrial adhesives market, which was valued at approximately $60 billion in 2023, price competition is a significant factor for many customers.
Availability of Substitutes and Alternatives
While 3M boasts many unique, patented products, the existence of alternative solutions, especially in more commoditized markets, significantly impacts customer bargaining power. For instance, in the adhesives market, while 3M has specialized offerings, general-purpose tapes and glues from competitors provide readily available substitutes. This means customers can often find comparable, albeit less advanced, products at lower price points.
Customers can leverage the availability of these alternatives to negotiate better pricing or more favorable contract terms with 3M. If 3M's prices are perceived as too high, a customer might opt for a substitute product, forcing 3M to reconsider its pricing strategy to retain business. This dynamic is particularly relevant in sectors where innovation cycles are shorter or where the unique benefits of 3M's products are not critical to the end application.
Consider the office supplies sector, where 3M's Post-it Notes face competition from numerous other brands offering similar sticky notes. In 2024, the global office supplies market was valued at over $250 billion, with a significant portion of that driven by consumables where brand loyalty can be less entrenched than in high-tech industrial applications. This broad market presence of alternatives empowers buyers.
- Differentiated Products vs. Generic Substitutes: 3M's strength in innovation creates differentiated products, but generic or simpler alternatives exist for many applications, especially in less specialized segments.
- Customer Leverage: The presence of these alternatives gives customers the power to negotiate better prices and terms, or to switch suppliers if 3M's offerings become uncompetitive.
- Market Dynamics: In 2024, the vastness of markets like office supplies, with numerous competing brands for common items, highlights how easily customers can find substitutes, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
Customer Information and Transparency
Customers today have unprecedented access to information, allowing them to easily compare products, scrutinize pricing, and read reviews. This heightened transparency directly fuels their bargaining power, as they can readily identify the best value. For instance, in 2024, online review platforms and price comparison sites have become indispensable tools for consumers across all sectors.
This informed consumer base, especially larger industrial buyers who undertake rigorous procurement processes, can leverage detailed product specifications and market pricing to negotiate more favorable terms. 3M, like many other manufacturers, faces pressure from these well-informed customers who can easily switch suppliers if better deals are available. The ability for customers to quickly assess alternatives significantly strengthens their position in negotiations.
- Informed Purchasing Decisions: Customers can now easily access detailed product comparisons, pricing data, and user reviews.
- Enhanced Bargaining Power: Increased transparency empowers customers to negotiate better terms and prices.
- Impact on Industrial Buyers: Large industrial customers, in particular, benefit from thorough procurement processes that leverage this readily available information.
- Supplier Competition: This transparency intensifies competition among suppliers, as customers can swiftly identify and switch to more cost-effective or feature-rich alternatives.
The bargaining power of 3M's customers is moderate, influenced by the company's diverse product portfolio and strong brand recognition, yet tempered by the availability of substitutes in certain markets. While 3M's innovation creates differentiated products, customers can leverage generic alternatives, especially in commoditized segments, to negotiate better pricing. This is evident in markets like office supplies, where easy access to substitutes empowers buyers.
| Factor | Impact on 3M | Example/Data (2023/2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Diversification | Lowers individual customer power | 70+ industries served; $32.7 billion total sales in 2023 |
| Brand Loyalty | Reduces price sensitivity | Strong brands like Post-it, Scotch; Consumer segment resilience in 2023 |
| Availability of Substitutes | Increases customer power in commoditized areas | Global industrial adhesives market ($60 billion in 2023) has many alternatives |
| Customer Information Access | Enhances negotiation leverage | Online reviews and price comparison sites are prevalent in 2024 |
Same Document Delivered
3M Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete 3M Porter's Five Forces Analysis, providing an in-depth examination of the competitive landscape that directly impacts the company's strategic positioning. You're looking at the actual document, meticulously compiled to offer actionable insights into industry rivalry, the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threat of substitute products. Once your purchase is complete, you’ll gain instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file, ready for your immediate use and strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
3M faces significant competitive rivalry, operating in a landscape populated by numerous formidable global industrial and technology manufacturers. Companies like Honeywell, General Electric, and Danaher actively compete across 3M's diverse product lines, intensifying the struggle for market share.
This intense rivalry means that pricing pressures are a constant factor, and innovation cycles are often accelerated as competitors strive to differentiate their offerings. For instance, in the adhesives and tapes segment, 3M competes with players like Henkel and Avery Dennison, both of which have strong global presences and invest heavily in R&D.
3M actively pursues ongoing innovation and differentiation to stay ahead in its competitive landscape. The company's commitment to research and development is substantial, with a strategic goal of introducing approximately 1,000 new product launches between 2025 and 2027. This aggressive product pipeline is designed to fuel growth and create distinct market positions against competitors.
The competitive landscape for 3M is characterized by significant pricing pressures, a direct consequence of companies aggressively vying for market share. This dynamic forces 3M to meticulously calibrate its pricing strategies, aiming to stay competitive without sacrificing its profit margins, particularly in product categories where distinguishing features are less apparent.
In 2023, 3M reported a net sales decrease of 4.9% to $32.67 billion, reflecting some of these market pressures. For instance, in its Safety and Industrial segment, which faces intense competition from numerous global and regional players, pricing was a key factor influencing sales volume.
Diversified Portfolio and Segment-Specific Rivalry
3M's extensive product range means it encounters a diverse array of competitors, each specializing in specific market segments. This necessitates tailored competitive strategies for areas like Safety & Industrial, Transportation & Electronics, and Consumer goods, demanding continuous monitoring of rivals' actions within each distinct market.
The intensity of competition varies significantly across 3M's business units. For instance, in the Safety & Industrial segment, 3M competes with established players like Honeywell and DuPont, as well as numerous smaller, specialized firms. In Transportation & Electronics, it faces rivals such as Corning and TE Connectivity, while the Consumer segment sees competition from giants like Procter & Gamble and SC Johnson, alongside many private label brands.
- Safety & Industrial: Competitors include Honeywell, DuPont, Stanley Black & Decker.
- Transportation & Electronics: Rivals are Corning, TE Connectivity, Amphenol.
- Consumer: Key competitors are Procter & Gamble, SC Johnson, Kimberly-Clark.
Global Reach and Regional Competition
3M's competitive rivalry is intense, extending beyond global giants to include formidable regional and local competitors. This dynamic is particularly evident in diverse markets where tailored products and localized strategies often hold sway. For instance, in the Asia-Pacific region, 3M contends with established players like Nitto Denko in specialized adhesive tapes and films, forcing 3M to continuously innovate and adapt its offerings.
Navigating varied regulatory landscapes and distinct market preferences significantly amplifies competitive pressures. Companies must not only meet global standards but also comply with country-specific requirements, adding complexity and cost. This is a critical factor in sectors like healthcare and safety, where product approvals and certifications differ widely. In 2024, the semiconductor industry, a key market for 3M's advanced materials, saw significant regional investment and expansion, intensifying rivalry from local material suppliers in South Korea and Taiwan.
- Global Presence, Local Battles: 3M competes with multinational corporations like DuPont and Henkel on a global scale, but also faces strong regional players in specific product categories and geographic markets.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Differing regulations across countries, especially in sensitive sectors like healthcare and automotive, create unique competitive challenges and require localized compliance strategies.
- Market Dynamics: Local market preferences and established distribution networks for regional competitors can offer significant advantages, necessitating flexible and responsive market approaches from 3M.
- Innovation Race: The need to stay ahead of both global and local competitors drives continuous investment in research and development, with particular focus on areas like sustainable materials and digital integration in 2024.
3M operates in a highly competitive arena against numerous global industrial and technology manufacturers, including significant players like Honeywell, General Electric, and Danaher, who vie for market share across its diverse product lines.
This intense rivalry translates into constant pricing pressures and accelerated innovation cycles as competitors seek differentiation, a trend exemplified in the adhesives market where Henkel and Avery Dennison are strong global rivals.
3M's strategy to counter this involves substantial investment in research and development, aiming for approximately 1,000 new product launches between 2025 and 2027 to secure distinct market positions.
In 2023, 3M's net sales saw a 4.9% decrease to $32.67 billion, partly due to competitive pressures in segments like Safety & Industrial, where pricing significantly impacted sales volume.
| Key Competitors | Relevant Segments | 2023 Net Sales (USD Billion) |
| Honeywell | Safety & Industrial, Transportation & Electronics | 39.8 |
| General Electric | Aerospace, Healthcare (historically) | 68.4 |
| DuPont | Safety & Industrial, Electronics & Imaging | 13.0 |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Technological advancements are a significant threat of substitutes for 3M. For example, the rise of advanced materials science and digital solutions can offer alternatives to 3M's established product lines. In 2023, R&D spending by major industrial conglomerates like 3M often exceeded billions of dollars, signaling a constant drive for innovation that can either create or neutralize substitute threats.
3M's vast product diversification, spanning industrial adhesives, consumer goods like Scotch tape, and advanced electronic materials, significantly reduces the threat of substitutes. If a competitor introduces a superior alternative in one segment, like a new type of adhesive, 3M's overall business remains robust due to its presence in many other unrelated markets. This broad portfolio means that a threat to one product doesn't cripple the entire company.
3M's formidable brand loyalty and stellar reputation for quality significantly dampen the threat of substitutes. Products like Post-it Notes and Scotch Tape are household names, built on decades of reliable performance. This ingrained trust means customers are less likely to explore cheaper alternatives, even when faced with price differences, as they prioritize 3M's proven track record and consistent quality.
Cost-Effectiveness of Substitutes
The threat of substitutes for 3M's diverse product portfolio is amplified when alternative solutions provide comparable functionality at a substantially lower price point. For instance, in the adhesives market, lower-cost generic brands can sometimes erode market share from 3M's premium offerings if the performance differential is not perceived as significant by the end-user. This cost-effectiveness of substitutes directly pressures 3M to maintain a competitive edge not just through innovation but also through efficient manufacturing and supply chain management.
To counter this, 3M must relentlessly pursue innovation and process optimization. This ensures that their products continue to offer a superior value proposition, balancing performance with cost. For example, 3M's ongoing investment in advanced materials science aims to create products that are not only more effective but also more economical in their total cost of ownership over time, thereby mitigating the allure of cheaper, less durable alternatives. In 2023, 3M reported significant investments in R&D, underscoring their commitment to this strategy.
- Cost-Sensitive Markets: In segments where price is a primary purchasing driver, the threat from lower-cost substitutes is particularly acute.
- Performance vs. Price Trade-off: 3M must continually demonstrate that its product's superior performance justifies any price premium over substitutes.
- Innovation as a Defense: Continuous development of new and improved products with unique features is crucial to staying ahead of substitute threats.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlining production and reducing costs allows 3M to price its offerings more competitively against substitutes.
Regulatory Changes and Sustainability Trends
Evolving regulations and a growing demand for sustainable solutions present a significant threat of substitution for 3M. As environmental standards tighten and consumer preferences shift towards eco-friendly alternatives, products that do not align with these trends face increased pressure from substitutes. This is particularly relevant for industries where 3M's materials are integral.
3M is proactively managing this threat. The company has committed to phasing out PFAS manufacturing by the end of 2025, a move that directly addresses regulatory scrutiny and market demand for safer materials. Furthermore, 3M's investment in climate tech solutions signals a strategic pivot to capitalize on, rather than be disrupted by, sustainability trends.
- Regulatory Pressure: Increasing global regulations on chemicals like PFAS, which 3M has historically produced, create opportunities for substitute materials that are perceived as less harmful.
- Consumer Demand for Sustainability: A growing segment of consumers and businesses actively seek products with a lower environmental footprint, driving demand for sustainable alternatives across various sectors.
- 3M's Strategic Response: The planned discontinuation of PFAS manufacturing by the end of 2025 and significant investments in climate technology demonstrate 3M's commitment to mitigating the threat of substitution by adapting its product portfolio and innovation focus.
The threat of substitutes for 3M is multifaceted, stemming from technological advancements, cost-sensitive markets, and evolving regulatory landscapes. While 3M's diversification and brand loyalty offer some insulation, the company must continuously innovate and optimize operations to maintain its competitive edge against alternatives that may offer similar functionality at a lower price or with a more favorable environmental profile.
For instance, in 2023, 3M's commitment to phasing out PFAS manufacturing by the end of 2025 directly addresses regulatory pressures and growing consumer demand for sustainable materials, highlighting the dynamic nature of substitute threats. This strategic move, coupled with investments in climate tech, aims to preemptively neutralize potential disruptions and capitalize on emerging market preferences.
The company's ability to demonstrate superior value, balancing performance with cost, remains critical. As an example, in the adhesives market, generic brands can pose a threat if the perceived performance difference doesn't justify 3M's premium pricing, underscoring the need for ongoing product differentiation and efficient cost management.
| Factor | Impact on 3M | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Technological Advancements | New materials and digital solutions can offer alternatives to 3M's products. | Continuous R&D investment, focusing on disruptive innovation. |
| Cost-Sensitive Markets | Lower-cost substitutes can erode market share if performance parity is perceived. | Operational efficiency, value engineering, and demonstrating total cost of ownership benefits. |
| Sustainability & Regulations | Demand for eco-friendly alternatives and stricter chemical regulations (e.g., PFAS) create substitute opportunities. | Phasing out problematic chemicals (e.g., PFAS by end of 2025), investing in sustainable technologies. |
| Brand Loyalty & Quality | Established trust in brands like Post-it and Scotch Tape reduces customer willingness to switch. | Maintaining high product quality and consistent brand messaging. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering industries where 3M operates, such as advanced materials or healthcare solutions, typically demands significant upfront capital. For instance, establishing state-of-the-art manufacturing plants for specialty adhesives or medical devices can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars, a considerable barrier for newcomers.
3M's long-standing presence allows it to leverage substantial economies of scale in both production and raw material procurement. This translates into lower per-unit costs, a competitive advantage that new entrants, lacking this volume and established supply chain relationships, would find extremely difficult to overcome in the near term.
3M's brand equity, cultivated over a century, presents a formidable barrier to new entrants. Consumers and businesses alike trust 3M's consistent quality and innovation, fostering deep loyalty that new competitors would struggle to replicate. For instance, in 2023, 3M continued to invest heavily in marketing and brand building, reinforcing its established market presence.
3M's extensive portfolio of over 120,000 patents, as reported in their 2023 filings, creates a formidable barrier to entry. This proprietary technology, especially in areas like adhesives and abrasives, necessitates substantial R&D investment for any new competitor to develop comparable, non-infringing products. For instance, their Post-it Notes technology, protected by patents, made it incredibly difficult for early imitators to replicate the product's unique functionality and market appeal.
Extensive Distribution Channels and Global Reach
The threat of new entrants for 3M, particularly concerning its extensive distribution channels and global reach, is significantly mitigated by the sheer scale and complexity of its established networks. Building comparable infrastructure and securing access to the diverse customer base that 3M serves globally would require immense capital investment and time.
Newcomers would struggle to replicate 3M's established relationships with retailers, industrial suppliers, and direct-to-consumer platforms across numerous international markets. For instance, in 2024, 3M's global sales reached approximately $32.7 billion, underscoring the breadth of its market penetration and the difficulty for any new competitor to achieve similar reach quickly.
- Established Global Networks: 3M boasts a deeply entrenched global distribution system, reaching a vast array of industries and consumers worldwide.
- High Entry Barriers: Replicating 3M's extensive sales channels and customer relationships would demand substantial financial resources and considerable time, creating a significant barrier for new entrants.
- Market Access Challenges: New companies would face considerable hurdles in gaining access to the diverse markets and customer segments that 3M currently serves effectively.
Regulatory Hurdles and Compliance Costs
The threat of new entrants for 3M is significantly influenced by substantial regulatory hurdles and compliance costs, particularly in sectors like healthcare and advanced materials. For instance, in 2024, the medical device industry, a key area for 3M, continued to face complex approval processes and evolving quality standards. New companies entering these markets must navigate extensive testing, documentation, and adherence to international regulations, which can easily run into millions of dollars and several years of effort.
These regulatory burdens act as a formidable barrier, deterring potential competitors. Consider the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval process for new medical devices; it can be lengthy and expensive, requiring rigorous clinical trials and quality management systems. Similarly, environmental regulations for chemical production and industrial products, areas where 3M operates, demand significant upfront investment in compliant manufacturing processes and ongoing monitoring.
- Regulatory Complexity: Industries like healthcare and specialized industrial materials demand adherence to strict, often evolving, regulations.
- High Compliance Costs: New entrants face substantial expenses for product testing, certification, and maintaining compliance with standards.
- Time Investment: Obtaining necessary regulatory approvals can be a lengthy process, delaying market entry and increasing initial capital requirements.
- Impact on Innovation: While protecting consumers, these hurdles can slow the pace of new product introductions, favoring established players with existing compliance infrastructure.
The threat of new entrants for 3M is considerably low due to the high capital requirements needed to establish operations in its diverse sectors, such as advanced materials and healthcare. For example, building the sophisticated manufacturing facilities required for specialty chemicals or medical components can cost hundreds of millions of dollars, a significant deterrent for newcomers.
3M's established brand loyalty and extensive patent portfolio, encompassing over 120,000 patents as of 2023, create substantial barriers. Replicating the trust consumers place in 3M's quality and navigating its proprietary technologies demands immense R&D investment and time, making it difficult for new competitors to gain traction.
The company’s vast global distribution network and established customer relationships, evidenced by its $32.7 billion in global sales in 2024, are also major entry deterrents. New entrants would struggle to match 3M's market reach and access to diverse customer segments, requiring significant capital and time to build comparable infrastructure.
Furthermore, stringent regulatory environments in key 3M markets, like healthcare, impose high compliance costs and lengthy approval processes. Navigating FDA regulations for medical devices, for instance, can cost millions and take years, favoring established players with existing compliance frameworks.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High cost for specialized manufacturing facilities | Significant financial barrier |
| Brand & Patents | Established brand loyalty and extensive patent portfolio (>120,000 as of 2023) | Difficult to replicate trust and technology |
| Distribution & Relationships | Global reach and deep customer ties ($32.7B sales in 2024) | Challenging to match market access |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex and costly compliance in sectors like healthcare | Time-consuming and expensive market entry |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including publicly available financial statements, industry-specific market research reports, and insights from leading financial news outlets to provide a comprehensive view of competitive dynamics.
