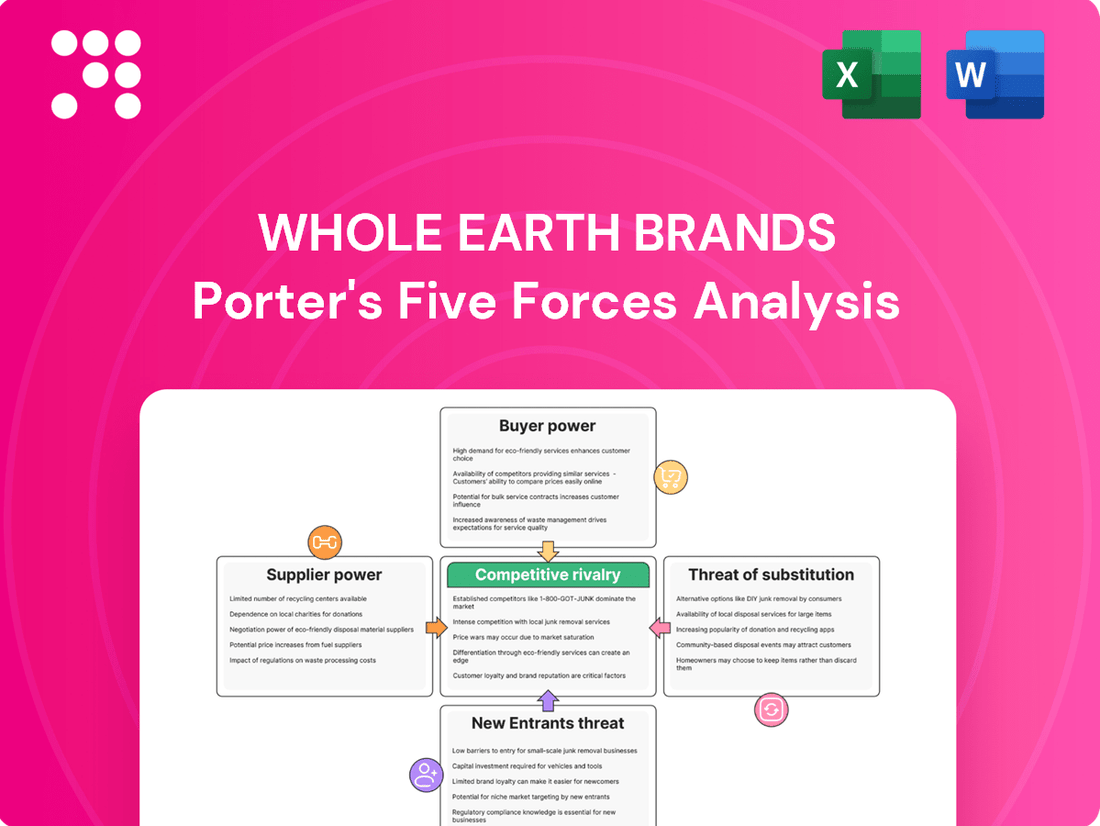
Whole Earth Brands Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Whole Earth Brands Bundle
Whole Earth Brands faces a dynamic competitive landscape, with moderate bargaining power from both buyers and suppliers. The threat of new entrants is present, but barriers to entry exist within the established beverage and food sectors. Understanding these forces is crucial for strategic planning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Whole Earth Brands’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for Whole Earth Brands is significantly shaped by the concentration of specialized ingredient providers, especially for niche plant-based sweeteners such as stevia and monk fruit extracts. While the demand for natural sweeteners is expanding, a limited number of suppliers offering high-quality or sustainably sourced ingredients can exert greater influence.
For instance, the global stevia market was valued at approximately USD 1.1 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, but the supply of premium-grade stevia extracts can be concentrated among a few key players, potentially increasing their leverage over buyers like Whole Earth Brands.
Whole Earth Brands' strategy of maintaining a broad portfolio of natural and plant-based ingredients helps to dilute this supplier dependency. By sourcing a variety of raw materials from different suppliers, the company can mitigate the risk of any single supplier holding excessive power.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Whole Earth Brands is significantly influenced by the switching costs associated with its key ingredients. If changing suppliers for a critical component requires extensive reformulation, rigorous testing, or costly re-certification processes, suppliers naturally hold more leverage. This complexity makes it harder for Whole Earth Brands to simply move to a competitor, thus strengthening the supplier's position.
Whole Earth Brands' ongoing supply chain reinvention project, initiated in recent years, aims to mitigate these supplier-driven costs. By actively working to diversify its supplier base and streamline sourcing operations, the company is strategically attempting to reduce the financial and operational burdens of switching. This proactive approach is designed to increase flexibility and lessen dependence on any single supplier, thereby diminishing their bargaining power.
The availability of substitute inputs significantly impacts the bargaining power of suppliers for Whole Earth Brands. If the company can readily switch between different plant-based sweeteners or utilize synthetic alternatives in some product formulations, the leverage of individual ingredient suppliers diminishes. For instance, the market offers a wide array of sugar substitutes, providing Whole Earth Brands with considerable flexibility in sourcing.
Supplier's Ability to Forward Integrate
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into the branded consumer goods market directly competes with Whole Earth Brands. While less common for raw agricultural producers, some specialized ingredient manufacturers could develop their own consumer-facing products, increasing supplier power. The significant investment in branding, marketing, and distribution required for consumer packaged goods (CPG) acts as a deterrent for many raw material suppliers.
For instance, the global CPG market, valued at trillions of dollars, demands substantial capital for market entry and brand building. This high barrier makes it challenging for many ingredient suppliers to successfully transition to competing directly with established brands like Whole Earth Brands in 2024.
- Deterrent Investment: The CPG sector requires significant capital for brand development, marketing campaigns, and establishing robust distribution networks.
- Specialized Ingredient Manufacturers: A subset of suppliers with unique or proprietary ingredients might consider forward integration, posing a more direct competitive threat.
- Market Landscape: The established presence and brand loyalty of companies like Whole Earth Brands in the natural and organic food sector create a challenging environment for new entrants.
Importance of Input to Whole Earth Brands' Product Quality
The bargaining power of suppliers for Whole Earth Brands is significantly influenced by the criticality of their inputs to the company's product quality and distinct brand promise. If a particular ingredient, such as specialized plant-based extracts, is fundamental to achieving the 'natural tasting' profile that defines Whole Earth Brands' offerings, the supplier of that ingredient can wield considerable leverage. This leverage might translate into the ability to command higher prices or dictate more favorable payment and delivery terms, especially if alternative suppliers cannot replicate the unique quality or specific characteristics of the input. For instance, in 2023, the global market for natural sweeteners, a key ingredient category for many of Whole Earth Brands' products, saw price increases due to supply chain disruptions and growing consumer demand for natural alternatives.
Consider the following factors impacting supplier power:
- Ingredient Uniqueness: Suppliers providing proprietary or highly specialized ingredients essential for Whole Earth Brands' unique flavor profiles and health claims hold greater power.
- Brand Reliance: The extent to which Whole Earth Brands' brand identity and consumer perception are tied to specific, high-quality ingredients directly amplifies supplier influence.
- Supplier Concentration: If only a few suppliers can provide the necessary quality or volume of a critical ingredient, their bargaining power increases.
- Switching Costs: High costs associated with finding and qualifying new suppliers for specialized ingredients can lock Whole Earth Brands into existing relationships, strengthening supplier positions.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Whole Earth Brands is moderated by the availability of substitute ingredients and the company's efforts to diversify its sourcing. While some specialized natural sweeteners may have concentrated supply chains, the broader market for sugar alternatives provides flexibility. Whole Earth Brands' strategic initiatives to build stronger supplier relationships and explore new sourcing regions in 2024 aim to further balance this power dynamic.
| Factor | Impact on Whole Earth Brands | Data Point/Example (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Moderate to High for niche sweeteners | Global stevia market projected to grow, but premium extract supply can be concentrated. |
| Switching Costs | Significant for specialized ingredients | Reformulation and testing for new sweeteners can be costly and time-consuming. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Lowers supplier power | Wide range of natural and artificial sweeteners available in the market. |
| Criticality of Input | Increases supplier power | Ingredients vital for unique flavor profiles and brand promise can command higher prices. |
What is included in the product
This analysis of Whole Earth Brands' competitive landscape reveals the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, all crucial for understanding its market position and strategic opportunities.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a clear, actionable breakdown of Whole Earth Brands' Porter's Five Forces, enabling proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customer price sensitivity for Whole Earth Brands is a key consideration. As consumers become more budget-conscious, particularly with rising inflation, they might seek out more affordable options. This could mean choosing traditional sugar or lower-cost artificial sweeteners over Whole Earth Brands' plant-based and healthier alternatives.
Whole Earth Brands' reliance on major supermarket and hypermarket chains grants these large retailers significant bargaining power. Their substantial order volumes allow them to negotiate favorable pricing and terms, directly impacting Whole Earth Brands' margins.
The concentration of sales through a few dominant retail players amplifies this customer leverage. For instance, in 2024, the top three supermarket chains in the U.S. accounted for over 60% of grocery sales, highlighting the immense purchasing power concentrated in a few hands.
The expanding influence of online retailers further empowers consumers by increasing choice and price transparency. This shift in distribution channels means customers can more easily compare prices and switch brands, adding another layer to their bargaining strength.
Consumers have a significant bargaining power due to the vast availability of substitutes for Whole Earth Brands' products. The sweetener market is flooded with options, from natural sweeteners like stevia and monk fruit to artificial sweeteners and even traditional sugar. This abundance means customers can easily switch brands or product types if they perceive a better value proposition elsewhere.
Switching costs for consumers in the sweetener category are practically non-existent. There's no significant financial outlay or learning curve involved in trying a different brand of stevia or opting for a different type of sweetener altogether. This ease of transition empowers consumers to demand lower prices and higher quality, directly impacting Whole Earth Brands' pricing power and market share.
For instance, in 2024, the global market for natural sweeteners, a key category for Whole Earth Brands, was projected to reach over $10 billion, with a compound annual growth rate of around 7%. This robust growth indicates intense competition and a wide array of choices for consumers, further amplifying their bargaining power.
Customer Information and Health Awareness
Customers today are incredibly well-informed about what they consume. They actively seek out details on nutritional content, ingredients, and emerging health trends. This knowledge base significantly boosts their ability to make smart choices, directly impacting the bargaining power they hold.
This heightened health awareness translates into a strong preference for attributes like clean labels, plant-based options, and sugar-free products. Consumers are not just looking for these features; they are comparing brands, scrutinizing claims, and demanding transparency, which gives them considerable leverage.
- Informed Consumerism: A 2024 Nielsen report indicated that over 70% of consumers globally check ingredient lists before purchasing food and beverage items.
- Demand for Transparency: Surveys from early 2024 show that 65% of consumers are willing to pay a premium for products with clear, understandable ingredient lists.
- Health Trend Adoption: The plant-based food market alone saw a global growth of 15% in 2023, demonstrating a clear consumer shift towards health-conscious options.
Product Differentiation and Brand Loyalty
Whole Earth Brands, with brands like Equal and Whole Earth Sweetener, operates in a market where product differentiation and brand loyalty can be fluid. While established names exist, the sweetener category often sees consumers easily switching between options if perceived differences are minimal. This can lead to customers prioritizing price or promotions over brand allegiance, impacting bargaining power.
The degree of true differentiation in the broad sweetener market is a key factor. If consumers don't see a significant distinction between various healthy sweetener alternatives, their loyalty to a specific brand like Whole Earth Brands might be less robust. This lack of strong differentiation empowers customers to switch to competitors more readily.
For Whole Earth Brands to mitigate this, cultivating a strong brand identity and highlighting unique taste profiles are paramount. For instance, in 2023, the global sugar substitutes market was valued at approximately $13.5 billion, indicating a competitive landscape where distinct product attributes are crucial for customer retention and reducing customer bargaining power.
- Brand Strength: While Whole Earth Brands has recognized names, the overall sweetener market can be prone to brand switching if differentiation is low.
- Perceived Value: Consumers may not perceive significant differences between various healthy sweetener options, increasing their willingness to switch.
- Price Sensitivity: Weak differentiation often translates to higher price sensitivity among customers, allowing them to leverage price as a primary decision factor.
- Loyalty Drivers: Unique taste profiles and strong brand messaging are critical for building and maintaining customer loyalty, thereby reducing customer bargaining power.
The bargaining power of customers for Whole Earth Brands is significant due to the availability of numerous substitutes and minimal switching costs in the sweetener market. Consumers are increasingly informed about ingredients and health trends, actively comparing options and demanding transparency. This empowers them to readily switch brands if they perceive better value or if differentiation is low, impacting Whole Earth Brands' pricing flexibility and market position.
| Factor | Impact on Whole Earth Brands | Supporting Data (2024 Estimates/Trends) |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of Substitutes | High | Global natural sweeteners market projected over $10 billion, with ~7% CAGR. |
| Switching Costs | Very Low | Minimal financial or learning curve for consumers to try new sweeteners. |
| Consumer Information & Health Awareness | High | Over 70% of consumers check ingredient lists; 65% prefer clear labels. |
| Brand Differentiation | Moderate to Low | Sweetener market can be prone to brand switching if perceived differences are minimal. |
Full Version Awaits
Whole Earth Brands Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Whole Earth Brands, offering a detailed examination of industry competition, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and substitute products. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive instantly after completing your purchase, ensuring full transparency and immediate usability for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The sugar substitute and healthier food sectors are bustling with a wide array of competitors, from established giants in the food industry to niche, specialized brands. Whole Earth Brands finds itself in a competitive environment where companies offer a spectrum of sweeteners, including natural options, artificial sweeteners, and sugar alcohols, alongside a variety of other health-conscious food products. This fragmentation of the market naturally fuels intense rivalry as numerous players contend for consumer attention and market share.
The global market for healthy foods and sugar substitutes is booming, with consumers increasingly prioritizing wellness and seeking alternatives to sugar. This robust growth, projected to see the sugar substitute market alone reach substantial figures by 2025, naturally draws in new entrants and encourages existing companies to scale up their operations.
This dynamic environment, characterized by a high industry growth rate, makes the market highly attractive. However, it also intensifies competitive rivalry as more companies vie for market share, leading to increased promotional activities and price pressures.
Whole Earth Brands carves out its niche by championing plant-based, zero- and low-sugar, and clean label offerings. This strategy appeals to a growing health-conscious consumer base.
However, the competitive landscape is intense, with many rivals also pushing innovation in these very segments. Competitors are frequently launching new product formulations, exploring diverse taste profiles, and integrating novel functional benefits to capture market share.
For instance, in 2024, the global plant-based food market continued its robust growth, with projections indicating it could reach over $160 billion by 2030, highlighting the crowded nature of this space. The ability of Whole Earth Brands to consistently innovate and clearly articulate its unique selling points is therefore paramount to maintaining a competitive edge.
Brand Identity and Consumer Loyalty
Whole Earth Brands' established brands, like Equal, benefit from historical consumer recognition, a significant asset in a competitive market. However, the dynamic nature of the healthy food sector means that brand loyalty isn't guaranteed. New entrants and aggressively marketed alternatives can quickly capture consumer attention, posing a continuous challenge to maintaining market share.
The company's ability to build and sustain a strong brand identity is crucial for weathering this competitive storm. This involves not only product quality but also effective marketing that resonates with evolving consumer values and preferences. For instance, in 2023, the global sweetener market, where Equal operates, saw continued growth, but also increased competition from natural and plant-based alternatives, highlighting the need for adaptive branding strategies.
- Brand Recognition: Equal boasts decades of consumer familiarity, providing a foundational advantage.
- Evolving Preferences: The healthy food market is prone to rapid shifts, potentially eroding established loyalty.
- Competitive Marketing: New and trendy products often employ aggressive marketing, challenging existing brands.
- Loyalty as a Mitigator: Strong brand identity and deep consumer loyalty are key defenses against competitive rivalry.
Exit Barriers and Industry Consolidation
High fixed costs in manufacturing, R&D, and global distribution act as significant exit barriers. These costs can trap companies in the market even when profitability is low, contributing to sustained intense rivalry. For instance, the consumer packaged goods sector, where Whole Earth Brands operates, often involves substantial upfront investment in production facilities and marketing.
The consumer health and food industries have seen notable consolidation. Whole Earth Brands itself went private in 2021 through an acquisition by an affiliate of CVC Capital Partners. This move suggests a strategic effort to streamline operations and enhance competitive positioning away from public market scrutiny. Such transactions often aim to unlock value and achieve greater efficiencies.
- Exit Barriers: High fixed costs in manufacturing, R&D, and distribution can make exiting the industry difficult, forcing companies to compete even in less profitable times.
- Industry Consolidation: Recent transactions, like Whole Earth Brands' privatization in 2021, highlight a trend of industry consolidation aimed at improving competitive advantage and operational efficiency.
- Strategic Maneuvers: Companies engage in strategic actions, such as mergers and acquisitions, to gain market share and operational efficiencies in response to competitive pressures.
Whole Earth Brands operates in a highly competitive market, facing rivals ranging from large food conglomerates to specialized health brands. The intense rivalry is fueled by the sector's rapid growth and increasing consumer demand for healthier options and sugar alternatives. For example, the global sweetener market continued its growth trajectory in 2023, but this expansion also brought more competitors vying for consumer loyalty through innovation and aggressive marketing.
The company's established brands, like Equal, benefit from brand recognition, but this advantage is constantly challenged by new entrants and evolving consumer preferences. In 2024, the plant-based food market alone was projected to exceed $160 billion by 2030, underscoring the crowded nature of the health-conscious food space and the need for continuous innovation to maintain market share.
High fixed costs in manufacturing and distribution create significant exit barriers, compelling companies to remain competitive even during periods of lower profitability. This dynamic, coupled with industry consolidation trends such as Whole Earth Brands' privatization in 2021, intensifies the competitive landscape as firms strategically position themselves for greater market share and efficiency.
| Metric | 2023 Data/Projection | Implication for Rivalry |
|---|---|---|
| Global Sweetener Market Growth | Continued growth (2023) | Attracts new entrants, intensifies competition |
| Plant-Based Food Market Projection | Over $160 billion by 2030 (2024 outlook) | High competition in a growing segment |
| Whole Earth Brands Privatization | 2021 | Strategic move to enhance competitive positioning |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Whole Earth Brands is significant, stemming from a broad spectrum of alternative sweeteners. Consumers have a wide array of choices, from natural options like stevia and monk fruit to artificial sweeteners such as aspartame and sucralose. In 2024, the global market for sugar substitutes was valued at approximately $11.7 billion, with projections indicating continued growth, highlighting the competitive landscape.
Beyond direct sugar replacements, other categories also pose a threat. Sugar alcohols like erythritol and xylitol, while often grouped with sweeteners, offer different taste profiles and functionalities that can appeal to certain consumer segments. Furthermore, the ongoing innovation in food science continually introduces novel ingredients that could potentially disrupt the market for plant-based sweeteners.
Consumers are increasingly opting for whole food alternatives like fruits, fruit purees, honey, and maple syrup to replace manufactured sweeteners. This shift directly challenges the market for processed sweeteners, impacting companies such as Whole Earth Brands.
The growing popularity of 'whole, unprocessed plant foods' signifies a significant threat, as these natural options fulfill the same functional need as traditional sweeteners. For instance, the global market for natural sweeteners is projected to reach $27.3 billion by 2027, indicating a strong consumer preference for these alternatives.
A significant and growing threat to Whole Earth Brands comes from consumers actively reducing or eliminating added sugars and sweeteners from their diets. This trend means that even if a product offers a sugar substitute, many consumers are now seeking options with no added sweetness at all, effectively bypassing the entire category of sweeteners.
For instance, a 2024 report indicated that over 60% of consumers are actively trying to cut down on sugar intake, a figure that has steadily climbed from previous years. This suggests that the market for sugar substitutes, while growing, faces an even larger, more fundamental shift in consumer preference toward unsweetened products.
Price-Performance Trade-off of Substitutes
The attractiveness of substitute products for Whole Earth Brands' offerings is heavily influenced by the price-performance trade-off. Consumers weigh the cost against perceived benefits like taste, health impact, and calorie count.
While natural sweeteners might command a premium, artificial sweeteners often present a zero-calorie, lower-cost alternative. Traditional sugar, a ubiquitous substitute, remains the most budget-friendly option for many consumers.
This dynamic means consumer choices can shift significantly based on individual priorities, with cost-consciousness or health goals driving the adoption of different substitutes.
- Natural Sweeteners: Often perceived as healthier but can carry a higher price point, impacting consumer adoption for budget-conscious buyers.
- Artificial Sweeteners: Offer a compelling zero-calorie proposition at a generally lower cost than natural alternatives, appealing to calorie-aware consumers.
- Traditional Sugar: Remains a dominant substitute due to its low cost and widespread availability, posing a significant challenge for premium-priced alternatives.
- Consumer Prioritization: The decision between these substitutes hinges on whether consumers prioritize price, health benefits, or taste, creating a complex competitive landscape.
Evolving Health Perceptions and Research on Sweeteners
The threat of substitutes for Whole Earth Brands' products, particularly its sweeteners, is significantly influenced by evolving health perceptions and ongoing scientific research. Shifts in public opinion regarding the safety and health impacts of both artificial and natural sweeteners can dramatically alter consumer choices. For instance, growing concerns about certain artificial sweeteners, or even some natural alternatives, can push consumers to seek out other options or even return to traditional sugar, or opt out of sweeteners altogether.
This dynamic creates a tangible threat. Consider the market for low-calorie sweeteners; a significant portion of consumers are actively seeking out products perceived as healthier. In 2024, reports indicated a continued rise in consumer demand for "clean label" ingredients, with many actively scrutinizing ingredient lists for artificial additives. This trend directly impacts the appeal of traditional artificial sweeteners, making natural alternatives or even sugar itself more attractive to a segment of the market, depending on the specific health narrative gaining traction.
- Consumer preference shifts: Public perception of sweetener safety is a key driver, impacting demand for products like Whole Earth Brands' stevia-based offerings.
- Research influence: New scientific studies on sweeteners can rapidly change market attractiveness, potentially favoring or disfavoring certain ingredients.
- "Clean label" trend: In 2024, a significant consumer push for natural and recognizable ingredients continues, posing a challenge to artificial sweeteners.
- Market volatility: The sweetener market faces ongoing disruption as consumers react to health news and research, creating an unpredictable substitute landscape.
The threat of substitutes remains a potent force for Whole Earth Brands, driven by a diverse and evolving consumer landscape. The availability of numerous sweeteners, from established artificial options to emerging natural alternatives, means consumers have ample choices. In 2024, the global sugar substitute market was valued at approximately $11.7 billion, underscoring the intense competition and the constant need for differentiation.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | Consumer Appeal Drivers | Impact on Whole Earth Brands |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Sweeteners (Stevia, Monk Fruit) | Perceived health benefits, plant-based | Health consciousness, "clean label" trend | Direct competition, potential for premium pricing |
| Artificial Sweeteners (Aspartame, Sucralose) | Zero/low calorie, cost-effective | Calorie reduction, budget-consciousness | Price pressure, potential health concerns |
| Traditional Sugar | Low cost, widely available, familiar taste | Cost, taste preference, habit | Dominant benchmark, price sensitivity |
| Whole Foods (Fruits, Honey) | Unprocessed, natural sweetness | Holistic health, avoidance of additives | Bypasses sweetener category entirely |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the global food and beverage sector, especially with branded products like Whole Earth Brands, demands significant upfront capital. This includes building or acquiring manufacturing plants, investing in research and development for new product lines, and funding extensive marketing campaigns to build brand recognition. For instance, establishing a new, modern food processing facility can easily cost tens of millions of dollars.
Beyond production, creating a robust distribution network to reach consumers worldwide is another major capital drain. This involves logistics, warehousing, and partnerships with retailers, all requiring substantial financial commitment. The sheer scale of investment needed to compete effectively makes it a formidable hurdle for aspiring companies.
Whole Earth Brands benefits from strong brand loyalty for its established products, such as Equal and Canderel, which have built significant consumer recognition over time. This loyalty makes it difficult for new entrants to capture market share without substantial investment in marketing and brand development to overcome existing consumer preferences.
Newcomers face a significant hurdle in establishing effective distribution channels and securing prominent shelf space in major retail locations globally. This existing network, built by Whole Earth Brands, represents a considerable barrier to entry, requiring new players to forge their own partnerships and logistics infrastructure.
Sourcing premium, consistent, and sustainable plant-based ingredients, particularly specialized sweeteners like stevia and monk fruit, presents a considerable challenge for newcomers. Whole Earth Brands, for instance, relies on established relationships with growers and processors to ensure a steady supply of these key components.
Developing unique formulations that deliver appealing taste and adhere to clean label standards requires substantial investment in research and development, often involving proprietary technologies. This R&D intensity acts as a significant barrier, making it difficult for new companies to quickly replicate the product quality and market appeal that established players like Whole Earth Brands have cultivated.
Regulatory Hurdles and Food Safety Standards
The food industry, including segments where Whole Earth Brands operates, faces significant regulatory hurdles. New entrants must comply with rigorous food safety standards, labeling requirements, and ingredient approval processes, which vary by region. For instance, in the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) enforces strict regulations, while the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) oversees similar matters in Europe. Navigating these complex and often costly regulatory landscapes can be a substantial barrier to entry, particularly for companies introducing novel ingredients or making specific health claims.
These regulatory requirements translate into significant upfront investment for new market participants. Obtaining necessary certifications and ensuring compliance with evolving standards demands considerable financial and human resources. For example, the cost of conducting extensive safety testing and securing approvals for new food additives or processing methods can easily run into hundreds of thousands, if not millions, of dollars. This financial burden acts as a deterrent, limiting the number of new companies that can realistically enter the market and compete with established players like Whole Earth Brands.
The complexity is further amplified when considering international markets. A new entrant aiming for global reach must satisfy the distinct regulatory frameworks of each target country. This often involves a lengthy and resource-intensive process of dossier preparation, submission, and review. The time lag associated with these approvals can delay market entry and impact a company's ability to capitalize on emerging trends, thereby protecting existing market share for established brands.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: New entrants can expect to spend significant capital on meeting food safety, labeling, and ingredient approval regulations.
- Time to Market: Navigating diverse international regulatory frameworks can add months or even years to a product's launch timeline.
- Ingredient Approval Challenges: Novel ingredients or those with specific health claims face particularly stringent and costly approval processes globally.
Potential for Retaliation by Incumbents
Existing players, including Whole Earth Brands, possess significant resources and established market standing. They can effectively deter new entrants through aggressive tactics like price wars, escalating marketing expenditures, or forging exclusive distribution partnerships. This capacity for retaliation raises the barrier to entry.
Whole Earth Brands' transition to a private entity in 2024 could be interpreted as a strategic maneuver. This move may aim to optimize operations and bolster its competitive stance in the face of evolving market dynamics and potential new market entrants.
The threat of new entrants is further moderated by the capital-intensive nature of the food and beverage sector, particularly in areas like sustainable sourcing and production. For instance, establishing the necessary infrastructure for plant-based product manufacturing can require substantial upfront investment.
- Incumbent Retaliation: Established companies can engage in price cuts or increased advertising to make it harder for newcomers.
- Whole Earth Brands' Strategy: Going private in 2024 might be a move to become more agile and competitive.
- Capital Requirements: Significant investment is often needed for production and distribution in the food industry.
The threat of new entrants into the branded food and beverage sector, where Whole Earth Brands operates, is generally considered moderate to high. This is primarily due to the significant capital required for manufacturing, distribution, and marketing, alongside strong brand loyalty enjoyed by established players.
Newcomers must overcome substantial barriers related to economies of scale, regulatory compliance, and securing prime retail placement. For example, the global food and beverage market is projected to reach over $8 trillion by 2025, indicating substantial revenue potential but also the scale of investment needed to capture even a small share.
Whole Earth Brands' position, strengthened by its 2024 transition to private ownership, allows for more focused strategic investments to maintain its competitive edge against potential new market participants.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Establishing manufacturing, R&D, and distribution networks demands tens of millions of dollars. | High barrier, requiring substantial funding. |
| Brand Loyalty | Established brands like Equal and Canderel have strong consumer recognition. | Difficult for new brands to gain market share without significant marketing investment. |
| Distribution Channels | Securing shelf space and logistics infrastructure is challenging. | Requires forging new partnerships and building infrastructure. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Compliance with food safety, labeling, and ingredient approvals varies by region. | Costly and time-consuming, especially for novel ingredients. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Whole Earth Brands Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial reports, industry-specific market research, and relevant trade publications. This blend of data allows for a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.
