Mahindra & Mahindra Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Mahindra & Mahindra Bundle
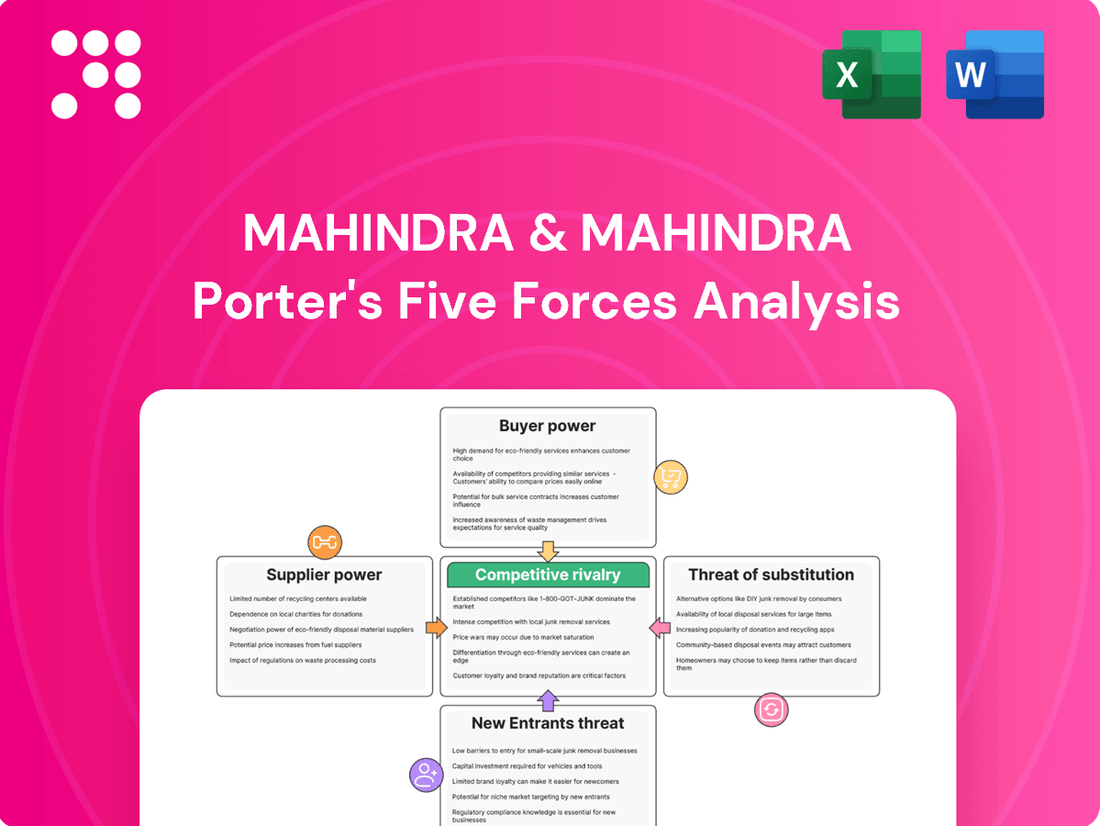
Mahindra & Mahindra's Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals a dynamic competitive landscape, highlighting moderate buyer power and the significant threat of substitutes in the light commercial vehicle segment. Understanding the intensity of rivalry and the bargaining power of suppliers is crucial for navigating this market effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Mahindra & Mahindra’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Mahindra & Mahindra (M&M) faces significant supplier bargaining power due to its reliance on a concentrated base for crucial components like engines and transmissions. This is particularly true for specialized parts where few suppliers exist, giving them leverage. For instance, the global semiconductor shortage in 2021-2022 significantly impacted the automotive industry, including M&M, as chip manufacturers could dictate terms and pricing due to limited alternatives and high demand.
Mahindra & Mahindra faces significant switching costs when changing suppliers for critical automotive components. These costs can include substantial investments in retooling manufacturing lines, rigorous new supplier quality assurance processes, and the inherent risk of production delays during the transition. For example, a switch in a key electronic control unit supplier might necessitate recalibrating entire vehicle systems, a process that is both time-consuming and expensive.
Although Mahindra has strategically worked to consolidate its supplier network and centralize procurement to gain economies of scale, this effort can inadvertently strengthen the bargaining power of its remaining, specialized suppliers. The intricate nature of integrating new vendors for highly technical parts, such as advanced engine management systems or specific sensor technologies, means that established suppliers with proven track records and deep integration into Mahindra's existing product development cycles often hold considerable leverage. This is particularly true for components requiring proprietary knowledge or specialized manufacturing capabilities, where finding readily available alternatives is challenging.
Suppliers providing highly differentiated or technologically advanced components, such as those crucial for electric vehicle (EV) battery technology or advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), wield significant bargaining power. Mahindra's strategic emphasis on these emerging technologies, including its significant investments in EV development, means its reliance on cutting-edge suppliers will only grow.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Mahindra & Mahindra's manufacturing processes, while less common, could significantly bolster supplier leverage. This scenario is more probable for suppliers possessing strong research and development capabilities and unique, proprietary technologies. For instance, a specialized component manufacturer with patented innovations could potentially decide to produce finished assemblies, directly competing with Mahindra.
Mahindra & Mahindra's strategic decision to locate its manufacturing facilities in close proximity to key suppliers is a deliberate measure to curb supplier power. This geographical advantage helps to minimize logistics expenses and shorten lead times, thereby creating a more integrated and efficient supply chain. By reducing dependency on external transportation and fostering closer relationships, Mahindra can better manage its supplier relationships and mitigate the risk of excessive supplier influence.
- Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers with advanced R&D and proprietary technology pose a greater risk of integrating forward, potentially manufacturing components currently produced by Mahindra.
- Mitigation Strategy: Mahindra's plant locations near essential suppliers reduce logistics costs and lead times, a tactic that also serves to diminish supplier bargaining power.
- Example Scenario: A supplier of advanced automotive sensors with unique patented technology might consider manufacturing the entire sensor module, directly impacting Mahindra's internal production.
Importance of Supplier to Mahindra's Business
For certain specialized suppliers, Mahindra & Mahindra's business can constitute a substantial portion of their revenue, granting Mahindra some leverage in negotiations. This is particularly true for suppliers whose product lines are highly tailored to Mahindra's needs.
Conversely, for large, globally diversified suppliers, Mahindra might represent only a small fraction of their overall client base. In such scenarios, Mahindra's individual importance to the supplier is diminished, which in turn reduces Mahindra's bargaining power.
Mahindra's strategic initiatives to optimize its supply chain, including efforts to enhance transparency and build stronger supplier partnerships, are crucial for effectively managing these supplier relationships and mitigating potential power imbalances.
- Supplier Dependence: Mahindra's reliance on specific component suppliers can influence negotiation outcomes.
- Supplier Concentration: The number of suppliers available for critical components impacts Mahindra's leverage.
- Switching Costs: The cost and complexity for Mahindra to switch suppliers affect their bargaining power.
- Supplier Profitability: The profitability of suppliers can influence their willingness to negotiate terms with Mahindra.
Mahindra & Mahindra (M&M) faces a moderate to high level of bargaining power from its suppliers, particularly for specialized and technologically advanced components. The company's strategic investments in areas like electric vehicles (EVs) and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) mean it relies on suppliers with cutting-edge technology, giving those suppliers significant leverage. For example, the global shortage of automotive chips in 2021-2022 demonstrated how critical component suppliers can dictate terms due to high demand and limited alternatives, impacting M&M's production schedules and costs.
| Factor | Mahindra & Mahindra's Position | Supplier Bargaining Power |
| Supplier Concentration | Relies on a concentrated base for crucial components like engines and transmissions. | High for specialized parts with few suppliers. |
| Switching Costs | High costs associated with retooling and quality assurance for new suppliers. | High, as M&M faces significant investment and risk in changing vendors. |
| Component Differentiation | Increasing reliance on suppliers of advanced EV battery technology and ADAS. | High, as these suppliers offer critical, unique technologies. |
| Supplier Profitability | Varies; large, diversified suppliers may have less dependence on M&M. | Lower for M&M when dealing with globally diversified suppliers. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Potential for suppliers with proprietary technology to integrate forward. | Moderate to High, especially for tech-centric suppliers. |
What is included in the product
Mahindra & Mahindra's Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the intense competitive rivalry, significant buyer bargaining power, and moderate threat of new entrants within the automotive sector, impacting its pricing and market strategy.
Instantly visualize competitive pressures with a clear, actionable Porter's Five Forces analysis for Mahindra & Mahindra Porter, simplifying complex market dynamics.
Effortlessly adapt the analysis to changing market conditions by swapping in new data, ensuring strategic relevance and informed decision-making.
Customers Bargaining Power
Mahindra & Mahindra caters to a broad spectrum of customers, from individual car buyers and farmers to large commercial fleet operators, impacting their bargaining power. For example, in the automotive segment, while individual buyers might have limited power, large fleet purchases can exert more influence on pricing and terms. In 2023, Mahindra's automotive division saw strong sales growth, indicating a healthy demand that can somewhat temper customer price sensitivity.
Customers in both the automotive and farm equipment sectors face a plethora of alternatives, significantly amplifying their bargaining power. This abundance of choice directly translates into greater leverage for buyers when making purchasing decisions.
Within the highly competitive Indian automotive market, customers have a wide array of options from major players like Maruti Suzuki, Tata Motors, and Hyundai. These manufacturers offer diverse product portfolios, ranging from entry-level hatchbacks to premium SUVs, often coupled with aggressive pricing strategies, further empowering consumers with choice.
For instance, in the passenger vehicle segment in India, as of early 2024, the market share distribution shows significant competition, with Maruti Suzuki leading, followed by Hyundai and Tata Motors, indicating that no single player dominates to the extent that customers lack alternatives.
Price sensitivity significantly impacts Mahindra & Mahindra, particularly in India's price-conscious markets. For instance, in the tractor segment, rural buyers often consider affordability as a primary decision factor. Mahindra's ability to offer competitive pricing, especially on its entry-level models, is key to capturing market share in these regions.
In 2023, the Indian automotive market saw a considerable focus on value-for-money propositions, with consumers actively comparing prices across brands. Mahindra's strategic pricing, including attractive financing options and a diverse product portfolio catering to different budget segments, helps mitigate the intense pressure from customers seeking lower prices.
Brand Loyalty
Mahindra & Mahindra enjoys a significant advantage due to robust brand loyalty, especially within its popular utility vehicle and tractor segments. This loyalty translates into high repurchase rates, demonstrating a strong customer preference for Mahindra products. For instance, in the fiscal year 2024, Mahindra's automotive segment saw sustained demand, with its popular Scorpio and XUV series continuing to perform well, reflecting this ingrained customer trust. This deep-seated loyalty acts as a crucial buffer, effectively dampening the bargaining power of customers by making them less sensitive to price changes or competitor offerings.
- Brand Loyalty in Key Segments: Mahindra's strong customer allegiance in utility vehicles and tractors significantly curbs customer bargaining power.
- High Repurchase Rates: Consistent repeat purchases underscore customer satisfaction and preference, allowing Mahindra to maintain pricing stability.
- Reduced Price Sensitivity: Loyal customers are less likely to switch brands based on minor price differences, enhancing Mahindra's pricing power.
- FY24 Performance Indicators: The sustained demand for models like the Scorpio and XUV series in FY24 highlights the effectiveness of Mahindra's brand building and customer retention strategies.
Customer Expectations for Innovation and Quality
Customers today have very high expectations for innovation and quality, especially in the automotive industry. The rapid advancements in electric vehicles and integrated technology mean buyers are constantly looking for the latest features and superior performance. This trend puts pressure on manufacturers like Mahindra to continuously innovate.
Mahindra's strategic response includes launching new models equipped with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and expanding its electric vehicle (EV) portfolio. For instance, the company has been investing heavily in its EV business, aiming to introduce several new electric SUVs by 2030. This proactive approach addresses the growing demand for sustainable and technologically advanced vehicles. However, it also means customers are empowered to demand even more, setting a higher bar for future product development and potentially influencing pricing and profit margins.
- Customer demand for advanced features: The automotive market sees a strong push for features like connected car technology and enhanced safety systems.
- Mahindra's EV investment: Mahindra plans to invest significantly in its electric mobility division, signaling a commitment to meeting evolving customer preferences for sustainable transportation.
- Impact on bargaining power: As customers become more informed and have access to a wider range of innovative options, their ability to negotiate better terms or switch to competitors increases.
The bargaining power of customers for Mahindra & Mahindra is influenced by several factors, including the availability of substitutes, price sensitivity, and brand loyalty. In the competitive Indian automotive market, customers have numerous choices from various manufacturers, which generally increases their leverage.
Mahindra's strong brand loyalty, particularly in its utility vehicle and tractor segments, helps to mitigate some of this customer power. For example, in FY2024, the sustained demand for models like the Scorpio and XUV series indicated strong customer trust. However, the increasing demand for technological advancements, such as in electric vehicles, means customers are also more informed and can exert pressure for innovation and better value.
| Factor | Impact on M&M's Bargaining Power | Supporting Data (as of early 2024/FY24) |
| Availability of Substitutes | Increases customer power | Highly competitive Indian auto market with brands like Maruti Suzuki, Hyundai, Tata Motors offering diverse options. |
| Price Sensitivity | Increases customer power | Price-conscious markets, especially in rural tractor segment; focus on value-for-money propositions. |
| Brand Loyalty | Decreases customer power | Strong loyalty in UV and tractor segments; high repurchase rates for models like Scorpio and XUV. |
| Demand for Innovation | Increases customer power | Customer expectations for EVs and advanced tech (ADAS); M&M's significant EV investment aims to meet this. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Mahindra & Mahindra Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete Mahindra & Mahindra Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape of the commercial vehicle sector. You'll gain insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. The document you see here is precisely what you'll download immediately after purchase, offering a ready-to-use strategic assessment.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Mahindra & Mahindra contends with a crowded field of rivals across its varied business interests. In the automotive arena, it faces strong competition from domestic giants like Maruti Suzuki and Tata Motors, alongside international powerhouse Hyundai Motor India Ltd. These companies vie for market share with a wide range of vehicles and aggressive pricing strategies.
The farm equipment sector presents a similarly competitive landscape. Mahindra & Mahindra’s key rivals here include TAFE and Escorts Group, both significant Indian manufacturers. Furthermore, global players such as John Deere and CNH Industrial maintain a strong presence, offering advanced technology and extensive distribution networks, intensifying the rivalry for agricultural machinery sales.
The Indian automotive market, especially the SUV segment, is booming, and this rapid growth naturally fuels intense competition. As more consumers opt for SUVs, companies like Mahindra are battling fiercely for a larger slice of this expanding pie.
Mahindra & Mahindra has been a standout performer, reporting robust growth in its SUV sales. For instance, in the fiscal year 2024 (FY24), Mahindra's automotive division saw a remarkable 25% year-on-year growth in total vehicle sales, with SUVs being a primary driver, significantly outperforming the broader industry's expansion.
Mahindra & Mahindra faces intense competition, driving a strong focus on product differentiation and innovation. The company is actively introducing new and updated vehicle models, including its electric SUV lineup, to stand out in a crowded market and meet changing customer demands.
In 2024, Mahindra launched the XUV400 electric SUV, showcasing advanced features and a competitive range, aiming to capture a larger share of the burgeoning EV market. This strategy of continuous product enhancement is crucial for maintaining market relevance and attracting discerning buyers.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
Mahindra & Mahindra operates in industries with substantial fixed costs. The automotive sector, for instance, requires massive investments in manufacturing facilities, research and development for new models, and extensive distribution and service networks. Similarly, the farm equipment business demands significant capital for production lines and technological advancements. These high upfront costs mean that companies must achieve high sales volumes to break even and become profitable.
This cost structure naturally fuels intense competition. To recoup their investments and spread the fixed costs over a larger production base, companies like Mahindra are incentivized to compete aggressively on price and market share. This can lead to price wars and a constant drive to innovate and capture customer loyalty, as any underutilization of capacity directly impacts profitability. For example, in 2023, the Indian automotive industry saw a significant push in production as companies aimed to optimize their manufacturing capacity amidst evolving demand patterns.
Furthermore, high exit barriers exacerbate this competitive rivalry. Once a company has invested heavily in specialized plants and equipment, it becomes very difficult and costly to divest or repurpose these assets if the business segment becomes unprofitable. This means that even during downturns, companies are often compelled to stay in the market and continue competing, rather than exiting, which can prolong periods of intense rivalry and pressure on margins.
The implications for Mahindra & Mahindra are clear:
- High fixed costs necessitate a focus on operational efficiency and sales volume to achieve profitability.
- Intense competition arises from the need to utilize capacity and spread R&D and manufacturing expenses.
- Significant exit barriers mean companies remain in the market, intensifying rivalry even in challenging economic conditions.
- Mahindra must continuously innovate and manage its cost structure to maintain a competitive edge in these capital-intensive sectors.
Market Share and Leadership Positions
Mahindra & Mahindra (M&M) commands a formidable presence, notably as the world's largest tractor producer by volume. This leadership extends to significant market share within India's SUV and electric three-wheeler sectors. However, this strong standing fuels intense rivalry, with competitors actively seeking to gain ground.
The competitive landscape is dynamic, with players like Maruti Suzuki consistently vying for dominance. For instance, in the fiscal year 2025, Maruti Suzuki experienced a slight dip in its market share, highlighting the ongoing battle for customer preference and market penetration.
- World's largest tractor manufacturer by volume.
- Significant player in Indian SUV and electric three-wheeler markets.
- Faces intense competition from rivals aiming to capture market share.
- Maruti Suzuki's market share dip in FY25 exemplifies competitive pressures.
Mahindra & Mahindra faces a highly competitive environment across its diverse business segments, particularly in automotive and farm equipment. The company's leadership in tractor volumes and strong position in India's SUV market are constantly challenged by both domestic and international rivals. This intense rivalry is further amplified by high fixed costs and significant exit barriers inherent in these capital-intensive industries.
Competitors like Maruti Suzuki and Hyundai in the automotive sector, and TAFE and John Deere in farm equipment, actively employ aggressive pricing and innovation strategies. For example, Maruti Suzuki's market share fluctuations in FY25 underscore the continuous battle for customer preference. Mahindra's response includes strategic product launches, such as the XUV400 electric SUV in 2024, to differentiate its offerings and maintain market relevance.
The automotive industry's growth, especially in the SUV segment, fuels this competition, compelling companies to optimize production capacity and manage costs effectively. Mahindra's FY24 automotive division growth of 25% year-on-year demonstrates its ability to navigate this landscape, but the need for continuous innovation and operational efficiency remains paramount.
| Rival | Segment | Key Competitive Action/Status (as of 2024/FY25) |
|---|---|---|
| Maruti Suzuki | Automotive | Market share fluctuations in FY25, continuous product offerings. |
| Hyundai Motor India Ltd. | Automotive | Strong international presence, aggressive pricing and product portfolio. |
| TAFE | Farm Equipment | Significant Indian manufacturer, competes on technology and distribution. |
| John Deere | Farm Equipment | Global player, advanced technology, extensive distribution networks. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For urban commuters, the availability of public transportation and ride-sharing services presents a viable alternative to owning a personal vehicle, potentially dampening demand for Mahindra & Mahindra's passenger car segment. For instance, in India, the ride-sharing market experienced significant growth, with companies like Ola and Uber expanding their fleets and service areas, making car ownership less essential for many city dwellers.
However, this threat is somewhat contained for Mahindra due to its substantial market share in utility vehicles and commercial segments. These vehicles are often purchased for specific functional needs, such as cargo transport or agricultural use, where public transport or ride-sharing are not practical substitutes. Mahindra's Scorpio and Bolero models, for example, remain popular in rural and semi-urban areas for their ruggedness and utility, areas less penetrated by these substitute services.
The presence of a strong used vehicle market significantly impacts the new vehicle segment for companies like Mahindra & Mahindra. In 2024, the Indian used car market continued its robust growth, with estimates suggesting it could reach over 5 million units annually. This offers a more budget-friendly option for consumers, directly competing with new vehicle sales, especially for those prioritizing cost-effectiveness.
For Mahindra's Porter, the availability of pre-owned vehicles, including tractors and commercial vehicles, presents a clear substitute. Price-sensitive buyers, a significant demographic in India, may opt for a used Porter instead of a new one, thereby limiting Mahindra's market share and pricing power in the new segment. The used vehicle market's expansion, fueled by easier financing options and increased trust in certified pre-owned programs, amplifies this threat.
While advanced farm equipment from companies like Mahindra & Mahindra is becoming more prevalent, traditional farming methods, particularly those relying heavily on manual labor, can still serve as a substitute. This is especially true for small and marginal farmers who may face financial limitations in acquiring modern machinery. For instance, in 2023, a significant portion of agricultural work in India still involved manual labor, highlighting the persistent presence of these alternative methods.
However, several factors are actively diminishing the viability of these substitutes. Increasing labor shortages, driven by rural-to-urban migration, are making manual labor more expensive and less reliable for farmers. Furthermore, government initiatives aimed at promoting agricultural mechanization, such as subsidies and training programs, are actively encouraging the adoption of modern farm equipment, thereby reducing the attractiveness of traditional, labor-intensive practices.
Non-Traditional Mobility Solutions (Automotive)
The rise of micro-mobility solutions like electric scooters and bicycles, particularly in urban centers, poses a potential long-term substitute threat. While these currently have a limited direct impact on Mahindra's primary SUV and commercial vehicle markets, their growing adoption signifies a shift in personal transportation preferences.
Mahindra is proactively addressing this evolving landscape through strategic investments in electric mobility. For instance, the company's commitment to electric vehicles, including its planned investments of over ₹10,000 crore in EV manufacturing and infrastructure by 2027, demonstrates a forward-looking approach to counter potential substitution.
- Emerging Non-Traditional Mobility: Electric scooters, e-bikes, and shared mobility platforms are gaining traction, especially in urban areas.
- Limited Direct Impact on Core Segments: These substitutes currently do not directly compete with Mahindra's core SUV and commercial vehicle offerings.
- Mahindra's EV Investment: The company is investing heavily in electric mobility to adapt to changing consumer preferences and mitigate future substitution risks.
- Long-Term Substitution Threat: The increasing popularity of these alternatives represents a potential long-term challenge to traditional vehicle sales.
Rental or Leasing of Equipment (Farm Equipment)
The rental and leasing of farm equipment pose a significant threat to manufacturers like Mahindra & Mahindra. Farmers, especially those with smaller operations or tighter budgets, frequently choose to rent or lease machinery instead of buying it outright. This practice directly impacts the demand for new tractor and equipment sales.
This trend is particularly relevant in markets where capital expenditure is a major consideration for farmers. For instance, in India, where a substantial portion of agricultural landholdings are small, rental markets for tractors and harvesters have seen considerable growth. Reports from 2023 and early 2024 indicate a steady increase in equipment rental services, driven by cost-effectiveness and flexibility for farmers.
While this might seem like a direct reduction in sales, it also opens avenues for Mahindra. The company's financial services division could expand its leasing offerings, or new business models focused on equipment-sharing platforms could emerge. The key is to adapt to this evolving customer preference.
- Rental Market Growth: The global farm equipment rental market is projected to grow, offering farmers flexibility and reducing upfront costs.
- Impact on Sales: Increased reliance on rentals can dampen the demand for new equipment purchases, affecting unit sales volumes for manufacturers.
- Opportunity for Leasing: Mahindra can leverage its financial services to offer competitive leasing solutions, capturing revenue from farmers who prefer not to own equipment outright.
- Emerging Business Models: The rise of equipment-sharing platforms presents another potential area for Mahindra to explore, either through direct participation or partnerships.
The threat of substitutes for Mahindra & Mahindra is multifaceted, encompassing alternative transportation and farming methods. While ride-sharing and public transport offer substitutes for personal vehicles in urban settings, Mahindra's strength in utility vehicles and commercial segments, catering to specific functional needs, mitigates this risk. The used vehicle market, however, presents a more direct challenge, with its continued expansion in 2024 offering budget-friendly alternatives that impact new vehicle sales across segments.
Furthermore, traditional farming methods persist as substitutes for modern machinery, particularly for small farmers. Yet, factors like increasing labor costs and government support for mechanization are diminishing the appeal of these older practices. Emerging micro-mobility solutions also represent a long-term substitution threat, prompting Mahindra's significant investment in electric vehicles to stay ahead of shifting consumer preferences.
The rental and leasing of farm equipment also directly competes with new sales, especially for cost-conscious farmers. This trend, evident in India's growing equipment rental market, necessitates adaptation from manufacturers like Mahindra, potentially through expanded leasing offerings or participation in equipment-sharing platforms.
| Substitute Category | Mahindra Segment Impacted | 2024 Market Trend/Data | Mahindra's Response/Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ride-sharing/Public Transport | Passenger Vehicles | India's ride-sharing market continues robust expansion. | Focus on UVs and commercial vehicles with specific functional needs. |
| Used Vehicle Market | All Vehicle Segments | Indian used car market projected to exceed 5 million units annually. | Leveraging financial services for new vehicle sales, exploring certified pre-owned programs. |
| Traditional Farming Methods | Farm Equipment | Significant use of manual labor in Indian agriculture persists. | Promoting mechanization through subsidies and training programs. |
| Micro-mobility (e-scooters, e-bikes) | Passenger Vehicles (long-term) | Growing adoption in urban centers signifies preference shift. | Strategic investment in electric mobility (over ₹10,000 crore by 2027). |
| Farm Equipment Rental/Leasing | Farm Equipment | Steady growth in equipment rental services in India. | Expanding leasing offerings via financial services, exploring equipment-sharing models. |
Entrants Threaten
The automotive and farm equipment sectors, where Mahindra & Mahindra operates, demand immense upfront capital. Establishing research and development, building state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, and creating robust distribution and service networks all necessitate billions of dollars. For instance, a new automotive plant can easily cost upwards of $1 billion, a figure that presents a formidable hurdle for potential new players.
Mahindra & Mahindra's formidable brand loyalty, especially in its core segments like tractors and utility vehicles, presents a significant barrier to new entrants. This loyalty is built over decades and reinforced by a vast, established distribution and after-sales service network spanning India and international markets.
Newcomers would face immense challenges in replicating Mahindra's reach and customer trust, requiring substantial capital investment and a long-term commitment to build a comparable presence. For instance, in the fiscal year 2023-24, Mahindra's automotive segment alone saw a significant increase in sales, underscoring the strength of its market penetration.
The automotive and farm equipment industries face substantial regulatory hurdles, acting as a significant barrier for potential new entrants. Mahindra & Mahindra, for instance, must adhere to stringent emission standards like BS-VI in India and similar global regulations, alongside evolving safety norms and manufacturing policies. Successfully navigating these complex requirements and securing necessary government approvals often demands significant capital investment and specialized expertise, making it difficult for newcomers to enter the market.
Access to Technology and Intellectual Property
Developing cutting-edge technologies, such as electric vehicle powertrains and autonomous driving systems, demands substantial research and development expenditure and access to proprietary intellectual property. Mahindra's ongoing investment in R&D, exemplified by its commitment to electric mobility solutions, establishes a significant hurdle for potential new competitors aiming to enter the automotive sector.
Mahindra & Mahindra's strategic investments in advanced technology and its robust intellectual property portfolio act as a formidable barrier to entry for new players. For instance, the company's significant push into electric vehicles, with substantial capital allocation towards battery technology and charging infrastructure, requires new entrants to match these investments to compete effectively. In 2023, Mahindra announced plans to invest over ₹1,000 crore in its electric vehicle business, highlighting the scale of resources needed.
- High R&D Investment: New entrants must commit billions to develop comparable technologies, a significant deterrent.
- Intellectual Property Protection: Mahindra's patents on key technologies create legal and operational barriers for those without similar IP.
- Technological Expertise: The specialized knowledge and skilled workforce required to innovate in areas like AI and advanced manufacturing are difficult and time-consuming to replicate.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Existing players like Mahindra & Mahindra leverage significant economies of scale in areas such as manufacturing, raw material procurement, and research and development. This allows them to achieve lower per-unit production costs, a critical advantage in the competitive automotive sector. For instance, in fiscal year 2024, Mahindra & Mahindra's consolidated revenue reached INR 257,131 crore, reflecting substantial operational volume.
New entrants would find it challenging to match these cost efficiencies without achieving comparable production volumes. This disparity in cost structures makes it difficult for new players to compete effectively on price against established manufacturers like Mahindra. The experience curve, where costs decrease with cumulative production, further solidifies the advantage of incumbents.
- Economies of Scale: Mahindra & Mahindra benefits from bulk purchasing and optimized production lines, reducing per-unit costs.
- Experience Curve: Accumulated production knowledge leads to greater efficiency and lower costs over time for established players.
- Cost Disadvantage for Newcomers: New entrants face higher initial costs due to smaller scale and lack of accumulated experience.
- Pricing Pressure: The cost advantage of incumbents puts significant pricing pressure on potential new market entrants.
The threat of new entrants for Mahindra & Mahindra is moderate, primarily due to the substantial capital requirements and established brand loyalty in its key automotive and farm equipment sectors. Navigating complex regulatory landscapes and replicating extensive distribution networks also pose significant challenges for newcomers.
Mahindra's significant investments in R&D, particularly in electric vehicle technology, and its protected intellectual property further solidify its competitive position. These factors create high barriers, making it difficult and costly for new companies to enter and compete effectively in the market.
The company's economies of scale in manufacturing and procurement allow for cost efficiencies that new entrants would struggle to match initially, putting them at a pricing disadvantage.
For example, Mahindra's consolidated revenue in FY2024 was INR 257,131 crore, indicating the scale of operations required to achieve cost competitiveness.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Mahindra & Mahindra leverages data from their annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research reports. We also incorporate information from automotive trade publications and government economic data to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
