Insulet Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Insulet Bundle
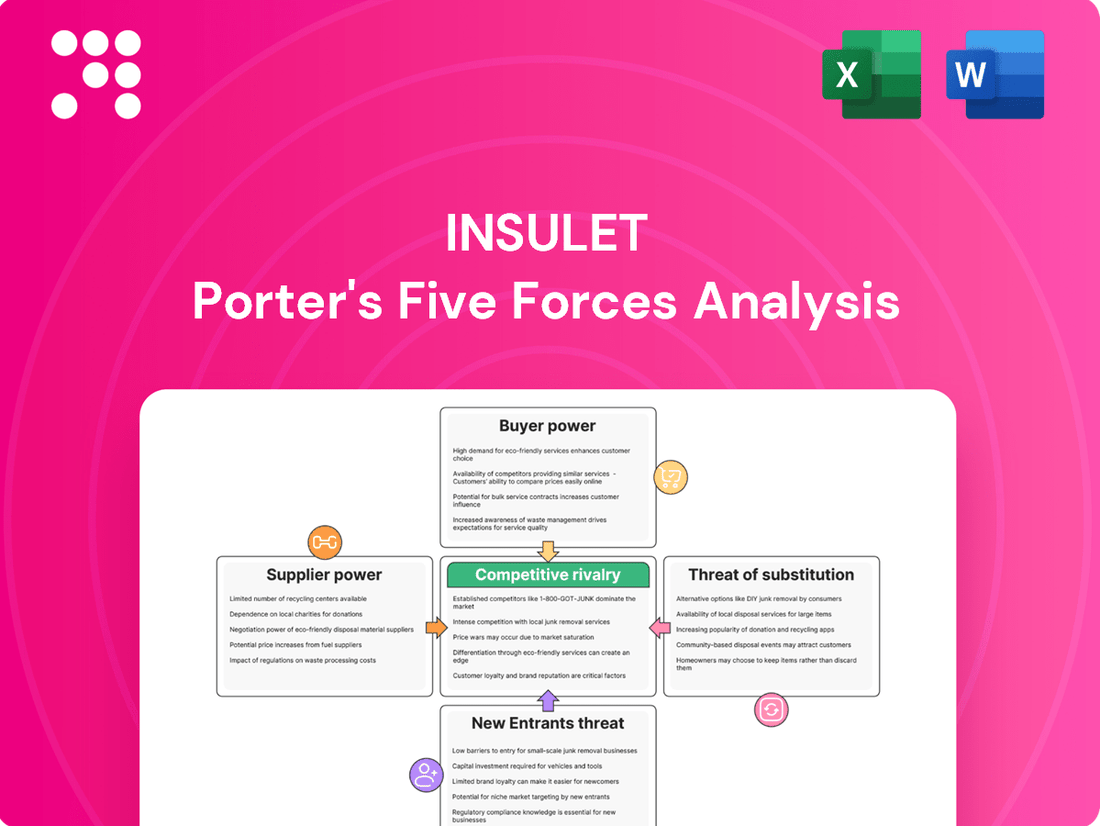
Insulet navigates a dynamic diabetes management landscape, facing intense rivalry and the ever-present threat of new entrants. Understanding the bargaining power of both buyers and suppliers is crucial for sustained growth.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Insulet’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Insulet's reliance on highly specialized components, such as the sensors and micro-electronics essential for its Omnipod system, places it in a potentially vulnerable position. These critical parts are often sourced from a select group of niche suppliers.
This dependence on a limited supplier base can grant these specialized providers significant bargaining power. They can leverage their unique offerings to influence pricing and dictate supply terms, which could lead to increased production costs for Insulet. The scarcity of readily available alternatives for these sophisticated components further solidifies the suppliers' leverage.
Suppliers possessing proprietary technology or patents for crucial components of Insulet's Omnipod system wield significant bargaining power. This exclusivity means Insulet faces substantial costs and extended timelines to develop or source alternatives if these suppliers dictate terms. For instance, if a key sensor technology is patented, Insulet's ability to negotiate pricing or supply is directly impacted, as seen in the medical device sector where specialized components often carry premium pricing due to R&D investment and regulatory hurdles.
A limited supplier base for critical components in the medical device sector, including those essential for Insulet's insulin delivery systems, significantly strengthens supplier bargaining power. When only a handful of manufacturers can meet the stringent quality and regulatory demands for specialized parts, these suppliers gain considerable leverage.
This concentration means Insulet faces fewer alternatives, allowing suppliers to dictate terms, influence pricing, and potentially control delivery schedules. For instance, in 2024, the medical device industry continued to grapple with supply chain disruptions, particularly for advanced materials and microelectronics, which are vital for Insulet's products. This environment inherently empowers suppliers who can reliably provide these high-demand, specialized inputs.
High Switching Costs for Insulet
Switching suppliers for critical components of Insulet's Omnipod system presents significant hurdles. These include the substantial costs and risks associated with redesigning the product, re-validating materials, and navigating intricate regulatory approval processes.
These high switching costs inherently strengthen the bargaining power of Insulet's existing suppliers. It becomes more challenging for Insulet to negotiate favorable terms or switch to alternative suppliers when faced with unfavorable conditions from current ones.
The process of onboarding new suppliers for such specialized medical devices is often extensive and time-consuming, further entrenching the power of established suppliers who already meet Insulet's stringent requirements.
- High Switching Costs: Redesign, material re-validation, and regulatory approvals are major deterrents to changing suppliers.
- Supplier Power: Insulet's dependence on specialized components limits its leverage in price negotiations.
- Operational Risk: Disruptions from a supplier change could impact product availability and patient care.
Potential for Forward Integration by Suppliers
The potential for suppliers to integrate forward into Insulet's market, meaning they could start manufacturing competing insulin delivery systems themselves, represents a theoretical, though less common, avenue for increased supplier bargaining power. If a critical supplier had the capacity and strategic inclination to become a direct competitor, they could leverage this possibility to negotiate more favorable terms with Insulet. This underlying threat of vertical integration by a supplier adds a layer of subtle influence to their negotiating position.
Insulet faces significant supplier bargaining power due to its reliance on highly specialized, proprietary components for its Omnipod system. The limited number of qualified suppliers for these critical parts, combined with high switching costs including redesign and regulatory re-validation, grants these providers considerable leverage. This situation was underscored in 2024 by ongoing supply chain challenges for advanced materials and microelectronics in the medical device sector, which further empowered reliable suppliers.
| Factor | Impact on Insulet | Supplier Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Components | High dependence on niche suppliers for sensors and micro-electronics. | Suppliers can dictate terms and pricing due to unique offerings. |
| Limited Supplier Base | Few manufacturers meet stringent quality and regulatory demands. | Suppliers have increased control over delivery and pricing. |
| High Switching Costs | Significant expenses and time for redesign, re-validation, and regulatory approvals. | Insulet is less able to negotiate or switch suppliers. |
| Proprietary Technology | Patented components limit Insulet's ability to find alternatives. | Suppliers can command premium pricing and favorable terms. |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for Insulet dissects the competitive intensity within the diabetes management device market, examining supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing players.
Instantly assess competitive pressures and identify strategic opportunities to optimize Insulet's market position and alleviate pain points related to market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of customers in the insulin delivery market is significantly influenced by the availability of alternative methods. Patients managing diabetes have a spectrum of choices beyond Insulet's Omnipod, including traditional multiple daily injections (MDI), other tethered insulin pumps, and increasingly sophisticated smart insulin pens. This variety means individuals are not locked into a single solution, allowing them to compare features, costs, and ease of use.
For instance, the market for insulin pens has seen innovation with smart pens that track dosage and timing, offering a less invasive option than pumps. Similarly, established pump manufacturers continue to offer tethered systems that may appeal to different patient preferences or insurance formularies. This competitive landscape directly empowers customers, as they can switch to a more suitable or cost-effective delivery method if Insulet's offerings do not meet their evolving needs or financial considerations.
The bargaining power of customers, particularly in the context of payers like insurance companies and government healthcare programs, is a significant force for Insulet. These entities dictate which insulin delivery systems are approved and at what price, directly influencing patient access and out-of-pocket costs. Their negotiating leverage with manufacturers like Insulet can steer patient choices, making them a powerful intermediary.
In 2024, the healthcare landscape continues to see payers exert considerable influence. For instance, Medicare and private insurers negotiate reimbursement rates for durable medical equipment, which includes insulin pumps. Any shift in these reimbursement policies favoring competing technologies could directly impact Insulet's market share by making alternative solutions more financially attractive to patients.
Patients and their healthcare providers are more informed than ever about diabetes management technologies. Digital health solutions and easily accessible medical information mean customers can readily compare products like Insulet's Omnipod against competitors, scrutinizing features, benefits, and costs. This heightened awareness directly translates into increased bargaining power.
For instance, a 2024 report indicated that over 70% of patients actively research their treatment options online before consulting a doctor, a significant jump from previous years. This access to comprehensive data empowers them to negotiate more effectively, demanding specific features or better pricing, thereby increasing Insulet's customer bargaining power.
Switching Costs for Patients
Switching from one insulin pump system to another, or even from multiple daily injections (MDI) to a pump, can present a learning curve for patients. This often involves training, adapting to new routines, and navigating potential changes in insurance coverage. For instance, in 2024, a patient transitioning to a new pump system might spend several hours in training sessions and require a period of adjustment to integrate the device seamlessly into their daily life.
The perceived ease or difficulty of these transitions directly impacts patient bargaining power. If switching costs are low, or if competing technologies offer demonstrably superior benefits, patients may feel more empowered to explore and adopt alternative products. This willingness to switch can pressure existing providers to maintain competitive pricing and service levels.
- Learning Curve: Patients often require dedicated time and training to become proficient with new insulin pump technologies.
- Routine Adjustment: Adapting to a new device can involve changes in daily schedules, meal planning, and physical activity.
- Insurance Navigation: Securing coverage for a new pump system can involve administrative hurdles and potential out-of-pocket expenses.
- Technological Appeal: Significant advancements in competing systems can lower the perceived switching costs for patients seeking better outcomes.
Growing Focus on Convenience and Discretion
Insulet's Omnipod is designed for discretion and convenience, a major draw for users. However, if competitors emerge offering similar or superior ease of use, comfort, or integration with other digital health tools, customers gain leverage. The market is seeing a growing emphasis on solutions that seamlessly integrate into daily life, meaning innovative competitive products can significantly boost customer bargaining power.
For instance, advancements in wearable technology and connected health platforms by rivals could present compelling alternatives to the Omnipod. In 2024, the digital health market continued its rapid expansion, with wearable device shipments projected to reach over 1.1 billion units globally, highlighting the increasing customer expectation for integrated and user-friendly health management solutions.
- Convenience is Key: Customers increasingly seek medical devices that are unobtrusive and easy to manage.
- Competitive Innovation: The development of similar tubeless or discreet delivery systems by competitors directly challenges Insulet's market position.
- Digital Integration: The ability of competing devices to connect with broader digital health ecosystems can enhance their appeal and customer bargaining power.
- Market Trends: The strong growth in the wearable tech sector in 2024 underscores the demand for lifestyle-integrated health solutions.
The bargaining power of customers in the insulin delivery market is substantial, driven by the availability of diverse alternatives and increasing patient education. In 2024, over 70% of patients actively researched treatments online, empowering them to compare features and costs, which directly influences their ability to negotiate with providers like Insulet. This informed decision-making, coupled with the potential for switching to competing systems like smart insulin pens or other pump technologies, significantly amplifies customer leverage.
Payers, including insurance companies and government programs, also wield considerable bargaining power. Their decisions on reimbursement rates for devices like Insulet's Omnipod can make certain technologies more or less financially attractive to patients. For example, Medicare and private insurers' negotiations in 2024 on durable medical equipment pricing can directly impact patient access and choice, thereby increasing customer bargaining power by favoring cost-effective alternatives.
The ease of switching between insulin delivery systems is another critical factor. While a learning curve exists, advancements in competitor technologies and the growing demand for integrated digital health solutions can lower perceived switching costs. The global wearable tech market's expansion in 2024, with shipments exceeding 1.1 billion units, highlights customer expectations for user-friendly, lifestyle-integrated health management, which can pressure Insulet to remain competitive on features and pricing.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of Alternatives | High | Smart pens and other pump systems offer direct competition. |
| Customer Information & Research | High | >70% of patients research treatments online, increasing informed choices. |
| Payer Influence (Reimbursement) | High | Insurers negotiate pricing, impacting patient access to devices. |
| Switching Costs (Learning Curve) | Moderate | While training is needed, tech advancements can reduce perceived switching costs. |
| Convenience & Digital Integration | Increasing | Demand for user-friendly, connected health solutions grows. |
Same Document Delivered
Insulet Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Insulet Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You'll gain a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the insulin delivery device market.
The document displayed here is the part of the full version you’ll get—ready for download and use the moment you buy. This in-depth analysis will equip you with critical insights into Insulet's strategic positioning and the external factors shaping its industry.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Insulet operates in a highly competitive arena, facing formidable rivals like Medtronic and Tandem Diabetes Care. These established companies offer their own insulin pump systems and continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), directly challenging Insulet for market share and customer loyalty.
The intensity of this rivalry means Insulet must continually innovate and focus on patient acquisition and retention strategies. For instance, Tandem Diabetes Care reported strong revenue growth in 2023, highlighting the dynamic nature of this market and the need for Insulet to maintain its competitive edge.
The diabetes technology market is a hotbed of innovation, with companies like Insulet constantly pushing the boundaries of automated insulin delivery (AID) systems and continuous glucose monitoring (CGM). This rapid pace means new, improved products, such as smaller insulin pumps and longer-lasting sensors, are frequently introduced, fueling intense competition. For instance, the global diabetes device market was valued at approximately $53.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, driven by these technological leaps.
The diabetes device market is expanding due to rising diabetes rates, but acquiring new patients, particularly those moving from manual insulin injections, remains a fierce battleground. Companies are heavily promoting their products and pursuing broader approvals, such as for type 2 diabetes, to secure a bigger slice of this growing patient population.
Insulet's first-quarter 2025 performance highlights strong uptake of its Omnipod system, demonstrating its effectiveness in navigating this competitive landscape and capturing market share.
Product Differentiation and Ecosystem Integration
Companies in the insulin delivery market, including Insulet, are heavily focused on differentiating their products. This often involves unique design elements, such as Insulet's tubeless Omnipod system, alongside advanced features like smartphone connectivity and seamless integration with continuous glucose monitors (CGMs).
The competitive landscape is increasingly shaped by the development of comprehensive, integrated ecosystems. These ecosystems combine hardware devices with digital health platforms, aiming to provide a holistic management solution for diabetes patients and their healthcare providers. This integration is a critical factor in winning customer loyalty and heightening the rivalry among established players and emerging innovators.
- Product Differentiation: Insulet's Omnipod DASH and Omnipod 5 systems offer tubeless insulin delivery, a key differentiator from traditional insulin pumps with tubing.
- Ecosystem Integration: The Omnipod 5 system integrates with Dexcom CGMs, allowing for automated insulin delivery adjustments based on glucose readings, a significant competitive advantage.
- Market Impact: By 2024, the demand for integrated diabetes management solutions continues to grow, pushing competitors to enhance their connectivity and user experience features to remain competitive.
Aggressive Marketing and Strategic Partnerships
Insulet operates in a market where competitors frequently launch aggressive marketing campaigns and present clinical trial data to capture market share. For example, Tandem Diabetes Care has actively promoted its t:slim X2 insulin pump with advanced features, directly challenging Insulet's Omnipod system.
Strategic partnerships are a key battleground, with companies forming alliances to offer integrated solutions. Insulet itself has a significant partnership with Abbott for its FreeStyle Libre continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system. This trend is evident across the industry, as pump manufacturers collaborate with CGM providers to enhance user experience and data accessibility.
The drive to expand into new international markets further intensifies this rivalry. Companies are investing heavily to secure regulatory approvals and establish distribution networks in regions like Europe and Asia, aiming to broaden their customer base and solidify global presence. This global push means that competitive pressures are not confined to domestic markets.
- Aggressive Marketing: Competitors utilize extensive advertising and clinical data dissemination.
- Strategic Alliances: Partnerships between insulin pump and CGM makers are common to offer integrated solutions.
- Global Expansion: Companies are actively pursuing market entry and growth in international territories.
- Customer Acquisition: The overarching goal of these strategies is to win and retain a larger customer base.
Competitive rivalry is a defining characteristic of Insulet's market, with major players like Medtronic and Tandem Diabetes Care vying for dominance. These competitors offer comparable insulin delivery systems and continuous glucose monitors, intensifying the battle for market share and patient adoption. The market's dynamism is evident in companies like Tandem Diabetes Care, which reported significant revenue growth in 2023, underscoring the need for Insulet to continuously innovate and focus on customer retention.
The diabetes technology sector is characterized by rapid innovation, leading to frequent introductions of advanced products such as smaller insulin pumps and longer-lasting sensors. This technological race fuels intense competition, as companies strive to offer superior automated insulin delivery (AID) systems and continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) capabilities. The global diabetes device market, valued at approximately $53.6 billion in 2023, is projected for substantial growth, largely driven by these technological advancements.
Insulet's first-quarter 2025 performance showcases a strong uptake of its Omnipod system, demonstrating its ability to navigate this competitive environment and gain market traction. The company's success is partly due to its product differentiation, such as the tubeless design of its Omnipod system, and its integration capabilities, like the Omnipod 5's synergy with Dexcom CGMs for automated insulin delivery adjustments.
| Competitor | Key Products | 2023 Revenue (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| Medtronic | MiniMed Insulin Pumps, Guardian CGM | $31.2 billion (Diabetes Segment) |
| Tandem Diabetes Care | t:slim X2 Insulin Pump | $798 million |
| Insulet | Omnipod DASH, Omnipod 5 | $1.4 billion |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Traditional multiple daily injections (MDI) represent a substantial threat to insulin pump adoption, including systems like Insulet's Omnipod. As of 2024, the cost-effectiveness of MDI remains a primary driver for many individuals managing diabetes, with a significant portion of the patient population continuing to rely on this method due to lower upfront and ongoing expenses compared to pump therapy. This accessibility makes MDI a persistent and powerful substitute.
The evolution of smart insulin pens further strengthens the substitute threat. These devices, which began gaining traction in the late 2010s and continued to see development through 2024, offer enhanced tracking of insulin doses and timing, often syncing with mobile applications. This digital integration provides users with valuable data insights, mimicking some of the benefits of pump systems without requiring the user to wear a dedicated pump device, thereby increasing the attractiveness of the MDI approach.
Traditional tethered insulin pumps from competitors like Medtronic and Tandem Diabetes Care represent significant substitutes for Insulet's Omnipod. Patients may opt for these systems if they offer perceived advantages in specific features, established relationships with their healthcare providers, or more favorable insurance coverage, even if the core benefit of insulin delivery is similar.
The market share of these traditional pumps underscores their substitutability. For instance, in 2023, Medtronic and Tandem Diabetes Care collectively held a substantial portion of the insulin pump market, indicating a strong preference among certain patient segments for their established technologies over newer, tubeless alternatives.
For individuals managing type 2 diabetes, the increasing availability and effectiveness of oral medications and non-insulin injectable therapies pose a significant threat to insulin pump manufacturers like Insulet. Drugs such as GLP-1 receptor agonists, exemplified by the strong market performance of semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy) and tirzepatide (Mounjaro, Zepbound), are demonstrating remarkable efficacy in improving glycemic control and promoting weight loss, often delaying or even eliminating the need for insulin therapy.
These advancements in pharmacotherapy offer compelling alternatives that can reduce the perceived necessity of insulin pumps for a growing segment of the diabetes population. For instance, in 2024, the market for GLP-1 receptor agonists continued its robust expansion, with sales projected to reach tens of billions of dollars globally, indicating a substantial shift in treatment paradigms. This trend directly impacts the addressable market for insulin delivery devices, as patients and physicians opt for these less invasive and increasingly effective oral and injectable non-insulin options.
Emerging Breakthroughs and Curative Therapies
The threat of substitutes for Insulet's insulin delivery systems, like the Omnipod, is evolving with advancements in diabetes treatment. While current solutions focus on delivery, potential curative therapies pose a long-term risk. These include breakthroughs in stem cell research and islet cell transplantation, which aim to restore natural insulin production.
Furthermore, the development of highly effective non-insulin pharmacological interventions could significantly reduce the reliance on external insulin delivery. For instance, advancements in incretin mimetics or novel oral medications that improve insulin sensitivity or secretion could diminish the market for insulin pumps and pens. Though these curative or near-curative approaches are not yet mainstream, their progress warrants close monitoring by Insulet and its competitors.
- Stem Cell Therapies: Research continues into generating insulin-producing beta cells from stem cells, potentially offering a functional cure for Type 1 diabetes.
- Islet Cell Transplantation: While established, improvements in donor availability and immune suppression could make this a more viable, long-term alternative to insulin therapy.
- Advanced Pharmacological Interventions: Next-generation drugs targeting the root causes of insulin resistance or beta-cell dysfunction could reduce the need for exogenous insulin.
- Market Impact: A successful curative therapy could fundamentally disrupt the diabetes device market, impacting companies like Insulet that specialize in insulin delivery.
Lifestyle Management and Prevention Programs
Intensive lifestyle management and prevention programs represent a significant threat of substitutes for Insulet's diabetes management devices. For individuals with pre-diabetes or early-stage type 2 diabetes, these programs, focusing on diet, exercise, and weight loss, can lead to improved glycemic control or even remission. For example, studies have shown that lifestyle interventions can be as effective as some medications in managing type 2 diabetes. This non-device, non-pharmacological approach offers a compelling alternative for a segment of the market.
The effectiveness of these programs can reduce the perceived need for advanced diabetes management technologies. If individuals can achieve their health goals through lifestyle changes alone, they may not seek out or continue using devices like insulin pumps. This directly impacts Insulet's potential customer base and market penetration.
- Threat of Substitutes: Lifestyle Management and Prevention Programs
- Impact on Diabetes Management: Intensive lifestyle interventions can significantly improve glycemic control or achieve remission for individuals with pre-diabetes or early-stage type 2 diabetes.
- Non-Technological Alternative: These programs offer a substitute for medical devices by focusing on diet, exercise, and weight management, potentially reducing reliance on technology.
- Market Segment Vulnerability: Individuals successfully managing their condition through lifestyle changes may opt out of or discontinue the use of advanced diabetes management devices.
The threat of substitutes for insulin delivery systems like Insulet's Omnipod remains significant, primarily from traditional multiple daily injections (MDI) and evolving smart insulin pens. As of 2024, MDI's cost-effectiveness continues to be a major factor for many, with a substantial portion of the diabetes population relying on it due to lower initial and ongoing expenses. Smart insulin pens, with their dose tracking and app syncing capabilities, offer data insights similar to pumps, making the MDI approach more appealing without the need for a separate pump device.
Competitors' traditional tethered insulin pumps also represent strong substitutes. Patients might choose these systems based on specific features, established healthcare provider relationships, or more favorable insurance coverage, even if the core function of insulin delivery is comparable. The market share held by companies like Medtronic and Tandem Diabetes Care in 2023 highlights the preference for their established technologies among certain patient groups over newer, tubeless alternatives.
Furthermore, advancements in non-insulin therapies, particularly GLP-1 receptor agonists such as semaglutide and tirzepatide, pose a growing threat, especially for individuals with type 2 diabetes. These medications are highly effective in improving glycemic control and aiding weight loss, potentially delaying or eliminating the need for insulin therapy altogether. The robust global expansion of the GLP-1 market in 2024, with projected sales in the tens of billions, signifies a major shift in treatment paradigms, directly impacting the addressable market for insulin delivery devices.
Longer-term, potential curative therapies like stem cell research and islet cell transplantation represent a fundamental threat, aiming to restore natural insulin production. While not yet mainstream, progress in these areas warrants close monitoring. Intensive lifestyle management and prevention programs also serve as substitutes, particularly for those with pre-diabetes or early-stage type 2 diabetes, as they can improve glycemic control or lead to remission through diet, exercise, and weight loss, potentially reducing the perceived need for advanced diabetes management technologies.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | Market Relevance (as of 2024) | Impact on Insulet |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multiple Daily Injections (MDI) | Lower cost, widely accessible, familiar technique. | Continues to be the dominant method for many diabetes patients. | Represents a persistent, cost-driven alternative to pump therapy. |
| Smart Insulin Pens | Enhanced dose tracking, app connectivity, data insights. | Gaining traction, offering some pump-like benefits without wearable device. | Increases the attractiveness of injection-based therapy. |
| Traditional Tethered Pumps | Established technology, feature variations, brand loyalty. | Significant market share held by competitors like Medtronic and Tandem. | Offers alternative pump solutions based on features and provider relationships. |
| Non-Insulin Pharmacotherapies (e.g., GLP-1s) | Improved glycemic control, weight loss, potential to delay/eliminate insulin. | Rapid market growth, billions in global sales, shifting treatment paradigms. | Reduces the addressable market for insulin delivery devices, especially for Type 2 diabetes. |
| Lifestyle Management & Prevention | Diet, exercise, weight loss for improved glycemic control or remission. | Effective for pre-diabetes and early Type 2 diabetes. | Can reduce the perceived need for technological interventions. |
| Curative Therapies (Future) | Stem cell therapy, islet transplantation. | Under active research and development. | Potential to fundamentally disrupt the insulin delivery market if successful. |
Entrants Threaten
The medical device sector, especially for insulin delivery systems like those Insulet offers, faces significant hurdles due to strict regulations. Agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) impose rigorous standards that new entrants must meet.
Securing market approval requires extensive clinical trials to prove both safety and effectiveness, a process that can take years and involve substantial financial investment. Navigating these complex and lengthy bureaucratic procedures acts as a powerful deterrent for potential new competitors.
For instance, the average cost to bring a new medical device to market can range from millions to tens of millions of dollars, with regulatory compliance being a major component of that expense. This high cost and time commitment effectively raises the barrier to entry, protecting established players like Insulet.
Developing innovative, safe, and effective insulin delivery systems like Insulet's Omnipod demands significant upfront investment. This includes extensive research, intricate product design, and the continuous technological refinement necessary to stay competitive. For instance, companies in the medical device sector often spend upwards of 10-15% of their revenue on R&D, a substantial barrier for newcomers.
Insulet benefits from deeply entrenched brand loyalty among its user base and a robust distribution network. This makes it challenging for new competitors to gain traction. For instance, Insulet's Omnipod system has a dedicated following, built over years of consistent performance and patient support, a loyalty that new entrants would struggle to replicate quickly.
Intellectual Property and Patent Protection
Insulet's strong intellectual property, particularly its patents on the Omnipod's tubeless design and automated insulin delivery, acts as a formidable barrier for new entrants. This extensive patent portfolio, which includes hundreds of granted patents and pending applications, forces potential competitors to either invest heavily in developing entirely novel, non-infringing technologies or engage in expensive licensing negotiations. For instance, Insulet reported holding over 1,400 patents and patent applications globally as of its 2023 annual report, underscoring the depth of its IP protection.
The significant R&D investment required to circumvent Insulet's patented innovations further deters new players. Developing alternative tubeless insulin delivery systems or unique automated algorithms that do not infringe on existing patents is a complex and costly undertaking. This high barrier means that only well-funded and technologically advanced companies could realistically challenge Insulet's market position, thereby limiting the immediate threat of new entrants.
- Insulet's extensive patent portfolio significantly raises the cost and complexity for new entrants aiming to compete in the tubeless insulin delivery market.
- Developing alternative technologies that avoid patent infringement requires substantial R&D investment, acting as a deterrent.
- The need for costly licensing agreements further restricts the options available to potential new competitors.
Economies of Scale in Manufacturing and Supply Chain
Established companies in the diabetes device market, like Insulet, benefit significantly from economies of scale in their manufacturing and supply chain operations. This allows them to spread fixed costs over a larger production volume, leading to lower per-unit costs for their insulin pumps and related consumables. For instance, in 2024, major players continued to invest heavily in optimizing their production lines, further solidifying these cost advantages.
New entrants face a considerable hurdle in achieving similar cost efficiencies. Without the established infrastructure and high production volumes, their initial per-unit manufacturing and procurement costs are inherently higher. This makes it difficult for them to compete on price with incumbent firms, particularly as affordability becomes a more critical factor for patients and healthcare systems.
- Manufacturing Efficiency: Larger production runs reduce the cost per insulin pump manufactured.
- Procurement Power: Established firms secure better pricing on raw materials and components due to higher order volumes.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Extensive logistics networks and distribution channels lower shipping and inventory costs.
- R&D Amortization: High development costs are spread over a larger sales base, reducing the impact on individual product pricing.
The threat of new entrants for Insulet is considerably low due to several formidable barriers. The stringent regulatory landscape, demanding extensive clinical trials and FDA approval, requires millions in investment and years of effort. For example, the average cost to bring a new medical device to market can easily exceed $10 million, with a significant portion dedicated to regulatory compliance. This high financial and time commitment effectively shields established players like Insulet.
Insulet's robust intellectual property, including hundreds of patents for its Omnipod system, forces potential competitors to invest heavily in developing non-infringing technologies or face costly licensing. By 2023, Insulet held over 1,400 patents and applications globally, creating a significant hurdle for newcomers. Furthermore, the economies of scale enjoyed by Insulet in manufacturing and procurement, with ongoing investments in production optimization in 2024, result in lower per-unit costs that new entrants struggle to match.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (Illustrative) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Hurdles | Strict FDA approval processes, clinical trials | High cost and time to market | Average medical device market entry cost: $10M+ |
| Intellectual Property | Extensive patent portfolio on Omnipod technology | Requires costly R&D or licensing | Insulet patents: 1,400+ (as of 2023) |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to high production volume | Price disadvantage for new entrants | 2024: Continued investment in production optimization by incumbents |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Insulet Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from Insulet's investor relations materials, competitor financial reports, and industry-specific market research from firms like Grand View Research and Mordor Intelligence.
