Enterprise Mobility Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Enterprise Mobility Bundle
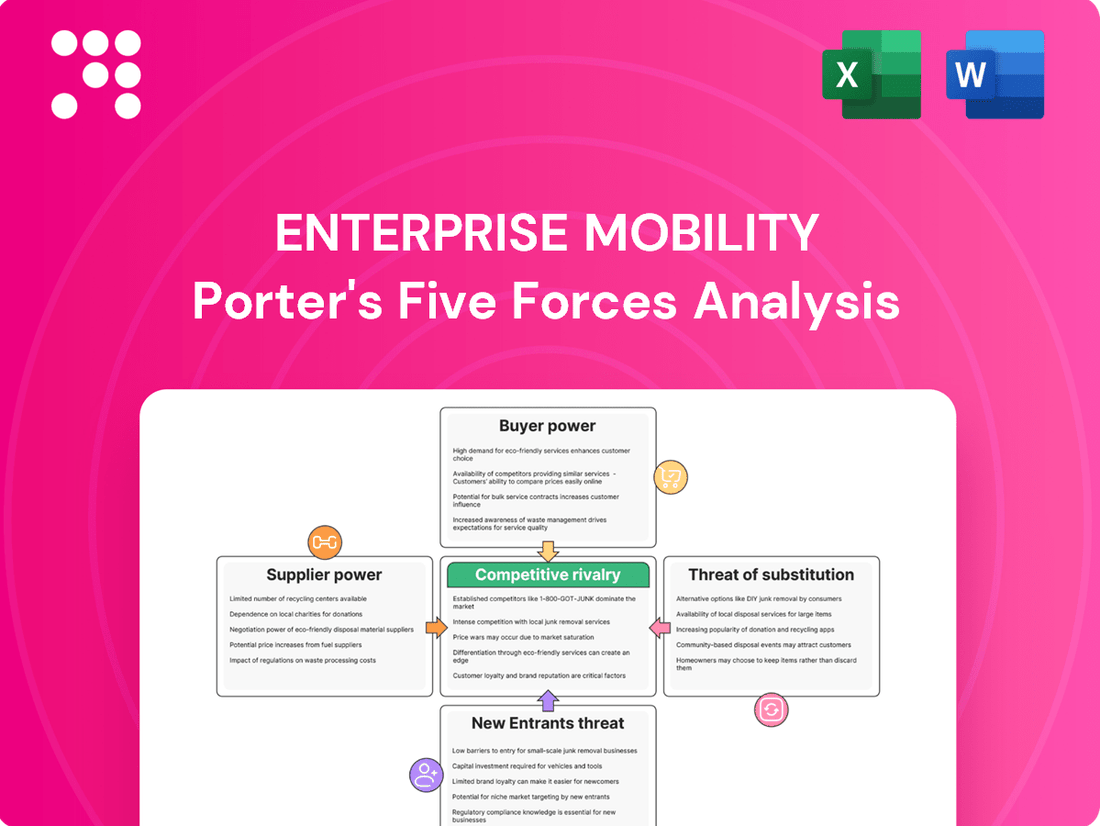
Enterprise Mobility faces a dynamic competitive landscape shaped by five key forces. Understanding the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry is crucial for strategic success.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Enterprise Mobility’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Enterprise Mobility's dependence on a limited number of major automotive manufacturers significantly shapes its bargaining power. When acquiring its fleet, the sheer volume of vehicles Enterprise Mobility purchases can grant it some leverage. However, this is counterbalanced by the manufacturers' own production priorities. For instance, rental companies often favor SUVs and trucks, and if Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) shift their production towards higher-trim, more expensive models, it can restrict the availability of the standard, more affordable vehicles Enterprise Mobility relies on, thereby reducing its negotiating strength.
The wholesale used vehicle market significantly impacts Enterprise Mobility's fleet management. Strong demand and high prices in the used car market in recent years have allowed rental companies to recoup more of their initial investment when selling off older vehicles, effectively lowering their net acquisition costs for new fleets. For instance, in 2023, the average wholesale price for used vehicles remained elevated compared to pre-pandemic levels, benefiting fleet disposals.
Looking ahead, the expected normalization of the used vehicle market, anticipated between mid-2025 and 2027, could alter these dynamics. As supply chains normalize and new vehicle production increases, wholesale used car prices are projected to decline. This trend may lead to higher vehicle acquisition costs for rental companies and potentially slower fleet depreciation, impacting profitability.
Technology and software providers are increasingly influential in enterprise mobility. The integration of advanced solutions like AI-powered fleet management and real-time telematics is becoming crucial for operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. For instance, by mid-2024, many logistics companies reported significant improvements in route optimization and fuel savings, often exceeding 15%, directly attributable to sophisticated software platforms.
The specialized nature of these technology providers can grant them considerable bargaining power. Companies heavily reliant on their proprietary software for critical functions such as dispatch, customer relationship management, and predictive maintenance may find it difficult and costly to switch providers. This dependency, coupled with the ongoing development and integration of new features, allows these suppliers to command premium pricing and favorable contract terms.
Fuel Suppliers and Energy Costs
Enterprise Mobility's operational costs are significantly impacted by the bargaining power of fuel suppliers, especially with a large fleet relying on gasoline and diesel. Volatile fuel prices, a persistent concern in 2024, directly affect profitability. For instance, average gasoline prices in the US hovered around $3.50-$3.70 per gallon throughout much of 2024, a key input cost for many rental fleets.
The ongoing transition to electric vehicles (EVs) introduces a new dynamic. Enterprise Mobility's growing investment in EVs means new supplier relationships are forming with battery manufacturers and charging infrastructure providers. The concentration of battery production, for example, could grant significant bargaining power to a few key manufacturers, potentially increasing costs for EV acquisition and maintenance.
- Impact of Fuel Price Volatility: Fluctuations in gasoline and diesel prices directly influence Enterprise Mobility's fuel expenses, a major component of operating costs.
- Emerging EV Supplier Landscape: The shift to EVs creates reliance on new suppliers, including battery producers and charging network operators, whose market positions will determine their bargaining power.
- Battery Technology and Costs: The cost and availability of EV batteries, a significant factor in the total cost of ownership for electric fleets, are largely dictated by battery manufacturers.
- Charging Infrastructure Dependence: Enterprise Mobility's ability to effectively deploy and manage its EV fleet is also tied to the availability and pricing of charging infrastructure, often provided by specialized companies.
Real Estate and Airport Concessions
Airport authorities and commercial real estate owners wield significant bargaining power, especially for prime rental locations within airports. These entities often control access to a captive audience of travelers, making their concessions highly desirable for businesses in the enterprise mobility sector. For instance, in 2024, airport retail revenue globally continued its strong recovery, with many major hubs reporting pre-pandemic or even exceeding pre-pandemic sales figures, underscoring the value of these locations.
The substantial fixed costs associated with securing and maintaining these prime airport spaces, such as high rental rates and common area maintenance fees, directly impact operational expenses for mobility providers. Competition for these limited, high-traffic locations is fierce, further strengthening the hand of airport authorities and landlords in negotiating lease terms. This can lead to rental agreements that are heavily weighted in favor of the lessor, potentially squeezing profit margins for businesses operating within these concessions.
- High Demand for Airport Concessions: Prime airport locations offer unparalleled access to a concentrated customer base of travelers, driving up demand and thus the bargaining power of airport authorities.
- Fixed Cost Implications: Significant fixed costs, including rent and service charges, for these premium spaces directly influence the profitability of mobility service providers.
- Competitive Landscape: Intense competition among businesses vying for limited airport concession space allows airport operators to dictate more favorable terms.
- Rental Agreement Influence: The power dynamic often results in rental agreements that favor landlords, impacting the operational expenses and pricing strategies of mobility companies.
The bargaining power of suppliers in enterprise mobility is multifaceted, encompassing vehicle manufacturers, technology providers, and fuel suppliers. For instance, in 2024, the automotive industry's continued focus on higher-margin vehicles meant that rental companies like Enterprise Mobility faced potential shortages of more basic models, impacting their fleet acquisition flexibility. Similarly, specialized software providers for fleet management, offering AI-driven optimization, commanded premium pricing due to their critical role in efficiency gains, with some logistics firms reporting over 15% improvements in route planning by mid-2024. The dependence on these proprietary systems makes switching providers costly and complex.
Fuel suppliers remain a significant factor, with gasoline prices in the US averaging between $3.50 and $3.70 per gallon throughout 2024, directly impacting operational costs for traditional fleets. The burgeoning electric vehicle (EV) segment introduces new supplier dynamics, particularly with battery manufacturers. The concentration of battery production, a key component in EV costs, grants these suppliers substantial leverage over pricing and supply, influencing the total cost of ownership for electric fleets. Charging infrastructure providers also hold sway, as the availability and cost of charging solutions directly affect EV fleet deployment.
| Supplier Category | Key Influence Factors | 2024 Data/Trends |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturers | Production priorities, model availability, pricing | Shift towards higher-trim models, potential impact on standard vehicle availability. |
| Technology & Software Providers | Proprietary systems, integration complexity, innovation | High demand for AI fleet management; significant efficiency gains reported (e.g., >15% route optimization). |
| Fuel Suppliers | Commodity price volatility, supply chain stability | Average gasoline prices ~$3.50-$3.70/gallon, impacting operating expenses. |
| EV Battery Manufacturers | Production concentration, technological advancements, raw material costs | Growing influence due to critical role in EV cost and performance. |
| Charging Infrastructure Providers | Network availability, pricing models, interoperability | Essential for EV fleet operational viability. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers the competitive intensity and attractiveness of the Enterprise Mobility market by examining the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing players.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats in the enterprise mobility landscape by visualizing the impact of each of Porter's Five Forces on your strategy.
Customers Bargaining Power
Leisure travelers, a key customer base for Enterprise Mobility, exhibit substantial price sensitivity. This means they are highly influenced by the cost of rental services when making decisions.
The widespread availability of online comparison tools empowers these travelers to easily shop around for the best deals. Furthermore, their readiness to opt for less convenient pickup or drop-off locations to secure lower prices directly pressures Enterprise Mobility's pricing strategies.
For instance, in 2024, the average daily rental rate for leisure travel in major US cities saw fluctuations, with discounts of up to 15% available for bookings made weeks in advance or at off-airport locations, underscoring this sensitivity.
Corporate clients often hold significant bargaining power, especially when renting vehicles in large volumes or through extended contracts. This can pressure rental companies on pricing and terms.
Enterprise Mobility counters this by leveraging its strong brand and effective loyalty programs like Enterprise Plus. These initiatives encourage repeat business and build customer relationships, offering value that extends beyond simple cost considerations, thereby reducing the clients' inclination to switch based solely on price.
In 2024, Enterprise Mobility continued to focus on these customer-centric strategies. While specific figures for loyalty program impact are proprietary, Enterprise's consistent market leadership, evidenced by its extensive fleet and widespread network, suggests strong customer retention and a successful mitigation of buyer power among its corporate accounts.
Customers increasingly expect flexible, immediate, and digital booking experiences, including shorter booking windows and contactless services. This shift significantly bolsters their bargaining power, forcing rental companies to adapt to evolving preferences.
The widespread availability of self-service options and mobile applications empowers customers, enabling them to compare prices and book rentals with ease. This digital self-sufficiency demands continuous innovation from rental companies to meet these heightened expectations and maintain competitiveness.
Demand for Diverse Vehicle Types
Enterprise Mobility faces a significant bargaining power from customers demanding a wider variety of vehicle types. Shifting consumer tastes towards specific segments like SUVs and premium luxury rentals directly influence Enterprise's fleet management and acquisition strategies. For instance, in 2024, the continued strong consumer preference for SUVs meant that a larger proportion of Enterprise's fleet investments were allocated to these popular models, potentially increasing the cost per vehicle and impacting overall fleet utilization if demand fluctuates.
The increasing demand for premium categories and the burgeoning interest in electric vehicles (EVs) further amplify customer leverage. As more customers seek out these specialized options, Enterprise must adapt its offerings. This adaptation can involve higher acquisition costs for EVs and premium models, which, if not met with commensurate rental rates or sufficient demand, can empower customers by giving them more choices and greater negotiation power, especially if competitors offer similar vehicles at more attractive prices.
- Shifting Preferences: Customer demand for SUVs and luxury vehicles in 2024 has led Enterprise to adjust its fleet composition, prioritizing these higher-demand segments.
- Premium and EV Impact: The rise in demand for premium vehicle classes and electric vehicles grants customers increased bargaining power due to the specialized nature and potentially higher costs of these options.
- Fleet Investment Decisions: Enterprise's purchasing decisions are heavily influenced by these evolving customer preferences, impacting fleet diversity and acquisition costs.
Customer Satisfaction and Online Reviews
Customer satisfaction is a critical lever for Enterprise Mobility, directly influencing its bottom line through repeat business and brand loyalty. In 2024, companies across sectors are seeing a significant impact from customer experience, with reports indicating that over 80% of consumers will switch brands after just one negative experience. This heightened sensitivity means that Enterprise Mobility's service quality and the ease of its digital interactions are paramount.
The rise of online review platforms and social media has dramatically amplified the customer's voice, effectively consolidating their collective bargaining power. A study from BrightLocal in 2023 found that 98% of consumers read online reviews for local businesses, and nearly 90% trust online reviews as much as personal recommendations. This transparency means that a single negative review can quickly reach a vast audience, pressuring Enterprise Mobility to maintain high standards or risk losing potential customers.
- Customer satisfaction directly impacts repeat business: In 2024, a positive customer experience is a key differentiator.
- Digital convenience is a major driver of satisfaction: Customers expect seamless, easy-to-use mobile solutions.
- Online reviews amplify customer voice: Platforms like Google Reviews and Yelp give customers significant power.
- Social media acts as a powerful feedback channel: Negative experiences can go viral, impacting reputation and sales.
Customers wield significant power through their ability to compare prices easily, their preference for specific vehicle types, and their demand for digital convenience. This forces Enterprise Mobility to continually adapt its fleet and service offerings to meet evolving expectations. For example, in 2024, the strong consumer pull towards SUVs meant Enterprise allocated more resources to these vehicles, influencing fleet costs.
The growing demand for premium and electric vehicles (EVs) further empowers customers, as these specialized options often come with higher price tags and require specific fleet investments. Enterprise must balance these demands with profitability, giving customers leverage when competitors offer similar vehicles at competitive rates.
Customer satisfaction, amplified by online reviews and social media, is a critical factor in 2024. With nearly 90% of consumers trusting online reviews, a single negative experience can significantly impact Enterprise's reputation and customer acquisition efforts, reinforcing the customer's bargaining power.
| Customer Influence Factor | Impact on Enterprise Mobility | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity & Comparison | Pressures pricing strategies, necessitates competitive offers. | Leisure travelers sensitive to discounts up to 15% for advance/off-airport bookings. |
| Vehicle Preference Shifts | Requires fleet adjustments, impacting acquisition costs and utilization. | Continued strong consumer preference for SUVs in 2024 led to increased fleet allocation. |
| Digital Expectations | Demands investment in user-friendly apps and contactless services. | Customers expect seamless, immediate booking and self-service options. |
| Online Reputation | Necessitates high service standards to mitigate negative reviews. | 98% of consumers read online reviews; 90% trust them as much as personal recommendations. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Enterprise Mobility Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Enterprise Mobility Porter's Five Forces Analysis, providing a thorough examination of the competitive landscape. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted file you will receive instantly upon purchase, offering immediate insights into the forces shaping the enterprise mobility market.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The car rental market is characterized by intense competition among a few major players. Enterprise Mobility, Avis Budget Group, and Hertz Corporation collectively dominate, holding a substantial portion of the market share. This concentration means these giants frequently engage in price wars and compete aggressively on the breadth of their fleet and the quality of their customer service.
Enterprise Mobility faces varied competitive intensity depending on the market. In airport markets, competition is often fierce with major global brands, whereas local markets might see smaller, regional players. For instance, the car rental market in major hubs like London Heathrow Airport is densely populated with brands, driving down prices, while a smaller city airport might have fewer options.
The company's broad service portfolio means it competes on multiple fronts. In car rental, it goes head-to-head with Avis and Hertz. Simultaneously, its fleet management services contend with companies like Element Fleet Management, and its truck rental operations compete with Ryder and Penske. This diversification creates a complex competitive landscape where success in one segment doesn't guarantee dominance in another.
Customer segments also present distinct competitive dynamics. Leisure travelers often prioritize price and convenience, leading to intense price wars. Business travelers, however, may value service quality, loyalty programs, and integrated billing, creating a different competitive battleground. Commercial fleet management clients expect tailored solutions and cost-efficiency, attracting specialized competitors.
Dynamic pricing strategies significantly intensify competitive rivalry in the enterprise mobility sector. Companies constantly adjust rental rates based on fluctuating supply, demand, and seasonal trends, creating a highly competitive pricing environment.
For instance, in 2024, ride-sharing platforms like Uber and Lyft frequently employ surge pricing during peak hours or special events, a tactic that directly impacts competitor pricing. This constant price adjustment means that a company offering a slightly lower rate can quickly gain market share, forcing others to respond in kind.
The volatility of these rental rates, driven by real-time market conditions, necessitates agile pricing models. This agility, while beneficial for consumers, fuels intense competition among mobility providers, as they strive to capture demand by offering the most attractive price points at any given moment.
Technology-Driven Differentiation
Technology-driven differentiation is increasingly central to competition in enterprise mobility. Companies are battling fiercely to offer superior mobile apps, seamless contactless payment options, and AI-powered operational efficiencies. For instance, in 2024, many retail and logistics firms are investing heavily in AI to optimize delivery routes and personalize customer interactions, directly impacting market share.
Continuous innovation in customer experience and operational efficiency is no longer optional; it's a necessity for survival and growth. Businesses that fail to adapt to new technological capabilities risk falling behind rivals who are leveraging these advancements to attract and retain customers. The global mobile app market, valued at over $300 billion in 2023, continues to grow, highlighting the importance of app-based competitive strategies.
- Mobile App Superiority: Companies are differentiating through intuitive user interfaces, robust functionality, and personalized content delivery via their mobile applications.
- Contactless Integration: The adoption of contactless technologies, from payments to service delivery, is a key battleground, enhancing convenience and safety for users.
- AI-Powered Operations: Artificial intelligence is being deployed to streamline back-end processes, improve customer service through chatbots, and offer predictive analytics, creating significant operational advantages.
- Innovation in CX and Efficiency: Businesses are prioritizing R&D to consistently improve the customer journey and internal operational workflows, which directly translates to competitive edge.
Fleet Modernization and EV Adoption
The drive for fleet modernization, particularly the shift to electric and hybrid vehicles, intensifies competitive rivalry. Companies are actively investing in upgrading their fleets to align with customer expectations and growing environmental awareness. This modernization is not just about sustainability; it's a strategic move to reduce operational costs and enhance brand image.
In 2024, many logistics and transportation companies are prioritizing the integration of electric vehicles (EVs) into their operations. For example, UPS announced plans to acquire 175 electric vehicles from the UK-based firm Arrival, adding to its existing fleet of over 10,000 alternative fuel and advanced technology vehicles. This investment reflects a broader industry trend where companies are diversifying their fleets to include a mix of traditional, hybrid, and fully electric options.
- Fleet Modernization as a Competitive Differentiator: Companies are leveraging updated fleets, including EVs and hybrids, to offer more sustainable and cost-effective services, thereby attracting environmentally conscious customers and gaining a competitive edge.
- Investment in Diverse Fleets: To meet varied operational needs and customer demands, businesses are investing in a range of vehicle types, from smaller electric delivery vans to larger hybrid trucks, balancing range, payload, and charging infrastructure capabilities.
- Impact of EV Adoption on Operational Costs: The adoption of EVs, while requiring upfront investment, promises lower running costs due to reduced fuel and maintenance expenses, which can translate into more competitive pricing strategies.
- Environmental Consciousness and Brand Reputation: Companies with modern, eco-friendly fleets often benefit from enhanced brand reputation, appealing to a growing segment of consumers and corporate clients who prioritize sustainability in their partnerships.
Competitive rivalry within enterprise mobility is fierce, driven by a concentrated market of major players like Enterprise Mobility, Avis, and Hertz, who frequently engage in price wars and compete on fleet size and service quality. This intensity is amplified by dynamic pricing strategies, where real-time adjustments based on supply and demand create a constant battle for customer acquisition through the most attractive rates.
Technology is a major battleground, with companies vying for superiority in mobile app functionality, contactless integration, and AI-powered operational efficiencies to enhance customer experience and gain an edge.
Furthermore, the push for fleet modernization, particularly the adoption of electric and hybrid vehicles, intensifies competition as companies invest in sustainability and cost reduction to attract environmentally conscious customers and improve brand image.
The enterprise mobility sector sees significant competition through various strategic initiatives, including fleet modernization and technology adoption.
| Competitive Factor | Key Players Involved | 2024 Market Trend/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Price Competition | Enterprise Mobility, Avis, Hertz | Intensified by dynamic pricing, with average daily rental rates fluctuating based on demand and seasonality. |
| Technology & Apps | All major players | Increased investment in AI for operational efficiency and enhanced mobile app user experience; global mobile app market growth exceeding 300 billion USD in 2023. |
| Fleet Modernization (EVs) | Enterprise Mobility, Hertz, Avis | Growing adoption of EVs; UPS's 2024 order of 175 Arrival EVs highlights industry shift towards electrification. |
| Service Diversification | Enterprise Mobility, Element Fleet Management, Ryder | Competition across car rental, fleet management, and truck rental segments, requiring specialized strategies for each. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Ride-sharing and ride-hailing services like Uber and Lyft present a substantial threat to traditional car rental companies, particularly for shorter trips and within urban environments. These platforms offer unparalleled convenience and immediate availability, often making them a more attractive option than renting a car for a few hours or a day. This accessibility directly competes with car rental's core value proposition for many customers.
The ease of booking through a mobile app and the pay-per-use model of ride-sharing significantly reduce the perceived need for car ownership and, by extension, short-term car rentals. For instance, in 2024, ride-hailing services continued to solidify their presence in major metropolitan areas, with millions of daily rides facilitated globally, directly siphoning demand that might have otherwise gone to rental agencies.
Dedicated car-sharing platforms like Zipcar, Getaround, and Turo present a significant threat by offering convenient, short-term vehicle access without the traditional burdens of ownership or long-term rental agreements. These services are particularly appealing to urban dwellers and those needing occasional vehicle use, directly competing with the need for traditional car rentals for short trips or specific needs.
The flexibility of hourly or daily rentals, coupled with app-based accessibility, makes car-sharing a compelling substitute for conventional car rental agencies. For instance, in 2024, the global car-sharing market continued its robust growth, with user numbers expanding significantly, especially in major metropolitan areas where the convenience factor is paramount. This increasing adoption directly erodes the demand for traditional rental services for many use cases.
Robust public transportation networks, including buses, trains, and subways, along with burgeoning micromobility options like e-scooters and bike-sharing, present significant substitutes for enterprise mobility solutions, particularly in urban environments. These alternatives offer cost-effective and often time-efficient ways for employees to commute, directly impacting the demand for company-provided or managed transportation. For instance, many cities are actively investing in expanding their public transit infrastructure; in 2024, New York City's MTA continued its significant capital improvement program, aiming to enhance service reliability and capacity, making public transit a more attractive option for a larger segment of the workforce.
The increasing availability and adoption of these substitute modes of transport can diminish the necessity for private vehicles or ride-sharing services for business travel or employee commutes. Cities that prioritize and fund these alternatives, such as London with its extensive cycle hire scheme and integrated public transport, effectively reduce the reliance on more carbon-intensive or privately managed mobility options. This shift can pressure enterprises to re-evaluate their mobility strategies, potentially leading to reduced fleet sizes or a greater emphasis on supporting sustainable, shared, or public transit options for their employees.
Personal Vehicle Ownership (Long-Term)
While younger demographics, particularly millennials, show a declining interest in personal vehicle ownership, opting more for car-sharing and rental services, the fundamental option of owning a personal vehicle remains a potent long-term substitute for enterprise mobility solutions. This trend was evident in 2024 as ride-sharing services continued to grow, but the inherent cost-effectiveness and convenience of personal vehicles for those who choose to own them significantly limit the market for extended rentals or subscription-based mobility. For instance, in 2023, the average cost of owning a new car in the US was estimated to be around $10,728 annually, encompassing depreciation, fuel, insurance, and maintenance, a figure that, while substantial, offers a predictable and constant utility for the owner.
The enduring appeal of personal vehicle ownership stems from its unparalleled flexibility and the sense of autonomy it provides. Even as car-sharing platforms saw increased adoption, the ability to have a vehicle readily available at any time, without the need for booking or shared usage, remains a significant draw. This convenience factor, coupled with the potential long-term cost savings for frequent users compared to per-use rental fees, acts as a strong deterrent for many from fully embracing alternative enterprise mobility models. For example, a study in early 2024 indicated that individuals commuting over 15 miles daily found personal vehicle ownership to be more economical than relying solely on ride-sharing or car rental services.
- Declining Ownership Trend: Younger demographics, especially millennials, are increasingly choosing car-sharing and rental over personal vehicle ownership, impacting traditional automotive markets.
- Personal Vehicle as Substitute: The fundamental option of owning a personal car remains a strong long-term substitute for enterprise mobility solutions.
- Cost-Effectiveness & Convenience: For owners, personal vehicles offer predictable costs and unmatched convenience, limiting the appeal of extended rentals.
- Usage Economics: In 2023, annual car ownership costs in the US averaged over $10,000, yet the constant availability and flexibility often outweigh rental expenses for frequent users.
Remote Work and Virtual Travel
The rise of remote work and sophisticated virtual meeting platforms presents a significant indirect threat to corporate car rental demand. Companies are increasingly opting for virtual collaboration, which directly curtails the need for business travel, a primary driver for car rentals.
This trend, amplified by advancements in teleconferencing technology, means fewer employees are commuting to physical offices or traveling for in-person meetings. For example, a 2024 survey indicated that over 60% of companies now offer hybrid or fully remote work options, a substantial increase from pre-pandemic levels.
Consequently, the sustained shift away from physical commutes and business trips directly impacts the demand for corporate car rentals. This is evident as many businesses re-evaluate their travel budgets and explore cost-saving alternatives like virtual attendance for conferences and internal meetings.
- Reduced Business Travel: Virtual meeting technologies directly substitute the need for many business trips.
- Hybrid Work Models: The widespread adoption of hybrid work reduces daily commutes and associated travel needs.
- Cost Savings: Companies are prioritizing virtual solutions to cut down on travel expenses, impacting car rental usage.
- Technological Advancements: Improved quality and accessibility of virtual collaboration tools make them a viable alternative to physical travel.
The threat of substitutes for enterprise mobility is significant, encompassing various alternatives that reduce reliance on traditional car rentals or company-owned fleets. These substitutes range from readily available ride-sharing services and car-sharing platforms to robust public transportation and the burgeoning micromobility sector.
Furthermore, the increasing adoption of remote and hybrid work models, coupled with advancements in virtual collaboration tools, directly diminishes the need for business travel, a key segment for car rental companies. The convenience, cost-effectiveness, and flexibility offered by these substitutes pressure traditional enterprise mobility providers to adapt.
| Substitute Type | Key Features | Impact on Enterprise Mobility | 2024 Market Insight |
| Ride-Sharing/Hailing | On-demand, app-based, pay-per-use | Reduces need for short-term rentals, impacts urban business travel | Millions of daily rides globally, solidifying urban presence |
| Car-Sharing | Flexible hourly/daily rentals, app-based | Competes for short trips, appeals to occasional users | Robust global market growth, increasing user numbers |
| Public Transit/Micromobility | Cost-effective, eco-friendly, convenient in urban areas | Decreases reliance on private vehicles for commutes | Significant investment in infrastructure expansion |
| Virtual Collaboration | Remote meetings, reduced business travel | Cuts demand for corporate car rentals, impacts travel budgets | Over 60% of companies offer hybrid/remote work |
Entrants Threaten
The significant capital outlay needed to build a competitive fleet is a major hurdle for new entrants in the enterprise mobility sector. Acquiring a diverse range of vehicles, from sedans to specialized vans, requires millions in upfront investment. For instance, a fleet of 1,000 vehicles, depending on type and specifications, could easily cost upwards of $30 million, a substantial barrier for smaller companies or startups.
Established players like Enterprise Mobility benefit from economies of scale and long-standing relationships with automotive manufacturers, often securing preferential pricing and bulk purchase agreements. This access to favorable terms, coupled with robust financing options, allows incumbents to maintain a cost advantage that new entrants struggle to match. In 2024, Enterprise Mobility reported managing a fleet of over 2 million vehicles globally, a testament to their scale and purchasing power.
Established brand recognition and customer trust are significant barriers for new entrants in the mobility sector. Companies like Enterprise Rent-A-Car, National, and Alamo have spent decades building a loyal customer base through consistent service and strong reputation, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction.
In 2024, the rental car market, a key component of enterprise mobility, continues to be dominated by these established players. For instance, Enterprise Holdings, which owns Enterprise Rent-A-Car, National Car Rental, and Alamo Rent a Car, reported significant revenue growth, underscoring their market leadership and the challenge new entrants face in replicating this scale and trust.
The sheer scale of Enterprise Mobility's operational network presents a significant hurdle for new entrants. Replicating their thousands of rental locations, strategically positioned in airports, downtown areas, and local neighborhoods worldwide, demands immense capital investment and time. This extensive physical footprint, coupled with the complex logistical infrastructure for vehicle maintenance, fleet management, and customer service, creates a formidable barrier to entry.
Regulatory Hurdles and Insurance Costs
New entrants in the enterprise mobility sector face substantial regulatory hurdles. Obtaining necessary operating licenses, complying with diverse local and national transportation laws, and meeting stringent safety standards demand significant upfront investment and ongoing effort. For instance, in 2024, the average cost for a commercial driver's license endorsement can range from $500 to $1,500, excluding the time and resources needed for training and testing.
The financial burden of insurance further acts as a deterrent. Operating a fleet of vehicles, especially for commercial purposes, necessitates comprehensive and often expensive insurance policies to cover liability, damage, and potential accidents. In 2023, the average annual commercial auto insurance premium for a small business with a few vehicles could easily exceed $5,000, with larger fleets facing exponentially higher costs, making it a formidable barrier for startups lacking established capital.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: Startups must budget for licensing fees, legal consultations, and adherence to evolving transportation regulations, which can amount to tens of thousands of dollars annually.
- Insurance Premium Escalation: The high cost of comprehensive fleet insurance, often running into hundreds of thousands of dollars for larger operations, significantly impacts profitability and initial capital requirements.
- Navigating Complex Legal Frameworks: Understanding and implementing compliance with varying state and federal transportation laws requires specialized legal expertise, adding to operational overhead.
Technological Investment and Scalability
New entrants in enterprise mobility face a substantial hurdle due to the significant capital required for advanced technological infrastructure. This includes sophisticated booking platforms, real-time telematics for fleet management, and increasingly, AI-powered tools for route optimization and predictive maintenance. For instance, developing a robust, scalable, and secure mobile platform often necessitates millions in upfront investment for software development, hardware integration, and ongoing maintenance.
Achieving technological scalability is a complex and costly challenge for newcomers. As user bases and operational demands grow, the underlying technology must be able to expand seamlessly without compromising performance or security. Integrating new innovations, such as advanced analytics or autonomous vehicle technology, further adds to the expense and complexity, creating a high barrier to entry. For example, a new ride-sharing service might need to invest upwards of $50 million in its initial technology stack to compete with established players.
- High Capital Outlay: Significant investment is needed for booking systems, telematics, and AI management tools.
- Technological Complexity: Integrating and scaling new innovations is a costly and intricate process.
- Example Investment: A new ride-sharing platform could require over $50 million for its initial technology infrastructure.
- Ongoing Costs: Continuous investment in software updates, security, and new feature development is essential.
The threat of new entrants in enterprise mobility is generally low, largely due to the substantial capital investment required. Building a competitive fleet alone can cost tens of millions of dollars, a significant barrier for startups. Established players also benefit from economies of scale, preferential pricing with manufacturers, and strong brand loyalty, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on cost and trust.
Furthermore, the extensive operational networks and technological infrastructure of incumbents demand immense upfront investment and time to replicate. New entrants also face complex regulatory compliance and high insurance premiums, adding further financial strain. For instance, in 2024, Enterprise Mobility managed over 2 million vehicles globally, highlighting the immense scale new entrants must overcome.
| Barrier to Entry | Estimated Cost/Challenge | Impact on New Entrants |
| Fleet Acquisition | $30M+ for 1,000 vehicles | High capital requirement |
| Economies of Scale | Preferential pricing, bulk agreements | Cost disadvantage for newcomers |
| Brand Recognition & Trust | Decades of customer loyalty | Difficulty in customer acquisition |
| Operational Network | Thousands of locations, complex logistics | Immense capital and time investment |
| Technological Infrastructure | $50M+ for initial tech stack (e.g., ride-sharing) | High upfront investment and complexity |
| Regulatory Compliance | $500-$1,500 per CDL endorsement; ongoing legal fees | Significant administrative and financial burden |
| Insurance Premiums | $5,000+ annually for small fleets; much higher for large fleets | Major impact on profitability and initial capital needs |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Enterprise Mobility Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of diverse data, including industry analyst reports, company financial statements, market research databases, and technology trend publications.
