Ebix Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Ebix Bundle
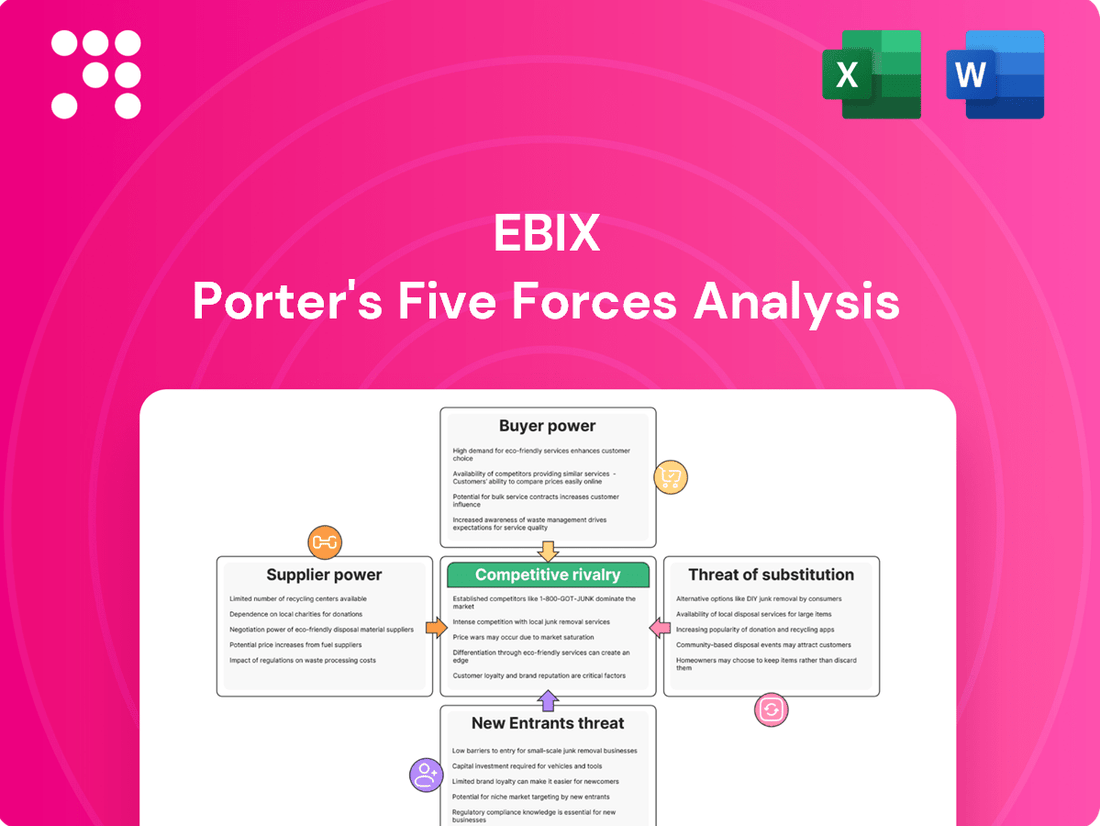
Ebix operates within a dynamic insurance and financial technology landscape, where understanding the competitive forces is paramount. Our Porter's Five Forces analysis delves into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within Ebix's markets.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Ebix’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Ebix's reliance on proprietary technology and niche expertise for its on-demand software and e-commerce services, especially within regulated industries like insurance and finance, significantly impacts supplier bargaining power. Suppliers offering unique solutions for agency management, CRM, and data exchange can leverage this specialization to command premium pricing.
The limited availability of vendors capable of providing specific, critical functionalities for Ebix's operations directly enhances the bargaining power of these select suppliers. This scarcity means Ebix has fewer alternatives, making it more susceptible to price increases or less favorable terms from these specialized providers.
The availability of highly skilled software developers, cybersecurity experts, and industry-specific consultants is absolutely critical for Ebix. These aren't just employees; they are the architects of Ebix's products and services. A tight labor market for these specialized roles significantly boosts their bargaining power.
When there's a scarcity of talent, especially in areas like advanced AI development or niche insurance technology, these skilled professionals can command higher salaries and better benefits. This directly impacts Ebix's operational costs and its ability to quickly staff up for new projects or expand existing ones. For instance, reports in late 2023 and early 2024 indicated a persistent shortage of cybersecurity professionals, with demand often outstripping supply by a considerable margin, a trend likely to continue.
Ebix's reliance on infrastructure and cloud service providers is a key consideration. As a company offering on-demand software and e-commerce services, Ebix needs stable and scalable IT infrastructure. This often translates to a significant dependency on cloud computing platforms.
If Ebix is heavily reliant on a limited number of major cloud providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud, these suppliers could wield considerable bargaining power. This power might manifest through increased pricing, less favorable service level agreements, or restrictions on how Ebix can utilize their services. For instance, a sudden price hike by a dominant cloud provider could directly impact Ebix's operational costs and profitability.
However, the competitive landscape among cloud providers is dynamic. The ongoing expansion and innovation from these major players, along with the emergence of specialized or regional cloud providers, could serve to mitigate the bargaining power of any single supplier. In 2024, the global cloud computing market was projected to reach over $600 billion, indicating substantial competition that could benefit users like Ebix by offering more choices and potentially better terms.
Data Providers and Integrations
Ebix's reliance on third-party data providers for its insurance exchange and automation services presents a potential area of supplier bargaining power. If key data feeds are concentrated among a few providers or require specialized, costly integrations, these suppliers can exert significant influence. For instance, in 2024, the global data analytics market was valued at approximately $30 billion, with specialized data providers for niche industries commanding premium pricing.
The complexity and cost associated with switching data providers or integrating new systems can further enhance supplier leverage. Ebix may face substantial expenses and operational disruptions if it needs to change its data sources. This situation is exacerbated when the data provided is proprietary or essential for Ebix’s core functionalities, limiting its ability to negotiate favorable terms.
- Data Dependency: Ebix's operational efficiency hinges on the accuracy and availability of data from external sources.
- Integration Costs: High switching costs for data integration platforms can lock Ebix into existing supplier relationships.
- Market Concentration: If critical data is supplied by a limited number of vendors, their bargaining power increases significantly.
- Value of Data: The unique or proprietary nature of data supplied to Ebix can give suppliers a distinct advantage in negotiations.
Impact of Recent Restructuring
Ebix's emergence from Chapter 11 in August 2024, under new ownership by Eraaya Lifespaces, significantly reshaped its supplier dynamics. While the restructuring aimed to bolster financial health, potentially enhancing Ebix's bargaining power, the immediate aftermath may have presented opportunities for critical suppliers to exert influence. The infusion of capital and a new strategic direction from Eraaya Lifespaces are expected to stabilize and improve future supplier negotiations.
The impact on supplier bargaining power is multifaceted:
- Improved Financial Stability: Following its August 2024 Chapter 11 emergence, Ebix's strengthened financial position, supported by Eraaya Lifespaces, likely reduced its reliance on any single supplier and improved its ability to negotiate favorable terms.
- Potential for Supplier Leverage: During the restructuring period, some key suppliers might have temporarily gained leverage due to Ebix's financial uncertainty, potentially leading to less favorable contract terms for Ebix.
- Long-Term Relationship Re-evaluation: The new ownership structure under Eraaya Lifespaces provides an opportunity for Ebix to re-evaluate and solidify relationships with its suppliers, potentially securing more advantageous agreements based on long-term stability and growth prospects.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Ebix is influenced by the concentration of critical technology providers and the specialized nature of the services they offer. When few vendors can supply essential components or expertise, such as niche software functionalities or specialized data analytics crucial for Ebix's insurance exchange platforms, these suppliers gain significant leverage. This scarcity allows them to potentially dictate terms and pricing, impacting Ebix's operational costs and flexibility.
| Supplier Factor | Impact on Ebix | 2024 Context/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Proprietary Technology & Niche Expertise | Enhances supplier leverage for specialized solutions | Limited availability of unique software for regulated industries |
| Availability of Skilled Labor | Tight labor markets for tech talent increase wage demands | Persistent shortage of cybersecurity professionals reported |
| Cloud Service Provider Dependence | Concentration among major providers can lead to pricing power | Global cloud market projected over $600 billion, indicating competition |
| Data Provider Concentration | Few critical data sources can lead to higher costs and lock-in | Data analytics market valued around $30 billion in 2024 |
What is included in the product
This analysis delves into the five forces shaping Ebix's competitive environment, examining industry rivalry, the threat of new entrants, buyer and supplier power, and the availability of substitutes.
Effortlessly identify and quantify competitive pressures with a visual, interactive dashboard that simplifies complex market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Ebix's core business revolves around integrated solutions like agency management, customer relationship management (CRM), and data exchange platforms. These systems become deeply embedded in how their clients, primarily insurance and financial services firms, operate daily.
The cost for a client to switch from Ebix to a competitor is significant. This includes expenses for migrating vast amounts of sensitive data, retraining employees on new software, and the inevitable disruption to ongoing business operations. For example, a typical financial services firm might spend upwards of $100,000 to $500,000 on such a migration, depending on the complexity and data volume.
These substantial switching costs effectively limit customers' power to negotiate better terms or easily switch to another provider. This inherent lock-in strengthens Ebix's position by ensuring client retention and reducing the direct competitive pressure from rivals seeking to poach existing Ebix customers.
Customer concentration in niche markets can significantly amplify buyer bargaining power. If Ebix relies heavily on a few large clients within specific sectors, these customers gain leverage to negotiate better pricing or demand bespoke solutions. For instance, a substantial portion of revenue from a single large insurance carrier could give that carrier considerable sway over contract terms.
This concentration means that losing even one major client could have a disproportionate impact on Ebix's financial performance. In 2024, while Ebix serves many clients, a deep dive into its revenue breakdown would reveal if any single client or a small group of clients in a particular vertical, like the US life insurance sector, represent an outsized percentage of sales, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
Even with significant switching costs, Ebix customers possess considerable bargaining power due to the wide array of alternative software providers available. Numerous competitors, including Jones, Docutrax, RealPage, TrustLayer, AdvantageGo, and Guidewire InsuranceSuite, offer comparable or niche solutions within the insurance, financial services, and compliance management sectors.
This extensive competitive environment ensures that clients, despite the potential hassle of migrating, retain leverage. For instance, the global insurance software market was projected to reach over $30 billion by 2024, indicating a highly active and competitive space where customer choice is paramount. Ebix must therefore focus on delivering exceptional value and continuous innovation to maintain customer loyalty and mitigate this inherent bargaining power.
Price Sensitivity and Value Proposition
Customers, particularly those in budget-sensitive sectors or during periods of economic slowdown, exhibit heightened price sensitivity. Ebix's effectiveness in showcasing a tangible return on investment through process automation, operational efficiency, and adherence to regulatory standards is paramount in mitigating this. For instance, in 2024, businesses across various industries reported significant cost savings from adopting digital transformation initiatives, with many seeing ROI within 12-18 months.
The perceived value of Ebix's integrated platforms, which foster seamless interactions among clients, partners, and end-customers, plays a vital role in justifying its pricing structure and diminishing overt price-driven concerns. These platforms often centralize data and workflows, reducing manual effort and potential errors, which translates into tangible cost reductions for users. For example, a study in early 2024 indicated that companies utilizing integrated CRM and ERP systems saw an average 15% reduction in operational overhead.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers are more likely to scrutinize costs, especially when economic conditions are uncertain.
- Value Proposition: Ebix must clearly articulate the ROI derived from its solutions, such as cost savings and efficiency gains.
- Integrated Platforms: The ability of Ebix's offerings to connect various stakeholders enhances their perceived value, potentially offsetting price concerns.
- Competitive Alternatives: If substitute solutions offer similar benefits at a lower price point, customer bargaining power is amplified.
Industry Specificity and Regulatory Compliance Needs
Ebix operates in highly regulated sectors, notably insurance, where compliance with complex and frequently changing rules is paramount. This specialization means customers often prioritize providers who can guarantee adherence to these regulations, thereby diminishing their bargaining leverage if Ebix offers superior compliance solutions.
The need for robust regulatory compliance can lock customers into specific providers, especially when switching costs are high due to integration and data migration complexities. For instance, Ebix's role in the National Common Mobility Card (NCMC) rollout in India demonstrates its capability in navigating intricate industry-specific mandates.
- Industry Specialization: Ebix's focus on regulated industries like insurance creates a demand for specialized, compliant software.
- Reduced Customer Leverage: When customers require specific compliance features that Ebix excels at providing, their bargaining power is lessened.
- NCMC Project: Ebix's involvement in India's NCMC project showcases its ability to meet unique regulatory and industry demands, reinforcing customer reliance.
Despite significant switching costs, Ebix customers possess considerable bargaining power due to the wide array of alternative software providers. The global insurance software market was projected to reach over $30 billion by 2024, indicating a highly competitive space where customer choice is paramount.
Customers, particularly those in budget-sensitive sectors, exhibit heightened price sensitivity. Ebix's effectiveness in showcasing a tangible return on investment through process automation and operational efficiency is crucial in mitigating this. For example, businesses across various industries reported significant cost savings from adopting digital transformation initiatives in 2024, with many seeing ROI within 12-18 months.
Ebix's specialization in regulated sectors like insurance, where compliance is paramount, can diminish customer bargaining leverage if Ebix offers superior compliance solutions. Projects like India's NCMC demonstrate Ebix's ability to meet unique industry demands, reinforcing customer reliance.
| Factor | Impact on Ebix's Customer Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Example |
| Switching Costs | Lowers customer power | Migration costs can range from $100,000 to $500,000 for financial services firms. |
| Competitive Landscape | Increases customer power | Global insurance software market projected over $30 billion by 2024. |
| Price Sensitivity | Increases customer power | Companies saw average 15% reduction in overhead with integrated systems (early 2024). |
| Industry Specialization & Compliance | Lowers customer power | Ebix's role in India's NCMC project highlights its compliance capabilities. |
What You See Is What You Get
Ebix Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the exact Ebix Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive upon purchase, offering a comprehensive examination of competitive forces within the industry. Every detail, from the analysis of buyer and supplier power to the intensity of rivalry and threat of new entrants and substitutes, is presented as is, ensuring no discrepancies. You are viewing the final, professionally formatted document, ready for immediate download and application to your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Ebix operates within intensely competitive sectors such as insurance technology, financial services, healthcare, and e-learning, encountering a vast array of rivals. This crowded marketplace includes both large, established software providers and nimble, specialized startups focusing on specific market needs.
The competitive intensity is further amplified by the sheer volume of participants, with numerous alternatives like AdvantageGo, Sapiens, and Guidewire offering competing solutions. This broad spectrum of competitors means Ebix must continuously innovate and differentiate its offerings to maintain market share and attract new customers.
High switching costs, while a strong deterrent for new players entering the market, also intensify the battle among established competitors. Companies like Ebix, which benefit from these costs, must actively work to keep their existing clients happy. This often translates into competitive pricing strategies, continuous innovation to add value, and a strong emphasis on customer support to prevent churn.
For Ebix, its strategy of embedding its solutions deeply within client workflows and offering a broad suite of integrated services effectively capitalizes on these high switching costs. This integration makes it difficult and costly for clients to move to alternative providers, thereby solidifying Ebix's market position. For instance, in the insurance technology sector, where Ebix is a significant player, the cost and effort involved in migrating data, retraining staff, and reconfiguring business processes can be substantial, often running into hundreds of thousands or even millions of dollars for larger enterprises.
Ebix actively differentiates its offerings by providing a broad spectrum of on-demand software and e-commerce solutions designed to automate and simplify complex business operations. This focus on comprehensive integration helps it stand out in a crowded market.
A key differentiator for Ebix, particularly in India and Southeast Asia, is its innovative 'Phygital' strategy for EbixCash. This approach uniquely blends physical and digital service delivery, creating a distinct value proposition for customers in these regions.
The company's commitment to continuous innovation and specialization in critical areas such as agency management, customer relationship management (CRM), and secure data exchange is vital. These specialized capabilities allow Ebix to carve out a niche and maintain a competitive edge against a backdrop of increasingly commoditized software and service offerings.
Impact of Industry Trends and Technology Adoption
The P&C insurance software landscape is being reshaped by swift technological integration. Companies embracing AI/ML, cloud-native architectures, and low-code/no-code platforms are positioning themselves for stronger market standing. For instance, by mid-2024, a significant portion of insurance carriers were actively exploring or implementing AI for claims processing and underwriting, seeking efficiency gains.
This rapid evolution intensifies competitive rivalry. Insurers that can quickly adopt and leverage these innovations, offering more nimble and responsive software solutions, are likely to outpace slower adopters. Ebix's ability to maintain its competitive edge hinges on its commitment to research and development, ensuring its product suite remains aligned with these cutting-edge advancements and evolving industry demands.
- AI in Insurance: 2024 saw increased investment in AI for fraud detection and customer service, with some reports indicating a 25% reduction in processing times for AI-assisted claims.
- Cloud Adoption: By Q3 2024, over 60% of P&C insurers had migrated critical workloads to cloud platforms, enhancing scalability and data analytics capabilities.
- Agile Development: Competitors offering low-code/no-code solutions reported faster product development cycles, with some launching new policy administration features in weeks rather than months.
Market Growth and Strategic Acquisitions
The insurance and financial technology sectors are dynamic and growing, drawing in new competitors and intensifying existing rivalries. This expansion creates opportunities for companies like Ebix to grow, but also means they face more pressure from others vying for market share.
Ebix has a history of aggressive growth through acquisitions, having completed 27 such deals by July 2025. These strategic moves have helped it broaden its product portfolio and geographic presence, but also signal an active approach to navigating a competitive landscape.
Following its emergence from Chapter 11 bankruptcy, Ebix's new ownership under Eraaya Lifespaces is prioritizing international expansion and investment in cutting-edge technologies. This strategic direction suggests Ebix will continue to be an active participant, potentially increasing competitive pressures as it seeks new growth avenues.
- Growing Market Attracts New Entrants: The expanding insurance and fintech industries are a magnet for new companies, heightening competition.
- Ebix's Acquisition Strategy: With 27 acquisitions by July 2025, Ebix has consistently used M&A to gain market position and capabilities.
- Post-Bankruptcy Strategy: New ownership's focus on international growth and tech investment indicates continued aggressive competition.
Competitive rivalry within Ebix's operating sectors is fierce, driven by a mix of large incumbents and agile startups. The constant influx of new technologies, such as AI and cloud-native platforms, further escalates this competition, pushing companies to innovate rapidly to maintain relevance.
For instance, by mid-2024, over 60% of P&C insurers had moved key operations to the cloud, a trend that accelerates the need for technologically advanced solutions. Ebix's own aggressive acquisition strategy, with 27 deals completed by July 2025, highlights its proactive approach to navigating this dynamic and competitive environment.
| Competitor Type | Key Differentiators | Market Impact |
| Large Established Providers | Broad product suites, existing client relationships | Significant market share, high switching costs |
| Specialized Startups | Niche focus, agile development, cutting-edge tech (AI/ML) | Disruptive innovation, pressure on incumbents |
| Ebix | Integrated solutions, 'Phygital' strategy, aggressive M&A | Broadening capabilities, expanding geographic reach |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Manual processes and legacy systems represent a significant threat of substitutes for Ebix's software. Many companies, particularly smaller ones or those in slower-adopting sectors, continue to rely on spreadsheets, paper-based workflows, or older, customized systems. These alternatives, while inefficient and error-prone, bypass the upfront costs and implementation challenges associated with adopting new, comprehensive platforms like Ebix's. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 30% of small businesses still primarily use manual methods for critical functions like customer management or claims processing.
In-house software development presents a significant threat of substitutes for companies like Ebix, particularly for large financial institutions with substantial IT budgets and internal expertise. These entities can opt to build bespoke software solutions, offering unparalleled customization to meet specific operational needs. For instance, a major bank might invest millions in developing its own core banking system rather than relying on third-party vendors.
While in-house development offers tailored functionality, it comes with considerable drawbacks. The upfront investment can be enormous, with development cycles often stretching for years. Ongoing maintenance, updates, and the need for specialized IT talent also contribute to high operational costs, limiting its feasibility to only the largest and most resource-rich organizations. This makes it a less attractive substitute for the majority of Ebix's target market.
Businesses might choose to adapt general-purpose software, like Salesforce or SAP, and customize them for their financial operations instead of using industry-specific platforms. This can seem cheaper upfront, but it often results in integration headaches and missing crucial specialized features.
For example, while a generic ERP might cost $50,000 to implement, extensive customization to mimic insurance workflows could push that figure to $150,000 or more, plus ongoing maintenance. Ebix's specialized solutions, though potentially having a higher initial price tag, offer built-in industry functionality that generic software struggles to replicate efficiently.
The long-term total cost of ownership and the availability of deep, insurance-specific features are key differentiators. In 2024, many businesses found that the hidden costs and functional gaps of customized generic software outweighed the initial savings, reinforcing the value of purpose-built solutions.
Consulting and Outsourcing Services
Clients might opt for specialized consulting firms or external outsourcing providers to manage administrative and compliance functions instead of adopting comprehensive software platforms. These external services can target specific operational gaps, potentially offering a quicker solution without the extensive integration of a full software suite. For instance, many businesses in 2024 continue to leverage specialized BPO (Business Process Outsourcing) for tasks like payroll and HR, with the global BPO market projected to reach over $400 billion by 2027.
While these alternatives address immediate needs, they often fall short in providing the deep, real-time data integration and direct operational control characteristic of Ebix's on-demand SaaS solutions. This lack of integrated data flow can hinder strategic decision-making, especially for core business processes that benefit from a unified system. Ebix itself recognizes this dynamic, offering its own outsourced administrative and risk compliance services as an integrated component of its SaaS offerings, demonstrating a strategy to capture value from both software and service demand.
- Alternative Service Providers: Consulting firms and BPO providers offer specialized services that can substitute for integrated software solutions.
- Market Growth: The global BPO market is expanding, indicating a significant demand for outsourced administrative and compliance tasks.
- Control and Integration: Substitutes may lack the direct control and integrated data flow that Ebix's SaaS platforms provide.
- Ebix's Strategy: Ebix offers its own outsourced services, aligning with market trends and addressing potential substitute threats.
Emerging Technologies and Alternative Business Models
New technological advancements and disruptive business models represent a significant threat of substitutes for Ebix. For example, blockchain technology is emerging as a potential alternative for secure data exchange, and decentralized finance (DeFi) solutions could offer new ways to manage financial transactions, potentially bypassing traditional software intermediaries.
While these innovations are still in their early stages in many of Ebix's primary markets, their continued development necessitates vigilant monitoring and strategic adaptation. Failing to address these emerging alternatives could expose Ebix to future substitution risks, impacting its market position.
- Blockchain for secure data exchange: Offers a decentralized and immutable ledger, potentially reducing reliance on centralized data management systems.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Provides alternative financial transaction methods, potentially disintermediating traditional financial software providers.
- Market monitoring: Continuous tracking of technological advancements and evolving business models is crucial for proactive risk management.
- Adaptation strategy: Ebix must be prepared to integrate or counter these emerging substitutes to maintain its competitive edge.
The threat of substitutes for Ebix stems from various alternatives, ranging from manual processes to advanced technologies. Companies might continue using spreadsheets or legacy systems, bypassing the costs and complexities of new platforms, a trend observed with over 30% of small businesses still relying on manual methods in 2024. In-house software development by large institutions, while costly and time-consuming, offers tailored solutions that can compete with Ebix's offerings.
Customizing general-purpose software like SAP or Salesforce presents another substitute. While seemingly cheaper initially, these often lead to integration issues and a lack of specialized industry features, with customization costs potentially doubling the initial outlay. The total cost of ownership and the availability of insurance-specific functions remain key differentiators, with many businesses in 2024 finding generic software's hidden costs outweighing initial savings.
Specialized consulting firms and Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) providers also act as substitutes by managing specific operational or compliance functions. The global BPO market, projected to exceed $400 billion by 2027, highlights the demand for such services. However, these often lack the integrated data flow and direct operational control that Ebix's SaaS solutions provide.
Emerging technologies like blockchain for secure data exchange and Decentralized Finance (DeFi) for financial transactions pose future threats. While still nascent in many of Ebix's core markets, continuous monitoring and adaptation are crucial to mitigate these substitution risks and maintain a competitive edge.
| Substitute Type | Description | Key Considerations for Ebix | 2024 Relevance/Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Processes/Legacy Systems | Spreadsheets, paper-based workflows, older internal systems. | Bypass upfront costs and implementation challenges. | Over 30% of small businesses still use manual methods for key functions. |
| In-house Software Development | Large institutions building bespoke solutions. | Offers customization but incurs high development and maintenance costs. | Feasible only for the largest, most resource-rich organizations. |
| Customized General Software | Adapting ERPs or CRMs (e.g., SAP, Salesforce). | Potential integration headaches and missing specialized features. | Customization costs can double initial outlay; hidden costs often exceed savings. |
| Outsourced Services (BPO) | Consulting firms, BPO providers for specific functions. | Quicker solutions for specific gaps, but lack integrated data flow. | Global BPO market projected over $400B by 2027. |
| Emerging Technologies | Blockchain, DeFi. | Potential for secure data exchange and alternative transaction methods. | Requires vigilant monitoring and strategic adaptation. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the specialized software market that Ebix serves, particularly for insurance, financial, and healthcare sectors, demands significant upfront capital. This investment is crucial for developing sophisticated products, building robust infrastructure, and attracting skilled professionals. For instance, the average cost to develop enterprise-level software can range from hundreds of thousands to millions of dollars, a substantial hurdle for newcomers.
Ebix's core offerings, such as its agency management systems, customer relationship management (CRM) tools, and data exchange platforms, are inherently complex. Developing and maintaining these solutions requires ongoing and substantial investment in research and development (R&D). In 2024, companies in the software industry typically allocate between 10% to 20% of their revenue to R&D, highlighting the continuous financial commitment needed to stay competitive.
These high financial barriers effectively deter many potential new entrants. Companies without substantial financial backing or a clear path to significant funding will find it exceedingly difficult to compete. This situation benefits established players like Ebix, as it limits the pool of viable competitors and helps maintain market stability.
The insurance and financial sectors are heavily regulated, demanding significant expertise in compliance that can deter new players. Navigating this complex landscape, which includes obtaining various licenses, certifications, and adhering to strict data security standards, requires substantial investment and time. For instance, in 2024, the cost of regulatory compliance for financial institutions continued to rise, with many firms allocating over 10% of their IT budget specifically to meet these demands. Ebix's established track record and deep understanding of these intricate rules present a formidable barrier, as newcomers would need to dedicate considerable resources to achieve comparable credibility and operational adherence.
Building a strong brand reputation and fostering customer trust, particularly in sensitive sectors like insurance and financial services, is a monumental task that requires decades of consistent, reliable performance. Ebix, with its extensive history spanning nearly fifty years and a significant global footprint, has cultivated a deep well of established trust among its clientele.
Newcomers entering these markets face a considerable hurdle in persuading potential customers to abandon established, proven providers, especially when dealing with mission-critical business processes where reliability is paramount. For instance, in 2023, the global financial services sector saw significant investment in cybersecurity, highlighting the critical nature of trust and the potential reluctance of clients to switch to less-proven entities for sensitive data management.
Economies of Scale and Network Effects
Established players like Ebix leverage significant economies of scale in areas such as software development, marketing, and customer service. This allows them to achieve lower per-unit costs, making it challenging for new entrants to match their pricing or reinvestment capacity. For instance, Ebix's extensive customer base in 2024 likely translates to substantial cost efficiencies across its operations.
The integrated nature of Ebix's platforms fosters powerful network effects. As more clients and partners join, the value proposition for all users increases, creating a self-reinforcing cycle of growth. This dynamic makes it considerably harder for newcomers to attract a critical mass of users necessary to compete effectively.
- Economies of Scale: Lower operational costs for established firms like Ebix due to high production volumes.
- Network Effects: Increased platform value as more users join Ebix's ecosystem.
- Customer Lock-in: Existing relationships and integrated systems can make switching costly for clients.
- Brand Loyalty: Decades of operation build trust and recognition, a barrier for new, unproven competitors.
Access to Distribution Channels and Integrated Ecosystems
Newcomers face a steep climb in replicating Ebix's established distribution networks, especially its 'Phygital' approach that blends numerous physical locations with robust digital platforms. This extensive reach is a substantial hurdle for any new entrant aiming to compete.
Ebix's integrated ecosystem, offering a broad spectrum of services from agency management to financial exchange platforms, presents a significant barrier. A new entrant typically focusing on a single product would find it exceptionally difficult to match this comprehensive value proposition.
- Distribution Network: EbixCash boasts over 650,000 points of presence, a key differentiator in its 'Phygital' strategy.
- Integrated Services: The company's ability to provide a wide array of financial and insurance-related services under one umbrella makes it challenging for niche competitors.
- Ecosystem Lock-in: Customers are often drawn to the convenience and synergy of Ebix's integrated offerings, creating a form of ecosystem lock-in that deters switching.
The threat of new entrants for Ebix is relatively low, primarily due to the substantial financial capital required to enter its specialized software markets. Developing complex insurance, financial, and healthcare software demands millions in R&D and infrastructure. For instance, in 2024, the software development industry saw continued high investment in innovation, with many firms dedicating 10-20% of revenue to R&D.
Regulatory compliance in the insurance and financial sectors is another significant barrier. Navigating licensing, certifications, and data security rules requires substantial resources and time, with financial institutions in 2024 allocating over 10% of their IT budgets to compliance.
Furthermore, Ebix benefits from established brand loyalty and economies of scale. Its extensive network, with over 650,000 points of presence for EbixCash, creates powerful network effects and customer lock-in, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for software development and infrastructure. | Significant deterrent for underfunded competitors. | Enterprise software development costs: $100,000s to $Millions. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Complex licensing, certifications, and data security standards. | Demands expertise, time, and financial resources. | Financial institutions' IT budgets for compliance: >10%. |
| Brand Loyalty & Trust | Decades of reliable performance in sensitive sectors. | Difficult for new entrants to displace established relationships. | Financial services sector cybersecurity investment highlights trust's importance. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to high production volumes. | Challenging for new entrants to match pricing and reinvestment capacity. | Ebix's large customer base likely yields significant operational efficiencies. |
| Network Effects | Increased platform value with more users and partners. | Creates a self-reinforcing cycle of growth, hard for newcomers to break into. | Ebix's integrated ecosystem fosters synergy and convenience. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Ebix Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from industry-specific market research reports, financial statements of key players, and regulatory filings to provide a comprehensive view of competitive dynamics.
We leverage a combination of proprietary Ebix data, public company disclosures, and insights from leading market intelligence firms to accurately assess the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the intensity of rivalry.
