Cielo Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Cielo Bundle
Understanding Cielo's competitive landscape is crucial, and Porter's Five Forces provides the framework. While we've touched on key pressures, the full analysis delves into the intricate dynamics of buyer power, supplier leverage, and the threat of substitutes impacting Cielo.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Cielo’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of technology and infrastructure providers for Cielo is generally considered moderate to high. This is because Cielo's core operations heavily depend on specialized hardware for point-of-sale terminals and sophisticated software solutions, often supplied by a limited number of providers.
The complexity and proprietary nature of these technologies can create significant switching costs for Cielo, giving these suppliers leverage. For instance, in 2024, the global IT infrastructure market saw continued consolidation, potentially increasing the concentration of power among key providers of payment processing technology.
Cielo's bargaining power of suppliers is significantly influenced by global card networks such as Visa and Mastercard. These networks set the rules and interchange fees, directly affecting Cielo's operational costs and profitability. In 2024, interchange fees remain a critical component of acquirer revenue, though discussions around potential regulatory adjustments continue globally.
While Cielo is a dominant acquirer in Brazil, the sheer global scale and network effect of Visa and Mastercard grant them substantial leverage. They dictate terms for brand usage and transaction processing standards, making it challenging for acquirers like Cielo to negotiate favorable conditions. This reliance on a few key global players underscores the inherent supplier power in the payment processing industry.
Providers of cybersecurity and fraud prevention solutions hold significant sway in the digital payment ecosystem. As cyber threats become more complex, these specialized firms offer indispensable services that are difficult to replace, giving them considerable bargaining power.
For instance, in 2024, the global cybersecurity market was projected to reach over $270 billion, highlighting the critical demand for these services. Companies like Palo Alto Networks and CrowdStrike, leaders in this space, command premium pricing due to the essential nature of their offerings and the high switching costs for integrated security systems.
Supplier Power 4
Financial institutions that provide banking and settlement services to Cielo hold moderate bargaining power. These services are essential for managing the flow of money within the payment processing ecosystem, making them critical for Cielo's operations.
While Cielo can choose from several banks, the highly regulated nature of financial services and the deep integration required for seamless transactions create a degree of supplier interdependence. This means that switching providers isn't always straightforward or cost-free.
For instance, in 2024, major payment processors often rely on a few key banking partners for critical functions like fund settlement and liquidity management. The concentration of expertise and the stringent compliance requirements in these areas can amplify the suppliers' leverage.
- Interdependence: Banks are crucial for fund movement, creating reliance.
- Regulation: Strict financial regulations can limit switching options.
- Integration Costs: High costs associated with integrating new banking systems.
- Market Concentration: A limited number of providers for specialized financial services.
Supplier Power 5
The bargaining power of suppliers for Cielo, a major player in Brazil's payment processing market, is significantly influenced by the specialized nature of its infrastructure. The substantial capital investment needed to build and maintain proprietary payment processing systems, coupled with the requirement for highly skilled technical expertise, creates a considerable barrier to entry for potential alternative suppliers. This high switching cost and the limited availability of comparable alternatives strengthen the position of existing suppliers, allowing them to exert considerable leverage.
In 2024, the concentration of specialized technology providers in the payment infrastructure sector means that Cielo often relies on a select group of vendors for critical components and services. For instance, the development and maintenance of secure, high-volume transaction processing platforms demand specific software and hardware solutions that are not widely available. This reliance on a limited supplier base, combined with the ongoing need for updates and specialized support to ensure compliance and operational efficiency, reinforces supplier power within the industry.
- High Capital Investment: Building and maintaining a proprietary payment processing infrastructure requires hundreds of millions of dollars in upfront and ongoing investment, limiting the pool of potential new suppliers.
- Specialized Expertise: The need for deep technical knowledge in areas like cybersecurity, network management, and regulatory compliance for payment systems restricts the number of qualified suppliers.
- Limited Alternatives: The market for highly specialized payment technology and services is often concentrated, meaning few viable alternatives exist for critical components, thereby increasing supplier leverage.
- Switching Costs: The significant costs and operational disruptions associated with changing payment technology providers further entrench the bargaining power of incumbent suppliers.
Suppliers of specialized technology and infrastructure for Cielo, particularly those providing point-of-sale terminals and complex software, wield considerable power. This is due to the limited number of providers and the high switching costs associated with Cielo's reliance on these critical, often proprietary, systems. In 2024, ongoing consolidation in the IT infrastructure market further concentrated power among key payment technology providers, potentially increasing their leverage over acquirers like Cielo.
Global card networks such as Visa and Mastercard exert significant influence over Cielo by dictating interchange fees and transaction processing standards. These networks' vast scale and network effects grant them substantial leverage, making it difficult for acquirers to negotiate favorable terms. Discussions around potential regulatory adjustments to interchange fees continued globally in 2024, a key revenue component for acquirers.
Providers of essential cybersecurity and fraud prevention solutions also hold strong bargaining power. The increasing sophistication of cyber threats makes these specialized services indispensable and difficult to replace, allowing providers to command premium pricing. The global cybersecurity market's projected growth to over $270 billion in 2024 underscores the critical demand and the power of leading firms in this sector.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Cielo is amplified by the high capital investment and specialized expertise required for payment processing infrastructure. Limited alternatives and substantial switching costs solidify the leverage of incumbent suppliers, who often provide critical components and ongoing specialized support to ensure compliance and operational efficiency.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Level | Key Influencing Factors | 2024 Context/Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology & Infrastructure Providers | Moderate to High | Specialized hardware/software, limited providers, high switching costs | IT infrastructure market consolidation |
| Global Card Networks (Visa, Mastercard) | High | Network effects, control over standards and fees | Interchange fees critical to acquirer revenue; ongoing regulatory discussions |
| Cybersecurity & Fraud Prevention | High | Indispensable services, high switching costs, increasing threat landscape | Global cybersecurity market projected over $270 billion in 2024 |
| Financial Institutions (Banking/Settlement) | Moderate | Essential services, regulatory environment, integration complexity | Concentration of expertise in key banking partners for settlement |
What is included in the product
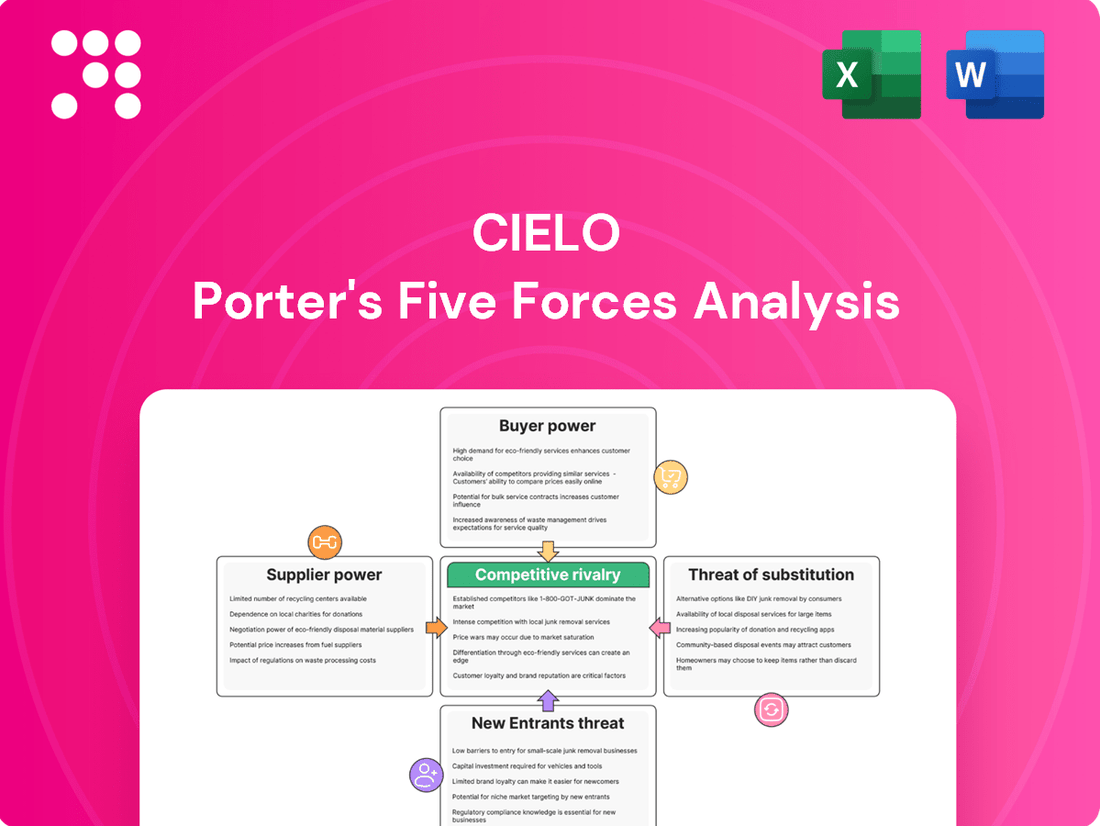
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for Cielo meticulously examines the competitive intensity, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the risk of substitutes impacting Cielo's market position and profitability.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of all five forces, simplifying complex strategic pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
Cielo's customer base is diverse, encompassing merchants of all sizes throughout Brazil. While the vast number of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) individually possess limited bargaining power, larger clients represent a significant concentration of transaction volume. For instance, in 2023, Cielo served a substantial number of merchants, with a notable portion of its revenue derived from larger accounts.
These major clients, due to their substantial transaction volumes, can negotiate more favorable terms, potentially impacting Cielo's fee structures and service level agreements. The ability of these large merchants to switch providers or consolidate their business with competitors can create downward pressure on pricing and margins for Cielo.
The bargaining power of customers for Cielo, a major payment processor in Brazil, has significantly increased due to the proliferation of competing acquirers and payment facilitators. Companies like StoneCo and PagSeguro, alongside numerous fintech startups, have entered the market, offering merchants a wider array of choices for payment processing services. This heightened competition directly translates to greater customer leverage.
Merchants, empowered by these numerous alternatives, are now more price-sensitive and can demand better terms and enhanced features from their payment processors. For instance, in 2024, the Brazilian fintech sector continued its rapid expansion, with new payment solutions constantly emerging, putting pressure on established players like Cielo to innovate and offer competitive pricing to retain their merchant base.
The growing popularity of Pix, Brazil's instant payment system, has significantly boosted merchant bargaining power. This low-cost payment method reduces their dependence on traditional card networks and acquirers like Cielo, giving them more leverage in negotiations.
In 2023, Pix transactions in Brazil surged, reaching over 20 billion operations, demonstrating its widespread adoption and impact on payment ecosystems. This shift means merchants can increasingly opt for Pix for certain sales, diminishing their need for card processing services and strengthening their position when discussing fees and terms with providers.
Bargaining Power of Customers 4
The bargaining power of customers, particularly merchants in the payment processing industry, is on the rise. Switching costs for merchants are diminishing as payment technologies become more standardized. This standardization, coupled with a competitive landscape offering diverse solutions, makes it easier for businesses to change providers if they find better rates or services.
The ease of integrating new Point of Sale (POS) systems and payment gateways further empowers merchants. This technological accessibility allows them to explore and adopt alternative payment solutions without significant disruption. For instance, the widespread adoption of cloud-based POS systems and APIs has streamlined the process of switching payment processors, reducing the friction associated with migration.
- Lower Switching Costs: Standardization in payment technologies reduces the effort and expense for merchants to change providers.
- Increased Provider Competition: A growing number of payment processors offer competitive pricing and features, giving merchants more options.
- Ease of Integration: Modern POS systems and payment gateways are designed for easier integration, facilitating quicker transitions between providers.
- Merchant Demand for Better Rates: Merchants are actively seeking cost savings, driving them to switch providers for more favorable transaction fees and service charges.
Bargaining Power of Customers 5
The bargaining power of customers, particularly merchants in Brazil's payment processing sector, is on the rise. As the market matures, pricing and service transparency increases, giving merchants more leverage. This heightened visibility allows them to compare offerings and negotiate better terms with providers like Cielo.
In 2024, this trend is evident as merchants actively seek cost efficiencies. For instance, the average interchange fees, a significant component of transaction costs, remain a key negotiation point. Merchants are increasingly aware of these costs and are pushing for reduced processing fees from acquirers.
Several factors contribute to this growing customer power:
- Increased Market Transparency: Regulatory efforts and industry data sharing have made pricing structures more visible, enabling merchants to benchmark Cielo's offerings against competitors.
- Consolidation of Merchant Base: Larger merchants and retail chains, by processing higher volumes, gain more significant bargaining power due to their substantial contribution to an acquirer's revenue.
- Availability of Alternatives: The expansion of fintech solutions and alternative payment methods provides merchants with more choices, reducing their dependence on traditional acquirers like Cielo.
- Focus on Cost Optimization: In the current economic climate, businesses are prioritizing cost reduction, making them more sensitive to transaction fees and more inclined to negotiate aggressively.
Cielo's customer bargaining power is amplified by the competitive landscape in Brazil's payment processing sector. The rise of numerous fintechs and alternative payment methods, like Pix, has given merchants more options and leverage. This increased choice allows them to demand better rates and services, putting pressure on Cielo's margins.
Merchants, especially larger ones processing high volumes, can negotiate more favorable terms due to their significant contribution to an acquirer's revenue. For instance, in 2023, the widespread adoption of Pix, with over 20 billion transactions, demonstrated its growing role and reduced merchant reliance on traditional card processing.
The decreasing switching costs, facilitated by standardized payment technologies and easier integration of new POS systems, further empower merchants to explore and adopt alternative solutions. This trend is expected to continue in 2024 as businesses prioritize cost optimization and seek the most competitive pricing.
| Factor | Impact on Cielo | Supporting Data/Trend |
| Competition | Increased pressure on pricing and services | Proliferation of fintechs and alternative payment providers in Brazil. |
| Alternative Payments | Reduced reliance on card processing | Pix transactions exceeded 20 billion in 2023, indicating strong adoption. |
| Switching Costs | Easier for merchants to change providers | Standardization of payment technologies and cloud-based POS systems. |
| Merchant Volume | Larger clients have greater negotiation power | Significant revenue concentration from larger accounts for Cielo. |
What You See Is What You Get
Cielo Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Cielo Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape of the airline industry. You're viewing the actual document, which will be instantly available for download upon purchase, offering a comprehensive understanding of industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Brazilian payment solutions market is a battleground with numerous participants, including established acquirers, agile fintechs, and major banks, creating a highly competitive environment for Cielo.
Cielo contends with formidable rivals like Rede, a long-standing player, and disruptive newcomers such as StoneCo and PagSeguro, which have rapidly gained market share through innovative offerings and aggressive expansion strategies.
In 2024, the Brazilian fintech sector continued its robust growth, with transaction volumes processed by companies like StoneCo and PagSeguro demonstrating significant year-over-year increases, intensifying pressure on incumbent acquirers like Cielo.
The introduction of Pix, Brazil's instant payment system, has dramatically intensified competitive rivalry among payment processors. Pix offers near-zero fees for consumers and substantially reduced costs for businesses, directly impacting the profitability of traditional card transaction fees. This has forced acquirers to compete more aggressively on price and service to retain and attract transaction volume.
By mid-2024, Pix transactions had surpassed traditional debit and credit card payments in Brazil, with billions of transactions processed monthly. This shift means companies like Cielo, which historically relied on interchange fees from card transactions, must innovate and adapt their business models to remain competitive in this new, fee-sensitive environment.
Competitive rivalry within the payment processing sector is intensifying as product differentiation becomes a significant challenge. Core payment processing services are increasingly viewed as commodities, forcing companies to compete on factors beyond basic transaction handling. This dynamic means players are aggressively pursuing market share through a combination of value-added services, cutting-edge technology, and aggressive pricing strategies. For instance, in 2024, major payment processors continued to invest heavily in areas like fraud prevention and data analytics to differentiate their offerings.
Competitive Rivalry 4
The competitive rivalry within the payment processing sector remains fierce, fueled by ongoing market expansion driven by increasing digital adoption and financial inclusion. This growth, however, acts as a magnet for new entrants, intensifying the struggle for merchant acquisition and transaction volume dominance.
Companies are strategically deploying significant capital into technological advancements and innovative solutions to secure and maintain their competitive standing. For instance, in 2024, major players continued to pour billions into R&D, focusing on areas like real-time payment processing, enhanced security features, and seamless integration with e-commerce platforms.
- Intensified Competition: The market's expansion due to digital growth attracts numerous new and existing players, leading to aggressive competition for merchants and transaction share.
- Technology Investment: Companies are heavily investing in technology and innovation to differentiate themselves and gain a competitive advantage.
- Market Share Battle: The fight for market share is particularly acute, with companies vying for dominance in acquiring new merchants and increasing transaction volumes.
- Innovation as a Differentiator: Continuous innovation in areas like payment speed, security, and user experience is crucial for survival and success.
Competitive Rivalry 5
Regulatory shifts, particularly Open Finance initiatives, are actively fostering a more competitive landscape within the financial sector. These regulations are designed to enhance financial accessibility and encourage data sharing, which in turn lowers the barriers to entry for new service providers. This dynamic directly intensifies rivalry, compelling established players like Cielo to continuously innovate and adapt their strategies to maintain a competitive edge. For instance, as of early 2024, several Latin American countries were actively progressing with their Open Finance frameworks, aiming to unlock greater market competition.
The increasing ease of data sharing and the potential for new market entrants to leverage this information means that differentiation and customer-centricity become paramount. Cielo must therefore focus on developing unique value propositions and enhancing its service offerings to stand out in this evolving environment. Failure to do so could lead to market share erosion as more agile, digitally-native competitors emerge, empowered by these regulatory changes.
- Open Finance initiatives are designed to democratize financial data.
- This regulatory push lowers barriers for new entrants, intensifying competition.
- Cielo must prioritize continuous innovation and strategic adaptation.
- Customer-centricity and unique value propositions are crucial for differentiation.
The competitive rivalry for Cielo is exceptionally high, driven by a crowded market of established players, agile fintechs, and banks, all vying for merchant transactions. In 2024, the continued growth of digital payments and the disruptive impact of instant payment systems like Pix have intensified this battle, forcing companies to compete aggressively on price and innovation.
| Competitor | Market Position (Est. 2024) | Key Differentiator |
|---|---|---|
| Rede | Major Acquirer | Extensive merchant network, established brand |
| StoneCo | Growing Fintech Acquirer | Integrated software solutions, focus on SMEs |
| PagSeguro | Leading Fintech Acquirer | Digital banking services, broad consumer reach |
| Banks (e.g., Itaú, Bradesco) | Significant Payment Providers | Existing customer base, bundled financial services |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant threat to Cielo's core credit and debit card processing business in Brazil is the rapid expansion of Pix, the instant payment system. Pix facilitates real-time, often free, transactions directly between bank accounts, directly challenging the need for traditional card infrastructure in many scenarios.
By mid-2024, Pix had become deeply ingrained in Brazilian commerce, with transaction volumes consistently surpassing those of credit and debit cards for certain payment types. This shift directly erodes the transaction fees that form a substantial part of Cielo's revenue, making it a potent substitute.
The threat of substitutes for traditional payment processing, like those offered by Cielo, is growing significantly. Digital wallets and mobile payment applications, often leveraging instant payment systems such as Pix in Brazil, provide consumers with convenient alternatives to using physical cards at point-of-sale terminals. This trend can reduce the necessity for traditional acquirer networks that companies like Cielo rely on for transaction processing.
Direct bank transfers like TED and DOC, along with the ubiquitous boleto bancário, have historically been substitutes for card payments. However, the rapid adoption of Pix, Brazil's instant payment system, has significantly diminished the speed advantage previously held by TED/DOC. As of early 2024, Pix transactions routinely settle in seconds, making older transfer methods feel comparatively slow.
Boleto bancário, while not offering instant settlement, remains a crucial alternative for a substantial portion of the Brazilian population, especially those without traditional bank accounts or for specific payment needs like utility bills and online purchases. In 2023, boletos continued to represent a significant volume of non-card transactions, demonstrating their persistent relevance as a payment substitute, particularly for lower-income segments and for recurring bill payments.
Threat of Substitutes 4
Emerging payment technologies represent a significant threat of substitutes for traditional payment processors like Cielo. For instance, QR code payments, which bypass traditional card networks, are gaining traction. In 2023, the global QR code payment market was valued at approximately USD 17.5 billion and is projected to grow substantially. This indicates a growing consumer preference for alternative, often more convenient, payment methods.
Furthermore, the potential for broader adoption of cryptocurrency payments could also disrupt the existing landscape. While currently niche, the increasing institutional interest and regulatory clarity surrounding digital assets suggest a future where cryptocurrencies might offer a viable alternative for transactions. This diversification of payment options directly challenges the established dominance of card-based systems.
- QR Code Payment Market Growth: The global QR code payment market reached roughly USD 17.5 billion in 2023, highlighting a significant shift towards alternative payment methods.
- Cryptocurrency Adoption: Increasing institutional interest and evolving regulations could pave the way for wider cryptocurrency usage in payments, posing a future substitute threat.
- Diversification of Payment Landscape: The rise of these new technologies diversifies payment options, potentially reducing reliance on traditional card networks and impacting established players.
Threat of Substitutes 5
Cash continues to be a significant substitute for electronic payments, especially in Brazil's informal economy and for everyday, smaller transactions. Despite the rapid growth of digital payment solutions, cash's tangible nature and widespread acceptance in certain segments mean it remains a viable alternative outside the formal electronic payment ecosystem.
In 2024, while Brazil has seen a substantial increase in Pix transactions, with over 170 million users by early 2024 and billions of transactions processed, cash still holds ground. For instance, a significant portion of retail sales, particularly in smaller businesses or for services rendered directly to consumers, still involves cash payments. This persistent preference for cash, even as digital alternatives gain traction, highlights a segment of the market that is not fully captured by electronic payment providers.
- Cash Prevalence: Remains a key substitute, particularly in informal sectors and for micro-transactions in Brazil.
- Digitalization Contrast: Despite the strong push towards digital payments like Pix, cash offers a tangible alternative.
- Market Segment: Represents a fundamental payment method outside the electronic payment ecosystem, impacting market share for digital providers.
- 2024 Data Point: Over 170 million Brazilians were Pix users by early 2024, yet cash transactions continue to be relevant for a substantial portion of daily commerce.
The threat of substitutes for Cielo's traditional payment processing services is substantial and evolving. Pix, Brazil's instant payment system, has rapidly become a dominant force, facilitating direct bank-to-bank transfers that bypass card networks entirely. By mid-2024, Pix transaction volumes frequently outpaced card transactions for many payment types, directly impacting Cielo's revenue streams from transaction fees.
Digital wallets and mobile payment apps, often built upon instant payment rails like Pix, offer consumers convenient alternatives to physical cards. This shift reduces the reliance on traditional acquirer infrastructure. Emerging technologies like QR code payments, which circumvent card networks, are also gaining traction, with the global market valued at approximately USD 17.5 billion in 2023, signaling a growing preference for these alternative methods.
| Substitute Method | Key Impact on Cielo | 2023/2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Pix (Instant Payment) | Directly erodes transaction fee revenue by offering free, real-time transfers. | Over 170 million users by early 2024; surpassed card volumes in many segments. |
| Digital Wallets/Mobile Payments | Reduces need for traditional card processing infrastructure. | Leverages instant payment systems like Pix for enhanced convenience. |
| QR Code Payments | Bypasses traditional card networks. | Global market reached ~USD 17.5 billion in 2023, indicating growing adoption. |
| Cash | Remains prevalent in informal economy and for smaller transactions. | Continues to be a significant alternative outside the electronic payment ecosystem. |
Entrants Threaten
The Brazilian payment processing market, despite its allure and significant growth potential, presents formidable hurdles for newcomers. These barriers are not minor; they demand considerable financial investment upfront, particularly for the essential technology infrastructure and robust security systems required in this sector.
Beyond technology, navigating the complex regulatory landscape in Brazil is a significant challenge. Obtaining the necessary licenses and adhering to stringent compliance standards requires time, expertise, and financial resources, acting as a substantial deterrent to potential entrants.
Furthermore, establishing a widespread network of merchants and building trust within the existing ecosystem is crucial for success. This network effect is hard to replicate, as established players already possess a large customer base and strong relationships, making it difficult for new entrants to gain traction quickly.
The threat of new entrants in Brazil's financial services sector, particularly for companies like Cielo, is significantly dampened by stringent regulatory requirements. The Central Bank of Brazil (BCB) imposes substantial hurdles, necessitating licenses and comprehensive compliance frameworks, including Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CTF) protocols. These rules are designed to safeguard financial stability and protect consumers, effectively creating a high barrier to entry.
Established network effects are a significant barrier for new entrants in the payment processing industry. For a company like Cielo, the more users and merchants that adopt its platform, the more valuable it becomes for everyone involved. This creates a powerful advantage that is difficult for newcomers to overcome, as building a comparable network requires substantial time and investment.
In 2024, the Brazilian payment market, where Cielo operates, saw continued growth in digital transactions. While specific figures for new entrant market share are not readily available, the dominance of established players like Cielo, with their deep integration into the financial ecosystem and existing customer relationships, highlights the challenge of disrupting this entrenched network. Gaining the trust and widespread adoption needed to compete effectively demands considerable resources and a clear value proposition that addresses this network advantage.
Threat of New Entrants 4
The threat of new entrants in the financial services sector, particularly in Brazil, is a significant consideration. The proliferation of fintechs and digital banks highlights how innovative, often low-cost business models can disrupt established players. These newcomers frequently leverage advancements like Pix, Brazil's instant payment system, to gain traction.
These new entrants often begin by targeting specific market segments or niches, offering specialized services before aiming for wider market penetration. This strategy allows them to build a customer base and refine their offerings without immediately confronting the full competitive might of incumbent institutions.
For instance, in 2023, the number of fintechs operating in Brazil continued to grow, with many focusing on areas like digital payments, credit, and investments. These agile companies can often bypass the legacy infrastructure costs faced by traditional banks, enabling them to offer more competitive pricing.
- Fintech Growth: Brazil's fintech sector saw substantial growth, with new digital banks and payment providers entering the market.
- Pix Adoption: The widespread adoption of Pix has lowered barriers to entry for digital payment solutions.
- Niche Focus: New entrants often start by targeting specific customer segments or financial product niches.
- Cost Advantages: Digital-native models typically possess lower operational costs compared to traditional banks.
Threat of New Entrants 5
The threat of new entrants into the market, as analyzed within Cielo Porter's Five Forces framework, is significantly influenced by the robust competitive responses from established players. These incumbents often employ strategies such as aggressive pricing to undercut newcomers, form strategic partnerships to solidify market share and create barriers to entry, and continuously innovate to offer enhanced value-added services. For instance, in the telecommunications sector, major players like AT&T and Verizon have historically responded to new entrants with significant capital investments in network upgrades and bundled service offerings, making it challenging for smaller, less capitalized companies to gain traction. In 2024, the ongoing 5G network build-out continues to represent a substantial capital expenditure, acting as a natural deterrent for potential new mobile virtual network operators (MVNOs) or infrastructure providers without substantial backing.
These established competitive tactics make it exceedingly difficult for new entrants to achieve sustainable profitability and scale rapidly in what is often a dynamic and capital-intensive market. The ability of incumbents to leverage existing customer bases, brand loyalty, and economies of scale further erects formidable barriers. For example, in the cloud computing space, established providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure benefit from massive existing infrastructure and a vast ecosystem of developers and partners, creating a high switching cost for potential customers and a steep learning curve for new competitors to navigate. The market capitalization of these giants, often in the hundreds of billions of dollars, underscores the financial muscle available to fend off new challengers.
- Aggressive Pricing: Incumbents can lower prices to make it unsustainable for new entrants to compete profitably.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborations with suppliers or distributors can lock out new players.
- Continuous Innovation: Ongoing development of new features and services maintains customer loyalty and raises the bar for competitors.
- High Capital Requirements: Significant upfront investment, such as in network infrastructure or research and development, deters many potential entrants.
The threat of new entrants in Brazil's payment sector is considerably low due to high capital requirements for technology and security, alongside complex regulatory hurdles. Established players like Cielo benefit from strong network effects, making it difficult for newcomers to gain widespread merchant adoption and customer trust.
New entrants often leverage agile, digital-native models and niche market focuses, as seen with the continued growth of fintechs in Brazil. The widespread adoption of instant payment systems like Pix has lowered some barriers, but incumbents' deep integration and existing customer relationships remain significant deterrents.
Established companies actively defend their market share through aggressive pricing, strategic partnerships, and continuous innovation. These tactics, coupled with the substantial capital needed for infrastructure, create formidable barriers that limit the impact of new competitors.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Cielo is built upon a robust foundation of data, including publicly available financial reports, industry-specific market research from firms like Euromonitor and IDC, and regulatory filings from relevant government bodies.
