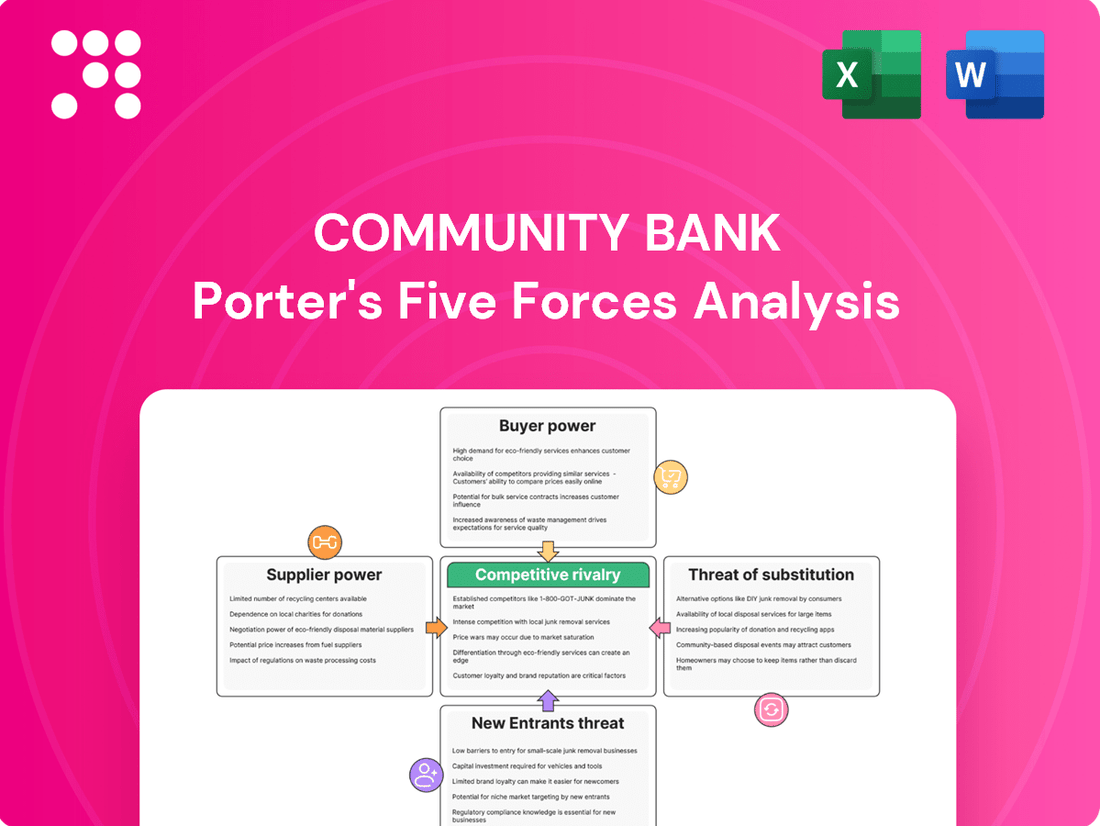
Community Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Community Bank Bundle
Community Bank faces a dynamic competitive landscape shaped by several key forces. Understanding the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of customers, and the threat of new entrants is crucial for strategic planning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Community Bank’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Depositors, as the primary source of capital for community banks, wield considerable bargaining power, particularly when interest rates are on the rise. In such environments, depositors can readily move their funds to accounts offering better yields or explore alternative investment avenues, forcing banks to compete more aggressively for deposits. This dynamic directly influences a bank's cost of funding and its overall profitability.
Community Bank System, Inc., like many of its peers, must offer attractive deposit rates to secure and retain customer funds. This necessity directly impacts its cost of capital and, consequently, its net interest margin. The sensitivity of depositors to interest rate changes has been a major focus for community bank executives throughout 2024 and into 2025, with many prioritizing strategies for deposit growth and retention.
Community Bank System, Inc. leans heavily on technology providers for its core banking systems, digital interfaces, and crucial cybersecurity. These specialized vendors can wield moderate to significant bargaining power, especially when switching costs are high or when they offer proprietary, advanced solutions such as AI for fraud detection. Banks are boosting tech investments, with the U.S. financial sector expected to spend over $100 billion on technology in 2024 alone.
The availability of skilled professionals across banking, wealth management, and insurance significantly impacts supplier power. A scarcity of qualified talent, especially in niche areas like cybersecurity or data analytics, can drive up labor costs and wage expectations. For instance, as of late 2024, the demand for financial analysts with expertise in AI and machine learning outstripped supply, leading to reported salary increases of 10-15% in some markets.
Community Bank System, Inc.'s diverse operations, spanning banking, wealth management, insurance, and employee benefits, necessitate a broad spectrum of specialized skills. This reliance on varied expertise means that shortages in any one area, such as experienced compliance officers or digital transformation specialists, can empower those suppliers of talent, potentially increasing recruitment and retention costs.
Impact of Regulatory Compliance Costs
Regulatory bodies, while not traditional suppliers, exert significant influence by imposing compliance costs, akin to a supplied 'price' for operating. The heightened focus in 2024 and 2025 on areas like liquidity management, concentrations in commercial real estate, and robust cybersecurity measures compels community banks to divert substantial financial and human resources towards meeting these requirements. This increased allocation effectively raises the cost of doing business within the banking sector.
Community banks are particularly susceptible to these evolving regulatory landscapes, facing a growing burden of compliance. This can be seen in the increasing complexity and cost associated with adhering to new capital requirements and data reporting standards. For instance, the cost of cybersecurity compliance alone saw an average increase of 15% for financial institutions between 2023 and 2024, according to industry reports.
- Increased regulatory scrutiny on liquidity management
- Stricter rules on commercial real estate concentrations
- Enhanced cybersecurity compliance mandates
- Rising operational costs due to adherence to new reporting standards
Access to Critical Market Data and Analytics
Access to critical market data and analytics is a significant factor influencing the bargaining power of suppliers for community banks. Providers of specialized information, particularly those offering AI-driven insights into customer behavior and fraud detection, can exert moderate influence. This is due to the essential nature of their services and the often proprietary technology involved. For instance, in 2024, community banks were increasingly investing in data analytics, with some reports indicating a 15-20% increase in spending on these technologies to better understand and serve their customer base.
These data and analytics providers are crucial for community banks to make sound lending and investment decisions. Services like credit rating agencies and advanced analytical platforms are not easily substituted. The proprietary nature of advanced AI tools, which can predict market trends or identify high-risk customers with greater accuracy, further solidifies the suppliers' position. For example, specialized fraud detection software, which can reduce losses by a significant percentage, becomes a non-negotiable expense for many institutions.
- Data providers offering unique AI-powered insights into customer behavior and fraud detection hold moderate bargaining power.
- The necessity of credit rating services and advanced analytics for informed decision-making underpins supplier influence.
- Community banks' increasing investment in data analytics, projected to rise further in 2025, highlights the demand for these critical supplier services.
- Proprietary technology and the specialized nature of data offerings contribute to the suppliers' leverage in negotiations.
The bargaining power of suppliers for community banks is a multifaceted issue, with key areas including depositors, technology providers, and specialized talent. Depositors, especially in a rising interest rate environment, can move funds, forcing banks to compete for capital, impacting funding costs. Technology vendors, particularly those offering proprietary solutions like AI for fraud detection, also hold significant sway due to high switching costs. The demand for skilled professionals in areas like cybersecurity and data analytics outstrips supply, driving up labor costs for banks.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Level | Key Factors | 2024/2025 Relevance |
| Depositors | High (especially with rising rates) | Interest rate sensitivity, availability of alternative investments | Banks focused on deposit growth and retention strategies. |
| Technology Providers (Core Banking, AI, Cybersecurity) | Moderate to High | Proprietary solutions, high switching costs, essential services | U.S. financial sector tech spending over $100 billion in 2024; increased investment in data analytics. |
| Specialized Talent (Cybersecurity, Data Analytics) | High (due to scarcity) | Demand exceeding supply, niche expertise | Salary increases of 10-15% for financial analysts with AI/ML skills in late 2024. |
| Data & Analytics Providers | Moderate | Unique AI insights, necessity for decision-making, proprietary tech | 15-20% increase in spending on data analytics by community banks. |
What is included in the product
Tailored exclusively for Community Bank, this analysis dissects the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of customers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, to illuminate its competitive environment.
Easily identify and mitigate threats from competitors and new entrants by visualizing the intensity of each force.
Gain clarity on supplier and buyer power to negotiate better terms and secure advantageous partnerships.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers can easily switch banks for basic deposit accounts and simple loans, with switching costs being quite low. This is largely due to the growth of digital banking and open banking regulations, which make it simpler for individuals to move their money or find better deals. For instance, in 2023, the number of customers using digital banking platforms for everyday transactions continued to climb, with many reporting satisfaction with the ease of account management and transfer capabilities.
This ease of movement puts direct pressure on Community Bank System, Inc. to remain competitive. They need to offer attractive interest rates on savings and checking accounts, along with user-friendly loan terms, to keep customers from looking elsewhere. Community Bank's recent partnerships to enhance their digital banking offerings directly address this, aiming to improve customer experience and retention in a market where digital mobility is key.
Customers in the banking sector have a wealth of options at their disposal, ranging from large national banks and member-owned credit unions to innovative fintech companies and online lenders. This extensive selection directly amplifies customer bargaining power. For instance, as of early 2024, the number of fintech startups in the US continued to grow, offering specialized services that challenge traditional banking models.
The financial services landscape is intensely competitive, extending far beyond the traditional brick-and-mortar banks. This broad availability of alternatives compels institutions like Community Bank System, Inc. to actively differentiate their services and cultivate robust customer relationships to retain market share. In 2023, deposits held by credit unions in the U.S. reached over $2.3 trillion, demonstrating a significant alternative for consumers.
In a crowded banking landscape, customers hold significant sway due to their sensitivity to pricing. This means Community Bank System, Inc. must carefully manage interest rates on deposits and loans, along with service fees, to stay competitive and keep customers loyal, directly affecting its bottom line.
For instance, as of early 2024, the Federal Reserve's benchmark interest rate remained elevated, pushing many customers to actively seek higher yields on their savings. This heightened focus on returns puts pressure on community banks to offer competitive deposit rates, potentially squeezing their net interest margins.
Information Transparency and Digital Tools
The internet and a proliferation of financial comparison tools have dramatically increased information transparency for community bank customers. This means individuals can easily see rates, fees, and service quality across numerous institutions. For instance, by mid-2024, platforms like Bankrate and NerdWallet allow consumers to compare savings account APYs, mortgage rates, and even customer service reviews with just a few clicks, significantly empowering their ability to seek out the best deals.
This enhanced access to information directly translates into stronger customer bargaining power. Armed with data, customers are more likely to switch providers or demand better terms, forcing community banks to compete more aggressively on price and service. Digital engagement is also a key driver here; banks that leverage digital tools to offer personalized experiences and competitive products find it easier to retain customers who might otherwise be swayed by transparently available, lower-cost alternatives.
- Increased Transparency: Online comparison sites allow customers to easily view and contrast rates, fees, and service quality from various financial institutions.
- Enhanced Negotiation Power: With readily available information, customers can more effectively negotiate terms or switch to providers offering more favorable conditions.
- Digital Engagement Impact: Banks focusing on digital tools for personalization and improved customer experience can better counter the bargaining power of informed customers.
- Market Data Example: By Q3 2024, the average savings account APY offered by online banks was often 1-2% higher than traditional brick-and-mortar institutions, a gap consumers are increasingly aware of.
Leveraging Multiple Service Needs for Better Terms
Customers who engage with Community Financial System, Inc. across various offerings, including banking, wealth management, and insurance, can wield greater influence to negotiate favorable terms or anticipate bundled advantages. This diversified approach, designed to offer a complete suite of financial solutions, not only cultivates customer loyalty but also amplifies the bargaining power of those utilizing multiple products.
The company's strategic focus on a diversified revenue stream is evident, with over 39% of its total income generated from these varied fee-based businesses. This broad service base means that a customer consolidating their financial needs with Community Financial System, Inc. has more options and can potentially leverage their relationship for better pricing or customized benefits.
- Diversified Customer Relationships: Customers using multiple services from Community Financial System, Inc. possess increased leverage.
- Bundled Benefits Expectation: Multi-product customers are more likely to negotiate for bundled services or preferential terms.
- Revenue Diversification Impact: Over 39% of the company's revenue comes from diversified fee income, highlighting the importance of these customer relationships.
- Loyalty vs. Leverage: While diversification fosters loyalty, it simultaneously empowers these customers with greater bargaining power.
Customers of community banks have significant bargaining power due to low switching costs and a wide array of available alternatives. This is exacerbated by increased price transparency, driven by digital platforms and comparison tools. As of mid-2024, online financial comparison sites readily display rates, fees, and service quality, empowering consumers to seek better deals.
The proliferation of fintech companies and credit unions, which held over $2.3 trillion in deposits in 2023, presents strong alternatives to traditional banks. This competitive landscape forces institutions like Community Bank System, Inc. to offer attractive rates and user-friendly services to retain customers. For example, by Q3 2024, online banks often offered savings account APYs 1-2% higher than traditional banks, a difference consumers are increasingly aware of.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Community Bank |
| Low Switching Costs | Ease of moving accounts due to digital banking and open banking initiatives. | Pressure to offer competitive rates and services to prevent customer attrition. |
| Availability of Alternatives | Numerous options including large banks, credit unions, and fintechs. | Need for differentiation and strong customer relationships to maintain market share. |
| Price Sensitivity | Customers actively seek better interest rates and lower fees. | Requires careful management of pricing strategies to protect net interest margins. |
| Information Transparency | Easy access to comparative data on rates, fees, and service quality. | Empowers customers to negotiate terms or switch providers, demanding aggressive competition. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Community Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Community Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, detailing the competitive landscape, threats, and opportunities facing the bank. You'll gain a comprehensive understanding of industry rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products. This professionally formatted document is ready for your immediate use and strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Community Financial System, Inc. faces intense competition from large national and regional banks. These behemoths wield substantial financial clout, boast expansive branch footprints, and often lead in technological innovation, allowing them to offer a broader suite of products and more competitive rates. For instance, as of Q1 2024, the largest U.S. banks by assets, like JPMorgan Chase and Bank of America, held trillions in assets, dwarfing community banks.
This disparity in resources means larger competitors can invest heavily in marketing and customer acquisition, putting significant pressure on smaller institutions. Community Financial System, Inc., while among the nation's top 100 banking institutions, still operates in an environment where these larger players can dictate terms and capture market share through scale and sophisticated offerings.
Community Financial System, Inc. operates in a landscape saturated with local community banks and credit unions, each vying for customer attention within their specific geographic areas. This intense rivalry is often built on strong personal relationships, making customer loyalty a key differentiator for success.
The competitive environment is further shaped by the fact that many of these local competitors face liquidity constraints, creating opportunities for market share gains for institutions like Community Financial System. As of the first quarter of 2024, the average liquidity coverage ratio for small community banks hovered around 12%, a metric that can limit their ability to expand lending and attract deposits aggressively.
Community Financial System, Inc. (CFS) actively combats intense banking rivalry by strategically diversifying its offerings beyond traditional lending and deposit services. By integrating employee benefits, insurance, and wealth management into its core business, CFS presents a more comprehensive value proposition to its customers, thus reducing direct competition focused solely on banking products.
This multi-faceted approach allows CFS to compete across a wider spectrum of financial needs. For instance, in 2023, CFS reported total revenue of $118.7 million, with its diverse segments contributing to this overall financial strength, allowing it to weather the pressures of a highly competitive banking landscape by not being solely reliant on net interest income.
The company's emphasis on its four primary business lines – community banking, wealth management, insurance, and employee benefits – is a testament to its strategy of leveraging diversification. This allows CFS to build deeper customer relationships and capture a larger share of their financial lives, thereby mitigating the impact of rivals who may only offer a narrower range of services.
Rivalry in Adopting New Technologies and Digital Services
Community banks are intensely focused on adopting new technologies and digital services, a key battleground for market share. Competitors are pouring resources into enhancing online and mobile platforms, leveraging AI for personalized services, and utilizing data analytics to streamline operations and improve customer engagement. This rapid digital transformation is crucial for community banks to stay relevant and meet the increasingly sophisticated demands of their customers.
The push for digital innovation is particularly pronounced in 2024 and 2025, as many community banks recognize the need for a significant overhaul to remain competitive against larger institutions and fintech challengers. This includes investments in:
- Enhanced Mobile Banking Apps: Offering seamless user experiences for transactions, account management, and new product applications.
- AI-Powered Customer Service: Implementing chatbots and virtual assistants to provide instant support and personalized recommendations.
- Data Analytics for Personalization: Utilizing customer data to tailor product offerings, marketing campaigns, and risk assessments.
- Cloud Computing Adoption: Migrating services to the cloud for greater scalability, flexibility, and cost efficiency in digital service delivery.
Pressure from Fluctuating Interest Rates and Deposit Wars
The prevailing high-interest rate environment has significantly escalated competition for deposits, leading to a fierce 'deposit war' among financial institutions. Banks are actively raising rates to attract and retain customer funds, directly impacting their cost of funding.
This intense competition places considerable pressure on net interest margins, forcing banks like Community Financial System, Inc. to carefully manage the delicate balance between achieving deposit growth and maintaining profitability. Bankers continue to view interest rates as a primary concern heading into 2025.
- Deposit Rate Increases: Banks are offering higher yields on savings accounts, money market accounts, and certificates of deposit to attract new customers and retain existing ones.
- Margin Compression: The increased cost of deposits directly squeezes the difference between what banks earn on loans and what they pay on deposits, impacting profitability.
- Customer Retention Strategies: Beyond rates, banks are focusing on enhanced customer service and digital offerings to retain deposits in a competitive landscape.
Community banks face fierce competition from larger national banks, which possess greater financial resources and technological capabilities, often leading to more attractive product offerings and rates. This rivalry is amplified by the presence of numerous local community banks and credit unions, all vying for the same customer base through personalized service and community ties.
The digital transformation is a key battleground, with institutions heavily investing in mobile banking, AI, and data analytics to enhance customer experience and operational efficiency. This arms race for digital superiority is critical for survival against both large incumbents and agile fintechs, especially as we move through 2024 and into 2025.
The current high-interest rate environment has intensified the competition for deposits, leading to a significant 'deposit war' where banks must offer higher yields to attract and retain funds. This directly impacts net interest margins, forcing careful management of funding costs and profitability.
| Competitor Type | Key Competitive Advantages | Impact on Community Banks |
|---|---|---|
| Large National Banks | Scale, Financial Resources, Technology, Brand Recognition | Pressure on pricing, market share erosion, need for significant investment in digital |
| Local Community Banks/Credit Unions | Personal Relationships, Local Focus, Agility | Intense local rivalry, focus on customer loyalty, potential for niche market dominance |
| Fintech Companies | Digital Innovation, Agility, Niche Specialization | Disruption of traditional services, pressure to adopt new technologies, customer acquisition challenges |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Fintech firms are rapidly introducing specialized, user-friendly digital alternatives for core banking functions such as payments, lending, and investments. These agile solutions directly compete with traditional offerings, potentially siphoning off customers and market share from community banks.
In 2024, the fintech sector continued its robust growth, with investment in financial technology reaching hundreds of billions globally, highlighting the significant threat posed by these innovative substitutes to established players like Community Financial System, Inc.
Community banks are actively seeking strategic alliances with fintech companies to integrate advanced technologies and remain competitive, recognizing the necessity of adapting to this evolving landscape.
Customers increasingly have access to a wider array of investment and wealth management options beyond traditional community banks. Independent investment firms, robo-advisors like Betterment and Wealthfront, and large brokerage houses such as Charles Schwab and Fidelity offer competitive alternatives. These substitutes often present diverse fee structures, highly specialized investment products, and the perception of superior returns, directly challenging the offerings of community banks.
For instance, as of early 2024, the robo-advisor market continued its expansion, with assets under management in the billions, demonstrating a clear customer preference for digital-first investment solutions. Community banks, including those like Community Financial System, Inc. with their own wealth management divisions, face significant pressure from these external competitors who can leverage technology and scale to attract a broad customer base seeking accessible and often lower-cost financial advisory services.
Credit unions present a significant threat of substitutes for community banks. As member-owned institutions, they often offer lower fees and a more personalized, community-centric banking experience. For instance, in 2023, credit unions saw their membership grow to over 136 million in the U.S., demonstrating their appeal as an alternative to traditional banks.
This member-owned structure can be particularly attractive to individuals and small businesses seeking a banking relationship that prioritizes customer benefit over shareholder profit. Community Bank System, Inc., like other community banks, faces this competitive pressure from credit unions which are not beholden to the same profit-maximizing imperatives.
Direct Lending and Funding Alternatives
The threat of substitutes for community banks is amplified by the rise of direct lending and alternative funding sources. For borrowers, platforms like Prosper and LendingClub, which facilitate peer-to-peer lending, offer a direct bypass of traditional bank intermediation. These platforms, though still a fraction of the overall lending market, are steadily growing, representing a tangible substitute for certain loan types.
Beyond peer-to-peer, crowdfunding platforms are also emerging as alternatives for capital raising, particularly for small businesses and startups. This disintermediation challenges the community bank's traditional role as a primary capital provider. The broader financial services landscape is increasingly populated by non-depository institutions offering specialized financial products.
- Peer-to-peer lending platforms continue to gain traction, with the global P2P lending market projected to reach over $300 billion by 2027, indicating a growing appetite for alternative credit sources.
- Crowdfunding has become a significant funding mechanism, with global crowdfunding volume exceeding $50 billion annually, providing entrepreneurs with viable alternatives to bank loans.
- Fintech companies are increasingly offering specialized lending solutions, often with faster approval times and more flexible terms than traditional banks, directly competing for borrower relationships.
Businesses Opting for Internal or Direct Funding Methods
Larger businesses are increasingly bypassing traditional community banks by leveraging their substantial internal cash flow for operations and expansion. This self-funding capability directly substitutes for the lending services that Community Financial System, Inc. might offer.
The issuance of corporate bonds presents another significant substitute. In 2024, corporate bond issuance remained robust, providing companies with a direct channel to raise capital from investors, thereby reducing their dependence on bank financing.
Access to direct capital markets, including private equity and venture capital, offers businesses alternative funding avenues. For instance, a significant number of tech startups in 2024 secured substantial funding rounds directly from venture capital firms, bypassing conventional bank loans.
- Internal Cash Flow: Many established corporations generate enough profit to fund their growth without external debt.
- Corporate Bonds: Companies can issue bonds to raise capital directly from the public markets.
- Direct Capital Markets: Access to private equity, venture capital, and other non-bank lenders provides alternative funding sources.
The threat of substitutes for community banks is significant, driven by an expanding ecosystem of financial technology firms offering specialized, user-friendly digital alternatives for core banking functions like payments and lending. These agile fintech solutions directly challenge traditional offerings, potentially capturing customers and market share. In 2024, global investment in fintech continued to surge, underscoring the competitive pressure from these innovative substitutes.
Customers also have broader access to investment and wealth management options beyond community banks, with robo-advisors and independent investment firms presenting competitive fee structures and specialized products. The robo-advisor market, for example, saw substantial growth in assets under management by early 2024, reflecting a clear customer preference for digital-first investment solutions.
Credit unions represent another key substitute, often providing lower fees and a more personalized, community-focused banking experience. With over 136 million members in the U.S. by 2023, credit unions demonstrate their appeal as an alternative to traditional banks, particularly for those prioritizing customer benefit.
Direct lending and crowdfunding platforms further substitute for traditional bank intermediation, offering borrowers and businesses alternative avenues for credit and capital. The global P2P lending market is projected to exceed $300 billion by 2027, and global crowdfunding volume surpasses $50 billion annually, highlighting the growing demand for these non-bank funding sources.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | 2024/Recent Data Point | Impact on Community Banks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fintech Platforms | Specialized, digital-first services (payments, lending, investments) | Hundreds of billions invested globally in fintech in 2024 | Siphoning customers, reducing traditional revenue streams |
| Robo-Advisors & Investment Firms | Diverse fee structures, specialized products, digital access | Billions in AUM for robo-advisors by early 2024 | Challenging wealth management offerings, attracting digitally-savvy investors |
| Credit Unions | Member-owned, lower fees, community focus | Over 136 million U.S. members in 2023 | Offering competitive rates and personalized service, appealing to cost-conscious customers |
| P2P Lending & Crowdfunding | Direct lending, alternative capital raising | P2P lending market projected over $300B by 2027; Crowdfunding volume >$50B annually | Disintermediating lending, reducing reliance on bank loans for businesses and individuals |
Entrants Threaten
The banking sector faces formidable barriers to entry due to stringent regulatory frameworks and substantial capital requirements. For instance, in 2024, the Basel III Endgame rules continue to impose rigorous capital adequacy ratios on banks, demanding significant financial reserves to absorb potential losses. This regulatory environment, coupled with the need for extensive compliance infrastructure, deters many potential new entrants from establishing traditional banking operations.
Newcomers to the banking sector face a substantial hurdle in cultivating trust and brand recognition, especially when competing against established institutions. Community banks, for instance, have the advantage of deep-rooted customer relationships and a reputation for reliability honed over decades of local engagement. Consider Community Financial System, Inc., which has consistently earned accolades as a ‘best bank’ within its service areas, a testament to the trust it has built.
New entrants face a substantial barrier due to the immense capital required to build extensive branch networks or sophisticated digital platforms, mirroring the approximately 200 customer facilities operated by Community Financial System, Inc. This necessitates significant investment in physical locations and cutting-edge technology to even approach competitive parity.
Achieving operational efficiencies and economies of scale presents another formidable challenge. Established institutions like Community Bank System have already optimized their processes and technology, making it difficult for newcomers to match their cost structures and service delivery speeds. Community Bank System's ongoing branch expansion plans further solidify this advantage.
Challenge of Securing a Stable, Affordable Deposit Base
A significant hurdle for new entrants in the banking sector is the difficulty in establishing a reliable and cost-effective deposit base. This funding is essential for supporting loan portfolios and overall operations. For instance, in early 2024, the average interest rate offered on savings accounts by challenger banks was often 1-2% higher than that of established institutions, directly impacting their net interest margins.
Established community banks benefit from long-standing customer loyalty and trust, which translates into a more stable and cheaper source of funds. New entrants, lacking this established base, may need to entice customers with premium interest rates, thereby increasing their cost of funds and potentially hindering their ability to compete on loan pricing. Indeed, a survey of community bank executives in late 2024 revealed that attracting and retaining deposits was cited as a top strategic priority, with many expecting this challenge to persist through 2025.
- Deposit Acquisition Costs: New banks may face higher marketing and promotional expenses to attract initial deposits.
- Customer Inertia: Existing customers are often reluctant to switch banks, even for slightly better rates.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Meeting capital requirements and compliance standards can also indirectly affect a new bank's ability to offer competitive deposit products.
Recruiting and Retaining Experienced Banking Professionals
New entrants face significant hurdles in attracting and keeping experienced banking talent. Building a team with expertise in crucial areas like compliance, risk management, and specialized financial services, such as wealth management, is a substantial challenge. For instance, in 2024, the demand for financial analysts and compliance officers remained exceptionally high, with reported salary increases of 5-10% in many regions, making it difficult for new players to compete with established institutions that already possess deep talent pools and robust HR structures.
Established banks leverage their existing workforce and employer branding to retain top performers, creating a barrier for newcomers. The competitive landscape for skilled professionals across the financial services sector is intense. In 2023, the U.S. banking industry employed over 2 million people, with a significant portion in specialized roles, highlighting the sheer scale of talent that new entrants must contend with.
- Talent Acquisition Costs: New entrants often face higher recruitment costs due to the need for competitive salaries and sign-on bonuses to attract experienced professionals away from established firms.
- Training and Development Investment: Significant investment is required to train new employees on specific banking systems, regulatory frameworks, and company culture, a burden less pronounced for incumbents.
- Retention Challenges: High demand for banking expertise means that experienced professionals may be more inclined to stay with established institutions offering greater job security and career progression opportunities.
The threat of new entrants for community banks is significantly mitigated by high capital requirements and rigorous regulatory oversight, as exemplified by ongoing Basel III Endgame compliance in 2024. These factors demand substantial financial reserves and complex infrastructure, acting as strong deterrents. Furthermore, the established trust and brand recognition of community banks, often built over decades of local engagement like that seen with Community Financial System, Inc., present a formidable challenge for newcomers seeking to attract customers.
Building out the necessary physical or digital infrastructure also poses a significant capital barrier, with established players operating extensive networks. For instance, Community Financial System, Inc. operates around 200 customer facilities, a scale difficult for new entrants to replicate. Achieving competitive economies of scale and operational efficiencies is another hurdle, as incumbents like Community Bank System have already optimized their cost structures and service delivery.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | Example/Data Point (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Substantial funds needed to meet regulatory capital ratios and operational setup. | Basel III Endgame capital adequacy ratios continue to demand significant reserves. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Compliance with extensive banking laws and standards. | Ongoing need for robust compliance infrastructure. |
| Brand Recognition & Trust | Difficulty in establishing a trusted reputation against incumbents. | Community banks benefit from decades of local engagement and proven reliability. |
| Infrastructure Investment | Cost of building branch networks or sophisticated digital platforms. | Community Financial System, Inc. operates approximately 200 customer facilities. |
| Economies of Scale | Inability to match cost efficiencies and service speed of established banks. | Community Bank System leverages optimized processes and ongoing expansion. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Community Bank Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial statements, regulatory filings, and industry-specific market research reports. We also incorporate data from local economic development agencies and community surveys to capture the unique dynamics of the banking environment.
