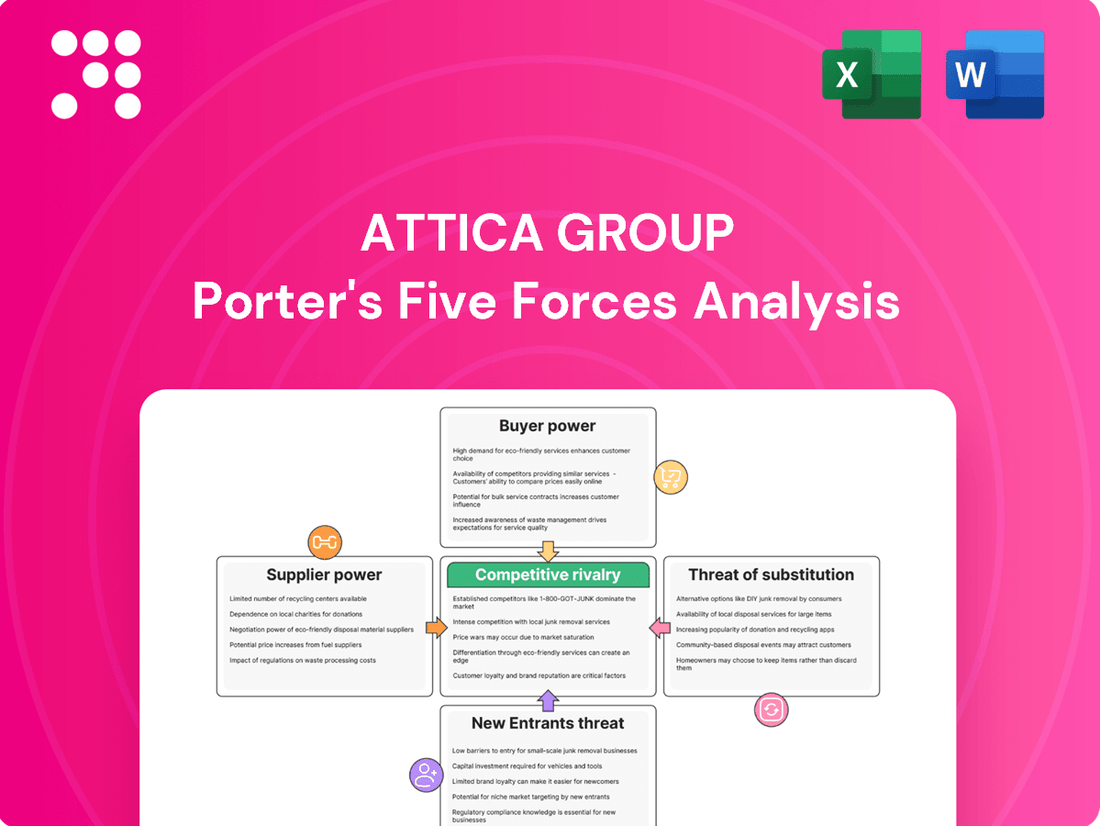
Attica Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Attica Group Bundle
Attica Group operates in a competitive landscape shaped by powerful buyer bargaining, moderate supplier influence, and a significant threat from substitute ferry services. The intensity of rivalry among existing players and the barrier to new entrants are also critical factors influencing their market position.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Attica Group’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Fuel is a major cost for Attica Group, directly impacting profitability. In 2024, fuel costs represent a substantial percentage of operating expenses for ferry operators, making them highly reliant on fuel suppliers. This reliance grants suppliers significant bargaining power, as disruptions or price hikes can severely affect Attica Group's bottom line.
Environmental regulations are intensifying this supplier leverage. By 2025, initiatives like the EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) and FuelEU Maritime will mandate cleaner, often more expensive, fuels. This regulatory push increases demand for specific compliant fuels, such as LNG or biofuels, giving suppliers of these alternatives considerable pricing power and control over availability for companies like Attica Group.
Attica Group's commitment to fleet modernization, including the acquisition of advanced vessels like the E-Flexer series due in 2027, amplifies its dependence on shipbuilders. This reliance translates into considerable leverage for shipyards, particularly those capable of delivering complex, environmentally compliant technologies. The substantial capital outlay for new builds and ongoing maintenance, encompassing specialized parts and green retrofits, means suppliers can command higher prices.
Technological solution providers wield considerable bargaining power in the maritime sector, driven by the industry's swift digital transformation. The increasing integration of AI, IoT, and automation for operational optimization, predictive maintenance, and efficiency gains means companies offering these advanced solutions, from specialized software to autonomous navigation systems, are in high demand.
This reliance on cutting-edge technology translates into significant power for these providers. Their specialized knowledge and unique, often proprietary, technologies can result in substantial upfront implementation costs and ongoing support expenses for shipping companies like Attica Group. For instance, the global maritime technology market was valued at approximately $20 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, underscoring the increasing dependence and thus, the leverage of these tech firms.
Human Resources and Labor Unions
The bargaining power of suppliers, particularly concerning human resources and labor unions, is a key consideration for Attica Group. The availability and cost of skilled crew members and onshore personnel directly influence operational efficiency and profitability. In 2024, the maritime industry continued to face challenges in securing qualified seafarers, potentially driving up labor costs.
Wage expenses represent a substantial portion of Attica Group's overall operating costs. Any upward pressure on wages, whether from market demand or union negotiations, can have a direct and significant impact on the company's bottom line. For instance, reports from early 2025 indicated that average seafarer wages saw a modest increase globally, reflecting ongoing supply-demand dynamics.
Labor unions can play a crucial role in shaping employment terms and conditions. Their ability to negotiate wages, benefits, and working hours for Attica Group's employees can lead to increased labor expenses. The strength and influence of these unions, coupled with the specialized nature of maritime skills, contribute to their bargaining power.
- Skilled Labor Scarcity: The global shortage of experienced maritime personnel in 2024-2025 puts upward pressure on wages for Attica Group's crew.
- Wage Sensitivity: Labor costs are a significant expense for Attica Group, making wage increases a direct threat to profitability.
- Union Influence: Labor unions can negotiate favorable terms for employees, potentially increasing Attica Group's operational costs through collective bargaining agreements.
- Industry Benchmarks: Attica Group's labor costs are often benchmarked against industry standards, which are influenced by union agreements and global labor market trends.
Port and Infrastructure Services
Attica Group's operations are significantly dependent on port and infrastructure services for its ferry routes in Greece and the Adriatic. These services include docking, loading, unloading, and passenger handling. The availability of prime port locations and specialized facilities can grant certain port authorities and their associated service providers, such as pilotage and stevedoring companies, a degree of bargaining power.
While there are many ports, the necessity for efficient and well-located facilities means Attica Group cannot easily switch providers without incurring substantial costs and operational disruptions. For instance, increases in port charges or delays caused by operational inefficiencies at critical hubs directly impact Attica Group's operating expenses and schedule reliability. In 2024, the maritime industry experienced fluctuating operational costs, with port fees and related services being a notable component of overall expenditure for ferry operators.
- Dependence on Key Ports: Attica Group utilizes specific ports for its extensive network, making it reliant on these locations.
- Specialized Service Providers: Services like pilotage and stevedoring are often provided by a limited number of specialized entities, enhancing their bargaining position.
- Cost and Schedule Impact: Any rise in fees or operational slowdowns at these ports directly affects Attica Group's profitability and on-time performance.
Attica Group faces substantial bargaining power from its fuel suppliers. Given that fuel costs represented a significant portion of operating expenses in 2024, any price hikes or supply disruptions directly impact profitability. The increasing demand for environmentally compliant fuels, driven by regulations like EU ETS and FuelEU Maritime by 2025, further strengthens the position of suppliers offering these alternatives, allowing them to command higher prices and control availability.
The maritime industry's reliance on technological advancements grants significant leverage to solution providers. Companies offering AI, IoT, and automation solutions are in high demand, with the global maritime technology market valued at approximately $20 billion in 2023. Attica Group's investment in fleet modernization, including advanced vessels, amplifies its dependence on shipbuilders and technology firms, leading to higher implementation and support costs.
Skilled labor scarcity in 2024-2025 continues to empower labor unions and seafarers, driving up wages for Attica Group. Labor costs are a major expense, and union negotiations can significantly increase operational costs through collective bargaining agreements, impacting profitability. Global seafarer wages saw a modest increase in early 2025, reflecting these market dynamics.
Port and infrastructure service providers also hold bargaining power due to Attica Group's dependence on specific, well-located facilities. Switching providers incurs substantial costs and operational disruptions. Fluctuations in port fees and operational inefficiencies at critical hubs, as seen in 2024, directly affect Attica Group's expenses and schedule reliability.
| Supplier Category | Key Dependence Factor | Impact on Attica Group | 2024/2025 Data Point | Supplier Bargaining Power Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuel Suppliers | High fuel cost percentage of OpEx | Profitability vulnerability to price hikes | Fuel costs a substantial % of operating expenses in 2024 | High |
| Fuel Suppliers | Demand for compliant fuels (e.g., LNG) | Pricing power for alternative fuels | EU ETS & FuelEU Maritime by 2025 | High |
| Shipbuilders & Tech Providers | Fleet modernization & advanced tech integration | High upfront and ongoing costs | Maritime tech market ~$20B in 2023 | High |
| Labor Providers (Seafarers/Unions) | Skilled labor scarcity | Upward pressure on wages | Modest global seafarer wage increase in early 2025 | High |
| Port & Infrastructure Services | Reliance on key, well-located ports | Cost & schedule disruption risk | Fluctuating port fees in 2024 | Medium to High |
What is included in the product
This analysis delves into the competitive forces impacting Attica Group, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the ferry and shipping industry.
Effortlessly assess the competitive landscape of the Attica Group with a visual breakdown of each force, enabling swift identification of key challenges and opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Attica Group's customers, particularly passengers, exhibit high price sensitivity. Greek ferry ticket prices are notably among the highest in Europe, with substantial increases in recent years making travel increasingly costly. This elevated pricing has contributed to a noticeable decline in passenger traffic observed in early 2025.
In response to this trend, ferry operators, including Attica Group, have been compelled to implement discounts and promotional offers to stimulate demand. The pronounced sensitivity to price empowers passengers to exert considerable pressure on ferry companies. They can opt out of travel altogether or seek more economical alternatives, especially for non-essential leisure journeys.
For passengers, particularly those traveling longer distances or seeking swift access to popular islands, air travel presents a direct substitute for ferry services. Many tourists arrive at their destinations via air, making flights a convenient alternative for initial travel to the broader region.
While ferries remain crucial for inter-island connections and transporting vehicles, the availability of air travel, even if indirect, significantly enhances customer choice. This competitive pressure is evident, as data from 2024 suggests a trend where some travelers opt for mainland destinations over island hopping due to the perceived high cost of ferry tickets, impacting passenger volumes.
Attica Group's leisure customer base is largely fragmented, with a vast number of individual passengers, especially tourists. This fragmentation means that each individual customer has very little direct bargaining power. For instance, in the first five months of 2025, a general sentiment of high prices among these individual travelers led to a noticeable dip in overall demand across the market, demonstrating the collective impact of their dissatisfaction.
While individual passengers might not negotiate prices directly, their collective sentiment can significantly influence market demand. The rise of social media and online review platforms in 2024 and continuing into 2025 allows customer dissatisfaction to spread rapidly. This amplified sentiment can sway purchasing decisions for a large segment of the market, indirectly affecting Attica Group's pricing power.
Bargaining Power of Commercial Freight Customers
Attica Group's commercial freight segment, which includes transporting trucks and private vehicles, faces potential pressure from large, concentrated customers. These major logistics companies or freight forwarders possess significant purchasing power, enabling them to negotiate favorable terms and rates. Their ability to commit to consistent, high-volume shipments can indeed exert downward pressure on the prices Attica Group can charge for freight services.
The bargaining power of these commercial freight customers is a key consideration. For instance, a large forwarder might represent a substantial portion of Attica Group's freight volume on certain routes. This concentration means that losing even one major client could have a noticeable impact on revenue for that specific service line.
- Customer Concentration: A few large logistics firms may account for a significant percentage of Attica Group's commercial freight volume.
- Volume Commitments: The ability of these customers to guarantee consistent, high-volume shipments strengthens their negotiating position.
- Price Sensitivity: For these clients, freight costs are a direct operational expense, making them highly sensitive to pricing and willing to switch providers for better rates.
- Market Dynamics: In 2024, the freight industry continues to be competitive, with many carriers vying for business, further empowering customers to demand lower prices.
Impact of Tourism Trends and Economic Conditions
Customer demand for ferry services is highly sensitive to broader tourism trends and economic health across Greece and Europe. When tourism falters or economies weaken, fewer people travel, which directly impacts ferry companies. This reduced demand gives customers more leverage because the companies are then vying harder for a smaller pool of passengers and cargo.
Attica Group experienced an increase in overall traffic volumes throughout 2024. However, the early months of 2025 saw a noticeable dip in passenger numbers. This trend highlights the direct correlation between economic conditions and customer bargaining power; as demand softens, customers gain more influence.
- Tourism Demand Sensitivity: Ferry services are intrinsically linked to the health of the tourism sector.
- Economic Downturn Impact: Recessions or slowdowns in Greece and Europe can significantly decrease travel, empowering customers.
- Attica Group's 2024-2025 Performance: While 2024 saw traffic growth, early 2025 indicated a decline in passenger volumes, suggesting increased customer bargaining power.
Attica Group faces significant customer bargaining power, particularly from price-sensitive passengers and concentrated freight clients. While individual passengers have limited power, their collective sentiment, amplified by social media, can influence demand. The availability of substitutes like air travel and the impact of economic conditions further empower customers, especially when demand softens, as seen in early 2025 after a stronger 2024.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on Attica Group |
|---|---|---|
| Individual Passengers (Leisure) | High price sensitivity, fragmented base, collective sentiment amplification via social media. | Pressure on ticket pricing, potential for demand reduction if prices are perceived as too high. |
| Commercial Freight Customers | Concentration of a few large clients, volume commitments, price sensitivity due to operational costs. | Ability to negotiate favorable rates and terms, potential revenue impact if major clients are lost. |
| Broader Market/Economic Conditions | Sensitivity to tourism trends and economic health, availability of substitutes (e.g., air travel). | Reduced demand during economic downturns increases customer leverage; companies compete harder for fewer customers. |
What You See Is What You Get
Attica Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Attica Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis, providing a detailed examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing information. You're looking at the actual, professionally written analysis; once your transaction is complete, you'll gain instant access to this valuable strategic tool.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Greek ferry market is a classic oligopoly, with Attica Group, Seajets, and Minoan Lines (part of the Grimaldi Group) holding the lion's share of the business. This means a handful of large companies control most of the routes and passenger traffic.
This concentrated structure naturally fuels fierce rivalry. Attica Group, for instance, reported a consolidated turnover of €454.1 million in 2023, highlighting the significant scale of operations and the stakes involved in competing for market dominance.
Competition often revolves around securing lucrative routes, optimizing fleet utilization, and offering competitive pricing, as these major players vie for passenger and cargo volume.
Attica Group's absorption of ANEK Lines in December 2023 was a game-changer, creating one of the largest passenger shipping operators globally by capacity. This move directly reduces the number of significant competitors in the market.
The consolidation intensifies rivalry among the remaining major players as they vie for market share, leveraging their expanded scale and broader network coverage. This aggressive M&A activity signals a heightened competitive landscape for passenger shipping services.
Attica Group's commitment to fleet modernization, including investments in methanol-ready and battery-notation vessels, pressures rivals to undertake similar capital-intensive upgrades. This focus on efficiency and environmental compliance means competitors must also allocate substantial funds to renew their fleets to maintain parity in speed, capacity, and regulatory adherence.
The industry-wide push for greener shipping, exemplified by Attica Group's 2024 investments in new vessels, escalates the competitive rivalry. Companies that fail to modernize risk falling behind in operational efficiency and environmental performance, potentially impacting their market share and attractiveness to environmentally conscious customers and investors.
Pricing Strategies and Promotions
Attica Group and its competitors have navigated a challenging pricing landscape. Despite increasing operational expenses, ferry operators implemented price adjustments and offered discounts, notably in early 2025. This strategy was a direct response to a downturn in passenger traffic, highlighting intense competition where pricing becomes a key lever for customer acquisition and retention. Such tactics can, however, exert downward pressure on overall profit margins for all players in the market.
The competitive dynamic is further illustrated by specific promotional activities. For instance, during the first quarter of 2025, several operators introduced limited-time offers, including:
- Early Bird Discounts: Up to 20% off for bookings made more than 30 days in advance.
- Family Packages: Bundled fares offering savings for groups of four or more.
- Off-Peak Reductions: Lower prices for travel during weekdays or non-holiday periods.
These promotions, while aimed at stimulating demand, underscore the aggressive pricing strategies employed to capture market share. The need to counter competitor pricing and attract price-sensitive travelers means that profitability can be significantly impacted by these ongoing promotional efforts.
Regulatory Compliance and Operational Costs
New European Union environmental regulations, such as FuelEU Maritime and the expanded EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) effective from 2025, are set to significantly increase operational expenses for shipping firms. These regulations will necessitate substantial investments in greener fuels and advanced technologies.
Companies that can effectively absorb or pass on these increased costs will likely gain a competitive edge. Conversely, those unable to manage these new financial burdens may face considerable disadvantages. For instance, the cost of compliant fuels could be 20-50% higher than traditional bunker fuels, impacting profitability for carriers that don't secure favorable contracts or invest in efficiency upgrades.
- Increased Operating Costs: New EU environmental mandates from 2025 will raise expenses for shipping companies.
- Investment Requirements: Adaptation requires capital outlay for compliant fuels or new technologies.
- Competitive Differentiation: Effective cost management of these new regulations can create a competitive advantage.
- Potential Disadvantage: Companies struggling with these costs may fall behind competitors.
Competitive rivalry within the Greek ferry market is intense, primarily driven by a few dominant players like Attica Group. This rivalry manifests in aggressive pricing strategies, such as early bird discounts and family packages, as seen in early 2025, to capture market share. The recent consolidation, with Attica Group acquiring ANEK Lines in late 2023, has further intensified competition among the remaining major operators.
The pressure to modernize fleets, exemplified by Attica Group's investments in methanol-ready vessels in 2024, forces competitors to also invest heavily in new technologies to remain competitive. Furthermore, upcoming EU environmental regulations from 2025 will increase operating costs, creating a competitive battleground for cost management and technological adaptation.
| Competitor | 2023 Turnover (Approx.) | Key Competitive Action |
|---|---|---|
| Attica Group | €454.1 million | Acquisition of ANEK Lines (Dec 2023), Fleet Modernization (2024) |
| Seajets | Not publicly disclosed | Aggressive route acquisition, Pricing promotions |
| Minoan Lines (Grimaldi Group) | Not publicly disclosed | Fleet upgrades, Intermodal service integration |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For passengers, especially tourists, air travel is a major substitute for ferries, particularly for reaching popular Greek islands or covering longer distances. Many international tourists fly directly to islands, bypassing mainland ferry connections and impacting demand for certain routes.
The speed and convenience of air travel often make it a preferred option, even with higher costs. In 2024, the average price for a short domestic flight in Greece saw an increase, potentially making the cost difference between air and ferry less prohibitive for some travelers.
While Attica Group primarily operates in mass-market ferry services, private or chartered maritime transport, including yachts and smaller local boat services, presents a potential substitute for specific market segments. These alternatives are particularly relevant for inter-island travel and bespoke tourist experiences, offering flexibility and exclusivity that larger ferry services may not provide.
For instance, the luxury yacht charter market has seen steady growth. In 2023, the global luxury yacht charter market was valued at approximately USD 10.5 billion and is projected to expand further. This segment can divert high-value leisure travelers who might otherwise opt for ferry services, especially for shorter, more personalized journeys.
For freight moving within mainland Greece or to areas reachable by road or rail, these modes present a viable alternative to Attica Group's ferry services. While ferries are indispensable for island logistics, land-based transport offers distinct advantages in speed, cost-effectiveness, and cargo capacity for continental routes. In 2023, the Greek road freight sector handled a significant volume, with estimates suggesting it accounts for over 50% of domestic freight movement, highlighting its substantial role.
Shift to Mainland Tourism
The rising cost of ferry travel presents a significant threat of substitutes for Attica Group. High ferry prices have prompted some travelers, particularly domestic ones, to explore mainland destinations instead of island hopping. This shift diverts potential customers away from ferry services towards alternative, often more affordable, land-based tourism options.
This trend has a direct impact on passenger volumes. For instance, in 2024, reports indicated a noticeable increase in domestic tourism focused on mainland Greece, driven by economic considerations. This behavioral change effectively reduces the overall market for island ferry services, as travelers substitute the ferry experience with road trips or train journeys to mainland attractions.
- Mainland Tourism Growth: Increased preference for domestic mainland travel as an alternative to island visits due to ferry costs.
- Reduced Passenger Pool: This substitution directly shrinks the number of potential customers for island ferry routes.
- Economic Sensitivity: Travelers, especially domestic ones, are increasingly price-sensitive, making mainland options more attractive.
- Impact on Revenue: A decline in ferry passengers directly affects Attica Group's revenue streams from ticket sales and onboard services.
Underdeveloped Hydroplane Services
Hydroplane services represent a nascent threat to Attica Group's ferry operations, particularly for passenger-only routes where speed is paramount. While currently underdeveloped, a significant expansion of hydroplane services could offer a faster inter-island transit option for Greek travelers.
For instance, if hydroplanes were to become more prevalent, they could siphon off passengers who value reduced travel times over the ability to transport vehicles. This potential shift in passenger preference highlights a vulnerability for ferry operators on routes where hydroplanes could compete effectively on speed alone.
- Underdeveloped Market: Hydroplane services in Greece are not yet a widespread or fully established mode of transport.
- Speed Advantage: For passengers not requiring vehicle transport, hydroplanes could offer a significantly quicker journey.
- Future Potential: Continued investment and development could make hydroplanes a more viable substitute in the coming years.
- Route Specificity: The threat is likely to be concentrated on routes where the speed advantage outweighs the lack of vehicle carriage.
Air travel and private maritime transport represent significant substitutes for Attica Group's ferry services. For passengers, especially tourists, flights offer speed and convenience, making them a preferred option for longer distances or direct island access. In 2024, the cost of domestic flights saw an increase, which could narrow the price gap with ferries for some travelers.
Luxury yacht charters also divert high-value leisure travelers, particularly for bespoke inter-island experiences. The global luxury yacht charter market was valued at approximately USD 10.5 billion in 2023, indicating a substantial segment that prioritizes exclusivity over mass transit.
Land-based freight transport is a substitute for cargo moving within mainland Greece, with road freight accounting for over 50% of domestic movement in 2023. Hydroplane services, though currently underdeveloped, pose a future threat for passenger-only routes where speed is a key differentiator.
| Substitute Mode | Attica Group Service Affected | Key Differentiator | 2023/2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air Travel | Passenger Ferries (especially long-distance/island routes) | Speed, Convenience | Domestic flight prices increased in 2024 |
| Private Maritime Transport (Yachts) | Passenger Ferries (luxury/bespoke travel) | Exclusivity, Flexibility | Global luxury yacht charter market valued at USD 10.5 billion in 2023 |
| Land Freight (Road/Rail) | Freight Ferries (mainland routes) | Speed, Cost-effectiveness (for mainland) | Road freight over 50% of Greek domestic freight in 2023 |
| Hydroplanes | Passenger Ferries (short-distance, passenger-only) | Speed | Underdeveloped market, potential future threat |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the passenger shipping industry, particularly with a modern fleet akin to Attica Group's, demands immense capital. This includes acquiring or building new, environmentally compliant vessels, which alone can run into hundreds of millions of dollars. For instance, a new large ferry can cost upwards of $150 million, making it a significant hurdle.
Beyond ships, new entrants must also invest heavily in port infrastructure, ticketing systems, and marketing. These substantial fixed costs create a formidable financial barrier, deterring many potential competitors from entering the market and challenging established players like Attica Group.
The maritime sector faces rigorous regulatory landscapes, with the European Union's Emissions Trading System (ETS) and FuelEU Maritime, alongside the International Maritime Organization's (IMO) environmental directives, creating substantial barriers. New entrants must immediately invest heavily in compliant technologies and cleaner fuels, such as alternative fuels or advanced exhaust gas cleaning systems, to meet these evolving mandates.
Attica Group benefits significantly from strong brand loyalty associated with its well-recognized names: Superfast Ferries, Blue Star Ferries, and Hellenic Seaways. This established reputation makes it challenging for newcomers to attract customers who are accustomed to the quality and reliability of these brands. For instance, in 2023, Attica Group reported a consolidated turnover of €764.9 million, indicating substantial customer engagement and a strong market presence built over years.
Limited Access to Key Port Infrastructure and Routes
The threat of new entrants in the ferry industry, particularly for operators like Attica Group, is significantly moderated by the limited access to prime port infrastructure and desirable routes. Established players often hold concessions or have long-term agreements for key port slots and the most profitable routes, especially in regions like the Eastern Mediterranean. For instance, Attica Group, a major player in Greece, has a substantial portion of the vehicle capacity on popular routes, making it difficult for newcomers to secure comparable operational advantages. This control over essential infrastructure and routes creates a substantial barrier, impacting a new entrant's ability to achieve operational efficiency and compete effectively on high-demand services.
- Limited Port Access: Newcomers face challenges securing berths at major ports, often already allocated to incumbents like Attica Group.
- Route Control: Established operators frequently dominate the most lucrative ferry routes, restricting new entrants' market penetration.
- Capacity Dominance: Attica Group's significant share of vehicle capacity on key routes presents a hurdle for new entrants aiming for competitive service levels.
- Infrastructure Investment: The high cost and difficulty of acquiring or leasing suitable port facilities and vessels deter potential new entrants.
Market Saturation and Oligopolistic Competition
The Greek ferry market is already a highly concentrated oligopoly, with Attica Group being one of the dominant players. This means that established companies like Attica Group possess substantial market power and can leverage it to deter new entrants. For instance, in 2024, the market share of the top three ferry operators in Greece remained exceptionally high, making it difficult for newcomers to capture a significant portion of demand.
Existing firms can retaliate against new entrants by initiating aggressive pricing strategies or by increasing their own capacity on popular routes. This creates a high barrier to entry, as new companies would need substantial capital and a well-thought-out strategy to compete effectively. The significant upfront investment required for acquiring and maintaining a fleet further exacerbates this challenge.
The threat of new entrants is therefore considered moderate to low due to these entrenched competitive dynamics. Potential new players face considerable hurdles in achieving profitability and sustainability against established, well-resourced operators who are adept at defending their market positions.
- Oligopolistic Market Structure: The Greek ferry sector is dominated by a few large companies, limiting opportunities for new businesses.
- Aggressive Competitive Responses: Existing players can use price wars and capacity increases to stifle new competition.
- High Capital Requirements: The substantial cost of acquiring and operating ferry fleets acts as a significant barrier to entry.
- Entrenched Market Power: Established operators have strong brand recognition and customer loyalty, making it hard for newcomers to gain traction.
The threat of new entrants for Attica Group is largely contained by the immense capital required to establish a competitive ferry operation. Acquiring even a single modern ferry can cost over $150 million, a substantial barrier given the need for fleets, port access, and robust ticketing systems. Furthermore, stringent environmental regulations, such as the EU's ETS and FuelEU Maritime, necessitate immediate, significant investment in compliant technologies, adding to the financial burden for any potential newcomer.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Attica Group |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High cost of vessels and infrastructure. | Significant barrier, deterring new entrants. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Compliance with environmental and maritime laws. | Increases upfront investment and operational complexity. |
| Brand Loyalty & Market Share | Attica's established brands and customer base. | Makes customer acquisition difficult for newcomers. |
| Infrastructure & Route Control | Limited access to prime ports and profitable routes. | Restricts operational efficiency and market penetration. |
| Competitive Intensity | Oligopolistic market and potential for price wars. | Deters new entrants due to high risk of retaliation. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Attica Group Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including Attica Group's annual reports, industry-specific market research from firms like Statista and IBISWorld, and insights from financial news outlets and maritime trade publications.
We leverage a combination of Attica Group's official disclosures, regulatory filings, and data from reputable financial databases such as S&P Capital IQ and Bloomberg to provide a robust assessment of the competitive landscape.
