ASMedia Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
ASMedia Bundle
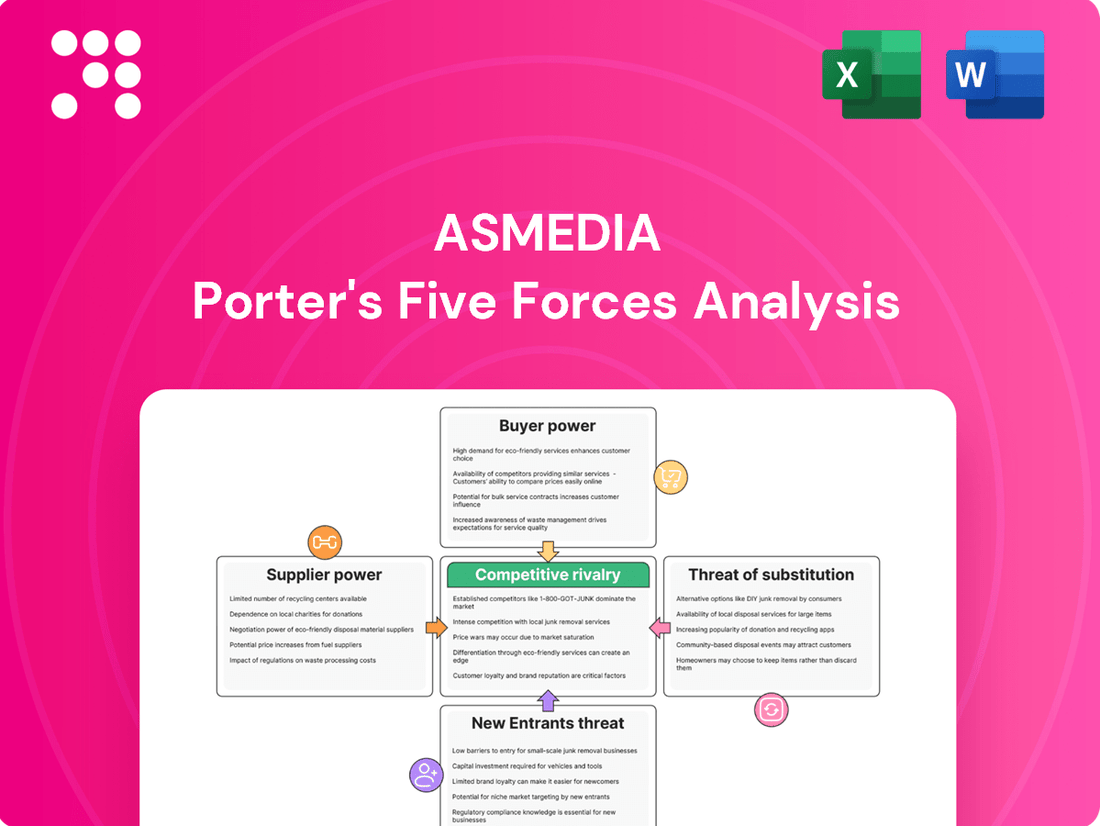
ASMedia's competitive landscape is shaped by the interplay of five key forces, revealing both opportunities and challenges within its semiconductor industry. Understanding the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threats of new entrants and substitutes is crucial for strategic planning.
This snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore ASMedia’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The semiconductor industry, particularly for fabless companies like ASMedia, faces supplier concentration for specialized equipment and raw materials. If a few dominant suppliers control essential inputs, they can dictate terms and prices, impacting ASMedia's costs and production schedules. For instance, companies like ASML hold a near-monopoly on extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography machines, critical for advanced chip manufacturing, giving them substantial leverage.
ASMedia's reliance on specialized inputs for its high-speed interface ICs, such as those for PCIe Gen5/6 and USB4, significantly influences supplier bargaining power. These advanced technologies often necessitate proprietary processes or unique materials from suppliers, limiting readily available alternatives.
For instance, the development of cutting-edge chipsets requires specialized foundries and advanced packaging solutions that may only be offered by a select few global manufacturers. If ASMedia faces a situation where only a handful of suppliers can meet the stringent technical specifications for these critical components, those suppliers gain considerable leverage in price negotiations and supply terms.
Switching semiconductor foundry partners or key material suppliers for companies like ASMedia involves significant expenses and time. This is largely due to the rigorous qualification processes required for new suppliers, the need for product re-design to accommodate different manufacturing specifications, and the potential for disruptions to the entire supply chain during the transition. For instance, in 2024, the lead time for qualifying a new semiconductor supplier can easily extend to 6-12 months, impacting product development schedules.
These high switching costs create a substantial barrier for ASMedia, effectively empowering its existing suppliers. This leverage allows suppliers to negotiate more favorable terms, potentially increasing prices or dictating contract conditions, thereby strengthening their bargaining power within the industry.
Threat of Forward Integration
The threat of forward integration by suppliers, while generally low for specialized IC design firms like ASMedia, remains a consideration. Should a major foundry or advanced materials supplier invest heavily in chip design capabilities, they could theoretically enter ASMedia's market, directly competing and reducing ASMedia's bargaining power. This scenario would transform a supplier into a rival, potentially impacting ASMedia's pricing and market share.
While ASMedia operates in a highly specialized niche, the broader semiconductor industry has seen consolidation and vertical integration. For instance, some large foundries are exploring design services, and material science companies are investing in advanced process development that could edge into design. For example, in 2024, TSMC, a leading foundry, continued to expand its advanced packaging and design enablement services, demonstrating a trend towards closer integration with the design process.
- Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers could develop their own chip designs, becoming direct competitors to ASMedia.
- Industry Trends: Consolidation and vertical integration in the semiconductor sector could empower suppliers to pursue design services.
- Example: Foundries like TSMC are increasingly offering advanced design enablement services, blurring the lines between manufacturing and design.
Importance of ASMedia to Supplier
ASMedia's significance to its suppliers plays a crucial role in determining their bargaining power. If ASMedia constitutes a substantial portion of a supplier's sales, that supplier has less leverage, as losing ASMedia as a client would significantly impact their revenue. For instance, if a key component supplier derives over 15% of its total revenue from ASMedia, its ability to dictate terms or raise prices would be considerably weaker.
Conversely, if ASMedia is a minor customer for a supplier, the supplier might prioritize larger, more lucrative clients. This could mean ASMedia faces challenges in securing critical resources or obtaining preferential pricing, especially if demand in the semiconductor market, projected to grow by approximately 8-10% in 2024-2025, intensifies competition for supply.
- Revenue Dependence: A supplier heavily reliant on ASMedia will have reduced bargaining power.
- Customer Size: ASMedia's status as a small customer can lead suppliers to prioritize larger clients.
- Market Conditions: Broader semiconductor market growth can shift the balance of power between ASMedia and its suppliers.
The bargaining power of suppliers for ASMedia is significantly influenced by industry concentration and the availability of substitutes for critical inputs. High supplier concentration, especially for specialized equipment like advanced lithography machines, grants dominant players considerable pricing and negotiation leverage. For instance, ASML's near-monopoly on EUV lithography machines underscores this power, impacting the entire semiconductor manufacturing chain.
| Factor | Impact on ASMedia | Example/Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High leverage for dominant suppliers | ASML's dominance in EUV lithography |
| Availability of Substitutes | Limited substitutes increase supplier power | Proprietary materials for advanced ICs |
| Switching Costs | High costs empower existing suppliers | 6-12 months to qualify new semiconductor suppliers |
| Supplier Dependence on ASMedia | Low dependence empowers suppliers | Suppliers prioritizing clients contributing >15% revenue |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects ASMedia's competitive environment by examining the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes.
Effortlessly visualize competitive intensity with a dynamic, interactive spider chart, instantly highlighting ASMedia's strategic positioning and potential vulnerabilities.
Customers Bargaining Power
ASMedia's customer concentration is a key factor in understanding its bargaining power. Its client roster features prominent names in personal computers, storage, and other electronics sectors.
When a few major customers represent a substantial chunk of ASMedia's revenue, these large clients gain significant leverage. This can translate into intense pressure on pricing and more demanding contract conditions, directly impacting ASMedia's profitability and flexibility.
For customers looking to switch away from ASMedia's high-speed interface ICs, the process isn't a simple plug-and-play. It often necessitates a complete redesign of their existing systems, which can be a time-consuming and expensive undertaking. This involves re-evaluating circuit layouts and ensuring compatibility with new components.
Beyond the initial redesign, customers must also go through a rigorous re-qualification process for the new components. This ensures that the alternative ICs meet ASMedia's established performance standards and reliability. Failure to do so could lead to product failures or even market delays, impacting their own revenue streams.
These significant hurdles, including system redesign and component re-qualification, directly translate into high switching costs for ASMedia's clientele. Consequently, this elevated barrier effectively diminishes the bargaining power of these customers, as the effort and expense involved in changing suppliers are substantial.
Customers in the electronics sector, especially those ASMedia serves, are typically quite knowledgeable about the costs of components and the other options available to them. This awareness, amplified by the intense competition within their own industries, often translates into significant price sensitivity for ASMedia's clientele.
For instance, in 2024, the average semiconductor component cost can fluctuate significantly, and ASMedia's clients are adept at comparing these prices across various suppliers. This makes them less likely to accept premium pricing without strong justification, thereby enhancing their leverage in negotiations.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Large customers, particularly those with substantial research and development resources, may explore the possibility of developing their own high-speed interface integrated circuits internally. This potential for backward integration, while requiring significant capital investment, grants these customers considerable leverage when negotiating with ASMedia.
For instance, major players in the consumer electronics or data center industries, who are ASMedia's key clients, often possess the technical expertise and financial capacity to undertake such vertical integration. This capability acts as a constant pressure point, influencing ASMedia's pricing strategies and product development roadmap.
- Customer Leverage: The ability of large customers to consider in-house chip design provides them with significant bargaining power.
- R&D Investment: Customers with strong R&D departments are more likely to pose a threat of backward integration.
- Capital Intensity: While costly, the pursuit of backward integration by customers can be a strategic move to control supply chains and costs.
- Market Dynamics: This threat influences ASMedia's competitive positioning and its approach to customer relationships.
Product Differentiation and Importance to Customer
ASMedia's capacity to provide unique, high-performance solutions, such as its USB4 and PCIe Gen5/6 offerings, significantly diminishes customer bargaining power. When customers rely on ASMedia for critical, hard-to-replicate technology, their ability to demand lower prices or more favorable terms is curtailed. This differentiation makes ASMedia's products less substitutable, strengthening the company's position.
Recent accolades and certifications serve as tangible proof of ASMedia's product differentiation. For instance, achieving certifications for advanced standards like USB4 Version 2.0, which offers speeds up to 80 Gbps, showcases the company's technological leadership. This advanced performance and validation reduce the likelihood of customers switching to competitors offering less sophisticated or unproven alternatives.
- Product Differentiation: ASMedia's focus on high-performance, certified solutions like USB4 and PCIe Gen5/6 limits customer options.
- Reduced Substitutability: The advanced nature of ASMedia's technology makes it difficult for customers to find comparable alternatives, thereby reducing their bargaining leverage.
- Importance to Customer: By providing critical components for next-generation connectivity, ASMedia embeds itself deeply into customer product roadmaps, increasing its value and reducing customer power.
- Recent Certifications: Achieving certifications for cutting-edge standards, such as PCIe Gen6, underscores ASMedia's technological edge and reinforces its value proposition to customers.
ASMedia's customers possess moderate bargaining power, primarily influenced by the high switching costs associated with redesigning systems and re-qualifying components. Their price sensitivity is also a factor, especially given the competitive landscape of the electronics industry. However, ASMedia's unique, high-performance offerings, like USB4 and PCIe Gen5/6, create differentiation that significantly limits customer leverage.
| Factor | ASMedia's Position | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|
| Switching Costs | High (System redesign, re-qualification) | Lowers customer power |
| Price Sensitivity | Moderate (Awareness of component costs) | Increases customer power |
| Product Differentiation | High (USB4, PCIe Gen5/6) | Lowers customer power |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Moderate (For large R&D-focused customers) | Increases customer power |
Same Document Delivered
ASMedia Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete ASMedia Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within its industry. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring a transparent and accurate transaction. This professionally formatted analysis is ready for your immediate use, providing valuable insights without any hidden surprises or placeholder content.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The high-speed interface IC market, especially for USB and PCIe technologies, is characterized by a significant number of established players. This crowded landscape means companies like ASMedia face intense competition from various sources.
The diversity of these competitors is also a key factor. It includes not only specialized IC designers but also larger, more diversified semiconductor giants that can leverage their broader product portfolios and market reach. For instance, major players in the USB controller market include Qualcomm, Realtek, and VIA Technologies, alongside ASMedia. Similarly, in the PCIe controller space, companies like Broadcom and Intel are significant competitors.
This broad base of competitors, each with different strengths and strategies, naturally escalates the rivalry. Companies are constantly striving to innovate, improve performance, and offer competitive pricing to capture market share. The market for these essential components is projected to see continued growth, with the global USB interface market expected to reach approximately $6.5 billion by 2026, according to some industry forecasts, further intensifying the competitive drive.
The semiconductor industry, encompassing segments like interface ICs, is on a growth trajectory, largely driven by the insatiable demand from AI and cloud computing. For instance, the global AI chip market was valued at approximately $20 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $100 billion by 2028, indicating robust expansion.
While a growing market often tempers direct competition, the semiconductor sector is characterized by extremely rapid technological evolution. This dynamic forces companies into aggressive competition to capture market share in emerging standards and next-generation products, even as the overall industry expands.
ASMedia carves out its competitive space by concentrating on advanced, high-speed interface technologies. The company is a notable player in USB4 and PCIe solutions, actively pursuing and achieving industry certifications for its products. This focus on specialized, high-performance components allows ASMedia to stand apart from competitors offering more generalized solutions.
The strength of ASMedia's product differentiation, particularly in areas like USB4, which saw significant adoption growth in 2024 with new device releases, helps to lessen the pressure of direct price wars. However, maintaining this advantage necessitates a relentless commitment to innovation, as the technology landscape, especially in high-speed interfaces, evolves rapidly.
Exit Barriers
ASMedia, like many in the semiconductor industry, faces significant exit barriers. The immense capital investment in research and development, coupled with long-term manufacturing partnerships and the critical protection of intellectual property, makes it exceedingly difficult and costly for companies to leave the market.
These high fixed costs mean that even when market conditions are unfavorable, companies are often compelled to stay and continue competing. This can lead to intensified rivalry, as firms strive to maintain market share and recoup their investments, even during economic downturns. For instance, the semiconductor industry's R&D spending alone can represent a substantial portion of revenue, with major players investing billions annually. In 2024, global semiconductor R&D spending was projected to reach over $100 billion, underscoring the significant financial commitment required.
The presence of these substantial exit barriers can therefore directly contribute to a more aggressive competitive landscape. Companies are less likely to withdraw, leading to a sustained battle for market position and profitability, even in challenging periods.
- High R&D Investment: Semiconductor companies invest heavily in innovation, with R&D often accounting for 15-25% of revenue.
- Manufacturing Partnerships: Long-term agreements with foundries create sunk costs and commitment.
- Intellectual Property: Patents and proprietary technologies represent significant assets that are difficult to divest.
- Capital Equipment Costs: Fabless companies still incur substantial costs for design tools and IP licensing.
Strategic Stakes
The market for high-speed interfaces is incredibly important for tech companies, especially with the growing need for quick data transfer in everything from smartphones to AI-powered systems. This importance naturally leads to intense competition.
Companies are fiercely battling for dominance and to secure vital intellectual property in this space. For instance, in 2024, the global semiconductor market, which underpins these interfaces, was projected to reach over $600 billion, highlighting the immense financial incentives driving this rivalry.
- Strategic Importance: The demand for faster connectivity is a key driver for innovation across multiple tech sectors.
- Aggressive Competition: Companies invest heavily in R&D to gain an edge in high-speed interface technology.
- Intellectual Property: Patents and proprietary designs are crucial battlegrounds for market leadership.
- Market Value: The significant financial stakes in the semiconductor industry fuel this intense competitive landscape.
The competitive rivalry in the high-speed interface IC market, where ASMedia operates, is exceptionally fierce. This is driven by a substantial number of established players and the rapid pace of technological advancement, forcing companies into aggressive competition for market share. The sheer financial stakes, with the global semiconductor market projected to exceed $600 billion in 2024, amplify this rivalry.
Companies like ASMedia must continuously innovate to differentiate themselves and avoid direct price wars. The strategic importance of fast connectivity across numerous tech sectors means significant investment in R&D, making intellectual property a critical battleground. This intense environment is further solidified by high exit barriers, such as massive R&D investments and long-term manufacturing commitments, which keep companies engaged even during challenging periods.
| Key Competitor Aspects | Description | Impact on ASMedia |
| Number of Competitors | Numerous established players and diversified semiconductor giants. | Intensifies rivalry and market fragmentation. |
| Technological Evolution | Rapid advancements in USB and PCIe standards. | Requires constant innovation and significant R&D investment. |
| Market Growth | Growing demand from AI, cloud computing, and consumer electronics. | Attracts more players, increasing competitive pressure despite market expansion. |
| Exit Barriers | High R&D costs, IP protection, and manufacturing commitments. | Leads to sustained competition and potential price wars during downturns. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
While ASMedia is a key player in USB, PCIe, and SATA interfaces, the threat of substitutes looms. Emerging technologies offering comparable or superior high-speed data transfer, or entirely different architectural approaches to connectivity, could siphon market share. For instance, advancements in optical interconnects or novel wireless protocols might present viable alternatives depending on their performance, cost-effectiveness, and ease of integration.
Customers consistently weigh the price-performance trade-off when considering substitute products. If a rival solution delivers similar functionality at a lower price point, or superior performance for a marginally higher cost, the allure of switching intensifies.
For instance, in the semiconductor industry, ASMedia's competitors might offer USB controllers with slightly lower data transfer speeds but at a significantly reduced cost. This price advantage could sway budget-conscious device manufacturers, even if it means a minor compromise in peak performance, thereby increasing the threat of substitution.
Customer willingness to switch to alternative interface technologies hinges on how easily they can integrate, if older systems still work with them, and the overall advantages they offer. ASMedia is actively working to make USB4 appealing by highlighting its ability to handle multiple functions with just one cable, thereby discouraging customers from seeking out other solutions.
Evolution of Industry Standards
The rapid evolution of industry standards presents a significant threat of substitutes for ASMedia. For instance, new generations of USB or PCIe interfaces can quickly render older ASMedia products obsolete, even if those products are still functional. This dynamic creates an internal substitution threat as customers naturally gravitate towards newer, more efficient technologies.
ASMedia actively manages this threat by maintaining a robust and forward-looking product roadmap. This ensures they are not only keeping pace with technological advancements but also leading them.
- USB 4 Version 2.0, announced in 2023, offers up to 80 Gbps, a substantial upgrade from USB 3.2 Gen 2x2's 20 Gbps, potentially making older USB controllers less attractive.
- PCIe 5.0, widely adopted in 2024, doubles the bandwidth of PCIe 4.0, impacting the market for older ASMedia PCIe switch and controller products.
- ASMedia's R&D spending in 2023 was approximately $130 million, reflecting a commitment to developing next-generation interconnect solutions to counter substitution threats.
Integrated Solutions from Competitors
Competitors are increasingly offering highly integrated chipsets that combine multiple functionalities. For instance, some System-on-Chip (SoC) designs might bundle high-speed interfaces, memory controllers, and even graphics processing units. This consolidation can reduce the demand for ASMedia's standalone ICs, as customers might opt for these all-in-one solutions. In 2023, the global SoC market was valued at approximately $250 billion, indicating a significant trend towards integration.
This integration presents a subtle yet potent threat of substitution. When a competitor’s chipset can perform the same functions as ASMedia’s discrete components, it directly diminishes the perceived need for ASMedia's products. This is particularly relevant in markets where space and power efficiency are paramount, such as mobile devices and embedded systems.
The strategic advantage for ASMedia lies in its specialization and performance in specific interface technologies. However, the ongoing push for miniaturization and cost reduction by competitors means that integrated solutions will continue to pose a significant substitution threat. The company must monitor these developments closely.
- Integrated Chipsets: Competitors bundling functionalities like high-speed interfaces reduce the need for standalone ASMedia ICs.
- SoC Market Growth: The global SoC market’s significant valuation highlights the trend towards integrated solutions.
- Substitution Impact: Integrated offerings can directly decrease demand for ASMedia's discrete components.
- Market Trends: Miniaturization and cost reduction drive the adoption of integrated solutions, posing a continuous threat.
The threat of substitutes for ASMedia is driven by evolving technologies and competitive integration strategies. Emerging high-speed interconnects and consolidated chipsets can siphon market share if they offer better price-performance or integration benefits.
ASMedia's USB4 Version 2.0, announced in 2023, offers up to 80 Gbps, significantly outperforming older USB 3.2 Gen 2x2. Similarly, PCIe 5.0 adoption in 2024 doubles the bandwidth of PCIe 4.0. ASMedia's 2023 R&D spending of approximately $130 million underscores its commitment to staying ahead of these substitution threats.
| Technology | ASMedia Offering | Substitute Threat Factor | Data Rate (Gbps) | Year Introduced/Significant Adoption |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USB | USB 3.2 Gen 2x2 | Lower performance | 20 | 2019 |
| USB | USB4 Version 2.0 | Higher performance | 80 | 2023 (Announced) |
| PCIe | PCIe 4.0 | Lower bandwidth | 16 (per lane) | 2017 |
| PCIe | PCIe 5.0 | Higher bandwidth | 32 (per lane) | 2019 (Spec), 2024 (Adoption) |
Entrants Threaten
Developing and manufacturing high-speed interface ICs demands significant capital for research and development, securing crucial intellectual property, and forging essential foundry partnerships. These substantial upfront investments create a formidable barrier, deterring potential new players from entering the ASMedia market.
The semiconductor industry thrives on innovation, making intellectual property and patents a significant barrier to entry. ASMedia's strong foundation in high-speed SERDES technology, evidenced by its numerous patents, significantly deters new competitors. For instance, ASMedia's commitment to developing and certifying its products for evolving standards such as USB4 and Thunderbolt 4 ensures a robust and defensible intellectual property portfolio. This extensive patent protection makes it exceedingly challenging for new entrants to replicate ASMedia's technological advancements and gain market traction.
Established players like ASMedia benefit significantly from economies of scale in design, testing, and volume production. For instance, in 2024, ASMedia's substantial production volumes likely allowed them to negotiate better component prices, a crucial advantage in the competitive semiconductor industry.
New entrants would face considerable difficulty in matching these cost efficiencies without first securing a substantial market share and accumulating years of experience. This inherent cost disadvantage makes it challenging for newcomers to compete on price against ASMedia's established operational advantages.
Access to Distribution Channels
New companies often struggle to get their products onto store shelves or into the hands of consumers because established players already control these crucial distribution channels. For ASMedia, its established relationships with major PC and electronics manufacturers are a significant barrier to entry for potential rivals. Securing design wins, which is essentially getting a company's chips chosen for inclusion in new products, is a complex process that new entrants find difficult to navigate.
ASMedia's existing partnerships mean they already have a foot in the door with key buyers. This long-standing trust and integration into the supply chains of major brands make it incredibly hard for newcomers to even get a chance to compete. For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor industry continued to see consolidation, with major players solidifying their market positions, further concentrating control over distribution networks.
- Established Relationships: ASMedia benefits from deep, long-standing ties with leading PC and electronics manufacturers, a critical advantage in securing market access.
- Design Wins: The process of getting ASMedia's technology incorporated into new products by major brands is a significant hurdle for new entrants, as these decisions are often based on proven reliability and existing partnerships.
- Market Concentration: In 2024, the semiconductor market showed continued concentration, meaning fewer, larger companies control a greater share of distribution channels, amplifying the challenge for new players.
Government Policy and Regulations
Government policies and regulations significantly shape the threat of new entrants in the semiconductor industry. For instance, initiatives like the CHIPS and Science Act in the United States, with its substantial funding for domestic semiconductor manufacturing, can lower entry barriers by providing financial incentives and support for new players.
However, the complex and evolving regulatory landscape, including export controls and intellectual property protections, can also act as a deterrent. In 2024, the global semiconductor industry continues to navigate these policy shifts, with governments worldwide actively seeking to bolster their domestic capabilities and secure supply chains.
- Government Support: Policies like the CHIPS Act (US) and similar initiatives in the EU and Asia aim to attract investment and reduce initial capital requirements for new semiconductor fabs.
- Trade Restrictions: Export controls, such as those implemented by the US on advanced chip technology to China, can limit the ability of new entrants in certain regions to access critical equipment and markets.
- Intellectual Property: Stringent IP laws and the high cost of patent litigation can be significant hurdles for smaller, new companies entering the market.
- Environmental Regulations: Increasingly strict environmental standards for manufacturing processes can add to the compliance costs and complexity for potential new entrants.
The threat of new entrants into ASMedia's high-speed interface IC market is generally low due to substantial capital requirements for R&D, IP, and foundry access, coupled with the industry's reliance on innovation and patents. Established economies of scale in production and strong distribution channel relationships further solidify ASMedia's position, making it difficult for newcomers to compete effectively on cost or market access.
Government policies, while sometimes offering support, also present complexities through trade restrictions and IP enforcement, adding to the barriers for potential new players. These combined factors create a formidable landscape for any aspiring competitor.
In 2024, the semiconductor industry continued to see significant investment in advanced manufacturing, with global government initiatives like the CHIPS Act supporting domestic production and potentially lowering some initial capital hurdles for new entrants. However, the intense competition and the need for deep technical expertise and established supply chain relationships remain significant deterrents.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | ASMedia Advantage (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High R&D, IP acquisition, foundry partnerships | Significant financial hurdle | Established R&D budget and foundry relationships |
| Intellectual Property | Patents in high-speed SERDES, USB4, Thunderbolt 4 | Difficult to replicate technology | Extensive patent portfolio protecting core technologies |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs with high volume production | Cost disadvantage for new entrants | Large production volumes leading to better component pricing |
| Distribution Channels | Established relationships with PC/electronics manufacturers | Difficulty securing design wins and market access | Long-standing partnerships with key buyers |
| Government Policy | CHIPS Act, export controls, IP laws | Can be supportive or restrictive | Navigates regulations, benefits from domestic support where applicable |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our ASMedia Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages a robust combination of primary and secondary data sources. This includes company annual reports, investor presentations, industry-specific market research reports, and regulatory filings to capture comprehensive competitive dynamics.
