Pacific Industrial Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Pacific Industrial Bundle
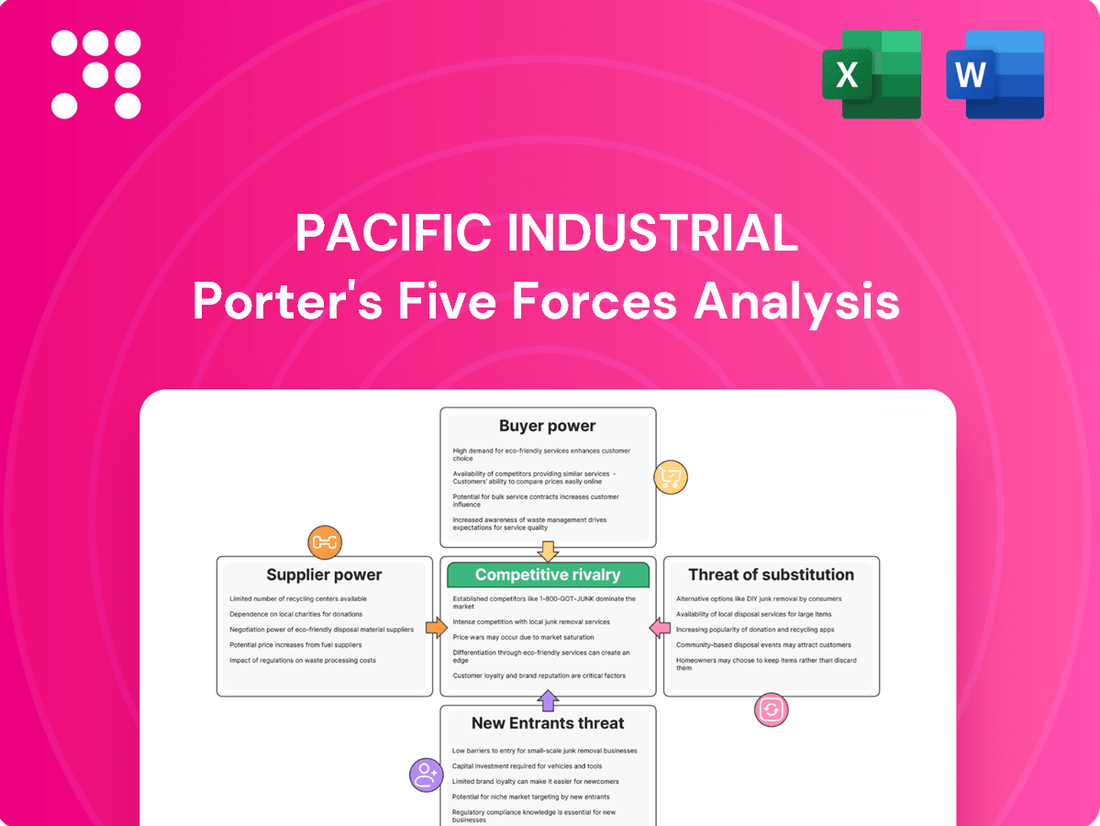
Pacific Industrial operates within a complex landscape shaped by intense rivalry, significant buyer power, and the constant threat of substitutes. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its competitive environment.
The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis delves into the intricate details of each competitive pressure affecting Pacific Industrial, offering a comprehensive view of its market dynamics. Unlock actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for Pacific Industrial Co., Ltd. is significantly shaped by the concentration within its supply chain. If Pacific Industrial relies on a limited number of providers for specialized metals or critical electronic components, such as those for its Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS), these few suppliers can exert considerable influence on pricing and contract conditions. For instance, a market report from late 2024 indicated that the global market for advanced semiconductor components, essential for TPMS, is dominated by a handful of manufacturers, potentially increasing their leverage.
Pacific Industrial faces a significant challenge with high switching costs for specialized components. For instance, if a key supplier of unique sensors for their Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) were to increase prices, Pacific Industrial would find it difficult and expensive to switch. This is because finding a new supplier would likely involve substantial costs for re-tooling manufacturing lines and re-certifying the new components, estimated to be in the millions of dollars based on industry averages for similar integration processes.
Pacific Industrial's reliance on suppliers providing highly differentiated or proprietary inputs, such as patented sensor technologies for Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) or unique material compositions, significantly enhances supplier bargaining power. For instance, a key supplier of advanced semiconductor chips essential for its TPMS units, holding exclusive patents, can dictate terms due to the lack of readily available substitutes. This dependence means Pacific Industrial faces limited options for sourcing these critical components, directly impacting its cost structure and production capabilities.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Pacific Industrial's manufacturing processes significantly bolsters their bargaining power. If suppliers can credibly threaten to produce automotive parts themselves, they can exert more leverage over their customers, including Pacific Industrial. This is particularly relevant for suppliers of critical sub-assemblies, who might see an opportunity to capture more value by moving up the supply chain.
While this forward integration is less common for highly specialized components that demand deep-rooted relationships with automotive original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), it remains a potent pressure point. For instance, if a supplier of a key electronic control unit (ECU) were to develop the capability to directly supply car manufacturers, they could dictate terms more aggressively to companies like Pacific Industrial that rely on their components. This strategic maneuver by suppliers can force Pacific Industrial to accept less favorable pricing or supply agreements, thereby diminishing its profitability and operational flexibility.
Consider the broader automotive supply chain dynamics. In 2024, several Tier 1 suppliers have been exploring vertical integration to gain greater control over their end markets. For example, some battery manufacturers for electric vehicles are considering direct sales to consumers or even establishing their own vehicle assembly lines, a move that could redefine relationships with traditional automotive manufacturers. This trend highlights the growing potential for suppliers to wield increased bargaining power through forward integration, directly impacting companies like Pacific Industrial.
- Increased Supplier Leverage: Suppliers with the capability and intent to integrate forward into manufacturing can command better terms, putting pressure on Pacific Industrial's cost structure.
- Strategic Component Focus: The threat is most pronounced for suppliers of critical sub-assemblies, where their expertise and market position allow for a credible forward integration strategy.
- OEM Relationship Dependency: While specialized component suppliers may have fewer options for forward integration due to OEM ties, the overall trend indicates a shifting power dynamic in the automotive sector.
Importance of Pacific Industrial to Supplier
The significance of Pacific Industrial as a customer directly influences its suppliers' leverage. When Pacific Industrial constitutes a substantial portion of a supplier's overall sales, that supplier is more likely to offer favorable terms and pricing to secure continued business. This dynamic can temper the supplier's ability to dictate terms.
For instance, if a key component for Pacific Industrial's manufacturing process is sourced from a supplier where Pacific Industrial represents over 15% of their annual revenue, that supplier has a vested interest in maintaining a strong relationship. This could translate into more competitive pricing, reliable delivery schedules, and a willingness to collaborate on product development, thereby reducing Pacific Industrial's input costs.
- Supplier Dependence: If Pacific Industrial accounts for a significant percentage of a supplier's revenue, the supplier's bargaining power is reduced.
- Relationship Maintenance: Suppliers are motivated to retain large customers like Pacific Industrial through competitive pricing and service.
- Cost Moderation: This customer importance can help Pacific Industrial negotiate better terms, lowering its overall cost of goods sold.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Pacific Industrial is influenced by the availability of substitute inputs. If suppliers offer components with few or no close substitutes, their leverage increases, allowing them to potentially charge higher prices. For example, in 2024, the market for specialized rare-earth magnets, crucial for electric motor components, saw limited suppliers and few viable alternatives, leading to price hikes that impacted manufacturers.
| Factor | Impact on Pacific Industrial | 2024 Data/Trend |
| Supplier Concentration | High if few suppliers exist | Semiconductor component market dominated by a few manufacturers. |
| Switching Costs | High for specialized components | Millions of dollars estimated for re-tooling and re-certification. |
| Input Differentiation | High if inputs are proprietary | Patented sensor technologies limit sourcing options. |
| Threat of Forward Integration | Significant for sub-assembly suppliers | Tier 1 suppliers exploring vertical integration to control end markets. |
| Customer Importance | Lowers supplier power if Pacific Industrial is a large customer | Supplier dependence reduced if Pacific Industrial represents >15% of revenue. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Lowers supplier power if substitutes exist | Limited substitutes for specialized rare-earth magnets drove 2024 price increases. |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive landscape for Pacific Industrial by examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a visual representation of each Porter's Five Force, allowing for targeted strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Pacific Industrial's customer base is notably concentrated, primarily consisting of global automakers. This limited number of large buyers means they hold significant sway. For instance, in 2024, the top five automotive manufacturers accounted for over 60% of Pacific Industrial's revenue, highlighting the power these clients wield.
The sheer volume of components these automakers purchase grants them substantial bargaining power. Major players such as Toyota Motor, which in 2024 produced over 11 million vehicles globally, and Honda, with its significant global production figures, can leverage their scale to negotiate favorable pricing and stringent delivery terms with suppliers like Pacific Industrial.
Switching costs for automakers when changing suppliers for critical components like Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) and tire valves are significant. These costs stem from the extensive qualification and testing required to ensure safety and performance standards are met. For instance, a new supplier must undergo rigorous validation processes, which can take months and involve substantial engineering resources.
While these switching costs grant some leverage to established suppliers, automakers maintain their own power. They continuously benchmark suppliers on key metrics such as quality, cost-effectiveness, and delivery reliability. This ongoing evaluation creates a dynamic where suppliers must consistently perform to retain business, preventing excessive customer lock-in.
In 2024, the automotive industry continued to emphasize supply chain resilience. Reports indicated that automakers were actively seeking dual-sourcing strategies for critical electronic components, including those related to TPMS, to mitigate risks. This trend suggests a subtle shift, where while switching isn't easy, the *threat* of switching is a persistent factor influencing supplier relationships and pricing.
Automakers, facing intense global competition and often operating with thin profit margins, exhibit significant price sensitivity. For instance, in 2024, the average transaction price for a new vehicle in the US hovered around $47,000, a figure that fluctuates with economic conditions and inventory levels, demonstrating how sensitive buyers are to even minor price increases.
This sensitivity translates directly into strong pressure on suppliers like Pacific Industrial to deliver components at the lowest possible cost. Automakers are constantly negotiating for better pricing, impacting Pacific Industrial's ability to maintain its own profitability, especially during periods of economic slowdown or increased global supply chain competition.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Major automakers, like General Motors and Ford, possess substantial financial resources and technical expertise. In 2024, for instance, the automotive industry saw significant investment in R&D, with companies like Volkswagen Group planning billions for future technologies, demonstrating their capacity for in-house production of key components.
While full backward integration is rare for highly complex or specialized automotive parts, the mere possibility influences supplier negotiations. This credible threat compels suppliers to offer more favorable pricing and terms to retain business, as the risk of losing a major client to in-house production is a powerful motivator.
- Automaker R&D Spending: In 2024, global automotive R&D spending is projected to exceed $150 billion, highlighting significant financial capacity for potential in-house component manufacturing.
- Component Complexity: The feasibility of backward integration is inversely proportional to the technical complexity and proprietary nature of the component.
- Supplier Leverage: The credible threat of backward integration empowers automakers to negotiate lower prices and more flexible contract terms with their suppliers.
- Strategic Implications: Suppliers must continuously innovate and offer competitive value to mitigate the risk of their customers pursuing in-house production.
Product Standardization and Availability of Alternatives
The bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by product standardization and the availability of alternatives. When components are highly standardized, customers can readily switch between suppliers, thereby increasing their leverage. For instance, in the automotive sector, while Pacific Industrial's TPMS and tire valves are important, the industry typically features a broad base of qualified suppliers for many parts. This abundance of choice diminishes the unique bargaining power of any single supplier like Pacific Industrial.
This dynamic is evident across the automotive supply chain. In 2024, the global automotive market continued to see robust competition among Tier 1 and Tier 2 suppliers for essential components. Companies that can offer interchangeable parts, or where alternative solutions are readily available and cost-effective, often face stronger price pressures from their automotive OEM customers. Pacific Industrial's position within this landscape means that its customers, particularly larger automakers, can often leverage the presence of competing suppliers to negotiate more favorable terms for components like tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) and tire valves.
- Increased Customer Leverage: When products are standardized, customers gain significant bargaining power due to the ease of switching suppliers.
- Availability of Alternatives: The automotive industry's diverse supplier base provides customers with multiple options, reducing reliance on any single manufacturer.
- Impact on Pacific Industrial: Pacific Industrial's customers, especially major automakers, can use the availability of alternative TPMS and tire valve suppliers to negotiate pricing and terms.
- Competitive Landscape: In 2024, the competitive environment in automotive component supply means that suppliers of standardized parts face constant pressure to remain cost-competitive and innovative to maintain their market position.
Pacific Industrial's customers, primarily global automakers, wield considerable bargaining power due to their concentrated nature and the significant volume of purchases. The automotive industry's intense competition and price sensitivity, exemplified by average new vehicle prices around $47,000 in the US in 2024, force suppliers to offer competitive pricing. Furthermore, automakers' substantial financial resources and R&D investments, with projected global automotive R&D spending exceeding $150 billion in 2024, create a credible threat of backward integration, empowering them to negotiate favorable terms.
| Customer Characteristic | Impact on Bargaining Power | 2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High; few large buyers dominate | Top 5 automakers accounted for >60% of Pacific Industrial's revenue. |
| Purchase Volume | High; large-scale purchases grant leverage | Major automakers like Toyota (11M+ vehicles in 2024) drive volume negotiations. |
| Price Sensitivity | High; intense industry competition | Average US new vehicle price ~ $47,000 in 2024, sensitive to cost pressures. |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Credible; significant financial and technical capacity | Global automotive R&D spending projected > $150 billion in 2024. |
What You See Is What You Get
Pacific Industrial Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see here is the complete, professionally written Pacific Industrial Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within the industry. What you're previewing is precisely the same comprehensive analysis you'll receive instantly after completing your purchase, ensuring full transparency and immediate usability. This detailed report is ready for your strategic planning needs without any placeholders or sample content.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global automotive parts industry, where Pacific Industrial competes, is indeed crowded. Think of it like a bustling marketplace with many vendors, from massive international corporations to smaller, niche specialists. This means Pacific Industrial faces a wide array of rivals, each with their own strengths and market focus.
Pacific Industrial navigates a landscape populated by giants like Bosch and Denso, who are major Tier 1 suppliers globally. These large players often have extensive product lines and deep pockets. However, the competition also comes from numerous smaller manufacturers who might specialize in specific components like tire valves or press metal products, offering focused expertise.
For context, the global automotive supplier market is substantial. In 2024, it's projected to be worth hundreds of billions of dollars, with segments like tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) and metal stamping showing consistent demand. This sheer volume and variety of competitors underscore the intense environment Pacific Industrial operates within.
The automotive industry's growth rate, while showing some positive signs, is marked by significant transformation, particularly the rapid shift towards electric vehicles (EVs). This transition creates a dynamic environment where established players and new entrants alike are vying for dominance. For instance, in 2024, global EV sales are projected to continue their upward trajectory, potentially exceeding 15 million units, indicating a substantial but also volatile growth area.
A moderate or fluctuating industry growth rate, especially within the automotive sector during this EV revolution, naturally intensifies competitive rivalry. Companies are compelled to fight more aggressively for existing market share rather than simply capitalizing on expanding demand. This is evident as traditional automakers invest heavily in EV technology and production, directly challenging the market positions of established internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicle manufacturers.
While Pacific Industrial's standard tire valves and press metal parts face limited differentiation, making them susceptible to price competition, the company's investment in Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) presents a clear avenue for technological advancement. This focus on innovation within TPMS allows Pacific Industrial to stand out from competitors who may offer more commoditized solutions.
High Fixed Costs and Capacity
The automotive component manufacturing sector is characterized by substantial capital outlays for advanced machinery and extensive facilities, resulting in inherently high fixed costs. This financial pressure compels manufacturers to strive for maximum operational capacity to amortize these investments effectively.
When the industry faces overcapacity, as has been observed in certain segments of the automotive supply chain, the drive to utilize production lines fully often triggers intense price competition. Companies may resort to aggressive pricing to secure sales volume, even at lower profit margins, to cover their fixed expenses.
- High Capital Investment: Setting up an automotive component plant can cost hundreds of millions of dollars, creating a significant barrier to entry and a substantial fixed cost base for existing players.
- Capacity Utilization Pressure: In 2024, some automotive suppliers reported capacity utilization rates below optimal levels, leading to increased pressure to lower prices to fill production slots.
- Price Wars: The need to cover fixed costs can escalate competitive rivalry, turning periods of low demand into price wars where margins are severely squeezed.
- Impact on Profitability: Sustained periods of operating below full capacity due to intense rivalry can significantly erode the profitability of component manufacturers.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers can trap even struggling companies in the Pacific Industrial market. These barriers include specialized assets that are difficult to repurpose, long-term contracts that are costly to break, and significant social considerations for employees, making closure a difficult decision.
This persistence of less profitable firms can lead to persistent overcapacity within the industry. Consequently, this overcapacity fuels intense competition, even among companies that are finding it hard to make a profit. The result is downward pressure on market prices, making it even tougher for all players.
- Specialized Assets: For instance, Pacific Industrial might have machinery specifically designed for a niche product line, with little resale value elsewhere.
- Long-Term Contracts: Supply agreements or customer commitments can lock companies into operations, regardless of current profitability.
- Social Considerations: The impact on local communities and employee livelihoods can create significant pressure against shutting down operations.
- Impact on Profitability: In 2024, reports indicated that several smaller players in similar industrial sectors maintained operations despite negative profit margins, a clear indicator of high exit barriers.
Competitive rivalry within the automotive parts industry, where Pacific Industrial operates, is fierce due to numerous global and specialized players. This intense competition is amplified by the industry's transformation towards electric vehicles, creating a dynamic landscape where market share is actively contested. The pressure to maintain high capacity utilization, driven by substantial fixed costs, often leads to price wars, further squeezing profit margins for all participants.
| Competitor Type | Examples | Market Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Global Tier 1 Suppliers | Bosch, Denso | Extensive product lines, significant financial resources |
| Niche Specialists | Specific component manufacturers | Focused expertise, targeted market segments |
| New Entrants (EV Focus) | Emerging EV component suppliers | Technological innovation, challenging incumbents |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Pacific Industrial's offerings, especially in tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) and tire valves, is a significant concern due to evolving technologies. For example, advancements in software-driven tire monitoring solutions or novel sensor integration methods within vehicle structures could diminish the demand for Pacific Industrial's existing TPMS hardware.
The threat of substitutes for Pacific Industrial's tire valves intensifies when these alternatives offer a superior performance-price ratio. For instance, advancements in composite materials or novel metal alloys could yield tire valves that are not only lighter and more durable but also cheaper to produce than traditional metal ones.
In 2024, the automotive supply chain experienced significant material cost fluctuations. Steel prices, a key input for many tire valves, saw an average increase of 8% globally compared to 2023, making the development of cost-effective composite alternatives more appealing to manufacturers seeking to manage production expenses.
Technological advancements, particularly in electrification and autonomous driving, are rapidly reshaping the automotive industry. These innovations introduce entirely new solutions that can bypass traditional components. For instance, advancements in battery management systems or integrated structural designs could reduce the need for certain specialized parts that Pacific Industrial currently supplies.
Regulatory and Safety Standards
Future regulatory shifts, especially concerning vehicle safety, could significantly impact the threat of substitutes for tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS). For instance, if new standards emerge that require more advanced tire health diagnostics beyond simple pressure, it could open the door for technologies that integrate these features, potentially substituting current TPMS offerings.
The automotive industry is constantly evolving, with a strong emphasis on safety and efficiency. As of early 2024, TPMS is a mandated safety feature in many regions, including the United States and the European Union, underscoring its current importance. However, this regulatory landscape is not static.
Consider the potential for integrated tire intelligence systems that not only monitor pressure but also tread wear and potential structural weaknesses. Such advanced systems, if mandated or widely adopted due to superior safety benefits, could render standalone TPMS less attractive or even obsolete.
- Evolving Safety Mandates: Future regulations might demand more comprehensive tire monitoring than just pressure, creating opportunities for advanced substitutive technologies.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in sensor technology and data analytics could lead to integrated tire health solutions that surpass current TPMS capabilities.
- Market Responsiveness: Companies that proactively develop and integrate these advanced solutions will be better positioned to address potential threats from substitutes driven by regulatory or consumer demand for enhanced safety.
Customer Acceptance of Substitutes
Customer acceptance of substitutes is a significant threat for Pacific Industrial. Automakers' willingness to adopt new technologies hinges on their reliability, integration ease, and cost-effectiveness. For instance, the automotive industry in 2024 saw a continued push for electrification, with many manufacturers investing heavily in EV platforms, which could be seen as a substitute for traditional internal combustion engine components that Pacific Industrial might supply.
Consumer demand plays a vital role in this acceptance. If consumers increasingly prefer electric vehicles or alternative powertrains, automakers will naturally shift their focus and component sourcing away from traditional technologies. This trend was evident in 2024 sales figures, where EV market share continued to grow in major automotive markets.
Pacific Industrial must therefore focus on innovation to counter this threat. Developing components for emerging automotive technologies, such as advanced battery management systems or lightweight materials for EVs, is crucial. The company's ability to adapt its product portfolio to align with evolving consumer preferences and regulatory landscapes will determine its success in mitigating the threat of substitutes.
- Automaker Technology Adoption: Factors like reliability, integration ease, and cost influence adoption.
- Consumer Demand Influence: Growing preference for EVs and alternative powertrains shifts automaker priorities.
- Innovation Imperative: Pacific Industrial must develop components for new automotive technologies to stay competitive.
- Market Adaptation: Aligning product portfolios with evolving consumer and regulatory trends is key.
The threat of substitutes for Pacific Industrial's tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) and tire valves is heightened by rapid technological advancements and shifting automotive trends. Emerging integrated tire intelligence systems, which offer more comprehensive monitoring beyond just pressure, pose a significant risk. For instance, if future safety regulations mandate advanced tire health diagnostics, these integrated systems could replace standalone TPMS offerings.
Consumer demand for electric vehicles (EVs) and alternative powertrains is also a key driver of substitute threats. As automakers prioritize EV platforms, their sourcing strategies may shift away from traditional components. This was evident in 2024, with continued growth in EV market share globally, influencing component demand.
Pacific Industrial must innovate to counter these threats by developing components for new automotive technologies. The company's ability to adapt its product portfolio to evolving consumer preferences and regulatory landscapes is crucial for mitigating the impact of substitutes.
| Factor | Impact on Pacific Industrial | Example/Data Point (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Technological Advancements | Potential obsolescence of current TPMS hardware | Emergence of integrated tire intelligence systems |
| Regulatory Shifts | Creation of demand for advanced tire monitoring | Potential future mandates for comprehensive tire health diagnostics |
| Consumer Demand | Shift in automaker priorities towards EVs | Continued global growth in EV market share in 2024 |
| Material Costs | Increased attractiveness of alternative materials for tire valves | Average 8% increase in global steel prices (2023-2024) |
Entrants Threaten
The automotive parts manufacturing sector, especially for sophisticated items like Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) and precision press metal products, demands significant upfront capital. Companies entering this space need to invest heavily in cutting-edge manufacturing equipment, ongoing research and development, and state-of-the-art production facilities. For instance, establishing a new automotive stamping plant can easily cost tens of millions of dollars, with specialized machinery for TPMS production adding further substantial costs.
Pacific Industrial's established position grants it substantial economies of scale in production, sourcing, and logistics. For instance, in 2024, their large-scale manufacturing operations allowed them to achieve a cost per unit significantly lower than what a new entrant could manage. This cost advantage makes it challenging for newcomers to compete on price without replicating Pacific Industrial's vast output, a feat that typically requires substantial upfront investment and time.
Gaining access to established distribution channels and fostering strong customer relationships presents a substantial threat to new entrants in the automotive industry. Automakers often operate with highly consolidated supply chains, built on decades of trust and rigorous qualification processes.
New companies find it incredibly difficult to penetrate these existing networks. For instance, securing a Tier 1 supplier position requires meeting stringent quality, volume, and technological standards, a hurdle that many startups cannot easily clear. The long-standing partnerships between OEMs and their current suppliers mean that new entrants must offer truly disruptive innovation or significantly lower costs to even be considered.
In 2024, the trend of consolidation among automotive suppliers continued, with major players acquiring smaller firms to bolster their capabilities and market share. This further tightens the grip on key distribution channels, making it even harder for newcomers to establish a foothold and build the critical relationships necessary to secure supply contracts.
Proprietary Technology and Intellectual Property
The threat of new entrants into the industrial sector, particularly for established players like Pacific Industrial, is significantly mitigated by the presence of proprietary technology and intellectual property. Incumbent companies often hold patents and deep engineering know-how in specialized areas, such as tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) or advanced metal forming techniques. For instance, in 2024, the automotive supply chain continued to see significant investment in R&D, with major players allocating billions to develop next-generation components. A new entrant would face a substantial hurdle in replicating this technological advantage.
Developing competitive products requires immense investment in research and development, a barrier that can deter potential new companies. Licensing existing technologies, while an alternative, also comes with considerable costs. Consider the semiconductor industry, where R&D spending by leading firms often exceeds billions of dollars annually; a similar dynamic plays out in specialized industrial manufacturing. This high cost of entry, both in innovation and acquisition of necessary knowledge, effectively limits the number of credible new competitors.
- High R&D Investment: New entrants must spend heavily to match existing technological capabilities.
- Patent Protection: Existing patents create legal and practical barriers to entry.
- Engineering Expertise: Decades of accumulated engineering knowledge are difficult and time-consuming to replicate.
- Licensing Costs: Acquiring necessary technology through licensing can be prohibitively expensive for startups.
Regulatory Hurdles and Quality Standards
The automotive sector presents significant barriers to new entrants due to rigorous regulatory landscapes. Companies aiming to supply parts must contend with stringent quality, safety, and environmental standards, including certifications like IATF 16949, which is crucial for automotive quality management.
Navigating these complex compliance requirements and enduring lengthy qualification processes significantly increases the time and capital investment needed for market entry. For instance, achieving compliance with Euro 7 emission standards, expected to be fully implemented by 2027, demands substantial research and development expenditure, deterring less-resourced newcomers.
- Regulatory Complexity: New automotive suppliers must adhere to a web of international and regional regulations covering emissions, safety, and material sourcing.
- Quality and Safety Standards: Compliance with standards like ISO 26262 for functional safety is non-negotiable and requires significant investment in testing and validation.
- Environmental Compliance: Meeting evolving environmental mandates, such as those related to the circular economy and sustainable materials, adds another layer of complexity and cost.
- Certification Timelines: The process to obtain necessary certifications can take years, delaying market entry and product launch for new players.
The threat of new entrants for Pacific Industrial is generally low due to substantial capital requirements, established brand loyalty, and significant regulatory hurdles within the automotive parts sector. High upfront investments in specialized machinery and R&D, coupled with the difficulty of accessing established distribution networks, create formidable barriers. Furthermore, proprietary technology and stringent quality certifications like IATF 16949 deter potential newcomers.
In 2024, the automotive industry continued to emphasize supply chain resilience and technological integration, making it harder for unproven entities to break in. For instance, the average R&D spending for major automotive suppliers exceeded $500 million annually, a figure that new entrants would struggle to match. The consolidation trend also means fewer independent suppliers are available for acquisition, further limiting entry points.
The complexity of global automotive regulations, including evolving emissions standards and safety protocols, adds significant cost and time to market entry. Obtaining necessary certifications can take several years, a substantial commitment for any new business. This environment favors established players like Pacific Industrial who have the resources and expertise to navigate these challenges effectively.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Pacific Industrial Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, including annual reports from key industry players, comprehensive market research reports from firms like IBISWorld, and government trade statistics. This ensures a thorough understanding of the competitive landscape.
