Dell Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Dell Bundle
Dell's competitive landscape is shaped by powerful forces, from the bargaining power of its customers to the constant threat of new entrants. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any business operating in the tech sector.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Dell’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Dell's reliance on a small number of suppliers for critical components significantly bolsters supplier bargaining power. For instance, in Q4 2023, Intel and AMD collectively supplied nearly 100% of Dell's primary semiconductor needs, with Intel holding a dominant 75.5% market share and AMD the remaining 24.5%. This concentrated supplier base means these manufacturers can exert considerable influence over pricing and availability, especially for proprietary or highly specialized chips essential to Dell's product line.
Changing core suppliers can incur substantial costs for Dell, including redesigning products, re-certifying components, and adjusting manufacturing processes. These significant investments can make it difficult for Dell to switch, thereby strengthening supplier leverage.
Dell's supplier switching costs were estimated at $87 million in 2024. This figure highlights the considerable financial commitment involved in shifting away from established partners, directly impacting Dell's ability to negotiate favorable terms.
These high switching costs reduce Dell's flexibility and increase the bargaining power of established suppliers. When it's expensive to leave, suppliers can often dictate terms more effectively, potentially impacting Dell's profitability and operational efficiency.
Supplier industry consolidation significantly amplifies their bargaining power. When fewer companies dominate the supply chain, as seen in the semiconductor industry, they have greater leverage over buyers like Dell. This limited competition means fewer alternatives for Dell, forcing them to accept less favorable pricing and terms.
For instance, in 2024, the global semiconductor market saw continued consolidation, with major players like Intel and AMD increasing their market share. This concentration means Dell has fewer options for critical components, potentially driving up costs and impacting profit margins due to the suppliers' enhanced ability to dictate terms.
Volume Purchases Provide Some Leverage
Dell's substantial purchasing volume, with strategic partnerships often valued in the billions of dollars, offers a significant degree of counter-leverage in negotiations with suppliers. This immense scale of operations allows Dell to secure more favorable terms, competitive pricing, and optimized delivery schedules, even when facing concentrated supplier markets.
For instance, in 2024, Dell's annual revenue reached approximately $88.4 billion, underscoring its massive procurement capabilities. This financial muscle translates directly into greater bargaining power.
- Negotiating Power: Dell's sheer size allows it to command better prices and terms than smaller competitors.
- Strategic Partnerships: Long-term, high-value relationships with key suppliers are crucial for maintaining this leverage.
- Volume Discounts: The ability to purchase components in massive quantities enables Dell to secure significant volume discounts, impacting its cost of goods sold.
- Supply Chain Efficiency: Dell leverages its purchasing power to influence supplier delivery schedules, ensuring a consistent and efficient supply chain.
Potential for Vertical Integration by Suppliers
Some critical component suppliers possess the capability to integrate forward, potentially entering Dell's end-product market and presenting a significant competitive threat. This threat is particularly relevant for suppliers of specialized components where their expertise could be leveraged to assemble and market finished products.
However, Dell's established global distribution network, a key asset built over decades, and its strong brand recognition create substantial barriers for most suppliers attempting direct competition. For instance, in 2024, Dell's revenue reached over $88 billion, underscoring the scale and reach a new entrant would need to overcome.
- Supplier Threat: Suppliers of critical components like high-performance processors or advanced display panels have the technical know-how to potentially produce finished devices.
- Dell's Defenses: Dell's vast distribution channels and brand loyalty, evidenced by its significant market share in enterprise and consumer segments, make it difficult for suppliers to compete directly.
- Market Dynamics: While the potential for supplier integration exists, the capital investment and market access required to challenge Dell's established position remain substantial hurdles for most component manufacturers.
Dell's bargaining power with suppliers is significantly influenced by its immense purchasing volume and strategic partnerships. With 2024 revenues exceeding $88 billion, Dell leverages this financial muscle to negotiate favorable pricing and terms. This scale allows for substantial volume discounts, directly impacting its cost of goods sold and supply chain efficiency.
| Metric | Value (2024) | Impact on Dell |
|---|---|---|
| Annual Revenue | ~$88.4 billion | Enables significant purchasing power and negotiation leverage. |
| Estimated Supplier Switching Costs | $87 million | Limits Dell's flexibility, increasing supplier leverage. |
| Intel Market Share (Semiconductors) | ~75.5% | Highlights concentration in critical component supply. |
| AMD Market Share (Semiconductors) | ~24.5% | Further emphasizes reliance on a limited number of key suppliers. |
What is included in the product
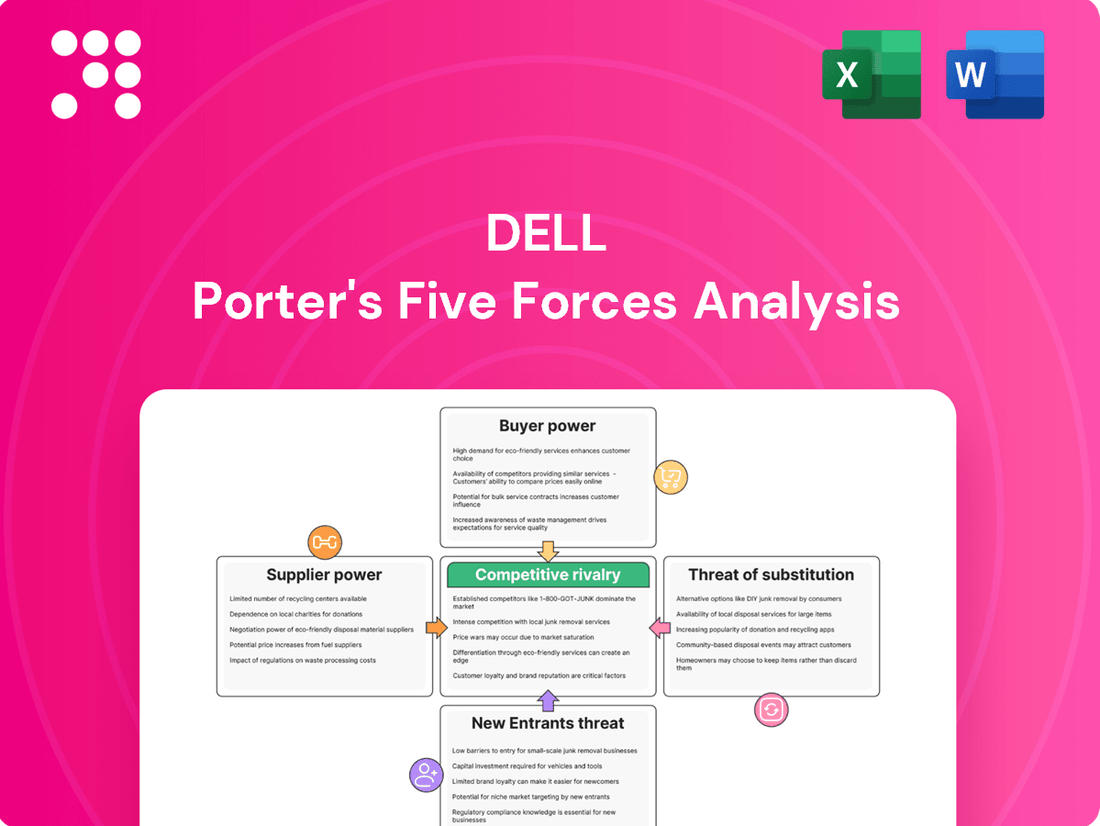
Dell Porter's Five Forces Analysis dissects the competitive intensity within Dell's operating environment by examining buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, threat of substitutes, and existing rivalry.
Quickly identify and address competitive threats with a visual representation of all five forces, simplifying complex market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
The sheer volume of choices available to customers in the technology sector significantly amplifies their bargaining power. Competitors like HP, Lenovo, and Apple offer a diverse range of products, giving buyers the freedom to easily switch if Dell's offerings don't meet their specific needs or price points.
This widespread availability of alternatives means customers can readily compare features, performance, and pricing across multiple brands. For instance, in 2024, the global PC market saw shipments from various vendors, with Dell holding a substantial but not dominant share, underscoring the competitive landscape where customer choice is paramount.
For many standardized hardware products, the cost for customers to switch between different brands is relatively low. This ease of switching makes customers highly price-sensitive and willing to move to competitors offering better deals or features.
In 2024, the consumer electronics market continues to see intense competition, with brands like Apple, Samsung, and HP vying for market share. The ability for consumers to easily find comparable specifications and pricing across these brands means that a slight price advantage or a more appealing promotional offer can easily sway purchasing decisions, directly impacting Dell's pricing power.
Customer price sensitivity is a key driver of bargaining power, and it's particularly pronounced in the consumer technology market. For instance, in 2024, the price elasticity of demand for consumer technology products was observed at 1.7, indicating that a 1% decrease in price leads to a 1.7% increase in demand. This high sensitivity means consumers can readily switch brands if prices are too high.
While large enterprise customers exhibit lower price sensitivity compared to consumers, their bargaining power remains significant. These clients often secure substantial discounts, with average discounts reaching 12.3% in 2024. This is primarily due to their high purchase volumes and the strategic value they represent to suppliers, enabling them to negotiate favorable terms.
Direct Sales Channel Impact
Dell's direct sales model significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. In 2024, this strategy fueled $61.4 billion in revenue, with online sales alone seeing a robust 16.7% growth. This direct engagement offers customers unparalleled transparency in pricing and extensive customization choices, putting them firmly in control of their purchasing decisions.
By cutting out intermediaries, Dell reduces information asymmetry. Customers gain direct access to product details and pricing, making it harder for sellers to exploit knowledge gaps. This direct line of communication and sales further empowers customers, allowing them to negotiate more effectively or easily switch to competitors offering better value.
- Direct Sales Revenue: Dell reported $61.4 billion in revenue from its direct sales model in 2024.
- Online Sales Growth: The company experienced a 16.7% growth rate in online sales during 2024.
- Customer Empowerment: Transparency in pricing and customization options are key benefits for customers.
- Reduced Information Asymmetry: Direct interaction minimizes knowledge gaps between buyers and sellers.
Diverse Customer Segments with Varying Power
Dell's customer base is incredibly diverse, ranging from individual consumers to massive enterprise clients. This segmentation significantly impacts customer bargaining power.
Large enterprises, which represented 36% of Dell's revenue in 2024, wield considerable influence. Their substantial order volumes and the potential for significant, long-term contracts allow them to negotiate favorable pricing and demand highly customized solutions and support services. For instance, the average purchase value for these clients was an impressive $127,500, underscoring their economic clout.
- Diverse Customer Base: Dell caters to individuals, SMBs, and large enterprises.
- Enterprise Influence: Large enterprises, making up 36% of Dell's 2024 revenue, have strong bargaining power.
- High Purchase Value: Average enterprise purchase values of $127,500 in 2024 highlight their economic leverage.
- Customization Demands: Volume buyers can demand tailored solutions and services, increasing their power.
Customers possess significant bargaining power due to the vast array of readily available alternatives in the technology market, allowing them to easily switch if Dell's offerings don't align with their price or feature expectations. This ease of switching, coupled with high price sensitivity, particularly in the consumer segment where price elasticity of demand was 1.7 in 2024, means customers can readily shift to competitors offering better value. Even large enterprise clients, despite lower price sensitivity, exert considerable influence through high purchase volumes, securing substantial discounts averaging 12.3% in 2024 and demanding customized solutions.
| Factor | Impact on Dell | Supporting Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of Substitutes | High customer choice amplifies bargaining power. | Dell holds a substantial but not dominant share in the competitive global PC market. |
| Switching Costs | Low switching costs make customers price-sensitive. | Customers can easily compare features and pricing across brands like HP, Lenovo, and Apple. |
| Price Sensitivity | Customers are willing to switch for better deals. | Price elasticity of demand for consumer tech was 1.7; average enterprise discounts reached 12.3%. |
| Customer Concentration | Large enterprises wield significant influence. | Enterprises, 36% of Dell's 2024 revenue, have high purchase values averaging $127,500. |
Same Document Delivered
Dell Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It provides a comprehensive analysis of Dell's competitive landscape through Porter's Five Forces framework, detailing the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products. This in-depth examination equips you with a clear understanding of the strategic factors influencing Dell's market position and profitability.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The technology landscape is fiercely contested, with Dell navigating intense rivalry from global giants like HP, Lenovo, and Apple. These competitors vie for market share across a broad spectrum of products, from personal computers to enterprise-level servers and storage solutions.
As of 2024, Dell holds the position of the world's third-largest PC vendor, underscoring the crowded nature of the market. This intense competition necessitates continuous innovation and strategic pricing to maintain its standing.
The personal computer market, particularly for standard hardware, is intensely price-sensitive. This sensitivity often fuels aggressive price wars among competitors, forcing companies like Dell to constantly evaluate their pricing strategies to remain competitive without sacrificing profitability. In 2024, the average selling price for consumer PCs saw fluctuations, with some segments experiencing slight declines due to promotional activities by major manufacturers.
The tech industry thrives on constant evolution, with rapid advancements and shrinking innovation cycles demanding significant investment in research and development. For instance, in 2024, major semiconductor companies like Intel and TSMC continued to pour billions into next-generation chip manufacturing, with TSMC alone planning over $28 billion in capital expenditures for advanced nodes.
To stay ahead, companies must relentlessly innovate, launching new products and features to capture market share and stand out. This pressure is evident in the smartphone market, where manufacturers like Apple and Samsung release updated models annually, incorporating features like improved camera technology and faster processors, driving consumer upgrades and intense competition.
Product Differentiation Challenges
Dell strives to differentiate its products through extensive customization options and a focus on quality. However, in the competitive hardware market, especially for standard components, achieving substantial differentiation is difficult. This often forces competition to pivot towards pricing strategies, operational efficiency, and the delivery of enhanced services.
The challenge in differentiating hardware, particularly for commodity parts, means that Dell often finds itself competing more intensely on price. For instance, in 2024, the PC market continued to see aggressive pricing strategies from major players, impacting profit margins for companies like Dell. This dynamic intensifies rivalry as customers can readily switch between brands based on cost, making unique product features less of a decisive factor.
- Customization vs. Commoditization: While Dell's build-to-order model offers customization, the underlying hardware components are often sourced from a limited number of global suppliers, leading to similar offerings across the industry.
- Price Sensitivity: In 2023, global PC shipments saw a decline, with vendors resorting to price reductions to stimulate demand, highlighting the ongoing price sensitivity of consumers and businesses.
- Service as a Differentiator: To combat hardware commoditization, Dell emphasizes its value-added services, such as technical support, warranty options, and managed IT solutions, as key differentiators.
Competition in Services and Solutions
Competitive rivalry in the technology sector, including for companies like Dell, has intensified significantly beyond just hardware. It now encompasses a broad spectrum of IT services, software development, and increasingly, cloud computing and artificial intelligence (AI) solutions. This diversification means companies are not just competing on product features but on their ability to offer comprehensive, integrated technology ecosystems and highly tailored solutions to meet evolving business needs.
The landscape is characterized by intense competition across these diverse offerings. For instance, in the cloud services market, major players are constantly innovating and expanding their capabilities. By the end of 2023, the global cloud computing market was valued at approximately $606 billion, with projections for continued substantial growth. This growth fuels competition as companies vie for market share by offering competitive pricing, advanced features, and specialized services.
Key aspects of this rivalry include:
- Intensified Competition in Services: Companies are no longer solely hardware vendors but are deep in the services arena, offering everything from managed IT services to cybersecurity and data analytics.
- Cloud and AI Dominance: The battleground has shifted to providing robust cloud infrastructure, advanced AI platforms, and integrated solutions that leverage these technologies for business transformation.
- Ecosystem Play: Success often hinges on building and managing a cohesive ecosystem of hardware, software, and services that work seamlessly together, creating stickiness and competitive advantage.
- Partnership and Integration: Companies are increasingly forming strategic partnerships and focusing on seamless integration of third-party solutions to broaden their offerings and appeal to a wider customer base.
The technology sector, where Dell operates, is characterized by exceptionally high competitive rivalry. This is driven by a large number of well-established global players, including HP, Lenovo, and Apple, all vying for market share across a wide range of products from PCs to enterprise solutions.
Dell's position as the third-largest PC vendor globally in 2024 highlights the crowded nature of this market, where continuous innovation and aggressive pricing are essential for survival. The intense price sensitivity, particularly in the standard hardware segment, often leads to price wars, impacting profit margins.
The rapid pace of technological advancement and shrinking innovation cycles necessitate substantial investments in research and development. Companies must constantly launch new products and features to differentiate themselves, a challenge amplified by the commoditization of hardware components.
To counter this, Dell emphasizes value-added services like technical support and managed IT solutions as key differentiators. However, the competition has expanded beyond hardware to services, cloud computing, and AI, creating a complex battleground where integrated ecosystems and tailored solutions are increasingly important.
| Competitor | 2024 PC Market Share (Approx.) | Key Offerings |
| HP | 19.5% | PCs, Laptops, Printers, Enterprise Solutions |
| Lenovo | 20.0% | PCs, Laptops, Servers, Smartphones |
| Apple | 9.0% | MacBooks, iMacs, iPads, iPhones (Integrated Ecosystem) |
| Dell | 16.5% | PCs, Laptops, Servers, Storage, Monitors, Services |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The increasing adoption of cloud computing and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) presents a significant threat of substitutes for Dell's traditional hardware business. Many companies are shifting to cloud-based solutions, reducing their reliance on on-premise servers and workstations. For instance, by the end of 2024, it's projected that over 90% of enterprises will utilize a multi-cloud or hybrid cloud strategy, aiming for greater agility and cost-efficiency.
This trend directly substitutes Dell's core offerings, as businesses can access computing power and software applications without purchasing and maintaining their own physical infrastructure. The flexibility and scalability offered by cloud providers mean that companies can often achieve similar or better performance at a lower total cost of ownership compared to traditional hardware investments.
Smartphones and tablets are increasingly stepping in as substitutes for traditional PCs, particularly for everyday consumer tasks like browsing, email, and social media. This trend is forcing hardware manufacturers, including Dell, to rethink their product strategies and focus on versatile devices. By mid-2024, global smartphone shipments were projected to reach over 1.2 billion units, highlighting the sheer volume of these alternative computing devices.
The increasing adoption of subscription-based IT services, including managed IT and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional hardware sales. These models allow companies to access necessary technology and support through recurring payments, bypassing the need for large upfront capital investments in physical infrastructure.
This shift is driven by the desire for greater flexibility and scalability, enabling businesses to adjust their IT spending based on evolving needs. For instance, the global managed services market was valued at approximately $250 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong preference for these alternative service delivery methods.
Open-Source Software Alternatives
The increasing adoption of open-source software presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional, proprietary software often bundled with hardware. This trend allows customers to bypass costly licensing fees associated with operating systems and applications, thereby reducing their dependence on specific vendors.
Open-source solutions empower users to create highly customized IT infrastructures, offering unparalleled flexibility and cost savings. For instance, the global open-source software market was valued at approximately $22.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a clear shift in customer preference towards these alternatives.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Open-source software often comes with no licensing fees, significantly lowering the total cost of ownership compared to proprietary alternatives.
- Flexibility and Customization: Users can modify and adapt open-source code to meet specific needs, fostering innovation and tailored IT environments.
- Reduced Vendor Lock-in: Adopting open-source solutions diminishes reliance on a single software provider, allowing for greater strategic freedom.
- Growing Market Share: The open-source segment continues to gain traction across various industries, from cloud computing to data analytics, demonstrating its increasing viability as a substitute.
Refurbished and Used Hardware Market
The growing market for refurbished and used hardware presents a significant threat of substitutes for Dell's new products. Customers seeking lower price points can opt for pre-owned devices, directly impacting sales volumes for new Dell hardware. For instance, in 2024, the global refurbished electronics market was valued at over $80 billion and is projected to grow substantially.
Dell's own involvement in asset recovery and resale programs, such as Dell Outlet, directly feeds into this substitute market. By refurbishing and selling its own used equipment, Dell not only captures value from its existing product lifecycle but also acknowledges and participates in the demand for more affordable alternatives.
- Market Size: The global refurbished electronics market is a multi-billion dollar industry, offering a tangible alternative for budget-conscious consumers and businesses.
- Price Sensitivity: Refurbished options provide a significant cost advantage, making them highly attractive to price-sensitive segments of Dell's customer base.
- Dell's Participation: Dell's own refurbishment and resale channels (e.g., Dell Outlet) directly contribute to the supply of these substitutes, highlighting the competitive pressure from within its own ecosystem.
The increasing adoption of cloud computing and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) presents a significant threat of substitutes for Dell's traditional hardware business. Many companies are shifting to cloud-based solutions, reducing their reliance on on-premise servers and workstations. For instance, by the end of 2024, it's projected that over 90% of enterprises will utilize a multi-cloud or hybrid cloud strategy, aiming for greater agility and cost-efficiency.
Smartphones and tablets are increasingly stepping in as substitutes for traditional PCs, particularly for everyday consumer tasks. By mid-2024, global smartphone shipments were projected to reach over 1.2 billion units, highlighting the sheer volume of these alternative computing devices.
The growing market for refurbished and used hardware presents a significant threat of substitutes for Dell's new products. Customers seeking lower price points can opt for pre-owned devices, directly impacting sales volumes for new Dell hardware. In 2024, the global refurbished electronics market was valued at over $80 billion and is projected to grow substantially.
| Substitute Area | Key Trend | Impact on Dell | Market Data (2024 Projections/Estimates) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud Computing & SaaS | Shift from on-premise to cloud infrastructure | Reduced demand for servers, workstations, and related hardware | >90% of enterprises using multi-cloud/hybrid cloud |
| Mobile Devices | Increasing capability of smartphones/tablets for tasks | Cannibalization of PC sales for certain use cases | >1.2 billion global smartphone shipments |
| Refurbished/Used Hardware | Growing demand for cost-effective alternatives | Direct competition for new hardware sales | >$80 billion global refurbished electronics market |
Entrants Threaten
High capital investment requirements pose a significant threat to Dell. Establishing state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities, robust research and development capabilities, and extensive global supply chains demands billions of dollars. For instance, building a new semiconductor fabrication plant alone can cost upwards of $20 billion, a prohibitive sum for most potential entrants.
Existing tech giants like Dell command significant brand loyalty, making it tough for newcomers to gain traction. In 2024, Dell continued to leverage its decades-long reputation for reliability and performance, a key factor for businesses making significant IT investments.
Furthermore, established players possess deeply entrenched distribution channels and strong customer relationships. Dell's direct sales model, honed over years, allows for efficient customer engagement and support, creating a significant barrier for new entrants aiming to replicate this reach and trust quickly.
Dell and other major players in the PC market enjoy substantial economies of scale. This means they can produce goods at a much lower cost per unit than smaller companies. For instance, in 2024, Dell's massive purchasing power allowed it to secure components at prices unavailable to startups.
This cost advantage is a significant barrier for new entrants. To compete on price, a newcomer would need to achieve similar production volumes, which is incredibly difficult and capital-intensive. Without matching these efficiencies, new companies would likely operate at a cost disadvantage from the outset.
Complex Supply Chain and Global Logistics
The intricate global technology supply chain presents a significant barrier to entry. Replicating Dell's sophisticated network, which manages specialized components and navigates complex international regulations, would require immense capital and established relationships. This complexity makes it difficult for newcomers to match Dell's operational efficiency and cost structure.
Dell's established global logistics capabilities, honed over decades, are a substantial deterrent to new entrants. The company's ability to manage a vast and diverse supplier base, coupled with its efficient warehousing and distribution systems, ensures timely delivery and cost control. For instance, in 2023, Dell reported managing over 100,000 suppliers globally, underscoring the scale of its operational footprint.
- Global Supply Chain Complexity: The technology sector relies on a highly intricate web of suppliers for specialized components, making it difficult for new players to establish reliable sourcing and production.
- Logistical Hurdles: Managing international shipping, customs, and inventory across numerous regions requires significant investment in infrastructure and expertise, a domain where Dell has a long-standing advantage.
- Economies of Scale in Logistics: Dell's high sales volume allows it to negotiate favorable rates with shipping carriers and optimize its logistics networks, creating a cost advantage that is hard for smaller entrants to overcome.
Intellectual Property and Regulatory Hurdles
The threat of new entrants is significantly mitigated by substantial intellectual property and regulatory barriers. Many industries are shielded by a dense network of patents and proprietary technologies, which makes it challenging for newcomers to create competitive products without infringing on established intellectual property rights. For instance, in the semiconductor industry, companies like TSMC and Intel hold thousands of patents, creating a high barrier to entry for any firm looking to develop advanced chip manufacturing processes.
Navigating the complex web of regulatory compliances further complicates market entry. These regulations can range from environmental standards to data privacy laws, requiring significant investment in legal expertise and compliance infrastructure. In the pharmaceutical sector, for example, the lengthy and costly process of obtaining drug approvals from bodies like the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) acts as a powerful deterrent to new players. In 2024, the average cost to bring a new drug to market was estimated to be over $2 billion, a figure that underscores the financial commitment required.
- Patent Protection: Companies in technology-driven sectors often hold extensive patent portfolios, making it legally perilous for new entrants to innovate without licensing agreements.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: Adhering to industry-specific regulations, such as those in finance or healthcare, demands substantial upfront investment and ongoing operational expenditure.
- High R&D Investment: Industries requiring significant research and development, like aerospace or advanced materials, necessitate massive capital outlays that are difficult for new firms to match.
The threat of new entrants for Dell is generally low due to several formidable barriers. High capital requirements for manufacturing and R&D, coupled with established brand loyalty and entrenched distribution channels, make it difficult for newcomers to compete effectively. Dell's significant economies of scale also provide a substantial cost advantage, further deterring potential market entrants.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example for Dell (2024 data where applicable) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Significant upfront investment needed for facilities, R&D, and supply chains. | Building a semiconductor fab can cost over $20 billion. |
| Brand Loyalty & Relationships | Existing customer trust and strong relationships built over time. | Dell's decades-long reputation for reliability in enterprise IT solutions. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to high production volumes. | Dell's purchasing power for components in 2024. |
| Distribution Channels | Established networks for reaching customers efficiently. | Dell's direct sales model and global logistics. |
| Intellectual Property & Regulations | Patents, proprietary technology, and compliance costs. | Semiconductor patents held by industry leaders; FDA drug approval costs over $2 billion. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Dell Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages data from Dell's annual reports and SEC filings, alongside industry-specific market research reports and competitor financial statements, to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
