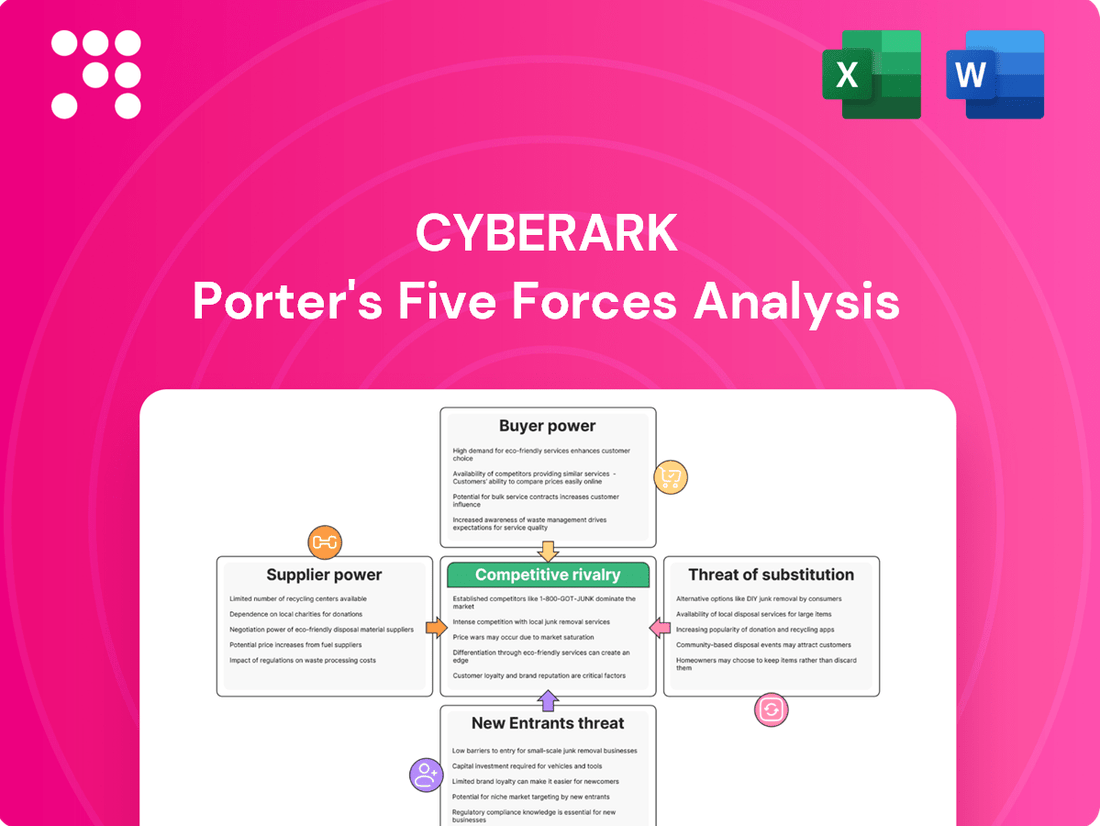
CyberArk Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
CyberArk Bundle
CyberArk's competitive landscape is shaped by intense rivalry, significant buyer power due to cloud adoption, and the looming threat of new entrants in identity security. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the cybersecurity market.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping CyberArk’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
CyberArk's core business revolves around software development, which inherently minimizes its dependence on suppliers of raw materials or basic physical components. This low reliance is a significant factor in limiting the bargaining power of such suppliers.
Because CyberArk's inputs are largely digital and intellectual property, suppliers of commoditized physical goods have very little leverage. Their products are typically easily replaceable, meaning CyberArk can switch suppliers with minimal disruption or cost, further diminishing supplier influence.
CyberArk's increasing reliance on cloud infrastructure providers like AWS and Azure for its SaaS offerings presents a key area of supplier power. As a significant portion of its operations and service delivery moves to the cloud, the terms and pricing set by these major providers directly impact CyberArk's cost structure and operational flexibility.
While these cloud giants hold considerable sway, CyberArk likely employs multi-cloud strategies to diversify its dependencies and enhance its negotiating leverage. This approach allows CyberArk to potentially secure more favorable terms by playing providers against each other, thereby mitigating the concentrated power of any single cloud infrastructure supplier.
The cybersecurity industry, including companies like CyberArk, faces a pronounced talent shortage. This scarcity elevates the bargaining power of skilled professionals, such as cybersecurity developers and security researchers, who are essentially critical 'suppliers' of essential expertise. Demand for these specialized roles consistently outstrips supply, giving these individuals considerable leverage.
To counter this, CyberArk, like its peers, must focus on robust strategies for attracting and retaining top talent. This includes offering competitive compensation packages, which in 2024 continued to be a primary driver in the tech sector, and cultivating a strong, supportive organizational culture that fosters growth and engagement among its workforce.
Software components and open-source contributions
CyberArk's reliance on third-party software and open-source components can influence supplier power. While proprietary or highly specialized components might present a concentrated supplier base, the vast ecosystem of readily available open-source libraries and commercial software modules generally mitigates this risk.
The widespread availability of alternatives for common software functionalities limits the bargaining power of individual suppliers. For instance, in 2024, the open-source software market continued its robust growth, with projects like Linux and various development frameworks offering extensive and often free alternatives to proprietary solutions.
- Broad Availability of Open-Source: The continuous development and adoption of open-source software provide CyberArk with numerous alternatives for various functionalities, reducing dependence on single vendors.
- Standardization of Components: Many software components, especially those related to common programming languages or operating systems, are standardized, allowing for easier substitution.
- Cost-Effectiveness of Open-Source: Open-source components often come with no licensing fees, presenting a cost advantage that further reduces the leverage of commercial software suppliers.
Partnerships with system integrators and MSPs
CyberArk's reliance on system integrators and Managed Service Providers (MSPs) for implementation and service delivery grants these partners a degree of bargaining power. Their ability to extend CyberArk's market reach and ensure customer success means they hold sway in the partnership dynamic.
These partners are essential for deploying and managing CyberArk's identity security solutions, making their expertise and network valuable assets. For instance, in 2024, many MSPs reported increased demand for cybersecurity services, including privileged access management, highlighting their critical role in the channel. This demand can translate into leverage when negotiating terms or demanding specific support from vendors like CyberArk.
- Partner Ecosystem Value: System integrators and MSPs are vital for CyberArk's go-to-market strategy, enabling broader customer access and specialized service delivery.
- Dependence on Partner Expertise: The complexity of cybersecurity solutions often necessitates skilled partners for successful implementation and ongoing management, creating reliance.
- Market Reach Amplification: Partners act as an extension of CyberArk's sales and support teams, significantly expanding its operational footprint and customer engagement capabilities.
CyberArk's bargaining power of suppliers is generally low due to its software-centric model, with few dependencies on raw materials. However, its reliance on cloud infrastructure providers like AWS and Azure, and the critical need for specialized cybersecurity talent, represent key areas where suppliers can exert influence. The company mitigates this by diversifying cloud usage and focusing on talent retention.
The cybersecurity talent market in 2024 remained highly competitive, with demand for skilled professionals significantly outpacing supply. This scarcity directly translates to increased bargaining power for these individuals, impacting CyberArk's recruitment and retention costs. For example, average salaries for cybersecurity analysts saw a notable increase throughout the year.
| Supplier Type | Level of Bargaining Power | Key Factors Influencing Power |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials/Physical Components | Low | Digital nature of software products, easy substitutability of any physical inputs. |
| Cloud Infrastructure (AWS, Azure) | Moderate to High | Significant operational reliance, potential for vendor lock-in, pricing power of major providers. |
| Specialized Talent (Developers, Researchers) | High | Scarcity of skilled professionals, high demand in the cybersecurity sector, competitive compensation landscape. |
| Third-Party Software/Open-Source | Low | Broad availability of alternatives, standardization of components, cost-effectiveness of open-source. |
| System Integrators/MSPs | Moderate | Essential for market reach and customer implementation, dependence on partner expertise, amplification of market reach. |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces shaping CyberArk's market, focusing on buyer and supplier power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the privileged access security sector.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each Porter's Five Forces, allowing for proactive strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers adopting CyberArk's comprehensive Privileged Access Management (PAM) solutions encounter significant hurdles when considering a switch. These high switching costs stem from the deep integration required with existing IT infrastructure, the extensive configuration needed to align with specific security policies, and the critical nature of PAM in safeguarding sensitive systems. For instance, a large enterprise might spend months, if not years, implementing and customizing CyberArk's suite, making a subsequent transition to a competitor a costly and disruptive undertaking.
The increasing criticality of identity security, driven by a surge in sophisticated cyber threats and evolving compliance mandates, significantly bolsters the bargaining power of customers in the cybersecurity market. Organizations recognize that robust identity security, especially Privileged Access Management (PAM), is no longer a secondary concern but a fundamental necessity for business continuity and data protection.
This elevated importance reduces customer price sensitivity. For instance, the average cost of a data breach in 2024 reached $4.73 million globally, according to IBM's Cost of a Data Breach Report. Consequently, businesses are more inclined to invest in comprehensive solutions like those offered by CyberArk, prioritizing effectiveness and reliability over minor cost savings, thereby limiting their ability to negotiate lower prices.
CyberArk's large enterprise customer base, including a significant portion of the Fortune 500, grants these clients considerable bargaining power. Their ability to negotiate bulk deals and demand tailored features or preferential pricing directly impacts CyberArk's revenue and profit margins.
Customer demand for integrated platforms
Customers are increasingly demanding integrated identity security platforms, moving away from siloed, point solutions. This shift benefits vendors like CyberArk that offer a unified approach across human, machine, and AI identities. For instance, in 2024, many organizations reported a desire to reduce vendor sprawl, with surveys indicating a preference for platforms that simplify management and enhance overall security posture.
This consolidation trend can amplify customer bargaining power. As businesses seek comprehensive solutions from a smaller number of trusted providers, they gain leverage in negotiating terms and pricing. The ability to consolidate security functions onto a single platform allows customers to demand more favorable contracts and potentially achieve cost savings.
- Consolidation Trend: Businesses are actively seeking unified identity security solutions.
- Vendor Advantage: Vendors like CyberArk offering integrated platforms are well-positioned.
- Increased Bargaining Power: Customers gain leverage by consolidating their security needs with fewer vendors.
- Demand for Simplicity: The drive for streamlined management fuels the demand for integrated platforms.
Growing adoption of cloud and AI agents expands addressable market
The increasing adoption of cloud computing and the rise of AI agents are significantly expanding CyberArk's addressable market. This trend means more organizations are looking for robust identity security solutions, creating a larger pool of potential customers. For instance, the global cloud computing market was projected to reach over $1.3 trillion in 2024, a substantial increase from previous years.
However, this expansion also presents a challenge to the bargaining power of customers. As the market grows and new customer segments emerge, CyberArk must continuously innovate to meet diverse and evolving security needs. Failing to adapt could empower customers to seek alternative solutions, especially as AI agents introduce new identity management complexities.
- Expanded Market: Cloud adoption and AI agents create new customer segments for identity security.
- Increased Competition: A larger market can attract more competitors, potentially increasing customer choice.
- Evolving Demands: CyberArk must adapt its offerings to the unique security requirements of cloud and AI environments.
- Customer Leverage: If CyberArk's solutions don't keep pace, customers may have greater power to negotiate or switch providers.
While CyberArk's extensive integration and the critical nature of PAM solutions create high switching costs, limiting customer power, the sheer size and influence of its enterprise client base, particularly Fortune 500 companies, still grant them significant negotiation leverage. These large clients can demand bulk discounts and customized features, directly impacting CyberArk's pricing and profitability.
The trend towards consolidating security solutions onto unified platforms, driven by a desire for simplified management, also enhances customer bargaining power. As organizations aim to reduce vendor complexity, they can negotiate more favorable terms with providers like CyberArk who offer comprehensive identity security across human, machine, and AI identities. This consolidation allows clients to exert greater influence over pricing and service agreements.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Observation (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| High Switching Costs | Lowers customer power | Deep integration, extensive customization, critical security function |
| Customer Size & Influence | Increases customer power | Large enterprise base (e.g., Fortune 500) can negotiate bulk deals and tailored features. |
| Consolidation Trend | Increases customer power | Demand for unified platforms allows negotiation leverage for simplified management and cost savings. |
| Criticality of Identity Security | Lowers customer power (reduces price sensitivity) | Average cost of data breach in 2024: $4.73 million (IBM). Focus on effectiveness over price. |
Preview Before You Purchase
CyberArk Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete CyberArk Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing competitive rivalry, the threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threat of substitutes. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file, ready for immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Privileged Access Management (PAM) market is characterized by robust competition, with established giants like BeyondTrust and Delinea, formerly ThycoticCentrify, directly challenging CyberArk. This mature yet expanding sector sees intense rivalry as these vendors vie for market share, often through feature innovation and strategic partnerships.
Large technology titans such as Microsoft, IBM, and Amazon Web Services (AWS) present a significant competitive force by offering integrated identity and access management (IAM) solutions. These offerings often overlap with or can act as substitutes for specific components of CyberArk's specialized privileged access management (PAM) suite. For instance, Microsoft's Azure Active Directory provides robust identity governance, while AWS offers a range of IAM services for cloud environments, potentially reducing the perceived need for standalone PAM solutions in certain use cases.
The sheer scale and vast resources of these tech giants intensify the competitive environment for CyberArk. Their ability to bundle security features into broader cloud or software-as-a-service (SaaS) platforms allows them to compete on price and convenience, particularly for organizations already invested in their ecosystems. This broad portfolio approach means customers might opt for a more unified, albeit potentially less specialized, security solution from a single vendor, thereby increasing pressure on CyberArk to continually differentiate its advanced PAM capabilities.
The cybersecurity sector thrives on relentless innovation, a necessity driven by an ever-changing threat landscape. This dynamic environment means companies like CyberArk must consistently invest in research and development to stay ahead. For instance, in 2024, cybersecurity spending globally was projected to reach over $200 billion, underscoring the immense pressure on vendors to deliver cutting-edge solutions.
Market fragmentation with niche and emerging players
While CyberArk holds a leading position in Privileged Access Management (PAM), the broader identity security landscape is quite fragmented. This means there are many smaller companies, often referred to as niche players, that focus on specific areas within identity security. For instance, some specialize in secrets management, a critical component for securing sensitive credentials, while others target particular challenges related to identity in cloud environments.
This market fragmentation intensifies competitive rivalry for CyberArk. These specialized competitors, while perhaps not offering a full suite of solutions like CyberArk, can be very agile and innovative within their focused domains. They often compete on price or offer highly tailored solutions that appeal to specific customer needs, creating pressure on market share and pricing.
- Niche Players in Identity Security: Companies like HashiCorp, with its Vault product, directly compete in the secrets management segment, a key area for CyberArk.
- Emerging Technologies: The rapid evolution of cloud computing and microservices has given rise to new identity management challenges, attracting startups and specialized vendors.
- Customer Specialization: Smaller, focused vendors can sometimes offer deeper expertise or more cost-effective solutions for specific identity security use cases, drawing away certain customer segments.
- Market Dynamics: As of early 2024, the identity security market continues to see significant investment, fueling the growth and emergence of new specialized players, thereby increasing overall competitive intensity.
Competition for skilled cybersecurity talent
The competition for skilled cybersecurity talent is incredibly intense, driving up recruitment and retention costs. This scarcity means companies, including CyberArk, must invest heavily to attract and keep top-tier professionals, directly impacting operational expenses and the capacity for innovation. For instance, in 2024, the global cybersecurity workforce gap was estimated to be around 3.5 million professionals, highlighting the extreme demand.
This talent war intensifies the competitive rivalry by limiting the pool of available expertise. Companies that can offer more competitive compensation, better benefits, and more engaging work environments have a distinct advantage. The ability to secure and retain these critical roles directly influences a company's ability to implement and manage advanced security solutions, a key differentiator in the market.
- Talent Scarcity: The global cybersecurity workforce gap reached approximately 3.5 million in 2024.
- Increased Costs: Fierce competition drives up salaries and benefits, impacting operational budgets.
- Innovation Impact: Limited talent can hinder a company's ability to adopt and deploy new security technologies.
- Retention Challenges: High demand makes retaining skilled professionals a significant ongoing challenge.
CyberArk faces intense competition from both established cybersecurity vendors and large technology conglomerates integrating identity solutions. Major players like Microsoft and AWS leverage their vast ecosystems to offer competing IAM services, potentially fragmenting CyberArk's specialized PAM market. This broad approach by tech giants, often bundled into cloud offerings, pressures CyberArk to continually highlight its advanced PAM capabilities and differentiation.
The PAM market is also characterized by numerous niche players, such as HashiCorp, specializing in areas like secrets management. These agile competitors can offer tailored solutions or compete on price, further intensifying rivalry. As of early 2024, significant investment in identity security fuels the emergence of these specialized vendors, creating a dynamic and fragmented competitive landscape.
| Competitor Type | Key Players | Competitive Impact |
| Established PAM Vendors | BeyondTrust, Delinea | Direct rivalry for market share through feature innovation. |
| Large Tech Conglomerates | Microsoft, IBM, AWS | Integrated IAM offerings; ecosystem bundling; price and convenience competition. |
| Niche Identity Security Players | HashiCorp (Vault) | Specialized solutions (e.g., secrets management); agility; potential price competition. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Basic Identity and Access Management (IAM) tools, often provided by major software vendors or available as open-source options, can indeed act as substitutes for certain fundamental access control needs. These generic solutions might handle user provisioning and basic authentication, offering a cost-effective alternative for organizations with less complex security requirements.
However, these substitutes typically fall short when it comes to the specialized, granular controls and robust auditing features that are critical for privileged access management. For instance, while a basic IAM might grant access, it often won't provide the session recording or detailed activity logging that dedicated Privileged Access Management (PAM) solutions like CyberArk offer, which is crucial for compliance and threat detection.
The market for IAM solutions is substantial, with the global IAM market size estimated to reach approximately $32.2 billion by 2024. This broad market includes many players offering foundational IAM capabilities, underscoring the availability of substitutes for less critical access management functions.
Manual processes and homegrown scripts present a significant threat of substitutes for dedicated Privileged Access Management (PAM) solutions. Organizations, particularly smaller ones or those operating with older IT infrastructure, may still depend on manual task execution, extensive spreadsheets, or internally developed scripts to oversee privileged accounts. While these methods are inherently less secure and far less efficient than a robust PAM system, their perceived low cost makes them a viable alternative for some, especially when budget constraints are a primary concern.
Cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and GCP offer native identity and access management (IAM) tools. These can be seen as substitutes for specialized Privileged Access Management (PAM) solutions, particularly for organizations focused solely on cloud-native operations. For instance, AWS IAM provides granular control over user permissions within the AWS ecosystem.
However, these native offerings often fall short when organizations manage hybrid or multi-cloud environments. They typically lack the centralized control, advanced credential vaulting, and session management capabilities that dedicated PAM solutions, such as CyberArk's, provide across diverse IT infrastructures. This fragmentation can create security gaps and operational inefficiencies, limiting their effectiveness as a complete substitute.
General endpoint security and network access control solutions
Broader endpoint security and network access control solutions can present a threat of substitutes to specialized Privileged Access Management (PAM) solutions like CyberArk. While these general tools may not offer the granular control over privileged accounts that PAM provides, they can fulfill some basic access management needs. For instance, endpoint security might enforce strong authentication for all users, including those with elevated privileges, thereby reducing the immediate perceived gap in security. Similarly, network access control can segment networks and restrict access based on user roles, which overlaps with PAM's goal of limiting exposure.
The market for endpoint security solutions is substantial and growing, indicating a significant potential for these tools to absorb some demand that might otherwise go to PAM. In 2024, the global endpoint security market was valued at approximately $15.5 billion, with projections showing continued growth. This broad adoption means many organizations already have these solutions in place, making it easier to leverage them for basic access control rather than investing in a separate PAM system.
The threat is amplified when these general solutions offer integrated features that mimic certain PAM functionalities at a lower cost. For example, advanced endpoint detection and response (EDR) platforms are increasingly incorporating identity and access management capabilities. This convergence means that a single, comprehensive security platform could potentially address both endpoint protection and a portion of privileged access needs, thereby diminishing the unique selling proposition of standalone PAM solutions.
- Reduced Perceived Need: General endpoint security and network access control can provide basic access controls, making organizations less inclined to seek specialized PAM for foundational security.
- Market Size and Adoption: The substantial and growing endpoint security market, valued at around $15.5 billion in 2024, signifies a large installed base of potential substitute solutions.
- Feature Convergence: The integration of identity and access management features into broader security platforms, such as EDR, offers overlapping functionality, potentially at a lower total cost of ownership.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Organizations may opt for more comprehensive, albeit less specialized, security suites that include access control elements, viewing them as a more cost-effective alternative to dedicated PAM solutions.
Passwordless authentication and Zero Trust initiatives
The increasing adoption of passwordless authentication and Zero Trust security models presents a potential threat of substitutes to traditional privileged access management (PAM) solutions. These evolving security paradigms focus on eliminating passwords and continuously verifying user identities, thereby reducing the attack surface associated with compromised credentials.
For instance, by 2024, a significant portion of enterprises are expected to have implemented at least one passwordless authentication method, with estimates suggesting over 50% of organizations will be on this path. This shift directly challenges the necessity of managing and rotating privileged passwords, a core function of many PAM tools.
- Passwordless Authentication Growth: Gartner predicted that by 2024, 50% of enterprise users would be using passwordless authentication for access to applications and data.
- Zero Trust Adoption: A 2023 report indicated that 70% of organizations were actively pursuing or had already implemented Zero Trust strategies, aiming to secure access based on continuous verification rather than implicit trust.
- Impact on PAM: These trends could diminish the perceived value of traditional PAM solutions that heavily rely on password vaulting and rotation, pushing them towards more comprehensive identity and access management integration.
The threat of substitutes for Privileged Access Management (PAM) solutions like CyberArk comes from a range of less specialized, often more affordable alternatives. Basic Identity and Access Management (IAM) tools, cloud provider native IAM, and even manual processes can address some fundamental access control needs, especially for organizations with simpler security requirements or tighter budgets.
The global IAM market, projected to reach around $32.2 billion by 2024, highlights the availability of many foundational IAM solutions. Furthermore, the substantial endpoint security market, valued at approximately $15.5 billion in 2024, shows how readily available broader security tools can offer overlapping functionalities, potentially reducing the perceived need for dedicated PAM.
The rise of passwordless authentication and Zero Trust models also poses a threat, as these paradigms aim to reduce reliance on traditional credential management, a core PAM function. Gartner predicted that by 2024, 50% of enterprise users would be using passwordless authentication, directly impacting the perceived necessity of password vaulting.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | Market Context (2024 Estimates) | Impact on PAM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic IAM Tools | User provisioning, basic authentication | Part of a $32.2B global IAM market | Addresses fundamental access needs, less granular control |
| Cloud Native IAM (AWS, Azure, GCP) | Granular control within specific cloud ecosystems | Integral to major cloud platforms | Limited in hybrid/multi-cloud, lacks centralized PAM features |
| Manual Processes/Scripts | Low-cost, homegrown solutions | Prevalent in smaller or legacy environments | Less secure, inefficient, but cost-effective for some |
| Endpoint Security/Network Access Control | Strong authentication, network segmentation | $15.5B global endpoint security market | Offers overlapping basic controls, potential for feature convergence |
| Passwordless/Zero Trust | Eliminates passwords, continuous verification | 50% enterprise adoption of passwordless by 2024 (Gartner) | Reduces reliance on password management, core PAM function |
Entrants Threaten
The development of sophisticated identity security solutions, akin to CyberArk's offerings, necessitates substantial investments in research and development, coupled with profound technical acumen and a nuanced grasp of emerging cyber threats. These considerable R&D expenditures, often running into hundreds of millions of dollars annually for established players, create a formidable financial hurdle for newcomers.
In the cybersecurity realm, a company's reputation and the trust it has cultivated are incredibly important. Newcomers face a steep climb in establishing the credibility that large enterprises demand when entrusting their most sensitive identities and access controls. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that over 70% of major corporations prioritize established vendor relationships and proven security track records when selecting identity and access management solutions, making it difficult for new entrants to gain traction.
The threat of new entrants is significantly mitigated by the extensive sales cycles and high customer acquisition costs prevalent in the privileged access management (PAM) market. Selling to large enterprises, a core customer base for companies like CyberArk, involves protracted negotiations, multiple stakeholder approvals, and often custom integration. This lengthy process, coupled with the substantial investment required for sales teams, marketing, and product development to meet enterprise-grade security and compliance standards, creates a high barrier to entry.
New players entering this space would need considerable financial resources and a long-term strategic vision to overcome these initial hurdles. For instance, the average sales cycle for enterprise software can range from six to eighteen months, demanding significant upfront investment in sales and marketing before any revenue is realized. This financial commitment and the need for proven reliability and extensive support infrastructure make it challenging for newcomers to gain traction against established vendors like CyberArk.
Regulatory compliance and certification requirements
The Privileged Access Management (PAM) market, where CyberArk operates, faces a significant barrier to entry due to extensive regulatory compliance and certification demands. For instance, mandates like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS require new players to invest heavily in understanding and implementing complex security protocols. This regulatory landscape means that any new entrant must dedicate substantial resources to achieve and maintain compliance, directly impacting their speed to market and initial operational costs.
Navigating these intricate certification processes is a major hurdle. New companies need to prove their solutions meet a multitude of security standards, which can be both time-consuming and expensive. For example, achieving certifications like ISO 27001 or SOC 2 requires rigorous auditing and ongoing adherence to best practices. This adds a considerable layer of difficulty and financial commitment for potential new entrants aiming to compete effectively in the PAM space.
The financial implications are substantial. A 2024 report by Gartner indicated that the average cost for a technology company to achieve initial compliance with major data privacy regulations can range from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars, depending on the scope. This significant upfront investment acts as a deterrent to smaller or less-funded organizations looking to enter the PAM market, thereby strengthening the position of established players like CyberArk.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS is mandatory for PAM solutions.
- Certification Costs: Achieving certifications like ISO 27001 and SOC 2 requires significant investment.
- Time to Market: Complex compliance processes delay the entry of new competitors.
- Financial Barrier: High initial costs for regulatory adherence deter new entrants.
Existing vendor lock-in and ecosystem integration
Existing vendor lock-in and ecosystem integration present a significant barrier for new entrants. Established players, such as CyberArk, have cultivated deep product integrations and robust partnerships within the broader IT and security ecosystem. This makes it difficult for customers to switch, as it often requires dismantling complex, interconnected systems.
Newcomers must not only offer a superior product but also provide compelling reasons for organizations to undertake the costly and disruptive process of migrating away from deeply embedded solutions. For instance, CyberArk's extensive integrations with identity providers, cloud platforms, and SIEM solutions create a sticky environment where switching costs are substantial.
- Customer Lock-in: CyberArk's solutions are often deeply embedded within an organization's IT infrastructure, making it challenging and expensive to replace.
- Ecosystem Integration: Strong partnerships with other technology vendors (e.g., Microsoft, AWS, Splunk) create a comprehensive security ecosystem that new entrants struggle to replicate.
- Switching Costs: The complexity of integrating and migrating away from established vendor solutions represents a significant financial and operational hurdle for potential new competitors.
The threat of new entrants in the Privileged Access Management (PAM) market, where CyberArk operates, is considerably low. This is primarily due to the immense capital required for research and development, coupled with the need for deep technical expertise to create sophisticated identity security solutions. For example, major cybersecurity firms often allocate hundreds of millions of dollars annually towards R&D, presenting a substantial financial barrier for any new player.
Furthermore, the cybersecurity sector demands a strong reputation and established trust, which new entrants find difficult to build quickly. Large enterprises, as highlighted by a 2024 industry report, prioritize vendors with proven track records, with over 70% of major corporations citing vendor relationships and security history as key selection criteria for identity and access management solutions. This makes it challenging for newcomers to gain initial market penetration.
The lengthy sales cycles and high customer acquisition costs in the PAM space also deter new entrants. Enterprise sales for solutions like CyberArk's involve complex negotiations, multiple approvals, and significant investment in sales, marketing, and product development to meet stringent enterprise security and compliance standards. This often translates to sales cycles of six to eighteen months, demanding considerable upfront investment before any revenue is generated.
Regulatory compliance and the associated certification costs create another significant hurdle. New entrants must invest heavily to understand and implement complex security protocols mandated by regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Achieving certifications like ISO 27001 or SOC 2, which involve rigorous auditing and ongoing adherence to best practices, can cost tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars, as noted in a 2024 Gartner report, further solidifying the advantage of established vendors.
Finally, existing vendor lock-in and deep ecosystem integration pose a substantial barrier. CyberArk's extensive partnerships and integrations with cloud platforms, identity providers, and SIEM solutions create a complex, interconnected environment. Migrating away from these deeply embedded systems represents a significant financial and operational challenge for organizations, making it difficult for new entrants to displace established players.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our CyberArk Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of industry-leading market research reports, financial disclosures from publicly traded companies, and insights from cybersecurity trade publications. We also leverage data from reputable technology analyst firms and government cybersecurity advisories to ensure a comprehensive view.
