China Southern Airlines Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
China Southern Airlines Bundle
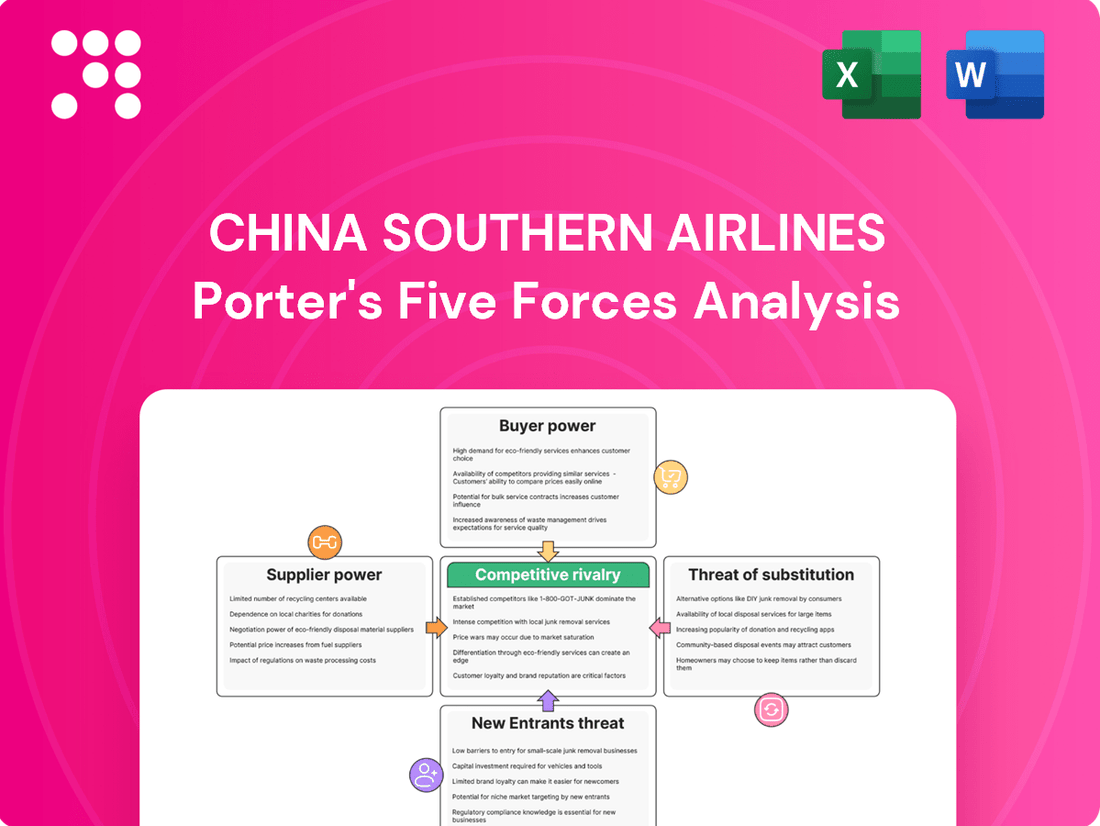
China Southern Airlines operates in a dynamic aviation landscape, facing significant pressure from intense rivalry among major carriers and the ever-present threat of new entrants eager to capture market share. Understanding the bargaining power of both its powerful suppliers and its price-sensitive customers is crucial for navigating this competitive terrain.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping China Southern Airlines’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The aviation sector is heavily reliant on a small number of major aircraft manufacturers, primarily Boeing and Airbus, and engine producers such as GE Aviation, Rolls-Royce, and Pratt & Whitney. This limited supplier base grants these companies substantial bargaining power over airlines, including China Southern Airlines. For instance, in 2023, Boeing and Airbus together accounted for nearly all commercial aircraft deliveries, underscoring their market dominance.
The high cost and complexity associated with switching aircraft or engine suppliers create significant barriers for airlines. China Southern Airlines, like its peers, faces immense financial and operational hurdles if it were to change its primary equipment providers, further solidifying the suppliers' leverage. The lead times for new aircraft orders can stretch for years, and the integration of new models requires extensive training and infrastructure investment.
China Southern Airlines, like other major carriers, faces significant supplier bargaining power due to high switching costs for aircraft and components. Once an airline invests in a specific aircraft model, such as Boeing 787s or Airbus A350s, the associated expenses for pilot retraining, specialized maintenance facilities, and stocking unique spare parts become enormous. This commitment locks airlines into long-term relationships with airframe and engine manufacturers, giving these suppliers considerable leverage in price negotiations and contract terms.
Aircraft and engine manufacturers hold significant leverage due to their highly specialized technology and intellectual property. This makes it challenging for airlines like China Southern to backward integrate or easily find alternative suppliers, giving these manufacturers considerable power in dictating terms and pricing.
Impact of Geopolitical Factors on Supply Chains
Geopolitical tensions, like the ongoing trade friction between the US and China, directly impact China Southern Airlines' access to critical aircraft components. These disputes can lead to increased tariffs and export restrictions on parts and engines, thereby strengthening the bargaining power of suppliers who control these essential inputs. For instance, disruptions in the supply of advanced avionics or specific engine models can force airlines to accept less favorable terms.
The reliance on a limited number of global manufacturers for sophisticated aircraft parts means suppliers hold significant leverage. When geopolitical events create uncertainty or restrict trade flows, these suppliers can dictate terms, leading to higher prices and longer lead times for airlines such as China Southern. This was evident in the extended delivery schedules for certain aircraft models and components during periods of heightened trade tensions.
- Disrupted Supply Chains: Geopolitical events can interrupt the flow of aircraft parts and engines, creating shortages.
- Increased Costs: Trade disputes and tariffs directly translate to higher procurement costs for airlines.
- Supplier Leverage: Limited global suppliers of specialized aviation technology gain greater bargaining power during geopolitical instability.
- Delivery Delays: Uncertainty in international trade can lead to significant delays in receiving crucial aircraft components, impacting operational planning.
Fuel Price Volatility
Fuel price volatility is a major concern for China Southern Airlines, even though oil producers aren't direct suppliers. The global oil market's unpredictable nature means aviation fuel costs can swing dramatically, directly affecting operational expenses and profit margins. For example, in early 2024, Brent crude oil prices fluctuated significantly, impacting airlines' cost structures.
Aviation fuel suppliers hold considerable power by dictating prices, which directly influences China Southern's bottom line. This bargaining power is amplified by the essential nature of fuel for airline operations. Airlines often have limited options to immediately switch fuel suppliers, especially in specific geographic locations.
- Global Oil Market Influence: The price of crude oil, a key input for jet fuel, is subject to geopolitical events, supply and demand dynamics, and economic conditions, leading to inherent volatility.
- Impact on Profitability: Fluctuations in fuel prices can significantly erode airline profits, as fuel often represents one of the largest operating cost components, sometimes exceeding 20% of total expenses.
- Limited Supplier Options: In many key operational hubs, the number of aviation fuel suppliers may be limited, granting those suppliers greater leverage in price negotiations with airlines like China Southern.
China Southern Airlines faces significant bargaining power from aircraft and engine manufacturers due to the concentrated nature of the industry. With Boeing and Airbus dominating aircraft production, and a few key players like GE Aviation, Rolls-Royce, and Pratt & Whitney leading in engine manufacturing, airlines have limited choices. This reliance, coupled with the immense costs and complexities of switching suppliers—including pilot training and specialized maintenance—gives these manufacturers substantial leverage in pricing and contract negotiations. For example, in 2023, Boeing and Airbus delivered nearly all commercial aircraft, highlighting their market control.
The bargaining power of aviation fuel suppliers is also a critical factor for China Southern Airlines. Fuel is a major operating expense, often exceeding 20% of total costs, and its price is highly volatile, influenced by global oil market dynamics. Limited supplier options in key operational hubs further amplify this power, allowing suppliers to dictate terms and impact airline profitability. For instance, Brent crude oil prices saw considerable fluctuations in early 2024, directly affecting airlines' cost structures.
| Supplier Type | Key Players | Impact on China Southern Airlines | 2023/2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aircraft Manufacturers | Boeing, Airbus | High bargaining power due to market concentration, high switching costs, and long lead times for new aircraft. | Boeing and Airbus accounted for almost all commercial aircraft deliveries in 2023. |
| Engine Manufacturers | GE Aviation, Rolls-Royce, Pratt & Whitney | Significant leverage due to proprietary technology and high integration costs for airlines. | These manufacturers supply the vast majority of engines for modern commercial aircraft. |
| Aviation Fuel Suppliers | Global oil producers & local distributors | Dictate fuel prices, a major operating expense, with limited immediate alternatives for airlines. | Brent crude oil prices experienced significant volatility in early 2024, impacting airline operating costs. Fuel can represent over 20% of an airline's expenses. |
What is included in the product
This analysis of China Southern Airlines reveals the intense rivalry among existing airlines, the bargaining power of its customers and suppliers, and the significant barriers to entry for new competitors.
Quickly assess competitive threats and opportunities for China Southern Airlines, enabling agile responses to market shifts.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers of China Southern Airlines face numerous choices, especially within China's bustling domestic air travel market. The presence of the 'Big Three' – China Southern, China Eastern, and Air China – along with a host of smaller regional airlines, creates a highly competitive environment. This intense rivalry directly translates into significant price sensitivity for consumers. For instance, in 2024, average domestic airfares in China saw fluctuations, with airlines frequently adjusting prices to attract passengers, demonstrating how competition directly impacts customer willingness to pay.
The bargaining power of customers for China Southern Airlines is significantly influenced by the availability of multiple airline choices. In 2024, China's aviation market features several major carriers like Air China, China Eastern Airlines, and Hainan Airlines, alongside a growing number of smaller regional players. This competitive landscape means passengers can easily compare fares, schedules, and service quality across different airlines for both domestic and international flights. For instance, a traveler looking for a flight from Beijing to Shanghai might find dozens of daily options from various carriers, allowing them to select the most cost-effective or convenient choice.
Online travel agencies (OTAs) and flight comparison websites significantly boost customer bargaining power for China Southern Airlines. These platforms create immense price transparency, allowing consumers to easily compare fares across numerous airlines. For instance, in 2024, platforms like Ctrip (Trip.com Group) and Skyscanner offer extensive visibility into flight prices, making it difficult for any single airline to command premium pricing without justification.
Growth of High-Speed Rail as an Alternative
China's high-speed rail network is rapidly growing, offering a compelling alternative to air travel for many domestic routes. This expansion directly impacts the bargaining power of customers by providing them with more choices, particularly for journeys under 1,000 kilometers.
As of late 2023, China's high-speed rail mileage exceeded 45,000 kilometers, making it the world's largest network. This extensive coverage means that for many city pairs, such as Beijing to Shanghai, high-speed rail offers competitive travel times and often lower prices compared to airfare, especially when factoring in airport transit and waiting times.
- Increased Customer Choice: The proliferation of high-speed rail provides passengers with a viable substitute for domestic flights, enhancing their ability to switch providers or demand better terms from airlines.
- Price Sensitivity: High-speed rail often presents a more budget-friendly option, making air travelers more sensitive to ticket prices and encouraging them to seek out cheaper alternatives.
- Convenience Factor: For many routes, city-center to city-center high-speed rail travel can be more convenient than flying, reducing overall journey time and increasing its attractiveness as a substitute.
Changing Passenger Demographics and Demand Patterns
China Southern Airlines faces increasing customer bargaining power due to shifting passenger demographics and evolving travel demands. The rise of inbound tourism and a growing appetite for diverse travel experiences mean customers are more discerning about service quality and value. This dynamic forces China Southern to be more responsive to passenger preferences, potentially impacting pricing strategies and service offerings.
The airline must adapt to cater to these changing needs, which can amplify customer leverage. For instance, in 2024, China Southern observed a significant uptick in demand for premium economy and business class services from international travelers, indicating a willingness to pay more for enhanced comfort and amenities. Conversely, budget-conscious domestic travelers continue to seek competitive pricing, creating a dual pressure on the airline's revenue management.
- Evolving Passenger Mix: A growing segment of international tourists, particularly from Southeast Asia and Europe, are choosing China Southern, bringing different service expectations compared to traditional domestic travelers.
- Diversified Travel Products: The demand for bundled travel packages, including flights, hotels, and local tours, is rising, giving customers more options and thus more power to negotiate better overall deals.
- Digital Empowerment: Online travel agencies and direct booking platforms provide customers with easy price comparison tools, intensifying competition and empowering them to seek the best value.
- Service Quality Expectations: With increased global travel exposure, passengers have higher expectations for in-flight services, punctuality, and customer support, making service delivery a key differentiator and a source of customer leverage.
China Southern Airlines' customers possess considerable bargaining power, largely driven by the intense competition within the Chinese aviation market. The presence of major carriers like Air China and China Eastern, alongside numerous regional airlines, ensures passengers have ample choices. This competitive landscape, further amplified by robust high-speed rail networks and digital comparison platforms, forces China Southern to remain price-competitive and responsive to consumer demands. For instance, in 2024, domestic airfares saw significant adjustments as airlines vied for passengers, highlighting the direct impact of competition on pricing.
| Factor | Impact on China Southern | 2024 Data/Observation |
|---|---|---|
| Airline Competition | High, leading to price sensitivity | Intense price competition observed on major domestic routes |
| High-Speed Rail | Provides viable alternative | China's high-speed rail network exceeded 45,000 km by late 2023 |
| Online Travel Agencies (OTAs) | Increases price transparency | Platforms like Ctrip offer extensive fare comparisons |
| Customer Expectations | Growing demand for service quality | Increased interest in premium services from international travelers |
Same Document Delivered
China Southern Airlines Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis for China Southern Airlines, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications for the company. The document displayed here is the part of the full version you’ll get—ready for download and use the moment you buy. You will gain insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the airline industry.
Rivalry Among Competitors
China Southern Airlines faces intense rivalry from Air China and China Eastern Airlines, often referred to as the 'Big Three' in China's aviation market. This concentrated competition means each player aggressively pursues market share, frequently leading to price wars that can compress profit margins for all involved.
China Southern Airlines operates within a fiercely competitive domestic aviation market, characterized by aggressive pricing and a constant struggle for prime routes and passenger traffic. This intense rivalry directly impacts operational pressures and contributes to a lower revenue per passenger-kilometer for the airline.
In 2024, the Chinese domestic aviation market saw a significant rebound in passenger numbers, with airlines like China Southern experiencing increased demand. However, this surge in travel also intensified competition, as carriers actively competed for market share, often through promotional fares, which can squeeze profit margins.
While domestic competition remains intense, Chinese airlines, including China Southern, are prioritizing the recovery and expansion of international routes. This strategic shift intensifies rivalry as carriers vie for valuable international routes and market share, a landscape significantly altered by the pandemic's impact on global travel.
For instance, in 2024, China Southern Airlines has been actively increasing its international flight frequencies. Data from early 2024 indicated a substantial rebound in international passenger traffic for the airline, with key routes to Southeast Asia and Europe showing strong recovery. This push for international presence means competing not only with other Chinese carriers but also with global airlines re-establishing their networks.
Price Wars and Pressure on Fares
The airline industry, including China Southern Airlines, frequently experiences intense price competition. This often manifests as price wars and promotional campaigns, which can significantly drive down average fares, particularly in the economy class segment. For instance, during periods of high competition, airlines might offer heavily discounted tickets to capture market share.
This constant pressure on ticket prices directly impacts China Southern's revenue streams. Even with a growing number of passengers, the reduced average fare per passenger can lead to a decline in overall financial performance. This dynamic is a critical factor for the airline to manage.
- Intensified Price Wars: Airlines frequently engage in promotional activities, leading to a downward trend in average economy-class fares.
- Revenue Impact: Despite increasing passenger volumes, the pressure on ticket prices directly affects China Southern's revenue generation.
- Financial Performance: The competitive pricing environment poses a challenge to maintaining healthy profit margins for the airline.
Fleet Expansion and Capacity Increases
China Southern Airlines, like other major carriers in China, is actively growing its fleet and boosting capacity. This aggressive expansion is a direct response to the robust demand for air travel within the country, aiming to capture market share and solidify its position. For instance, by the end of 2023, China Southern had a total of 910 aircraft, a notable increase from previous years, reflecting this commitment to growth.
However, this fleet expansion and capacity increase can significantly intensify competitive rivalry. When multiple airlines simultaneously add more aircraft and flights, it can lead to overcapacity on popular routes. This oversupply often forces airlines to lower ticket prices to fill seats, putting downward pressure on fares and impacting profitability for all players involved.
- Fleet Growth: China Southern's fleet size has been steadily increasing, with significant deliveries of new aircraft throughout 2023 and projections for continued expansion into 2024.
- Capacity Surge: The addition of new aircraft directly translates to increased available seat miles (ASMs), enhancing the airline's overall capacity to serve more passengers.
- Fierce Competition: This capacity build-up by China Southern and its domestic rivals heightens the intensity of competition, especially on high-demand domestic routes, often leading to price wars.
China Southern Airlines faces a highly competitive landscape, primarily from domestic giants Air China and China Eastern Airlines. This intense rivalry, particularly evident in 2024's post-pandemic travel boom, often leads to aggressive pricing strategies as each airline vies for market share and passenger traffic.
The pursuit of market dominance results in frequent price wars, especially on popular domestic routes, which can significantly compress profit margins. Even as passenger volumes recover, the downward pressure on fares impacts overall revenue generation for China Southern.
This competitive pressure is further amplified by fleet expansion; China Southern's substantial fleet growth, reaching 910 aircraft by late 2023, signals an intent to increase capacity. However, this capacity build-up by all major players can lead to oversupply, intensifying competition and driving down ticket prices.
| Airline | Fleet Size (approx. end 2023) | Domestic Market Share (approx. 2024) | International Route Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| China Southern Airlines | 910 | ~35% | Southeast Asia, Europe |
| Air China | 890 | ~30% | Europe, North America |
| China Eastern Airlines | 870 | ~28% | North America, Australia |
SSubstitutes Threaten
China's extensive high-speed rail network, the world's largest, presents a formidable substitute for airlines. By the end of 2023, China had over 45,000 kilometers of operating high-speed rail lines, making it a compelling alternative for many domestic routes, particularly those under 1,000 kilometers.
This widespread and efficient rail infrastructure directly challenges China Southern Airlines' domestic market share and its ability to set fares. Travelers often opt for the convenience and speed of high-speed rail, especially for intercity travel where the overall journey time, including airport transfers and security, can be comparable or even shorter than flying.
For shorter routes or regional travel within China, alternatives like long-distance buses and private cars pose a threat of substitution to China Southern Airlines. While not a direct competitor for extensive journeys, these options are attractive to budget-conscious travelers or those prioritizing flexibility. For instance, the extensive high-speed rail network in China, which saw significant expansion and upgrades leading into 2024, offers a compelling alternative for many inter-city routes, often at a lower cost and with comparable travel times for distances under 1000 kilometers.
The increasing sophistication and adoption of teleconferencing and virtual communication tools present a significant threat of substitution for China Southern Airlines, particularly in its business travel segment. As of early 2024, many companies continue to embrace hybrid or fully remote work models, reducing the perceived need for in-person meetings and thus, air travel. The cost-effectiveness and efficiency of virtual collaboration platforms directly compete with the expense and time commitment of business trips.
Impact of Economic Conditions on Travel Decisions
During economic downturns, travelers often seek more budget-friendly alternatives to air travel. This can include driving for shorter distances or opting for rail services, especially for domestic routes. For instance, in 2024, many consumers might reconsider flying for trips that could be reasonably completed by car, impacting airlines like China Southern.
When consumer spending power shrinks, discretionary purchases like air travel become more vulnerable to substitution. People might postpone vacations or choose closer destinations that don't require flights. This economic sensitivity means that even a slight dip in disposable income can lead to a noticeable shift away from air travel.
The threat of substitutes is amplified when alternative transportation becomes more attractive due to economic pressures.
- Reduced Consumer Spending: Economic downturns directly impact discretionary travel budgets, pushing consumers towards cheaper alternatives.
- Rise of Alternative Transport: Options like high-speed rail and personal vehicles become more appealing when airfares are perceived as too high relative to economic conditions.
- Impact on Demand: A significant portion of China Southern's passenger base may reduce travel frequency or switch modes during periods of economic contraction.
- Price Sensitivity: In 2024, with ongoing economic uncertainties in some regions, air travel pricing becomes a critical factor in modal choice.
Emergence of New Travel Habits and Preferences
The travel landscape is evolving, with post-pandemic shifts potentially favoring shorter domestic trips or more budget-friendly options. This could mean a rise in alternatives to traditional air travel for China Southern Airlines. For instance, the growth of high-speed rail networks within China offers a compelling substitute for many domestic routes, especially for journeys between major cities.
These changing traveler preferences directly impact the threat of substitutes. As more people prioritize convenience and cost, they might opt for:
- High-speed rail: Offering competitive travel times and often more accessible city-center stations.
- Personal vehicles: For shorter, more flexible domestic travel, especially in regions with well-developed road infrastructure.
- Bus services: Increasingly modernized and comfortable, providing a cost-effective alternative for certain routes.
The threat of substitutes for China Southern Airlines is significant, primarily driven by China's extensive high-speed rail network. By the end of 2023, over 45,000 kilometers of high-speed rail were operational, making it a strong alternative for many domestic routes, especially those under 1,000 kilometers.
This rail infrastructure offers competitive travel times and often greater convenience than air travel for intercity journeys, directly impacting China Southern's market share and pricing power. Furthermore, evolving consumer preferences and economic sensitivities in 2024 mean that budget-friendly alternatives like personal vehicles and modernized bus services are also gaining traction for shorter trips.
| Mode of Transport | Typical Use Case | Key Advantage | China Southern Airlines Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Speed Rail | Domestic intercity travel (under 1000 km) | Speed, convenience, city-center access | Direct competition, potential fare pressure |
| Personal Vehicles | Short to medium domestic trips | Flexibility, cost-effectiveness for groups | Substitution for leisure and regional travel |
| Buses | Budget domestic travel | Lower cost | Alternative for price-sensitive travelers |
| Virtual Communication | Business meetings | Cost savings, time efficiency | Reduced demand for business travel |
Entrants Threaten
The airline industry, including for giants like China Southern Airlines, demands substantial upfront capital. Think billions of dollars just to acquire a fleet of modern aircraft, build and maintain hangars, and establish the necessary operational infrastructure for safety and efficiency.
For instance, the average list price for a new Boeing 787 Dreamliner hovers around $338 million, and a single A380 can cost upwards of $450 million. China Southern, as of late 2024, operates a fleet of over 900 aircraft, illustrating the immense scale of investment required.
This massive financial barrier significantly discourages potential new entrants. It’s incredibly difficult for a new company to amass the capital needed to compete on a similar scale, thereby acting as a strong protective shield for established carriers like China Southern.
The civil aviation industry, particularly in China, faces formidable barriers to entry due to stringent regulatory requirements. Potential new airlines must obtain numerous licenses, certifications, and extensive safety approvals from bodies like the Civil Aviation Administration of China (CAAC). For instance, in 2023, the CAAC continued to emphasize rigorous safety standards and operational compliance, making it exceptionally challenging for unproven entities to secure the necessary permissions to operate.
China Southern Airlines, a dominant player in the Chinese aviation market, benefits significantly from deeply ingrained brand loyalty and powerful network effects. As one of the 'Big Three' carriers in China, it has cultivated a strong reputation over decades, supported by an extensive and well-established route network that caters to a vast customer base. This loyalty is further reinforced by sophisticated frequent flyer programs that incentivize repeat business, making it challenging for newcomers to attract and retain passengers.
New airlines entering the market face substantial hurdles in replicating China Southern's established brand recognition and its comprehensive network. Building a comparable customer base and achieving the same level of network density, which is crucial for offering convenient travel options, requires immense capital investment and time. For instance, in 2024, China Southern continued to operate a vast network, serving hundreds of domestic and international destinations, a scale that new entrants would find exceedingly difficult to match in the near to medium term.
Access to Airport Slots and Infrastructure
Securing prime airport slots and vital ground infrastructure presents a formidable barrier for potential new entrants into the airline industry, directly impacting China Southern Airlines' competitive landscape. Established carriers, including China Southern, often hold long-standing agreements and preferential access to these scarce resources at major hubs. This existing dominance makes it exceptionally difficult and costly for newcomers to acquire the necessary gates, maintenance facilities, and catering services to launch and sustain operations. For instance, in 2024, major airports like Beijing Capital International Airport (PEK) and Guangzhou Baiyun International Airport (CAN) experienced high slot utilization rates, with many prime times already allocated to incumbent airlines.
The control over airport slots and infrastructure acts as a significant deterrent. New airlines face substantial upfront investments and lengthy negotiation processes to gain even limited access. This scarcity can translate into operational inefficiencies and higher costs for new players, undermining their ability to compete on price or service. By 2024, the demand for slots at top-tier airports consistently outstripped supply, reinforcing the advantage of established airlines like China Southern.
- Limited Availability: Prime airport slots are a finite resource, often allocated based on historical usage, favoring incumbents.
- Infrastructure Dependence: Access to gates, maintenance, and catering services is critical and controlled by airport authorities or existing operators.
- High Entry Costs: New airlines must incur significant costs and navigate complex procedures to secure necessary operational infrastructure.
- Competitive Disadvantage: Incumbents with secured slots and infrastructure gain a crucial operational and cost advantage.
Government Support for Existing State-Owned Airlines
Government backing for state-owned entities like China Southern Airlines presents a significant barrier to new entrants. This support can manifest as direct financial aid, favorable regulatory treatment, and strategic planning assistance, effectively creating an uneven playing field.
For instance, in 2023, Chinese state-owned airlines received substantial government support to navigate post-pandemic recovery and infrastructure development. This often translates to lower borrowing costs and access to capital that private airlines struggle to match.
- Implicit Guarantees: Government ownership implies a safety net, reducing financial risk for state-owned carriers.
- Preferential Policies: New entrants may face stricter regulations or less favorable route allocations compared to established state-owned players.
- Capital Access: State-owned airlines can often access capital more readily and at lower rates due to government backing.
- Strategic Alignment: Government support ensures state-owned airlines align with national economic and development goals, potentially giving them an advantage in long-term planning and investment.
The threat of new entrants for China Southern Airlines is significantly low due to immense capital requirements, with fleet acquisition alone costing billions. Stringent regulatory hurdles from bodies like the CAAC, demanding extensive licenses and safety approvals, further deter newcomers.
Established brand loyalty and extensive route networks, built over decades and reinforced by frequent flyer programs, create a formidable challenge for new players to replicate. Securing critical airport slots and infrastructure at major hubs is also a major barrier, as these resources are often already controlled by incumbents.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example for China Southern (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Massive upfront investment for aircraft, infrastructure, and operations. | Extremely high, making it difficult to match scale. | Fleet of over 900 aircraft; new Boeing 787 ~$338M. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Strict licensing, certifications, and safety approvals from CAAC. | Time-consuming and costly, requiring proven operational capability. | CAAC's continued emphasis on rigorous safety standards in 2023. |
| Brand Loyalty & Network Effects | Decades of reputation building and extensive route coverage. | Difficult to attract and retain customers against established networks. | Hundreds of domestic and international destinations served. |
| Airport Slots & Infrastructure | Limited access to prime gates and operational facilities. | Leads to higher costs and operational inefficiencies for newcomers. | High slot utilization at major airports like PEK and CAN. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our China Southern Airlines Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, drawing from official company filings, aviation industry reports, and macroeconomic indicators.
We leverage insights from aviation market research firms, government aviation authorities, and financial news outlets to provide a comprehensive view of competitive forces.
