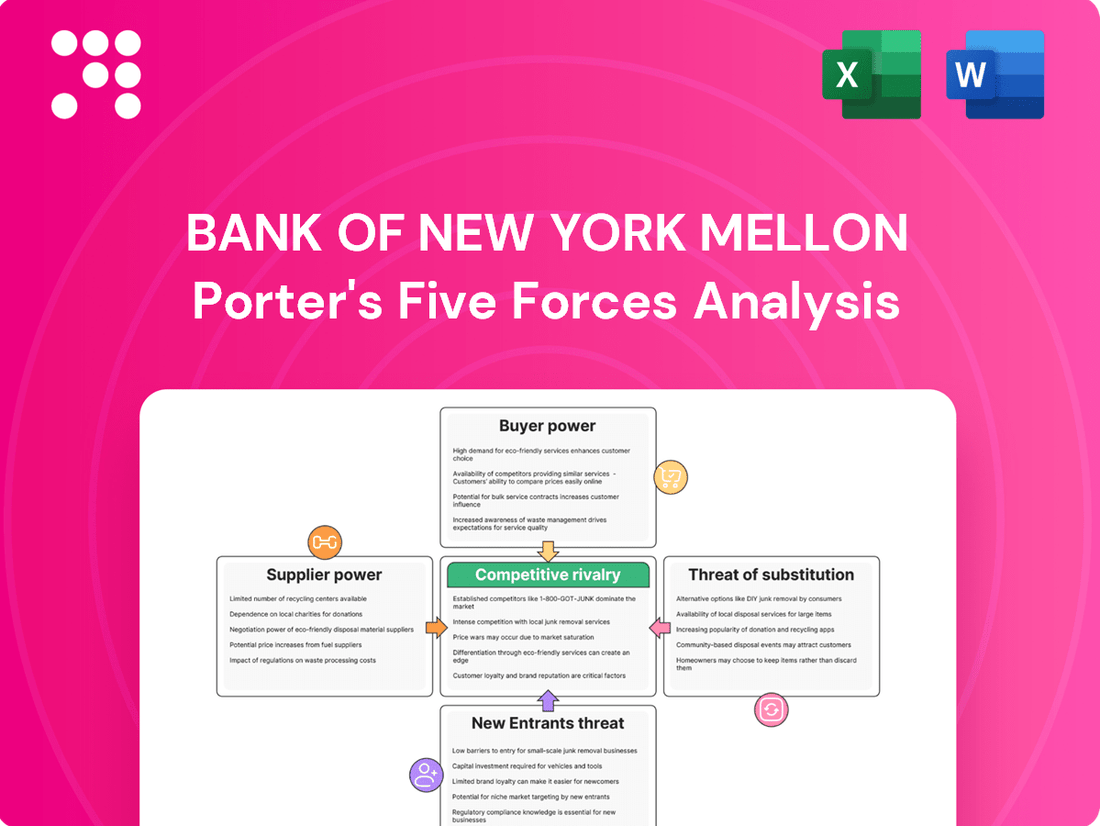
Bank of New York Mellon Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Bank of New York Mellon Bundle
The Bank of New York Mellon (BNYM) operates in a complex financial landscape, facing significant pressure from powerful buyers in the institutional investment space and intense rivalry from established global banks and emerging fintech players. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Bank of New York Mellon’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The Bank of New York Mellon (BNY Mellon) relies heavily on technology and software for its core operations, utilizing advanced systems like AI-powered analytics and cloud platforms. This dependence positions technology and software providers with moderate to high bargaining power, particularly when BNY Mellon utilizes specialized or proprietary systems where switching costs are substantial.
The significant investment and integration required for advanced financial technology mean that BNY Mellon faces considerable costs and operational disruption when changing vendors. For instance, in 2024, the global financial services sector continued to see increased spending on digital transformation initiatives, with cloud adoption and AI solutions being key drivers. This sustained demand for sophisticated tech solutions strengthens the leverage of leading providers.
The bargaining power of suppliers in the data and information services sector is significant for Bank of New York Mellon (BNY Mellon). Access to real-time market data, analytics, and financial intelligence is absolutely vital for BNY Mellon's core operations, including investment management and servicing. Suppliers who possess unique or difficult-to-replicate datasets can wield considerable influence, dictating terms and pricing.
The integration of new data feeds often involves substantial costs and technical effort, further solidifying the position of established data providers. For instance, in 2024, the market for financial data and analytics was projected to reach over $30 billion globally, with a significant portion of this revenue flowing to a few dominant players. This concentration of market power among data suppliers means BNY Mellon must carefully manage its relationships and consider the strategic implications of data sourcing.
The financial services sector, especially in niches like investment management and asset servicing, heavily relies on highly specialized talent. Professionals with expertise in finance, advanced technology, and regulatory compliance are in high demand.
A scarcity of these skilled individuals significantly amplifies their bargaining power. This can translate into increased labor costs and more complex recruitment processes for institutions like Bank of New York Mellon (BNY Mellon).
For instance, in 2024, the demand for AI and data science specialists within financial services continued to outpace supply, driving up compensation packages for these roles. BNY Mellon, like its peers, faces the challenge of attracting and retaining such critical talent to maintain its competitive edge.
Regulatory and Compliance Service Providers
Regulatory and compliance service providers, including legal experts and RegTech firms, wield considerable bargaining power over BNY Mellon. This stems from the critical nature of their services in navigating the complex and ever-changing global financial regulatory environment. The cost of non-compliance, which can include hefty fines and reputational damage, makes BNY Mellon highly dependent on these specialized suppliers.
The demand for specialized compliance knowledge and advanced RegTech solutions is robust, driven by increasing regulatory scrutiny worldwide. For instance, the global RegTech market was projected to reach approximately $11.1 billion in 2024, highlighting the significant investment in these services. This strong demand, coupled with the specialized expertise required, allows these providers to command higher prices and favorable terms.
- High Switching Costs: BNY Mellon faces substantial costs and operational disruption when attempting to switch compliance service providers due to the deep integration of these services into its core operations and the need for extensive due diligence.
- Concentration of Expertise: The market for highly specialized regulatory and compliance expertise is often concentrated among a limited number of firms, giving those firms greater leverage in negotiations.
- Criticality of Service: Failure to meet regulatory requirements can result in severe penalties, making BNY Mellon prioritize reliability and expertise over cost savings, thereby enhancing supplier power.
Infrastructure and Utility Providers
Infrastructure and utility providers hold moderate bargaining power over Bank of New York Mellon (BNY Mellon). Essential services like electricity and telecommunications are critical for BNY Mellon's extensive global operations, including its data centers. While many providers offer similar services, ensuring reliable uptime and connectivity in key financial hubs can limit BNY Mellon's ability to switch providers easily, especially for specialized or high-capacity needs.
The cost of utilities, while a significant operational expense, is generally a smaller portion of BNY Mellon's overall revenue compared to other inputs. For instance, in 2023, the average cost of electricity for commercial users in major financial centers like New York City remained relatively stable, though localized increases or specific contract terms could influence BNY Mellon's costs. The ability to negotiate long-term contracts or leverage its scale can mitigate some of this power, but reliance on a few key providers in certain regions remains a factor.
- Criticality of Services: Reliable power and high-speed telecommunications are non-negotiable for BNY Mellon's 24/7 operations and data integrity.
- Provider Concentration: In some operational hubs, there may be limited competition among providers of essential infrastructure, increasing their leverage.
- Cost Impact: While not the largest expense, significant price hikes from utility providers can affect operating margins, particularly for data-intensive functions.
The bargaining power of suppliers for BNY Mellon is notably influenced by the critical nature of specialized financial data and advanced technology. Providers of unique datasets or proprietary software systems can exert significant leverage due to high switching costs and the essential role these inputs play in BNY Mellon's operations. In 2024, continued investment in digital transformation across the financial sector underscored the demand for sophisticated tech solutions, bolstering the position of leading providers.
Skilled human capital, particularly in areas like AI, data science, and regulatory compliance, represents another source of supplier power. The scarcity of such talent in 2024 drove up compensation and made retention a challenge for institutions like BNY Mellon. This demand-supply imbalance grants these professionals considerable bargaining influence, impacting labor costs and recruitment strategies.
Regulatory and compliance service providers also hold substantial power, given the critical need for BNY Mellon to navigate complex global regulations. The potential for severe penalties for non-compliance makes BNY Mellon highly reliant on these specialized firms, whose expertise is in high demand, as evidenced by the projected $11.1 billion global RegTech market in 2024.
| Supplier Category | Key Factors Influencing Power | Impact on BNY Mellon |
| Technology & Software | High switching costs, proprietary systems, specialized integration needs | Moderate to High bargaining power, potential for increased costs |
| Data & Information Services | Unique/difficult-to-replicate datasets, criticality for core operations | Significant bargaining power, dictates terms and pricing |
| Specialized Talent (AI, Data Science, Compliance) | Scarcity of skills, high demand in financial services | Increased labor costs, complex recruitment, retention challenges |
| Regulatory & Compliance Services | Criticality of service, high cost of non-compliance, specialized expertise | Considerable bargaining power, commands higher prices and favorable terms |
| Infrastructure & Utilities | Reliability needs, provider concentration in certain hubs | Moderate bargaining power, potential impact on operating margins |
What is included in the product
This analysis of Bank of New York Mellon's competitive landscape examines the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, providing strategic insights into its market position.
Navigate competitive pressures with a dynamic, interactive model that visually highlights how each of Porter's Five Forces impacts BNY Mellon's strategic positioning.
Customers Bargaining Power
BNY Mellon's large institutional clients, including corporations and high-net-worth individuals, manage significant assets. In 2024, these clients, due to the sheer volume of their business, hold considerable sway in negotiating terms and demanding customized services, potentially influencing BNY Mellon's profitability through fee adjustments.
Customers in asset servicing and investment management are moving away from one-size-fits-all solutions. They now want services tailored specifically to their unique needs, like risk tolerance and investment goals. This shift empowers them to choose providers who can offer bespoke solutions, putting pressure on established players like BNY Mellon.
Consolidation within BNY Mellon's client base, particularly among large asset managers and pension funds, significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. As these entities grow larger and fewer in number, their individual importance to BNY Mellon increases, giving them greater leverage in negotiations.
This trend translates into a concentrated client segment where each major player holds substantial sway. For instance, a few mega-asset managers could collectively represent a significant portion of BNY Mellon's custody or fund administration revenue, enabling them to demand more favorable pricing or tailored services.
In 2024, the asset management industry continued to see significant M&A activity. Large players acquiring smaller firms means BNY Mellon is increasingly dealing with fewer, but much larger, clients who can dictate terms more effectively, potentially squeezing profit margins.
Information and Transparency
The increasing availability of financial data and market transparency significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. With readily accessible information on services, fees, and performance from various institutions, clients can efficiently compare offerings. This empowers them to seek out the best value, putting direct pressure on BNY Mellon to remain competitive in its pricing and service delivery. For instance, BNY Mellon's wealth management clients in 2024 have access to numerous platforms detailing investment performance and fee structures, enabling informed comparisons.
This heightened transparency means customers are less reliant on a single provider for information and can easily identify alternatives that better meet their needs. BNY Mellon, like other major financial institutions, must therefore focus on demonstrating clear value propositions and superior service quality to retain its client base. The ability for customers to readily compare BNY Mellon's digital platform features against those of fintech competitors, for example, underscores this shift.
- Informed Decision-Making: Customers can now easily compare BNY Mellon's fee structures and service offerings against competitors, leading to more discerning choices.
- Competitive Pressure: Increased transparency forces BNY Mellon to offer competitive pricing and superior service to retain clients.
- Digital Accessibility: Online platforms and financial aggregators provide customers with unprecedented access to comparative data, enhancing their bargaining power.
- Focus on Value: BNY Mellon must clearly articulate its value proposition to counter the ease with which customers can switch providers.
Switching Costs (Varying)
The bargaining power of customers for Bank of New York Mellon (BNY Mellon) is significantly influenced by switching costs, which can vary depending on the service. For intricate areas like asset servicing or corporate trust, transitioning to a new provider often entails substantial operational disruptions and integration expenses. This complexity can make customers hesitant to switch, thereby reducing their immediate bargaining power.
However, the financial landscape is evolving. The proliferation of integrated digital platforms and advancements in financial technology are beginning to lower some of these traditional barriers. For instance, as of 2024, many fintech solutions offer more streamlined onboarding processes and data migration tools, potentially making it easier for clients to move their business. This trend suggests a gradual shift where, for certain services, switching costs are becoming less prohibitive.
Consequently, while some customer segments still face high switching costs, others are experiencing a reduction in these barriers. This dichotomy directly impacts customer power. For services with high switching costs, BNY Mellon can maintain stronger pricing power. Conversely, for services where switching is becoming more feasible, customers gain increased leverage to negotiate terms and pricing.
- High Switching Costs: Complex asset servicing and corporate trust clients face significant operational and integration costs when changing providers.
- Technological Impact: Integrated digital platforms and new technologies are reducing switching barriers for some services.
- Customer Leverage: Reduced switching costs for certain services empower customers to negotiate more favorable terms.
- Market Dynamics: The evolving technological landscape influences the overall bargaining power of BNY Mellon's customer base.
BNY Mellon's clients, especially large institutional ones, wield significant power due to the substantial assets they manage. In 2024, these clients could negotiate favorable terms and demand customized services, impacting BNY Mellon's fee structures and profitability.
The increasing demand for tailored solutions over standardized offerings empowers clients to select providers that best fit their specific needs, creating competitive pressure on BNY Mellon.
Consolidation among BNY Mellon's clients, such as asset managers and pension funds, amplifies their individual leverage. As these entities grow larger, their importance to BNY Mellon increases, granting them greater negotiation power.
Greater market transparency and readily available financial data allow clients to easily compare BNY Mellon's services and fees with competitors, forcing the institution to offer competitive pricing and superior value to retain business.
| Client Segment | 2024 Asset Volume (Illustrative) | Impact on Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|
| Large Institutional Investors | Trillions USD | High - Can negotiate significant fee discounts and demand bespoke services. |
| Asset Managers | Billions to Trillions USD | High - Consolidation increases their individual leverage; demand for specialized services. |
| Corporations | Varies widely | Moderate to High - Dependent on the scale of services used; increasing demand for digital integration. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Bank of New York Mellon Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Bank of New York Mellon Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing competitive rivalry, the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, and the threat of substitute products. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted analysis you will receive instantly upon purchase, ensuring no surprises and immediate usability.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The financial services landscape, especially in asset servicing and custody, presents a fascinating mix of fragmentation and concentration. While numerous smaller firms compete in specialized niches, a handful of global giants, including BNY Mellon, dominate the broader market. This creates a competitive arena where firms must battle for market share against both peers and established behemoths.
This intense rivalry is further fueled by the robust growth observed in the asset servicing sector. For instance, global assets under custody and administration (AUC/A) for BNY Mellon reached a significant $45.4 trillion as of the first quarter of 2024. Such growth attracts new entrants and intensifies the efforts of existing players to capture and retain business, leading to constant innovation and strategic maneuvering.
The global custodian and asset servicing arena is fiercely contested, with giants like State Street, JP Morgan, and Citi vying for market share alongside BNY Mellon. This intense rivalry is fueled by the continuous demand for sophisticated, technologically driven, and universally available services.
Firms are heavily investing in digital transformation and artificial intelligence, aiming to differentiate themselves and capture a larger portion of the estimated $40 trillion in assets under custody and administration globally. For instance, BNY Mellon reported its custody assets under custody and administration reached $45.7 trillion as of Q1 2024, highlighting the sheer scale of the market and the stakes involved.
The financial services landscape is being reshaped by rapid technological advancements like artificial intelligence, blockchain, and sophisticated data analytics, intensifying competitive rivalry. BNY Mellon, like its peers, must invest significantly in these areas to boost efficiency, elevate client interactions, and launch novel offerings. For instance, in 2024, the financial technology sector saw substantial venture capital funding, with AI-driven solutions attracting a significant portion, underscoring the industry-wide push for technological differentiation.
Pressure on Fees and Margins
The financial services industry, particularly in custody and asset servicing, is intensely competitive. This rivalry, combined with client demands for greater cost efficiency and clearer pricing structures, puts considerable pressure on BNY Mellon's fees and overall profit margins. For instance, in 2024, many asset managers are seeking to consolidate providers to achieve economies of scale, which can lead to further fee negotiations.
To combat this, BNY Mellon must continuously refine its operations and develop services that offer tangible added value. This strategic focus is crucial for sustaining profitability amidst a challenging and price-sensitive market landscape.
- Intense Competition: Competitors like State Street and JPMorgan Chase actively vie for market share, driving down service fees.
- Client Demand for Cost Efficiency: Institutional investors and asset managers are increasingly scrutinizing costs, pushing for lower fees.
- Margin Pressure: The combined effect of competition and client demands directly impacts the profitability of BNY Mellon's core services.
- Operational Streamlining: BNY Mellon invests in technology and process improvements to reduce its own costs and offer more competitive pricing.
Regulatory Compliance and Capital Requirements
The financial services industry, particularly for institutions like Bank of New York Mellon (BNY Mellon), operates under a rigorous and constantly changing regulatory framework. These regulations, including capital adequacy rules such as Basel III and its subsequent iterations, impose substantial compliance costs and demand significant capital reserves. For instance, as of early 2024, major banks are still adapting to the finalization of Basel III rules, which aim to strengthen bank resilience. This creates a high barrier for new entrants, effectively limiting the number of new competitors.
However, these same regulatory and capital demands intensify rivalry among established players. Meeting and exceeding these requirements necessitates substantial investment in technology, risk management, and compliance personnel. This operational burden and the continuous need for capital allocation mean that firms must compete fiercely on efficiency and service quality to maintain profitability. BNY Mellon, like its peers, must navigate these complexities, which directly influences its competitive positioning.
- High Barriers to Entry: Stringent capital requirements and complex regulatory compliance, such as those mandated by Basel III finalization, significantly deter new entrants into the custody and asset servicing space.
- Increased Operational Costs: Existing institutions face substantial ongoing expenses related to compliance, risk management, and technology upgrades to meet evolving regulatory standards, impacting profitability.
- Intensified Rivalry: The need to absorb these costs and maintain competitive capital ratios fuels intense competition among established banks for market share and operational efficiency.
- Focus on Scale and Technology: Firms that can efficiently manage compliance and leverage technology to scale operations are better positioned, leading to a competitive advantage for larger, well-capitalized entities.
The competitive rivalry within the financial services sector, particularly for BNY Mellon, is exceptionally high. Major global players like State Street, JPMorgan Chase, and Citi are constantly vying for market share, driving innovation and pressuring fees.
This intense competition is further exacerbated by client demands for cost efficiency and greater value, forcing firms to invest heavily in technology and operational improvements to remain competitive.
BNY Mellon's reported custody assets under custody and administration reached $45.7 trillion as of Q1 2024, illustrating the vast scale of this competitive market and the significant stakes involved for all participants.
The industry's focus on digital transformation, including AI and blockchain, means that firms must continually adapt and invest to differentiate their offerings and maintain their market position.
| Competitor | Key Service Area | 2023/2024 Data Point (Illustrative) |
|---|---|---|
| State Street | Custody & Asset Servicing | Reported $43.9 trillion in AUC/A as of Q1 2024 |
| JPMorgan Chase | Custody & Fund Services | Significant global presence, competing for large institutional mandates |
| Citi | Securities Services | Strong global network, actively pursuing digital solutions |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Very large corporations and institutional investors, especially those with significant scale and advanced technological infrastructure, may choose to develop in-house solutions for critical functions like asset servicing, corporate trust, and treasury management. This can offer greater control and potentially lower costs compared to outsourcing. For instance, a pension fund managing trillions in assets might find it more economical to build its own post-trade processing capabilities.
Direct investment platforms and robo-advisors present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional asset management. These digital solutions offer accessible, often lower-fee alternatives for individuals seeking to manage their portfolios. For instance, by the end of 2023, the robo-advisor market was estimated to exceed $1.5 trillion globally, demonstrating a substantial shift in how assets are managed.
Emerging technologies like blockchain and distributed ledger technology (DLT) present a significant threat of substitution for traditional financial services. These innovations can enable direct peer-to-peer transactions, potentially bypassing intermediaries like BNY Mellon for custody and settlement. For instance, the tokenization of assets on a blockchain allows for fractional ownership and easier transfer, creating a more streamlined process.
Fintech Solutions and Embedded Finance
The threat of substitutes for Bank of New York Mellon (BNY Mellon) is amplified by the rapid growth of specialized fintech solutions. These agile companies often focus on niche areas like payments processing or digital lending, directly challenging BNY Mellon's traditional revenue streams. For instance, the global fintech market was valued at over $1.1 trillion in 2023 and is projected to reach $3.5 trillion by 2030, indicating a significant and growing competitive landscape.
Embedded finance presents another substantial substitute threat. This trend sees financial services seamlessly integrated into non-financial platforms, such as e-commerce sites or software applications. This disintermediation means customers may no longer need to interact directly with traditional banking institutions for many transactions. By 2025, the embedded finance market is expected to reach $7.2 trillion globally, underscoring its disruptive potential.
- Specialized Fintech Offerings: Fintechs provide focused, often more efficient, alternatives for specific services like cross-border payments or wealth management, chipping away at BNY Mellon's broad service portfolio.
- Embedded Finance Integration: Financial services are increasingly becoming a feature within other digital experiences, reducing reliance on traditional banking interfaces and customer relationships.
- Market Growth Data: The fintech market's projected growth to $3.5 trillion by 2030 and embedded finance's expected reach of $7.2 trillion by 2025 highlight the significant scale of these substitute threats.
- Customer Behavior Shift: Consumers and businesses are increasingly adopting digital-first solutions, favoring convenience and specialized functionality offered by fintech alternatives.
Alternative Financing and Private Markets
The rise of alternative financing, particularly private credit, presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional bank lending and capital market services. For corporate clients, these private markets offer bespoke solutions that can bypass traditional intermediaries. This trend is accelerating, with private credit assets under management projected to reach $2.7 trillion by the end of 2024, a substantial increase from previous years.
This growing accessibility to private capital can diminish the reliance of large corporations on services typically provided by institutions like BNY Mellon, impacting its treasury and corporate trust divisions. As of early 2024, private debt funds continue to attract significant investor interest, demonstrating a clear shift in how companies are accessing capital.
- Private credit assets are expected to surpass $2.7 trillion globally by the end of 2024.
- This growth directly challenges traditional bank lending models for corporate clients.
- BNY Mellon's treasury and corporate trust services may see reduced demand as companies opt for private market solutions.
The threat of substitutes for BNY Mellon is significant, as specialized fintech firms offer targeted solutions that can bypass traditional financial intermediaries. These agile companies often focus on specific services like cross-border payments or wealth management, directly competing with BNY Mellon's broader offerings. The global fintech market's impressive growth, projected to reach $3.5 trillion by 2030, underscores the increasing appeal and adoption of these specialized alternatives.
Embedded finance further amplifies this threat by integrating financial services into non-financial platforms, reducing the need for direct interaction with institutions like BNY Mellon. This trend is expected to see the embedded finance market reach $7.2 trillion globally by 2025, demonstrating a substantial shift in customer behavior towards convenience and seamless digital experiences.
| Substitute Area | Market Projection (2024/2025) | Impact on BNY Mellon |
|---|---|---|
| Fintech Solutions | Global Fintech Market Valued Over $1.1 Trillion in 2023, Projected to reach $3.5 Trillion by 2030 | Erodes market share in niche services, challenges traditional revenue streams. |
| Embedded Finance | Expected to Reach $7.2 Trillion Globally by 2025 | Disintermediates traditional banking relationships, reduces direct customer interaction. |
| Robo-Advisors | Global Market Exceeded $1.5 Trillion by End of 2023 | Offers lower-fee, accessible alternatives for asset management, impacting traditional advisory services. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the global financial services arena, particularly in specialized areas like asset servicing and custody, necessitates massive capital outlays. Think about the cost of building secure, cutting-edge technology platforms, maintaining robust cybersecurity, and meeting stringent regulatory mandates. For instance, in 2024, major financial institutions continue to invest billions annually in technology upgrades alone to stay competitive and compliant.
These considerable upfront costs act as a significant deterrent, effectively raising the barrier to entry. Only well-funded entities with deep pockets can realistically consider establishing a presence, thereby limiting the pool of potential new competitors for established players like Bank of New York Mellon.
The financial services industry, including banking giants like Bank of New York Mellon, is characterized by formidable regulatory barriers. New entrants must navigate a complex web of licensing requirements and compliance mandates, demanding significant upfront investment in legal and operational infrastructure. For instance, in 2024, the global financial sector continued to grapple with evolving regulations aimed at enhancing stability and consumer protection, such as stricter capital adequacy ratios and expanded anti-money laundering protocols, making market entry exceptionally challenging.
BNY Mellon's formidable brand reputation, cultivated over centuries, acts as a significant barrier to new entrants. This deep-seated trust is crucial in institutional finance where clients entrust trillions in assets. For instance, as of Q1 2024, BNY Mellon serviced approximately $47.1 trillion in assets under custody and administration, a testament to the trust clients place in their established operations and security protocols.
Economies of Scale and Network Effects
Incumbent financial institutions like BNY Mellon leverage substantial economies of scale, processing trillions of dollars in assets under custody and administration. This scale allows for significant cost efficiencies in transaction processing and operational overhead, making it challenging for new entrants to match their per-unit costs.
Network effects further solidify BNY Mellon's position. The more clients and financial instruments integrated into their systems, the more valuable the network becomes for all participants, creating a barrier to entry.
- Economies of Scale: BNY Mellon's vast operational infrastructure allows for lower per-transaction costs compared to smaller, newer firms.
- Network Effects: A broad client base and extensive connectivity enhance BNY Mellon's value proposition, attracting more participants and reinforcing its market dominance.
- Cost Disadvantage for New Entrants: New players would face immense capital requirements to build equivalent infrastructure and achieve competitive pricing.
Technological Investment and Expertise
While agile fintech startups can emerge, replicating Bank of New York Mellon's (BNY Mellon) established technological infrastructure, robust cybersecurity defenses, and specialized financial technology expertise presents a formidable challenge. This deep-seated technological moat acts as a significant barrier to entry.
The sheer scale of ongoing investment required in areas like artificial intelligence and digital transformation to compete at BNY Mellon's level is a substantial hurdle for potential new entrants. For instance, BNY Mellon's commitment to innovation is reflected in its significant technology spending, which in 2023 was in the billions of dollars, a figure difficult for many startups to match.
- High Capital Requirements: New entrants need substantial capital to build comparable IT infrastructure and cybersecurity measures.
- Specialized Expertise Gap: Acquiring the deep technical talent and regulatory knowledge necessary to operate in this space is a lengthy and costly process.
- Ongoing R&D Investment: Continuous investment in AI, blockchain, and other emerging technologies is essential, creating a perpetual cost barrier.
The threat of new entrants for Bank of New York Mellon (BNY Mellon) is considerably low due to exceptionally high barriers. These include massive capital requirements for technology and regulatory compliance, as seen with ongoing billions invested annually in upgrades by major financial institutions in 2024. Furthermore, established brands and deep client trust, evidenced by BNY Mellon servicing $47.1 trillion in assets under custody and administration as of Q1 2024, deter newcomers.
Economies of scale and network effects create significant cost advantages and value propositions that are difficult for new entrants to replicate. The specialized expertise and continuous R&D investment, particularly in areas like AI, also pose a substantial hurdle, with BNY Mellon's billions spent on technology in 2023 highlighting this challenge.
| Barrier Category | Specific Barrier | Impact on New Entrants | Example/Data Point (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Technology Infrastructure & Cybersecurity | Extremely High | Billions invested annually by major banks in tech upgrades (2024). |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Licensing & Compliance | Formidable | Evolving regulations like stricter capital adequacy ratios (2024). |
| Brand & Reputation | Client Trust | Significant | BNY Mellon servicing $47.1 trillion in assets (Q1 2024). |
| Economies of Scale | Operational Costs | Challenging to Match | Trillions in assets processed by incumbents. |
| Technology & Expertise | AI, Digital Transformation, Talent | High Barrier | BNY Mellon's billions in tech spending (2023). |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Bank of New York Mellon is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial data, including SEC filings and annual reports, complemented by industry-specific market research from firms like Gartner and IDC, and insights from financial news outlets.
We leverage data from regulatory bodies, investor relations materials, and competitive intelligence platforms to thoroughly assess the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, as well as the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
