Beam Therapeutics Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Beam Therapeutics Bundle
Beam Therapeutics operates in a highly innovative but intensely competitive gene editing landscape, where the threat of new entrants is significant due to the rapid scientific advancements and potential for disruptive technologies. Understanding the nuances of buyer power and the bargaining power of suppliers is crucial for navigating this dynamic market.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Beam Therapeutics’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Beam Therapeutics' reliance on highly specialized reagents and equipment for its groundbreaking base editing technology means a limited pool of suppliers exists. These suppliers, often the sole providers of cutting-edge components essential for gene editing advancements, wield considerable bargaining power. For instance, the market for sophisticated gene editing tools and delivery systems, such as lipid nanoparticles, is concentrated, allowing these specialized entities to command premium pricing.
For a company like Beam Therapeutics, the bargaining power of suppliers is significantly amplified by high switching costs within the biotechnology sector. These costs extend beyond mere financial outlays, encompassing the extensive time and resources required to re-validate materials and processes. For instance, changing a key reagent supplier could necessitate months of rigorous testing and quality control to ensure it meets the stringent standards of drug development.
The implications for Beam are substantial. Re-validation processes can lead to considerable delays in crucial clinical trial timelines, a critical factor in the fast-paced biotech landscape. Furthermore, navigating the complex regulatory pathways associated with any material change adds another layer of difficulty and expense. These combined factors create a strong incentive for Beam to foster and maintain stable relationships with its existing suppliers, even if current contract terms are not optimally favorable.
Many suppliers in the gene editing and biotechnology sector possess proprietary technologies and intellectual property that are absolutely essential for Beam Therapeutics' research and development efforts. This exclusivity means these suppliers have significant power when it comes to setting prices and negotiating terms, as Beam relies on their unique innovations.
Beam's reliance on these specialized, often patented, technologies can significantly restrict its options for finding alternative suppliers. This dependence directly translates into higher costs and less favorable contract conditions for Beam, impacting its operational expenses and strategic flexibility.
Quality and Reliability Requirements
The genetic medicine sector, including companies like Beam Therapeutics, faces exceptionally high quality and reliability demands. This means only a limited number of specialized suppliers can meet the rigorous standards required for raw materials and manufacturing processes. For instance, companies developing gene therapies often require GMP-certified facilities and highly purified reagents, a niche capability. This scarcity of qualified suppliers inherently strengthens their bargaining position.
Suppliers who can consistently provide materials that meet these stringent specifications hold significant sway. A failure in quality from a supplier could have catastrophic consequences for Beam Therapeutics, potentially jeopardizing clinical trial progress and delaying crucial regulatory approvals. This high-stakes environment gives these select suppliers considerable leverage in pricing and terms.
- Limited Supplier Pool: The specialized nature of genetic medicine inputs restricts the number of viable suppliers, concentrating power.
- High Switching Costs: Qualifying new suppliers for critical components in regulated industries like biotech is time-consuming and expensive, locking in existing relationships.
- Impact of Quality Failures: Any lapse in supplier quality can halt clinical trials and regulatory submissions, making reliability paramount.
Growing Demand in Biotechnology Reagents Market
The biotechnology reagents market, a crucial sector for companies like Beam Therapeutics, is experiencing robust expansion. This growth directly impacts the bargaining power of suppliers within this space. As demand escalates, suppliers find themselves in a stronger position to negotiate terms and pricing.
The market for biotechnology reagents, encompassing essential components for gene editing technologies, is on a significant upward trajectory. Projections indicate this market will surpass $93 billion by 2025, highlighting a substantial increase in the need for these specialized products across the industry.
- Market Growth: The biotechnology reagents market is expected to exceed $93 billion by 2025, demonstrating strong demand.
- Supplier Leverage: Increased demand enhances suppliers' ability to dictate higher prices and more favorable contract terms.
- Impact on Beam Therapeutics: For Beam Therapeutics, this means potentially higher costs for essential research and development materials.
Beam Therapeutics operates in a field where suppliers of highly specialized reagents and equipment hold significant sway. This is due to the limited number of entities capable of producing cutting-edge components essential for gene editing advancements, allowing them to command premium pricing. The market for sophisticated gene editing tools and delivery systems, such as lipid nanoparticles, is notably concentrated.
High switching costs further amplify supplier bargaining power for Beam. These costs involve not just financial outlays but also the extensive time and resources needed to re-validate materials and processes, a critical factor in drug development timelines. For instance, changing a key reagent supplier could necessitate months of rigorous testing and quality control to meet stringent drug development standards.
The implications for Beam are substantial, with re-validation processes potentially causing significant delays in clinical trial timelines. Navigating complex regulatory pathways for any material change adds further difficulty and expense, incentivizing Beam to maintain stable relationships with existing, even if not optimally favorable, suppliers.
Many suppliers in the gene editing sector possess proprietary technologies and intellectual property that are indispensable for Beam Therapeutics' research and development. This exclusivity grants these suppliers considerable power in setting prices and negotiating terms, as Beam relies on their unique innovations, directly translating into higher costs and reduced strategic flexibility.
The genetic medicine sector, including Beam Therapeutics, faces exceptionally high quality and reliability demands. This scarcity of qualified suppliers, capable of meeting rigorous standards for raw materials and manufacturing processes, inherently strengthens their bargaining position. For example, companies developing gene therapies often require GMP-certified facilities and highly purified reagents, a niche capability.
Suppliers who consistently provide materials meeting these stringent specifications hold significant leverage. A quality lapse from a supplier could jeopardize clinical trial progress and delay crucial regulatory approvals, giving select suppliers considerable power in pricing and terms.
The biotechnology reagents market, crucial for Beam Therapeutics, is experiencing robust expansion, which directly impacts supplier bargaining power. As demand escalates, suppliers are better positioned to negotiate terms and pricing. The market for these essential components is on a significant upward trajectory, projected to surpass $93 billion by 2025, indicating a substantial increase in demand across the industry.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Beam Therapeutics | Supporting Data (2024/2025 Projections) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Limited number of specialized providers for gene editing components. | Enables suppliers to command premium pricing and dictate terms. | Concentrated market for lipid nanoparticles and other gene editing delivery systems. |
| Switching Costs | High financial, time, and regulatory hurdles to change suppliers. | Locks Beam into existing supplier relationships, reducing negotiation leverage. | Months of re-validation required for critical reagents in drug development. |
| Proprietary Technology | Suppliers possess essential, often patented, technologies. | Creates dependence and limits Beam's sourcing options, increasing costs. | Exclusivity of unique innovations in gene editing tools. |
| Quality & Reliability Demands | Stringent standards for GMP-certified facilities and purified reagents. | Favors suppliers meeting high standards, increasing their leverage. | Niche capabilities required for gene therapy raw materials. |
| Market Growth | Increasing demand for biotechnology reagents. | Strengthens suppliers' ability to negotiate higher prices and favorable terms. | Biotechnology reagents market projected to exceed $93 billion by 2025. |
What is included in the product
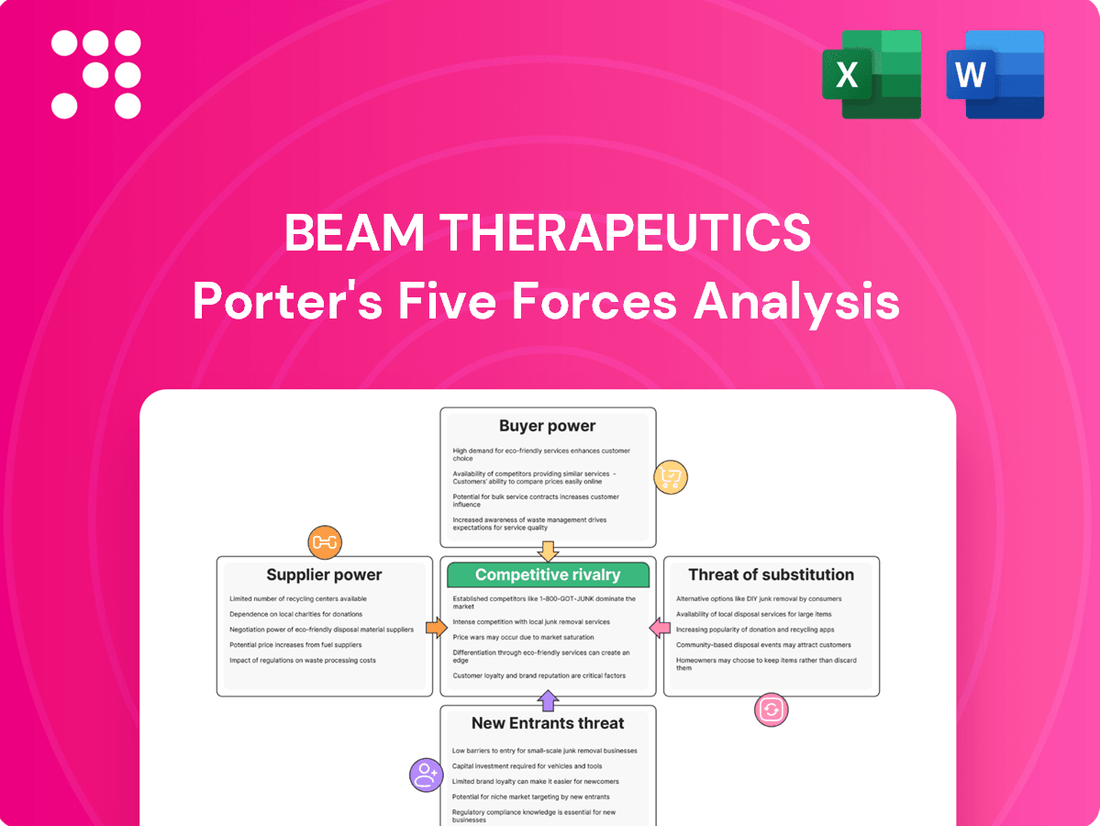
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for Beam Therapeutics dissects the competitive intensity, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the risk of substitutes within the gene editing therapy market.
Instantly assess competitive pressures with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces analysis, enabling Beam Therapeutics to strategically navigate the gene editing landscape and alleviate pain points related to market entry and differentiation.
Customers Bargaining Power
The immense cost of gene therapies, like those Beam Therapeutics is developing, significantly impacts customer bargaining power. For instance, Casgevy, a groundbreaking CRISPR therapy, carries a price of $2.2 million, a figure that limits individual patient negotiation.
While individual patients have little leverage, larger entities like insurance providers and national healthcare systems wield considerable power. These institutional buyers can negotiate aggressively on pricing, especially given the substantial investment required for these advanced treatments.
The complex and evolving regulatory and reimbursement landscape for gene therapies significantly influences customer power. Payer bodies and government agencies, like the FDA and EMA, play a crucial role in determining market access and pricing, effectively acting as powerful customers or gatekeepers.
Their decisions on approvals and reimbursement can dictate the commercial viability of Beam's products. For instance, the FDA's accelerated approval pathway, while beneficial for speed to market, often comes with post-market studies that can impact long-term reimbursement negotiations. In 2023, the average price for a gene therapy treatment exceeded $2 million, highlighting the intense scrutiny payers place on demonstrating value and durability.
Beam Therapeutics operates in a space where serious diseases often have very limited or no effective treatment options. This scarcity significantly weakens the bargaining power of customers, be they patients, their families, or even healthcare systems. When faced with life-threatening conditions, the demand for any potential cure or significant improvement becomes paramount.
For conditions with a high unmet medical need, like many of the genetic diseases Beam targets, customers are typically willing to accept higher prices for therapies that offer a chance at a cure or substantial life improvement. This dynamic is crucial for Beam's business model, as it allows for premium pricing on its innovative gene editing therapies. For instance, in 2024, the market for rare disease treatments continued to see strong pricing power due to these very factors.
Patient Advocacy and Clinical Trial Data
While individual patients typically possess limited direct bargaining power in the biopharmaceutical sector, patient advocacy groups can exert significant influence. These organizations can shape public perception and lobby for policy changes, indirectly impacting market access and pricing dynamics for innovative therapies. For instance, advocacy for rare diseases often drives awareness and support for treatments, potentially mitigating some customer price sensitivity.
The strength of clinical trial data plays a crucial role in shaping customer perception and demand. Beam Therapeutics has demonstrated the potential of its base editing technology with promising results for its lead program, BEAM-101, in sickle cell disease. Positive data showing clear therapeutic benefits can enhance a drug's perceived value, thereby reducing the bargaining power of customers who are eager for effective treatments.
- Patient advocacy groups can influence market access and public opinion.
- Strong clinical trial data, like that for BEAM-101 in sickle cell disease, can increase demand.
- Demonstrated therapeutic benefits reduce price sensitivity among potential customers.
Switching Costs for Healthcare Providers
Once Beam Therapeutics' gene therapies are adopted, healthcare providers face substantial switching costs. These include the expense and time for staff training on new administration and monitoring protocols, potential upgrades to existing infrastructure to handle specialized treatments, and the development of new patient management workflows. For instance, the complex nature of gene therapy administration often requires specialized pharmacy and infusion centers, representing a significant upfront investment.
These integration costs create a form of lock-in for healthcare providers. The effort and financial commitment involved in implementing a gene therapy make it difficult and costly for them to switch to a different therapeutic approach, even if alternatives emerge. This reduces their ability to exert significant bargaining power over Beam Therapeutics regarding pricing or terms.
The high switching costs for healthcare providers directly impact their bargaining power. As providers become more invested in a particular gene therapy, their flexibility to negotiate terms with the manufacturer diminishes, strengthening Beam Therapeutics' position. This is particularly relevant as gene therapies, like Casgevy which received FDA approval in late 2023 for sickle cell disease, represent a paradigm shift in treatment, necessitating significant provider adaptation.
- Significant Training Investment: Healthcare professionals require specialized training for gene therapy administration and patient monitoring, representing a substantial cost and time commitment.
- Infrastructure Adaptation: Implementing gene therapies may necessitate upgrades to existing medical facilities, including specialized pharmacies and infusion centers, adding to the provider's financial burden.
- Patient Management Protocols: Developing and integrating new protocols for patient selection, treatment delivery, and long-term follow-up for gene therapy patients creates operational complexity and cost.
The bargaining power of customers, particularly institutional buyers like payers and healthcare systems, is a significant factor for Beam Therapeutics. Their ability to negotiate prices is amplified by the high cost of gene therapies, which often exceed $1 million per treatment. In 2024, payers continued to scrutinize the long-term value proposition of these advanced therapies, demanding robust real-world evidence to justify pricing.
The limited number of approved gene therapies and the presence of unmet medical needs for many genetic diseases, however, somewhat temper this power. When few or no alternatives exist, customers have less leverage. For instance, the market for rare disease treatments in 2024 demonstrated continued strong pricing power due to these unmet needs.
Furthermore, the substantial investment healthcare providers make in training and infrastructure for gene therapies creates switching costs, further reducing their bargaining leverage. Beam's focus on potentially curative treatments for severe genetic disorders means that demand often outweighs the ability of customers to negotiate aggressively on price.
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Beam Therapeutics Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Beam Therapeutics, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications for the company. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive understanding of the industry's power dynamics. This includes insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the gene editing sector.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The gene editing landscape is fiercely competitive, featuring established giants like CRISPR Therapeutics and Editas Medicine, all vying for dominance alongside Beam Therapeutics. These companies bring substantial research and development prowess, robust intellectual property portfolios, and often advanced clinical trial pipelines to the table.
The gene editing market is anticipated to experience substantial growth, projected to reach approximately $10.5 billion by 2028, according to some market analyses. This expansion fuels an already intense competitive environment as companies race to develop and commercialize groundbreaking therapies.
The gene editing landscape is a hotbed of innovation, with breakthroughs in CRISPR, base editing, and prime editing constantly reshaping the field. This rapid pace fuels fierce competition as companies race to create more accurate, effective, and secure treatments. Beam Therapeutics, with its distinct base editing platform, faces rivals who are also pushing the boundaries of what's possible in genetic modification.
Developing precision genetic medicines, like those Beam Therapeutics focuses on, is incredibly expensive. Significant investment in research and development is essential to even enter this field.
Beam Therapeutics itself demonstrated this commitment, reporting research and development expenses of $367.6 million for the full year 2024. This substantial financial outlay underscores the high cost of innovation required to compete effectively.
These high R&D costs intensify rivalry. Companies are driven to achieve market leadership and successful product launches to justify and recoup these massive investments, creating a competitive pressure cooker.
Intellectual Property Landscape
The gene editing field is marked by intense competition, largely driven by the intricate and frequently litigious intellectual property (IP) landscape. Companies aggressively defend their patents and technological advancements, creating a dynamic environment where potential disputes and crucial licensing deals significantly shape market entry and competitive standing.
Beam Therapeutics, for instance, leverages its proprietary base editing technology as a core competitive advantage. This advanced platform, which allows for precise single-letter changes in DNA without double-strand breaks, is central to its strategy for developing novel therapies. The company has actively sought to build a robust IP portfolio around its base editing innovations.
As of early 2024, the gene editing sector continues to see substantial investment and patent filings. For example, in 2023, companies in the CRISPR and related gene editing spaces filed hundreds of new patent applications globally, reflecting the ongoing race to secure foundational and application-specific intellectual property. This high level of IP activity directly fuels competitive rivalry.
- Patent Protection: Companies like Beam Therapeutics prioritize securing broad patent protection for their core base editing technologies and specific therapeutic applications.
- Licensing Agreements: The complexity of IP often necessitates strategic licensing agreements, which can grant access to essential technologies or create revenue streams, impacting competitive dynamics.
- Litigation Risk: The potential for patent infringement lawsuits is a constant factor, requiring companies to carefully navigate the IP landscape and potentially leading to costly legal battles that can alter market positions.
- Innovation Pace: The rapid pace of innovation in gene editing means that companies must continuously develop and protect new intellectual property to maintain a competitive edge.
Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations
Strategic partnerships are a significant factor in the competitive landscape of gene editing. Companies often team up to share resources, expertise, and to speed up the journey from research to approved therapies. This can lead to more powerful players emerging.
Beam Therapeutics itself has entered into key collaborations, such as its agreements with Pfizer and Apellis. These alliances can amplify the competitive pressure on other firms. For instance, a partnership might grant one company access to a crucial technology or a broader patient population, making them a more formidable rival.
- Beam Therapeutics' collaborations with major pharmaceutical companies like Pfizer can accelerate their development timelines and market penetration.
- These strategic alliances can create significant barriers to entry for smaller competitors who lack similar access to resources and established networks.
- The success of such partnerships can lead to the formation of powerful, integrated competitors that possess a wider range of capabilities and a stronger market position.
Competitive rivalry within the gene editing sector is intense, driven by a race for technological supremacy and market share. Companies like Beam Therapeutics face established players and emerging innovators, all heavily investing in research and development to achieve breakthroughs. The high cost of innovation, exemplified by Beam's $367.6 million R&D spend in 2024, fuels this pressure, as firms strive for market leadership to recoup substantial investments.
The intellectual property landscape further intensifies competition, with companies aggressively protecting their innovations and navigating complex patent disputes. Beam Therapeutics' proprietary base editing technology is a key asset in this environment, where securing and defending patents is crucial for competitive advantage. The hundreds of patent applications filed globally in 2023 by gene editing companies highlight this ongoing IP race.
| Company | 2024 R&D Expenses (Millions USD) | Key Technology | Notable Partnerships |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beam Therapeutics | $367.6 | Base Editing | Pfizer, Apellis |
| CRISPR Therapeutics | Not specified (but significant) | CRISPR-Cas9 | Vertex Pharmaceuticals |
| Editas Medicine | Not specified (but significant) | CRISPR-Cas9 | Gilead Sciences |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For many of the genetic diseases Beam Therapeutics aims to address, traditional symptomatic treatments and existing therapies represent significant substitutes. These can range from pharmaceuticals that manage symptoms to surgical interventions that alleviate certain aspects of a condition, even if they don't correct the underlying genetic cause.
For instance, in sickle cell disease, while Beam is developing a potential cure, patients currently rely on pain management, blood transfusions, and medications like hydroxyurea. In 2024, the global sickle cell disease treatment market was valued at approximately $3.5 billion, indicating a substantial existing market for these less definitive but established treatments, which are often more accessible and familiar to both patients and physicians.
The availability of these less complex and often more affordable alternatives poses a threat. Patients and healthcare systems may be hesitant to adopt novel, potentially higher-cost gene editing therapies if existing treatments provide adequate symptom relief, especially if the long-term efficacy and safety profiles of new modalities are still being established.
Beyond base editing, other gene editing technologies like CRISPR-Cas9, TALENs, and ZFNs pose a significant threat of substitution. For instance, Casgevy, a CRISPR-based therapy, received regulatory approval in late 2023 for sickle cell disease, demonstrating the viability of these alternative modalities. While Beam highlights base editing's advantage in avoiding double-strand breaks, these competing technologies are rapidly evolving, potentially offering comparable therapeutic results across a range of diseases.
The threat of substitutes for Beam Therapeutics' cell and gene therapies is significant, as a wide array of competing treatments exist. These substitutes, while not always employing the same precise mechanism, aim to address similar patient needs in genetic diseases and oncology. For example, other gene editing technologies or even traditional cell therapies can offer alternative treatment pathways.
The market is also witnessing a notable expansion beyond oncology into non-oncology indications, broadening the scope of potential substitutes. This diversification means Beam's candidates face competition not just from direct gene editing rivals but also from therapies targeting the same non-cancerous diseases through different modalities. For instance, in 2024, the global gene therapy market was projected to reach tens of billions of dollars, indicating substantial investment and development across various therapeutic areas, many of which could offer substitute solutions.
Lifestyle Changes and Prevention
Lifestyle changes and preventative measures can serve as substitutes for genetic medicines like those developed by Beam Therapeutics. For instance, dietary adjustments or exercise regimens can mitigate the impact of certain metabolic disorders, thereby reducing the need for more advanced treatments. This can shrink the potential market for Beam's therapies, especially for chronic conditions where lifestyle interventions are a viable first-line approach.
Consider the market for certain inherited metabolic diseases. While Beam's gene editing technology offers a potential cure, proactive lifestyle management can significantly delay or lessen symptom severity. This is particularly true for conditions like phenylketonuria (PKU), where strict dietary adherence is crucial. In 2024, the global PKU treatment market was valued at approximately $1.5 billion, and a significant portion of this value is driven by specialized dietary products and management, representing a direct substitute for potential gene therapy interventions.
- Reduced Addressable Market: Lifestyle and preventative strategies can decrease the number of patients requiring Beam's precision genetic medicines, particularly for chronic or metabolic diseases.
- Dietary Interventions: For conditions like phenylketonuria, strict dietary management remains a primary substitute, impacting the potential patient pool for gene therapies.
- Preventative Healthcare Trends: Growing emphasis on wellness and early disease detection through lifestyle modifications can further erode the market for curative treatments.
Unapproved and Off-Label Treatments
Patients facing severe or terminal illnesses may explore unapproved or off-label treatments, or enroll in experimental trials conducted by competing biotechnology firms. This behavior introduces a subtle yet significant threat of substitution for Beam Therapeutics' pipeline candidates, as individuals actively seek alternatives beyond conventional treatment avenues.
For instance, in 2024, the landscape of gene therapy research saw continued innovation, with numerous companies advancing novel approaches. While specific data on patient migration to unapproved treatments for conditions targeted by Beam is proprietary, the overall growth in the gene therapy market, projected to reach tens of billions of dollars by the late 2020s, indicates a high level of patient and investor interest in alternative solutions.
- Patient desperation drives exploration of unapproved treatments.
- Experimental trials from other developers represent direct substitutes.
- This trend challenges the market exclusivity of Beam's pipeline.
The threat of substitutes for Beam Therapeutics is substantial due to existing treatments and evolving alternative technologies. While Beam focuses on base editing, other gene editing platforms like CRISPR-Cas9 are already reaching the market, as seen with Casgevy's approval for sickle cell disease in late 2023. Furthermore, traditional symptomatic treatments and lifestyle interventions remain viable alternatives, particularly for chronic conditions, limiting the immediate addressable market for novel gene therapies.
| Therapy Type | Example | 2024 Market Value (Approx.) | Substitute Threat Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Symptomatic Treatment | Hydroxyurea for Sickle Cell Disease | $3.5 billion (Sickle Cell Disease Market) | High |
| Gene Editing (CRISPR) | Casgevy | N/A (Newly approved) | High |
| Lifestyle Management | Dietary control for PKU | $1.5 billion (PKU Treatment Market) | Medium |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the precision genetic medicine field, especially with advanced technologies like base editing pioneered by Beam Therapeutics, demands substantial capital. This includes funding for extensive research, rigorous clinical trials, and the development of sophisticated manufacturing capabilities.
Beam Therapeutics itself highlights the significant financial commitment required, projecting a cash runway extending into 2027 or 2028. This substantial financial requirement acts as a formidable barrier, effectively deterring many potential new competitors from entering the market.
Extensive regulatory hurdles significantly deter new entrants in the gene therapy space. Companies like Beam Therapeutics must navigate a complex web of approvals from bodies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA). These processes involve lengthy and expensive preclinical and clinical trials, demanding substantial capital investment and scientific expertise.
The gene editing arena is crowded with intellectual property, creating significant hurdles for newcomers. Beam Therapeutics, for instance, possesses exclusive rights to its foundational base editing technology and its various uses. Any new company entering this space must contend with these existing patents, which could necessitate expensive licensing agreements or even legal battles over infringement, thereby raising the cost and complexity of market entry.
Need for Specialized Expertise and Talent
The development and successful commercialization of precision genetic medicines, like those Beam Therapeutics aims to deliver, require an exceptionally high level of specialized expertise. This includes deep knowledge in gene editing technologies, complex molecular biology, and the intricate processes of clinical development and regulatory approval.
New companies entering this field face a significant hurdle in assembling a team possessing this niche knowledge. The scarcity of readily available talent in areas such as CRISPR-based therapies and advanced biomanufacturing creates a substantial barrier to entry.
This talent gap directly translates into a higher cost and longer lead time for new entrants to establish themselves. For instance, the global demand for gene therapy specialists is projected to outpace supply, driving up recruitment costs and potentially delaying critical research and development milestones.
- Specialized Expertise: Gene editing, molecular biology, clinical development, and regulatory affairs are critical.
- Talent Scarcity: A limited pool of professionals with these specific skills exists globally.
- High Recruitment Costs: Companies must offer competitive compensation and benefits to attract top talent.
- Development Delays: Difficulty in hiring can slow down research, clinical trials, and product launches.
Established Clinical Pipelines and Partnerships
Established clinical pipelines and strategic partnerships act as significant deterrents to new entrants. Companies like Beam Therapeutics have already invested heavily in developing a robust pipeline of gene editing therapies and securing collaborations with major pharmaceutical firms. For instance, Beam Therapeutics has ongoing partnerships with Pfizer and Merck, providing them with access to significant funding and regulatory expertise, which are crucial for navigating the complex drug development process.
These existing relationships and advanced development stages create a substantial hurdle for newcomers. A new entrant would not only need to replicate the extensive research and development efforts but also establish comparable alliances to gain market traction and access necessary resources. The time and capital required to build a comparable clinical portfolio and forge such strategic partnerships can easily run into billions of dollars and several years, effectively raising the barrier to entry.
- Established Clinical Pipelines: New entrants face the challenge of building a comprehensive pipeline from the ground up, a process that is both time-consuming and capital-intensive, unlike established players who have already made significant progress.
- Strategic Partnerships: Existing collaborations with large pharmaceutical companies provide established players with crucial funding, expertise, and market access, which are difficult for new entrants to replicate quickly.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating the complex regulatory landscape for gene editing therapies requires significant experience and resources, areas where established companies have a distinct advantage.
- Capital Requirements: The immense financial investment needed for research, clinical trials, and regulatory approval makes it exceptionally difficult for new, unfunded entities to compete with well-capitalized incumbents.
The threat of new entrants in the precision genetic medicine sector, particularly for companies like Beam Therapeutics, is significantly mitigated by the immense capital requirements. Developing advanced therapies involves extensive R&D, costly clinical trials, and specialized manufacturing, creating a high financial barrier. For instance, Beam Therapeutics' projected cash runway into 2027-2028 underscores the substantial ongoing investment needed to sustain operations and advance its pipeline.
The sector is also heavily protected by intellectual property, with companies like Beam Therapeutics holding exclusive rights to foundational technologies. Navigating this IP landscape requires either costly licensing or the risk of infringement litigation, further increasing the cost and complexity for potential newcomers. This dense IP environment makes it challenging for new players to operate freely and develop competing technologies without significant legal and financial entanglements.
Furthermore, the need for highly specialized expertise in gene editing, molecular biology, and regulatory affairs presents a considerable hurdle. The scarcity of talent in these niche areas drives up recruitment costs and can lead to development delays, making it difficult for new entrants to assemble the necessary scientific and operational teams. This talent gap, coupled with the established clinical pipelines and strategic partnerships of incumbents, creates a formidable challenge for any new company seeking to enter this advanced field.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Beam Therapeutics is built upon a foundation of publicly available company filings, including SEC submissions and investor presentations. We supplement this with insights from reputable industry research reports and financial news outlets to capture the competitive landscape.
