BAC Holding International Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
BAC Holding International Bundle
BAC Holding International faces moderate threats from new entrants and substitutes, while buyer and supplier power are significant. The intensity of rivalry within its industry also demands careful strategic consideration.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping BAC Holding International’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
BAC Holding International, a financial institution, fundamentally depends on access to capital markets for its operational funding and to support its extensive loan portfolios. The suppliers in this context are primarily investors and bondholders, whose leverage is significantly shaped by prevailing global and regional economic conditions, the prevailing interest rate environment, and overall investor confidence in Central American markets.
For 2024, a stable economic outlook in Central America, coupled with anticipated interest rate decreases, is poised to diminish the cost of capital. This reduction in funding costs directly translates to a decrease in the bargaining power of these capital market suppliers, as BAC Holding International becomes less reliant on any single source of funding.
Technology and software providers hold significant bargaining power, especially for financial institutions like BAC Holding International that depend heavily on advanced systems for digital banking, cybersecurity, and overall operational efficiency. These specialized fintech and core banking system providers can command leverage if their offerings are proprietary, complex to integrate, or incur substantial costs when switching.
BAC's strategic push for digital transformation makes it a major client for these tech vendors. However, the growing adoption of composable architecture and API-driven solutions is starting to democratize the market, potentially lessening the traditional supplier lock-in and increasing BAC's flexibility in choosing and integrating different technological components.
The availability of skilled professionals, especially in digital banking, cybersecurity, and data analytics, is paramount for BAC Holding International. A scarcity of such talent in Central America, or intense competition from other industries, directly empowers employees, potentially driving up labor costs and complicating hiring efforts. BAC's substantial workforce, exceeding 20,000 individuals, underscores its considerable dependence on human capital.
Payment Network Operators
Payment network operators like Visa and Mastercard wield considerable influence over BAC Holding International. These networks are fundamental to BAC's operations, enabling billions of dollars in transactions annually across Central America. In 2024, BAC's significant contribution to the region's GDP, particularly in payment processing, underscores its dependence on these established payment infrastructures.
The bargaining power of these network operators stems from their critical role in facilitating global commerce and their extensive reach. BAC relies on their infrastructure to process payments efficiently and securely for its vast customer base.
- Network Dominance: Operators like Visa and Mastercard control the essential rails for electronic payments, making them indispensable for financial institutions.
- Interoperability Standards: These operators set the technical and operational standards that BAC must adhere to, limiting its flexibility.
- Switching Costs: While BAC is a major player, the cost and complexity of shifting to alternative payment networks can be substantial.
Data and Information Providers
The bargaining power of data and information providers for BAC Holding International is generally considered moderate. Access to reliable economic data, credit scoring information, and market intelligence is crucial for risk assessment, product development, and strategic decision-making within the financial services sector. Providers offering specialized data, proprietary information, or unique analytical tools can exert this influence.
BAC's reliance on external data sources, such as consumption indices and economic forecasts, highlights their dependence on these providers. For instance, in 2024, the global market for financial data and analytics was valued at approximately $35 billion, indicating a significant industry with numerous players. Providers who can offer unique insights or data that directly impacts BAC's competitive advantage will hold more sway.
- Data providers with proprietary or exclusive datasets can command higher prices.
- The availability of alternative data sources can mitigate supplier power.
- BAC's ability to negotiate terms depends on the volume and criticality of the data it consumes.
- Specialized analytical tools offered by data providers can increase their leverage.
The bargaining power of suppliers for BAC Holding International is multifaceted, encompassing capital markets, technology providers, skilled labor, payment networks, and data providers.
In 2024, a stable Central American economic outlook and anticipated interest rate decreases are expected to reduce the bargaining power of capital market suppliers by lowering the cost of funding for BAC. However, the financial institution's reliance on specialized technology providers for digital transformation and cybersecurity systems grants these suppliers significant leverage, though the rise of composable architecture may offer some mitigation.
The availability of skilled professionals, particularly in digital and data-intensive roles, directly impacts BAC's operational capacity, with a scarcity empowering employees and potentially increasing labor costs, a critical factor given BAC's workforce exceeding 20,000 individuals.
Payment network operators like Visa and Mastercard hold substantial power due to their indispensable infrastructure for BAC's transaction processing, which facilitates billions of dollars annually. Data providers' influence is moderate, varying with the uniqueness and criticality of the information they supply, as evidenced by the global financial data market's estimated $35 billion valuation in 2024.
What is included in the product
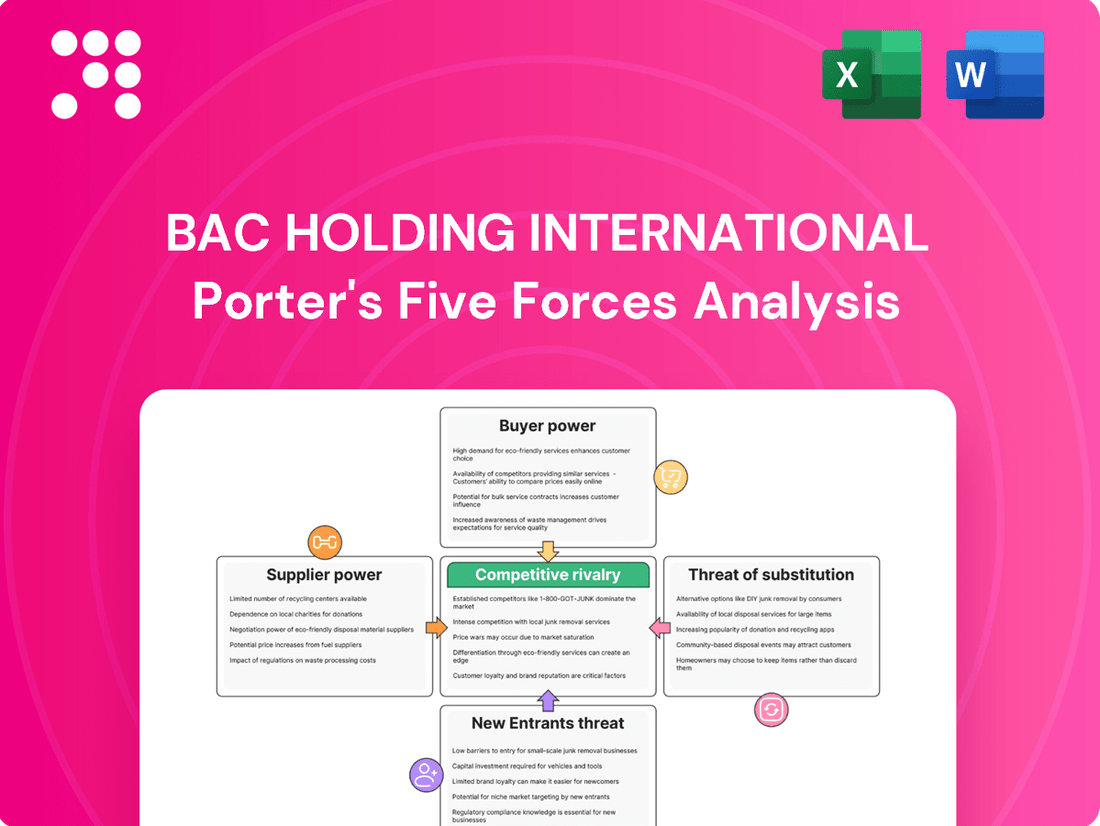
BAC Holding International's Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes on its profitability.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis, providing a clear roadmap to navigate market complexities.
Customers Bargaining Power
BAC Holding International's diverse customer base, spanning individual retail clients, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), and large corporations, significantly influences customer bargaining power. While individual retail customers might have limited sway due to smaller transaction volumes, their collective importance to BAC's deposit base and loan demand is substantial.
Large corporate clients, however, wield considerable leverage. Their higher transaction volumes and more intricate financial requirements mean they possess a greater ability to negotiate terms or switch to alternative financial institutions if dissatisfied. For instance, in 2024, large corporate banking relationships often involve customized pricing and service packages, reflecting the significant revenue potential each client represents.
For fundamental banking services like savings accounts and typical loans, customers often face minimal hurdles when switching providers, particularly with the growth of digital banking and aggressive pricing strategies. This ease of transition empowers customers, allowing them to easily shift their business to institutions offering more favorable terms or superior service. BAC Holding International's significant digital transaction volume, reaching 70% of total transactions in 2024, indicates a customer base well-acquainted with digital platforms, which can further simplify the process of migrating accounts.
Customers in the financial sector are increasingly empowered by readily available information. They can easily access details on interest rates, fees, and product features from numerous financial institutions, making comparison shopping a breeze. This heightened transparency directly fuels their ability to negotiate better terms.
For commoditized financial products, such as basic savings accounts or standard loans, price sensitivity among customers can be quite high. For instance, in 2024, average savings account interest rates across major banks hovered around 0.5% to 1%, with some online banks offering significantly higher yields, illustrating the competitive landscape. This compels BAC Holding International to adopt and maintain competitive pricing strategies to effectively retain its customer base.
Growth of Digital and Fintech Alternatives
The burgeoning fintech sector in Central America is significantly amplifying customer bargaining power. With a 25% surge in fintech companies between 2022 and 2023, customers now have a wider array of options beyond traditional BAC Holding International's offerings. These digital alternatives often present superior convenience, accessibility, and specialized financial solutions, empowering customers to switch providers if their needs aren't met.
This shift towards digital financial services means customers are less reliant on established institutions. They can readily compare and select fintech platforms that offer better rates, lower fees, or more user-friendly interfaces. This increased choice directly translates to greater leverage for customers when negotiating terms or demanding better service from any financial institution.
- Increased Customer Choice: Fintech growth provides alternatives to traditional banking.
- Convenience and Accessibility: Digital solutions often offer superior user experiences.
- Competitive Landscape: A 25% rise in Central American fintechs from 2022-2023 highlights this trend.
- Customer Leverage: More options empower customers to demand better terms and services.
Customer Loyalty and Relationship Banking
Established relationships and trust are key to customer loyalty in banking, even with more options available. BAC Holding International's strong presence and broad client network in Central America indicate deep-seated relationships, particularly for sophisticated corporate and investment banking needs. This loyalty can reduce the bargaining power of customers, as switching costs and the value of existing trust become significant factors.
In 2024, the financial services sector continued to see customers value personalized service and integrated solutions. For instance, a significant portion of customers in emerging markets, where BAC operates, prioritize convenience and established trust over solely seeking the lowest price. This loyalty is a critical factor in mitigating customer bargaining power.
- Customer Loyalty: BAC's extensive client base in Central America, cultivated over years, fosters loyalty, especially for complex financial needs.
- Relationship Banking: The bank's focus on building trust and offering integrated financial services strengthens customer ties, reducing their inclination to switch based on price alone.
- Mitigating Bargaining Power: Entrenched relationships and the perceived value of BAC's established network can limit the bargaining power of customers, particularly for corporate and investment banking services.
BAC Holding International faces moderate customer bargaining power, largely influenced by the ease of switching for basic services and the increasing availability of information and digital alternatives. While individual customers have limited sway, their collective impact is significant, and large corporate clients can negotiate favorable terms due to their substantial transaction volumes.
| Factor | Impact on BAC Holding International | Supporting Data/Trend (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Ease of Switching (Basic Services) | Moderate to High | Digital banking adoption at 70% of total transactions facilitates account migration. |
| Customer Information Availability | Moderate to High | Easy access to interest rates and fees from multiple institutions empowers comparison. |
| Fintech Competition | Moderate to High | 25% surge in Central American fintechs (2022-2023) offers customer alternatives. |
| Customer Loyalty & Relationships | Low to Moderate | Strong established relationships, especially for corporate needs, can mitigate switching. |
| Price Sensitivity (Commoditized Products) | Moderate to High | Savings account rates (0.5%-1%) highlight competitive pricing pressures. |
Full Version Awaits
BAC Holding International Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis for BAC Holding International, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring you get precisely what you need for your business strategy. This includes an in-depth examination of threats of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of substitute products or services, and intensity of rivalry among existing competitors within BAC Holding International's industry.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Central American financial market presents a dynamic competitive landscape for BAC Holding International. While dominant institutions like BAC exist, the market is also characterized by a significant number of local banks, other regional financial groups, and increasingly, agile fintech companies. This mix points to a degree of fragmentation, where numerous entities vie for market share.
Despite this fragmentation, a clear trend towards consolidation is observable. Traditional banks are actively seeking strategic alliances and mergers to enhance their competitive positioning and adapt to evolving market demands. Simultaneously, the growth of fintech startups introduces new competitive pressures, often forcing established players to innovate or partner.
Evidence of concentration in the broader Latin American financial technology sector, where the top five core banking system vendors hold a substantial 48% market share, suggests that similar dynamics of consolidation may be at play or will increasingly influence the Central American market. This indicates that while many players exist, a significant portion of the underlying technological infrastructure is controlled by a few key providers.
BAC Holding International faces significant competitive rivalry, particularly from established regional banks and the potential influx of international financial institutions. This dynamic intensifies competition for key customer segments and lucrative business lines.
As the leading financial group in Central America, BAC Holding International demonstrates a strong market position. However, this leadership also makes it a prime target for both existing regional competitors and global players looking to expand their footprint in promising markets.
The presence of strong regional and international players means BAC Holding must continuously innovate and offer competitive pricing and services to retain its market share. For instance, in 2023, the Central American banking sector saw increased activity from international investors, signaling a growing competitive landscape.
The banking landscape is fiercely competitive, with technological innovation and digital transformation serving as crucial differentiators. Banks and fintech companies are locked in a battle to provide customers with seamless digital experiences, highly efficient services, and tailored financial products. This intense rivalry necessitates continuous investment in cutting-edge technology.
BAC Holding International is actively addressing this competitive pressure through substantial investments in its digital infrastructure. By March 2025, the company reported that an impressive 95% of its transactions were conducted digitally. This statistic underscores BAC's commitment to meeting evolving customer expectations and staying ahead in a digitally driven market.
Macroeconomic Conditions and Market Growth
The competitive rivalry within BAC Holding International is significantly shaped by the macroeconomic conditions and market growth prospects across Central America. A robust economic expansion generally dilutes competitive intensity as a larger pie can satisfy more participants. However, periods of slower growth or economic instability can exacerbate competition as firms fight more aggressively for existing market share.
Looking ahead, forecasts for Central American GDP growth paint a generally positive picture for 2024 and 2025, which could temper rivalry. For instance, projections indicate that Central America’s GDP growth is expected to average around 3.5% in 2024, a slight uptick from previous years, potentially creating more room for all players.
- Economic Growth Trajectory: Central American economies are projected to see continued, albeit varied, GDP growth through 2024 and 2025, which can influence the intensity of competition.
- Market Saturation and Share: As markets expand, the pressure to gain or defend market share might lessen, but in slower growth phases, rivalry can sharpen considerably.
- Regional Economic Stability: Fluctuations in economic stability and political environments across Central American nations can introduce volatility, impacting strategic decisions and competitive dynamics.
- Impact on Investment: Favorable macroeconomic conditions encourage investment, potentially leading to new entrants or increased capacity from existing players, thereby affecting rivalry levels.
Regulatory Landscape and Compliance Costs
The regulatory environment significantly shapes competition in the banking sector. Stringent capital requirements, robust consumer protection laws, and rigorous anti-money laundering (AML) regulations are critical. For instance, in 2024, major banks like BAC Holding International continue to navigate complex compliance frameworks, which can involve substantial operational costs.
Adherence to these rules presents a cost burden, particularly for smaller financial institutions. However, these same regulations can also act as a barrier to entry, indirectly benefiting larger, established entities like BAC by creating a more stable, albeit costly, competitive landscape. BAC Holding International is indeed subject to consolidated supervision of banking groups, impacting its operational strategies.
- Capital Requirements: Basel III reforms, still being fully implemented in many jurisdictions through 2024, mandate higher capital ratios, affecting how banks allocate resources.
- Consumer Protection: Regulations like the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) rules in the US aim to ensure fair treatment of customers, adding compliance overhead.
- AML/KYC: Anti-money laundering and Know Your Customer (KYC) compliance costs for global banks can run into billions annually, a significant operational expense.
- Supervisory Oversight: BAC's adherence to consolidated supervision means its entire group's financial health and risk management practices are under scrutiny, demanding consistent compliance across all subsidiaries.
BAC Holding International operates in a highly competitive Central American financial market, facing rivalry from established regional banks, local institutions, and emerging fintech players. This intense competition is further fueled by ongoing market consolidation and the need for continuous technological innovation to meet evolving customer demands.
The company's leadership position makes it a target for both existing competitors and international firms seeking market entry, necessitating a focus on competitive pricing and service differentiation. For instance, in 2023, international investor activity in the Central American banking sector increased, highlighting a growing competitive dynamic.
BAC Holding International's significant investment in digital transformation, with 95% of its transactions conducted digitally by March 2025, is a direct response to this rivalry, aiming to enhance customer experience and operational efficiency.
Economic growth projections for Central America, with an estimated GDP growth of around 3.5% in 2024, could potentially temper competitive intensity by expanding the market pie for all participants.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant threat of substitution for BAC Holding International stems from the rapid advancement of fintech solutions. Digital wallets, mobile payment applications, and online lending platforms present convenient and often more affordable alternatives to conventional banking services, especially for routine transactions and smaller credit needs.
These fintech innovations directly challenge traditional banking models by offering streamlined user experiences and potentially lower fees. For instance, the number of fintech companies operating in Central America saw a notable increase of 25% between 2022 and 2023, highlighting their expanding reach and competitive pressure.
Cryptocurrencies and decentralized finance (DeFi) present a growing threat to traditional financial institutions. While still developing, these technologies offer alternative methods for value transfer and investment, potentially bypassing established banking systems. For instance, in 2023, the global cryptocurrency market capitalization fluctuated significantly but remained in the trillions, indicating substantial investor interest and a growing ecosystem.
The allure of lower transaction fees and increased accessibility makes blockchain-based finance a compelling substitute. In Latin America, a region with a significant unbanked population, fintech innovation, including blockchain solutions, is particularly robust. Reports from late 2023 and early 2024 highlight increasing adoption rates for digital payments and crypto-based remittances in several Latin American countries, suggesting a tangible shift in consumer behavior.
Informal lending and community-based financial services present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional banking, especially in Central America. These alternatives, often rooted in family or community ties, cater to populations and small businesses underserved by formal institutions. For example, in 2024, a substantial portion of the population in some Central American nations still relies on these informal channels due to historical low bank penetration rates, which hover around 40-50% in certain rural areas.
Direct Investment and Self-Financing
For individuals and businesses possessing ample capital, direct investments in assets outside of traditional banking or the option to self-finance business ventures present viable substitutes for conventional investment products and corporate loans. This bypasses the need for intermediaries like BAC Holding International.
As wealth management markets continue their expansion across Latin America, a growing segment of investors are actively exploring alternative assets that lie beyond the typical offerings provided by banks. This trend suggests a potential shift in demand away from traditional banking services.
- Direct Investment in Alternative Assets: Investors are increasingly allocating capital to real estate, private equity, venture capital, and commodities, seeking higher returns or diversification.
- Self-Financing Growth: Businesses with strong cash flow are opting to fund expansion and operational needs internally, reducing reliance on external debt financing.
- Latin American Wealth Growth: The region's wealth management market is projected to see significant growth, with estimates suggesting assets under management could reach trillions by the end of the decade, fueling demand for diverse investment avenues.
- Investor Appetite for Non-Traditional Products: A notable percentage of high-net-worth individuals in Latin America express interest in exploring investment opportunities outside of traditional bank-managed portfolios.
Non-financial Companies Offering Financial Services
Large technology and e-commerce giants are increasingly embedding financial services directly into their platforms, creating a significant substitution threat. These companies, like Amazon with its payment and lending services or Apple with Apple Pay and Apple Card, leverage vast existing customer bases and rich data to offer seamless financial solutions.
This trend blurs traditional industry boundaries, presenting an indirect competitive challenge to established financial institutions. For instance, by 2025, integrated payment solutions and socially driven payment systems are anticipated to see further evolution, making it easier for consumers to manage finances without directly engaging with traditional banks.
- Embedded Finance Growth: Companies like Square and PayPal have already demonstrated the power of integrated financial tools, with PayPal reporting over $1.3 trillion in total payment volume in 2023.
- Data Advantage: Tech firms possess unparalleled customer data, enabling highly personalized and targeted financial product offerings.
- Evolving Payment Systems: Trends point towards more sophisticated payment functionalities, including buy now, pay later (BNPL) integrations and peer-to-peer payment networks, which can bypass traditional banking channels.
- Industry Convergence: The financial services sector is witnessing a convergence with technology, where non-financial entities are becoming significant players in payment processing, lending, and even investment management.
The threat of substitutes for BAC Holding International is substantial, driven by the rise of fintech and alternative financial solutions. These substitutes offer convenience, lower costs, and increased accessibility, directly challenging traditional banking models.
Fintech innovations like digital wallets and online lending platforms are gaining traction, especially among younger demographics and for smaller transactions. In 2023, the global fintech market was valued at over $115 billion, demonstrating its significant and growing impact.
Cryptocurrencies and decentralized finance (DeFi) also represent a growing substitution threat, offering alternative means of value transfer and investment that can bypass traditional financial intermediaries. The total value locked in DeFi protocols reached hundreds of billions of dollars in late 2023, indicating substantial user adoption and capital flows.
Furthermore, informal lending networks and self-financing options are prevalent, particularly in regions with lower traditional banking penetration. For instance, in certain Latin American countries, a considerable percentage of the population still relies on informal financial channels, highlighting a persistent demand for alternatives.
| Substitute Category | Key Offerings | Impact on Traditional Banking | Growth Indicator (2023/2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fintech Solutions | Digital Wallets, Mobile Payments, Online Lending | Reduced transaction volume, competition for retail banking | Fintech market valued over $115 billion |
| Cryptocurrencies & DeFi | Decentralized exchanges, Stablecoins, Lending Protocols | Potential disintermediation, alternative investment channels | DeFi Total Value Locked in hundreds of billions USD |
| Informal Finance | Community lending, Peer-to-peer loans | Captures unbanked/underbanked segments, local market share | Significant reliance in certain Latin American regions |
| Embedded Finance | Financial services within non-financial platforms | Erosion of customer relationships, new competitive landscape | PayPal's total payment volume exceeded $1.3 trillion |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the traditional banking sector, like the one BAC Holding International operates in, demands significant upfront capital. This includes building and maintaining physical branches, investing in robust IT systems, and meeting stringent regulatory requirements, which can easily run into hundreds of millions or even billions of dollars.
These substantial capital barriers act as a powerful deterrent for many aspiring new players. For instance, BAC Holding International, as of the first quarter of 2024, reported total assets exceeding $38.4 billion, underscoring the immense scale of financial resources typically needed to compete effectively in this industry.
The financial sector, including entities like BAC Holding International, operates under a strict regulatory umbrella. This involves significant licensing prerequisites, ongoing compliance duties such as anti-money laundering protocols and consumer protection measures, and continuous oversight from governing bodies. For instance, BAC Holding International is subject to comprehensive regulations by the Superintendency of Banks of Panama.
Established financial institutions like BAC Holding International have cultivated significant brand recognition and customer trust over many years, making it a formidable barrier for new entrants. This deep-seated trust is crucial in the financial sector, where customers prioritize security and reliability, often sticking with familiar names for their banking and investment needs.
BAC Holding International, for instance, serves over 5 million clients, a testament to its established presence and the loyalty it commands. Replicating this level of trust and widespread recognition requires substantial time, investment, and a proven track record, which new competitors typically lack from the outset.
Economies of Scale and Distribution Networks
Existing players in the financial services sector, like BAC Holding International, benefit significantly from economies of scale. This allows them to spread costs across a larger volume of operations, technology investments, and marketing efforts, ultimately enabling more competitive pricing and a broader service offering.
Establishing extensive branch networks and robust digital distribution channels, as BAC has diligently built across Central America, represents a substantial capital outlay and a considerable time commitment. This infrastructure is a key deterrent for potential newcomers.
BAC's dominant position, evidenced by its 53% share of Central America's GDP in payment processing, creates formidable entry barriers. This market penetration means new entrants would face immense challenges in achieving comparable reach and customer adoption.
- Economies of Scale: BAC leverages scale in operations, technology, and marketing to offer competitive pricing.
- Distribution Networks: Significant investment in physical and digital channels across Central America acts as a barrier.
- Market Share: BAC's 53% share of Central America's GDP in payments demonstrates a strong competitive advantage.
Emergence of Fintechs and Niche Players
While traditional banking often involves substantial regulatory hurdles and capital requirements, the financial technology (fintech) landscape presents a different story. Agile fintech firms are increasingly challenging established players by focusing on specific market segments or employing innovative technologies. For instance, neobanks, which often operate without a traditional banking license, are making inroads by offering streamlined digital services, particularly to underserved populations.
The growing influence of these specialized companies is evident in market expansion. In Central America, the number of fintech companies saw a notable increase of 25% between 2022 and 2023, indicating a dynamic and evolving competitive environment.
- Fintechs bypass traditional licensing for niche services.
- Neobanks offer accessible financial solutions.
- Central American fintech sector grew 25% from 2022 to 2023.
- Agile startups disrupt established banking models.
The threat of new entrants for BAC Holding International is moderately high, primarily due to the rise of agile fintech companies that bypass traditional barriers. While significant capital and regulatory hurdles exist for new traditional banks, fintechs are innovating to offer specialized services, often targeting underserved markets.
These new players, particularly neobanks, are leveraging technology to provide streamlined digital experiences, challenging incumbents like BAC. The fintech sector's growth, exemplified by a 25% increase in Central America between 2022 and 2023, highlights the increasing competitive pressure from these less encumbered entrants.
Despite BAC's established scale, brand loyalty, and extensive distribution networks, the disruptive potential of fintechs remains a key consideration. Their ability to innovate and adapt quickly allows them to chip away at market share, particularly in digital-first customer segments.
| Factor | Impact on BAC | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High barrier for traditional banks. | BAC's established capital base provides a buffer. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Significant compliance costs for new entrants. | BAC's experience navigating regulations is an advantage. |
| Fintech Innovation | Lower barriers for specialized digital services. | BAC can partner with or acquire fintechs, or enhance its own digital offerings. |
| Brand Loyalty & Trust | Established players like BAC benefit from customer confidence. | Continued investment in customer service and security to maintain trust. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for BAC Holding International is built upon a foundation of industry-specific market research reports, financial statements from publicly traded competitors, and regulatory filings to capture the competitive landscape accurately.
