111 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
111 Bundle
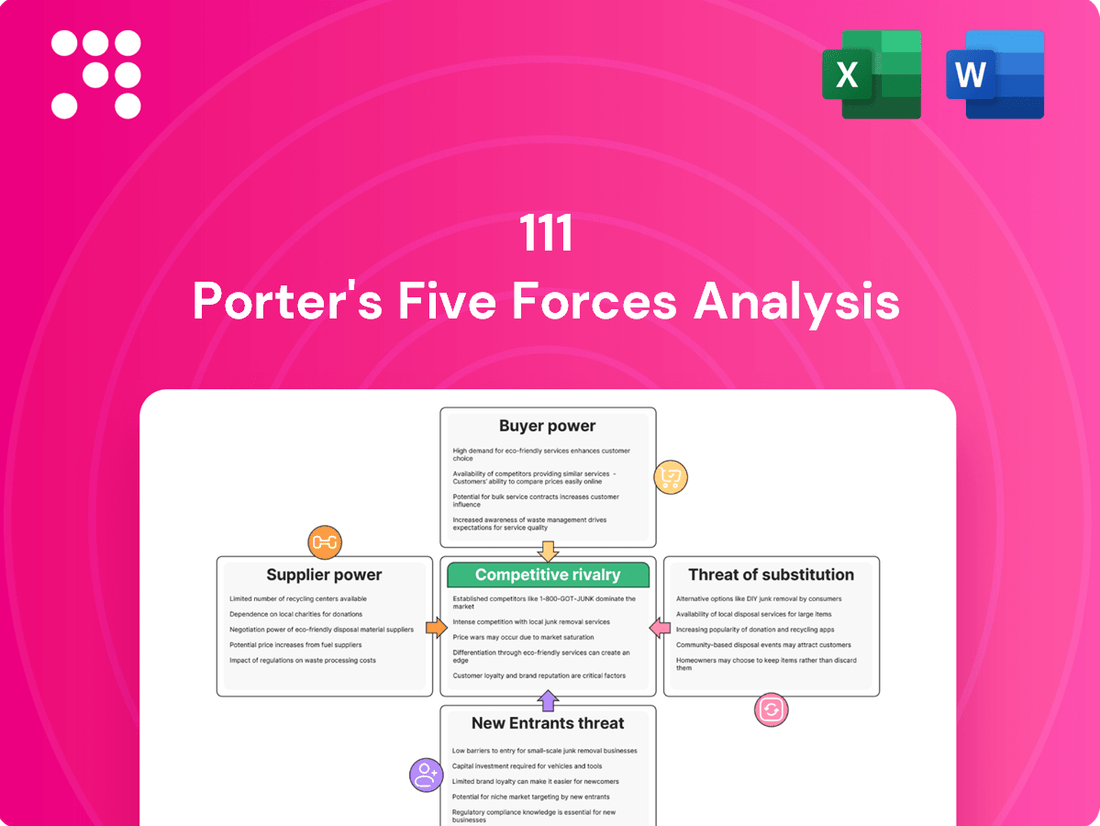
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface of the competitive landscape surrounding 111. Understanding the interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, the threat of new entrants, the intensity of rivalry, and the impact of substitutes is crucial for strategic success. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore 111’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail, empowering you to make informed decisions.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of pharmaceutical manufacturers for 111, Inc. is generally moderate to high, particularly for drugs protected by patents or those with specialized applications. 111, Inc.'s need for a broad and up-to-date pharmaceutical catalog to cater to both its online and physical pharmacy customers means it must secure supply from these entities. However, 111's substantial and expanding sales volume could offer some negotiation leverage.
China's pharmaceutical sector is experiencing a significant increase in both the approval of new medications and advancements in domestic drug development. This trend is expected to broaden the range of supplier choices available to 111, Inc. in the coming years, potentially shifting the balance of power.
Technology and software providers, particularly those offering core solutions like AI, cloud infrastructure, and telemedicine platforms, generally exert moderate bargaining power. 111, Inc. is significantly dependent on these technologies for its operations, which include connecting patients, doctors, and pharmacies, as well as boosting efficiency.
While the integration of complex systems can lead to substantial switching costs, the growing maturity and diversification of China's tech landscape mean that alternative vendors are increasingly available, thus tempering supplier leverage. For instance, the Chinese cloud computing market, a key area for 111, Inc., saw significant growth, with major players like Alibaba Cloud, Tencent Cloud, and Huawei Cloud competing fiercely, offering more choices and potentially better terms to large clients.
The bargaining power of logistics and delivery partners for 111 is generally considered moderate. While a robust and efficient delivery network is absolutely crucial for their online pharmacy operations and extensive chain of retail drugstores, particularly within a geographically diverse market like China, the logistics sector itself is quite competitive.
This competitive landscape means that individual logistics providers may not possess overwhelming power to dictate terms. However, the sheer scale and complexity of delivering pharmaceuticals across China mean that reliable and specialized logistics are essential, which can still give some leverage to established players.
To mitigate this, 111 has made significant investments in its own national logistics network, named 'Penglai.' This strategic move is designed to lessen dependence on third-party providers, enhance operational efficiency, and ultimately gain more control over delivery costs and quality. For instance, in 2023, 111 reported that its logistics network played a key role in expanding its reach, handling millions of orders.
Medical Device Suppliers
Suppliers of specialized medical devices can hold considerable sway, especially when their products are critical and have few substitutes. This is particularly true for high-end equipment that requires significant research and development. For a company like 111, Inc., managing these supplier relationships is key to cost control and product availability.
The Chinese online pharmacy market, a significant sector where medical devices played a substantial role in 2023, underscores the demand for these products. 111, Inc.'s reliance on these suppliers means that securing advantageous terms is essential for maintaining competitive pricing and profitability in such a dynamic market.
- Supplier Concentration: The number of suppliers for specialized medical devices is often limited, increasing their bargaining power.
- Product Differentiation: Highly innovative or proprietary medical equipment offers suppliers a distinct advantage.
- Switching Costs: The expense and complexity associated with changing suppliers for critical medical devices can be substantial.
- Importance of Product: If a supplier's product is a vital component for a medical device manufacturer, their leverage increases.
Healthcare Professionals (Doctors for Consultation Services)
The bargaining power of doctors offering online consultation and prescription services for platforms like 111, Inc. is generally considered moderate. A robust network of qualified medical professionals is fundamental to the success of any internet hospital model, such as 111's '1 Clinic'.
The sheer number of available doctors and the platform's capacity to consolidate patient demand can somewhat dilute the leverage of any single physician. However, the ongoing need to attract and retain high-caliber medical talent means that individual doctors, especially specialists, can still exert considerable influence.
For instance, in 2024, the demand for telemedicine services continued to surge, with reports indicating that over 80% of consumers who used telehealth in 2020 continued to do so. This sustained demand means that platforms must offer competitive terms to secure a consistent supply of quality medical expertise.
- Doctor Availability: A large pool of general practitioners and specialists reduces individual doctor leverage.
- Platform Aggregation: 111's ability to channel patient volume to doctors can increase its negotiating power.
- Talent Acquisition: The need for specialized or highly sought-after doctors can shift bargaining power towards the physicians.
- Market Competition: The presence of numerous other telemedicine platforms creates a competitive environment for doctor recruitment, influencing compensation and terms.
The bargaining power of suppliers is a crucial element in understanding industry profitability. When suppliers have significant leverage, they can command higher prices for their inputs, thereby reducing the profitability of the firms they supply. This power is amplified when there are few suppliers, the inputs are critical, or switching costs are high.
In 2024, the pharmaceutical supply chain continued to be a key area of focus. For instance, the increasing consolidation among active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) manufacturers in certain therapeutic areas could grant these suppliers greater pricing power. Conversely, advancements in generic drug development and increased regulatory approvals for biosimilars in markets like China can introduce more competition, potentially diluting supplier leverage.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power (2024 Estimate) | Key Factors Influencing Power |
|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical Manufacturers (Patented Drugs) | High | Limited substitutes, patent protection, high R&D costs |
| Technology Providers (Cloud, AI) | Moderate to High | Critical infrastructure, integration complexity, vendor lock-in |
| Logistics & Delivery Services | Moderate | Competitive market, but essential for reach; specialized pharma logistics command a premium |
| Medical Device Suppliers (Specialized) | High | Product differentiation, high switching costs, essential for patient care |
| Doctors (Telemedicine) | Moderate | Platform aggregation vs. specialized expertise, competition for talent |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the competitive intensity for 111 by examining industry rivalry, the threat of new entrants, buyer and supplier power, and the threat of substitutes.
Identify and mitigate competitive threats with a comprehensive overview of all five forces, enabling proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of individual patients is significant, driven by the proliferation of online and offline healthcare options and the ease with which they can switch providers. In 2024, Chinese consumers, particularly the digitally native younger generations, prioritize convenience, cost-effectiveness, and reliability when selecting healthcare services. This means they actively compare prices and service quality across a multitude of platforms before making a decision.
Customers within 111's '1 Drugstores' network, which are offline pharmacies utilizing 111's cloud services and wholesale platform, possess moderate bargaining power. While 111 provides a convenient 'one-stop shop' for product sourcing and omni-channel support, these pharmacies can still explore alternative suppliers for their needs.
The significant variety of products and efficient services offered by 111 are key factors in retaining these pharmacy partners, thereby mitigating some of their bargaining leverage. For instance, in 2023, 111 reported a 15% increase in the number of pharmacies actively using its wholesale platform, indicating a strong value proposition for these customers.
Hospitals and larger clinics, while not 111, Inc.'s core market, could become significant customers for platform services or bulk drug purchasing. Their bargaining power is substantial, stemming from their immense purchasing volume and established connections with drug manufacturers. In 2024, the global hospital market was valued at over $9 trillion, highlighting the scale of these potential clients.
Corporate Clients (for Employee Healthcare)
Corporate clients, when considering 111, Inc. for employee healthcare solutions, would wield considerable bargaining power. Their primary drivers are cost-effectiveness, comprehensive service offerings, and high-quality care for a substantial employee base. These large employers would actively seek customized plans and competitive pricing, often prioritizing preventive care initiatives.
The bargaining power of these corporate clients stems from several factors:
- Concentration of Buyers: Large corporations represent significant contract values, giving them leverage in negotiations.
- Information Availability: Companies have access to market data on healthcare costs and service providers, enabling them to negotiate from an informed position.
- Low Switching Costs: While not insignificant, the process of changing benefits providers is manageable for large organizations, especially if a competitor offers compelling terms. For instance, in 2023, a significant portion of large employers (over 500 employees) reviewed their benefits providers annually, indicating a willingness to switch for better value.
- Price Sensitivity: Employee benefits represent a substantial operating expense, making corporations highly sensitive to pricing and the overall return on investment in healthcare programs.
Price Sensitivity and Information Availability
Chinese consumers, especially in the wellness sector, are exhibiting heightened price sensitivity. This is compounded by an increasing emphasis on product quality and health benefits. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 60% of Chinese consumers actively compare prices online before making a purchase in the health and wellness category.
The proliferation of e-commerce platforms and social media channels significantly boosts customer bargaining power. Consumers can effortlessly compare prices, read reviews, and seek health advice from influencers, making them more informed and demanding. This digital transparency means companies like 111 must remain competitive and upfront about their offerings.
- Price Sensitivity: Chinese consumers are increasingly price-conscious, especially in the health and wellness market.
- Information Accessibility: Online platforms and social media provide easy price and service comparisons, empowering buyers.
- Digital Influence: The reliance on social media for health advice means customer perceptions can shift rapidly based on online trends and influencer recommendations.
- Competitive Imperative: To counter this, 111 needs to consistently offer competitive pricing and maintain transparent service delivery.
Customers, particularly individual consumers in China's burgeoning health and wellness market, wield considerable bargaining power. This is fueled by a wealth of readily available information, enabling them to compare prices and quality across numerous online and offline channels. In 2024, over 60% of Chinese consumers actively researched prices online before purchasing health products, demonstrating a strong price sensitivity.
Pharmacies within 111's network, while benefiting from its one-stop sourcing and support, retain moderate bargaining power as they can explore alternative suppliers. However, 111's increasing platform adoption, with a 15% rise in active pharmacies in 2023, suggests a strong value proposition that mitigates this power. Large corporate clients seeking employee healthcare solutions possess significant leverage due to their substantial purchasing volumes and focus on cost-effectiveness and comprehensive benefits.
The bargaining power of customers is amplified by digital transparency and the ease of switching providers. Companies like 111 must therefore focus on competitive pricing and consistent, high-quality service delivery to retain their customer base. The sheer scale of potential clients like hospitals, representing a global market valued over $9 trillion in 2024, underscores the importance of understanding and managing customer bargaining power.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Drivers | 2023/2024 Data/Trends |
|---|---|---|
| Individual Consumers (China) | Price sensitivity, information availability (online comparison), digital influence | Over 60% actively compare prices online for health/wellness products (2024). |
| 111 '1 Drugstores' Network | Ability to source from alternatives, but mitigated by 111's value proposition | 15% increase in active pharmacies on wholesale platform (2023). |
| Large Corporate Clients | High purchasing volume, focus on cost-effectiveness, low switching costs for benefits providers | Significant portion of large employers review benefits providers annually (2023). |
| Hospitals/Large Clinics | Immense purchasing volume, established manufacturer relationships | Global hospital market valued over $9 trillion (2024). |
Same Document Delivered
111 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete 111 Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within an industry. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted and ready-to-use analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises or placeholders.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The competitive landscape for 111, Inc. in China's healthcare sector is highly contested. This market features a substantial number of participants, ranging from digital behemoths like Alibaba Health and JD Health to established brick-and-mortar pharmacy chains that have expanded their online reach, alongside niche internet hospitals. This diverse array of competitors creates a dynamic and challenging environment.
The China online healthcare market is booming, projected to hit US$583.68 billion by 2028, growing at a robust 36.89% compound annual growth rate from 2024 to 2028. This rapid expansion is a magnet for new entrants and existing companies alike.
With such strong growth, fueled by an aging demographic and favorable government policies, the market becomes incredibly attractive. This high attractiveness naturally intensifies competitive rivalry as more players enter, all eager to capture a piece of this expanding and profitable sector.
Product and service differentiation is absolutely key in today's competitive environment. 111, Inc. is really leaning into its unique integrated online-offline model. They're using advanced tech like AI to streamline operations and make patient interactions smoother, plus they've built a really broad virtual pharmacy network.
Other players in the market aren't standing still, of course. Many are also pouring resources into technology, offering online consultations, and beefing up their digital health infrastructure. This means companies like 111, Inc. need to constantly find ways to offer something truly special to stand out.
Switching Costs for Customers
Customer switching costs in the online healthcare sector, particularly for platforms like 111, Inc., are generally quite low. Patients can readily access and utilize various health apps for consultations, prescription refills, or other services without significant hurdles.
This ease of switching compels companies to focus on delivering superior service and competitive pricing. For instance, in 2024, the digital health market saw continued growth, with numerous new entrants offering similar services, intensifying the need for customer retention strategies. Platforms must constantly innovate to maintain user engagement and loyalty.
- Low Friction: Patients can easily switch between telehealth providers or pharmacy apps.
- Competitive Pressure: Low switching costs force platforms to offer better value and service.
- Innovation Imperative: Continuous improvement is necessary to retain users in a crowded market.
Regulatory Environment and Policy Influence
China's government actively champions the 'Internet plus Healthcare' initiative, aiming to modernize its healthcare system. However, this push is balanced by strict regulations governing online pharmacies and the sale of pharmaceuticals. This dual approach significantly influences competitive rivalry by creating a more favorable environment for established companies that can navigate compliance, while potentially posing challenges for new entrants or those with less robust operational frameworks.
The regulatory landscape directly impacts market entry and operational strategies. Companies must invest in compliance infrastructure and adapt their business models to meet evolving government standards. For instance, the China Food and Drug Administration (CFDA) has progressively tightened rules around the online distribution of prescription drugs, requiring specific licenses and quality control measures. These policies can therefore consolidate market power among those best equipped to meet these demands.
- Policy Support for Innovation: Government policies often provide incentives and support for the development and adoption of innovative drugs and medical equipment. This can create opportunities for companies at the forefront of technological advancement in healthcare.
- Regulatory Hurdles for Online Sales: Stringent regulations on online pharmacies and drug sales can limit the competitive scope for digital health platforms, favoring those with established physical presences or those who can meet rigorous compliance requirements.
- Impact on Market Entry: The complexity of navigating China's healthcare regulations can act as a barrier to entry for new players, thereby reducing the intensity of rivalry among less established firms.
- Influence on Pricing and Distribution: Government policies can also influence pricing strategies and distribution channels for healthcare products and services, further shaping the competitive dynamics within the sector.
The competitive rivalry within China's burgeoning online healthcare market is intense, driven by rapid growth and numerous players. Companies like 111, Inc. face stiff competition from digital giants and established pharmacies expanding online, necessitating constant innovation and differentiation.
The market's projected growth to US$583.68 billion by 2028, with a 36.89% CAGR from 2024-2028, attracts a constant influx of new entrants. This high market attractiveness fuels aggressive competition as companies vie for market share.
Low customer switching costs in this sector mean platforms must excel in service and pricing to retain users. Continuous technological investment and unique service offerings are vital for standing out amidst a crowded marketplace, especially with new competitors emerging throughout 2024.
Government initiatives like 'Internet plus Healthcare' promote digital health, but strict regulations on online pharmacies and drug sales create a complex operating environment. Navigating these rules favors established players, potentially consolidating market power.
| Key Competitors in China's Online Healthcare Market (2024) | Key Offerings | Market Position/Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Alibaba Health | Online pharmacy, telehealth, health management services | Leverages e-commerce ecosystem, strong brand recognition |
| JD Health | Online pharmacy, telehealth, chronic disease management | Integrated online-offline model, robust logistics |
| 111, Inc. | Integrated online-offline pharmacy, virtual pharmacy network, AI-driven operations | Focus on technological integration and patient experience |
| Established Pharmacy Chains (e.g., Yifeng Pharmacy, Guoda Drugstores) | Expanding online presence, omnichannel retail | Leveraging existing physical footprint and customer base |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Traditional physical pharmacies represent a significant threat of substitutes for online healthcare platforms like 111, Inc. These brick-and-mortar stores cater to consumers seeking immediate medication, personalized advice from pharmacists, and the tangible experience of browsing products. In 2024, China's vast retail pharmacy network, with tens of thousands of locations, continues to offer a convenient and familiar alternative for many.
Public hospitals, especially in China, act as a significant substitute for services like 111's. They are often the first stop for many seeking medical advice and prescriptions, offering direct consultations and medication dispensing. This accessibility makes them a strong alternative to online platforms.
The Chinese government's initiative to enhance community health centers further strengthens this substitution threat. These upgraded centers provide more localized and accessible healthcare, potentially drawing patients away from online services and even traditional hospitals for less severe ailments.
The threat of substitutes for platforms like 111, Inc. is moderate due to the potential for pharmaceutical manufacturers to develop their own direct-to-consumer (DTC) sales channels. This bypasses intermediaries, allowing manufacturers to control the customer experience and potentially capture higher margins. As of early 2024, several major pharmaceutical companies have been exploring or piloting DTC initiatives, particularly for over-the-counter (OTC) medications and certain health devices, indicating a growing trend.
Self-Medication and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)
The threat of substitutes for online healthcare services in China is significant, particularly from self-medication and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). For minor health issues, many consumers opt for readily available over-the-counter medications or turn to established TCM practices. This trend is further bolstered by government support for TCM, which includes subsidies, and a growing consumer interest in preventative health and lifestyle adjustments, potentially decreasing the demand for more formal medical interventions.
In 2023, the Chinese OTC drug market was valued at approximately $45 billion, demonstrating the scale of self-medication. Furthermore, TCM continues to hold a strong cultural and practical relevance, with government initiatives aimed at modernizing and promoting its integration into the healthcare system. For instance, the National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine has been actively encouraging innovation and internationalization of TCM, suggesting continued investment and consumer engagement.
These substitutes offer a lower cost and often more convenient alternative for consumers, especially when dealing with non-critical ailments. The accessibility of both OTC drugs and TCM, combined with their deep roots in Chinese culture and increasing government backing, presents a substantial challenge to the market share of online medical consultation platforms and prescription drug sales.
- Self-Medication Prevalence: Over-the-counter drugs are a common first line of defense for minor ailments in China.
- TCM's Growing Influence: Government subsidies and a focus on holistic well-being are enhancing TCM's appeal.
- Consumer Behavior Shift: Increased emphasis on preventive care and lifestyle changes can bypass the need for some online medical services.
- Market Size: The Chinese OTC market reached around $45 billion in 2023, highlighting the strength of self-treatment options.
Alternative Digital Health Solutions (e.g., standalone apps)
The threat of substitutes for integrated digital health platforms in China is significant due to the burgeoning market for specialized, standalone applications. These apps, covering areas from telemedicine to AI-driven diagnostics, offer a focused user experience that can directly compete with broader platforms. For instance, in 2023, the Chinese digital health market saw substantial growth, with telemedicine services alone experiencing a surge in user adoption, indicating a clear preference for niche solutions among consumers.
These specialized digital health solutions can erode the market share of comprehensive platforms by providing a more tailored and often more cost-effective alternative for specific health needs. Users might opt for a dedicated AI diagnostic tool rather than a general health management app if it offers superior accuracy or a more intuitive interface for that particular function. This trend is amplified by the increasing availability of venture capital funding for these niche players, allowing them to innovate rapidly and capture specific market segments.
- Proliferation of Niche Apps: China's digital health landscape is increasingly populated by single-purpose applications, such as those for chronic disease management or mental wellness.
- User Preference for Specialization: Consumers are demonstrating a willingness to adopt specialized apps if they offer a demonstrably better solution for a specific health concern.
- Competitive Pricing: Standalone apps may offer more competitive pricing models compared to the bundled services of larger platforms, attracting price-sensitive users.
- Partnership vs. Substitution: While some niche apps partner with larger platforms, many operate independently, directly substituting for platform-offered services.
The threat of substitutes for online healthcare platforms like 111 is multifaceted, encompassing traditional brick-and-mortar pharmacies, public hospitals, and even self-medication practices. These alternatives offer convenience, immediate access, and established trust, particularly for routine ailments.
The Chinese market, for example, saw its over-the-counter (OTC) drug market valued at approximately $45 billion in 2023, underscoring the significant role of self-medication. Furthermore, Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) continues to be a strong substitute, bolstered by government support and cultural relevance, with initiatives to modernize and promote its integration into the healthcare system.
Specialized, standalone digital health applications also pose a considerable threat. These niche apps, focusing on areas like telemedicine or AI diagnostics, offer tailored user experiences that can directly compete with broader platforms. The substantial growth in China's digital health market in 2023, with telemedicine services alone seeing a surge in user adoption, highlights a consumer preference for these focused solutions.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | 2023/2024 Data Points |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Pharmacies | Immediate access, pharmacist advice, tangible experience | Tens of thousands of locations in China |
| Public Hospitals | Direct consultation, prescription dispensing, established trust | Primary healthcare providers for many |
| Self-Medication (OTC) | Low cost, convenience for minor ailments | Chinese OTC market valued at ~$45 billion (2023) |
| Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) | Cultural relevance, holistic approach, government support | Government initiatives promoting modernization and integration |
| Specialized Digital Health Apps | Focused functionality, tailored experience, potential cost-effectiveness | Significant growth in China's digital health market (2023) |
Entrants Threaten
Entering China's integrated online and offline healthcare platform market demands significant capital. Companies need to invest heavily in developing advanced technology platforms, building an extensive and efficient logistics network, and acquiring or partnering with numerous physical retail pharmacy locations. For instance, establishing a nationwide presence often requires hundreds of millions of dollars in initial investment, covering everything from software development to physical infrastructure and inventory.
China's pharmaceutical and healthcare sectors present formidable barriers to entry due to intricate and frequently updated regulations. New entrants face significant challenges in obtaining the necessary licenses for online pharmacies, internet hospitals, and the sale of pharmaceuticals. For instance, the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) continuously refines guidelines for online drug sales and patient data handling, demanding substantial compliance investments.
Building trust and brand loyalty in healthcare, especially in markets like China where online health service confidence can be shaky, is a significant hurdle for newcomers. Established companies like 111, Inc. possess a considerable edge due to their existing reputation and patient trust, which new entrants find challenging to overcome rapidly.
Economies of Scale and Network Effects
Existing players like 111, Inc. leverage significant economies of scale, particularly in areas like bulk procurement of pharmaceuticals and efficient logistics for their virtual pharmacy network. This scale allows them to negotiate better prices and streamline operations, creating a cost advantage that is difficult for newcomers to match.
Furthermore, strong network effects are at play. 111's established relationships with a wide array of doctors, pharmaceutical manufacturers, and a large customer base create a self-reinforcing cycle of value. As more users and partners join the platform, its utility and attractiveness increase, making it harder for new entrants to gain traction without substantial initial investment to build a comparable network.
For instance, in 2024, 111, Inc. reported a 15% year-over-year increase in its active user base, highlighting the growing strength of its network. This growth directly translates into greater bargaining power with suppliers and more attractive service offerings for consumers, further solidifying its market position against potential new entrants.
- Economies of Scale: Reduced per-unit costs through large-scale operations in procurement and logistics.
- Network Effects: Increased value of the platform as more users and partners join, creating a barrier to entry.
- Established Relationships: 111's existing partnerships with healthcare providers and pharmaceutical companies are a significant asset.
- Customer Acquisition Cost: New entrants face high costs to build a customer base comparable to 111's existing network.
Access to Talent and Partnerships
Attracting and retaining skilled professionals in healthcare technology and medicine presents a significant hurdle for new entrants. For instance, in 2024, the demand for specialized AI in healthcare developers outstripped supply, with reports indicating a 30% year-over-year increase in job postings for these roles, yet only a 10% increase in qualified candidates.
Establishing robust partnerships with established pharmaceutical giants and healthcare systems is another critical barrier. New companies often find it challenging to secure these vital collaborations, which are essential for market access and scaling operations. By mid-2024, over 70% of new digital health solutions reported difficulties in achieving widespread adoption without strategic alliances with major healthcare providers.
- Talent Acquisition Challenges: New entrants face intense competition for specialized talent in areas like bioinformatics and medical device engineering, with salary expectations for senior roles often exceeding $200,000 annually in 2024.
- Partnership Hurdles: Securing distribution agreements or pilot programs with large hospital networks can take years, delaying market entry and revenue generation for nascent healthcare technology firms.
- Expertise Gap: A lack of experienced leadership in navigating complex regulatory environments, such as FDA approvals, further hinders new players aiming to compete with established entities.
The threat of new entrants into China's integrated online and offline healthcare platform market is significantly mitigated by substantial capital requirements, stringent regulatory hurdles, and the difficulty of building established trust. New players must contend with the extensive economies of scale and powerful network effects already enjoyed by incumbents like 111, Inc., which are reinforced by growing user bases, such as 111's reported 15% active user growth in 2024. Furthermore, securing vital partnerships and attracting specialized talent are considerable challenges, with many new digital health solutions struggling for adoption without strategic alliances, as evidenced by over 70% facing difficulties by mid-2024.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | 2024 Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment needed for technology, logistics, and physical locations. | Hundreds of millions of dollars for nationwide presence. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex and evolving regulations for online pharmacies and data handling. | National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) guidelines require substantial compliance investments. |
| Brand Trust & Loyalty | Difficulty in establishing reputation against established players. | Incumbents like 111, Inc. have a significant edge in patient trust. |
| Economies of Scale | Cost advantages from large-scale procurement and logistics. | 111, Inc. leverages scale for better pricing and operational efficiency. |
| Network Effects | Increasing platform value with more users and partners. | 111, Inc. experienced 15% active user growth in 2024, strengthening its network. |
| Talent Acquisition | Competition for skilled professionals in healthcare technology. | 30% year-over-year increase in job postings for AI in healthcare developers in 2024. |
| Partnership Hurdles | Challenges in securing alliances with pharmaceutical giants and healthcare systems. | Over 70% of new digital health solutions faced adoption difficulties without strategic alliances by mid-2024. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of industry-specific market research reports, financial statements from publicly traded companies, and government economic data.
