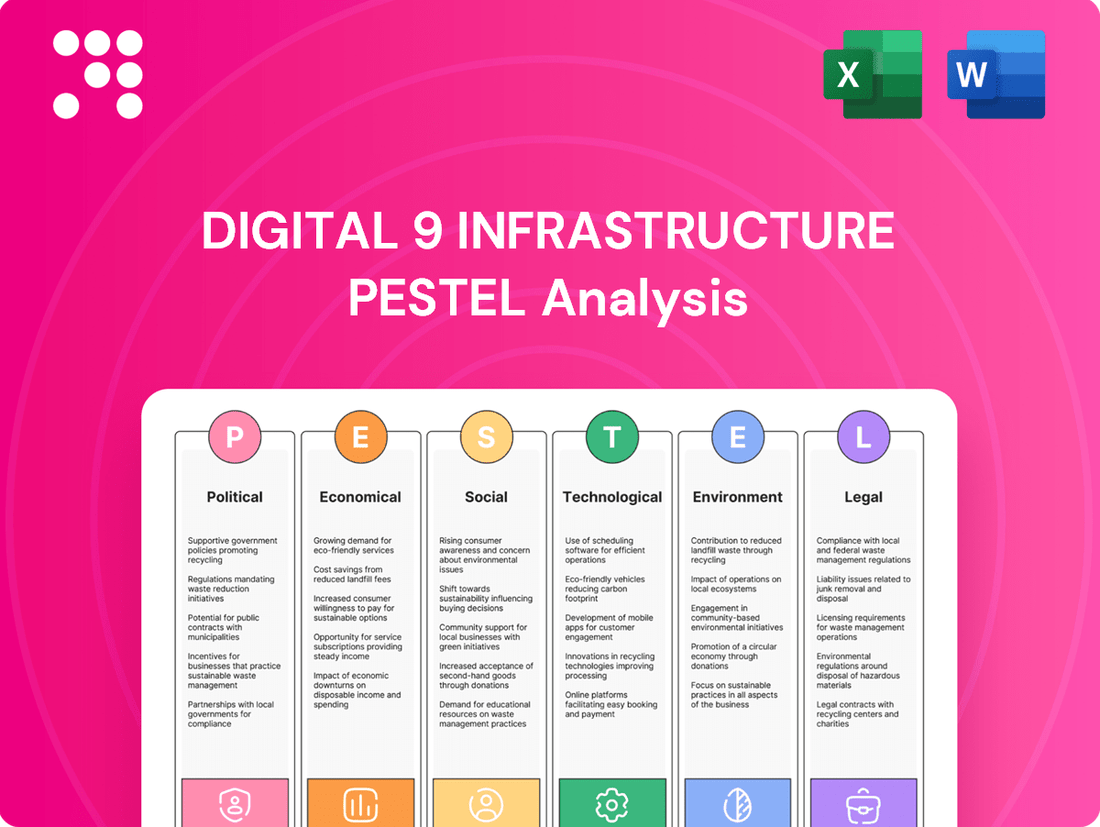
Digital 9 Infrastructure PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Digital 9 Infrastructure Bundle
Uncover the critical political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors shaping Digital 9 Infrastructure's trajectory. Our comprehensive PESTLE analysis provides the actionable intelligence you need to anticipate market shifts and capitalize on emerging opportunities. Download the full report now and gain a decisive competitive advantage.
Political factors
Government policy and regulation are critical drivers for digital infrastructure. Initiatives like the UK's Project Gigabit, aiming to deliver gigabit broadband to millions of homes by 2030, directly benefit companies like Digital 9 Infrastructure by creating demand and funding opportunities. This £5 billion program underscores a strong governmental commitment to expanding digital access.
However, evolving regulatory landscapes present both opportunities and challenges. Changes in data localization mandates or stricter foreign direct investment rules could affect Digital 9's ability to acquire and operate assets across different jurisdictions, potentially impacting cross-border data flows and ownership structures.
Geopolitical stability is a cornerstone for the security and operational integrity of global digital infrastructure, especially subsea fiber optic cables. In 2024, ongoing geopolitical tensions in regions like Eastern Europe and the Middle East continue to elevate the risk profile for these critical assets, impacting investment decisions and the continuity of data transmission. The potential for state-sponsored cyberattacks or physical sabotage on undersea infrastructure remains a significant concern, as highlighted by increased naval activity and reported incidents impacting critical communications. For instance, the Nord Stream pipeline sabotage in 2022 serves as a stark reminder of the vulnerability of essential infrastructure to geopolitical conflict, underscoring the need for robust security measures and diversified network routes.
Digital sovereignty initiatives are gaining significant traction globally, with many countries aiming to assert greater control over their digital ecosystems. For instance, the European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and its ongoing efforts to foster a European cloud infrastructure underscore this trend, impacting how data is handled and stored by multinational corporations.
These policies often translate into requirements for data localization, compelling companies to store data within national borders. This can increase operational costs and complexity for Digital 9 Infrastructure, potentially limiting their ability to leverage economies of scale across a global network. As of early 2024, several nations are actively debating or implementing stricter data localization laws, adding another layer of regulatory scrutiny.
Cybersecurity Policy
Governments are increasingly recognizing digital infrastructure as critical national infrastructure, leading to a strengthening of cybersecurity policies. This trend, evidenced by initiatives like the UK's Cyber Security and Resilience Policy Statement, signifies a proactive approach to protecting vital digital assets.
Stricter cybersecurity mandates and enhanced government oversight are becoming more common. These regulations can translate into significant additional compliance costs and new operational requirements for digital infrastructure providers. For example, in 2024, the EU's NIS2 Directive expanded cybersecurity obligations for critical entities, including those in the digital infrastructure sector, requiring robust risk management measures and incident reporting.
- Increased Compliance Burden: Companies must invest in advanced security technologies and personnel to meet evolving regulatory standards.
- Operational Adjustments: New protocols for data handling, threat detection, and response are often mandated, requiring process re-engineering.
- Potential Fines: Non-compliance with cybersecurity regulations can result in substantial financial penalties, impacting profitability.
- National Security Focus: Policies aim to safeguard critical digital networks from state-sponsored attacks and cybercrime, influencing investment and operational strategies.
Public-Private Partnerships
Governments are increasingly recognizing the critical role of digital infrastructure and are more willing to engage in public-private partnerships (PPPs) to accelerate its development. This willingness is driven by the need to bridge the digital divide and foster economic growth. For instance, in 2024, the UK government continued its commitment to expanding gigabit broadband through initiatives like Project Gigabit, which leverages private investment to reach hard-to-connect areas. This collaborative approach helps de-risk private sector investment by sharing financial burdens and providing a more predictable regulatory environment.
These partnerships are crucial for achieving widespread connectivity. They often involve governments providing upfront capital or guarantees, while private companies bring expertise in network deployment and operation. This model can lead to more efficient and faster rollouts, especially in rural or less commercially viable regions. For example, in the United States, the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, enacted in 2021 and continuing its impact through 2024-2025, allocates billions for broadband expansion, with a significant portion intended for state and local governments to partner with private entities.
The benefits extend beyond just deployment speed. PPPs can also ensure that digital infrastructure projects align with public policy objectives, such as affordability and accessibility. By working together, governments and private companies can create stable revenue streams for investors while ensuring that the infrastructure serves the broader public interest. This synergy is vital for building robust and equitable digital ecosystems.
- Increased government funding for broadband expansion through PPPs is a key trend in 2024-2025.
- PPPs help private companies overcome the financial risks associated with deploying infrastructure in challenging areas.
- Collaborations ensure digital infrastructure development meets public policy goals like affordability and universal access.
- The US Bipartisan Infrastructure Law is a prime example of government-led PPPs for digital infrastructure, with substantial funding allocated through 2025.
Government policies prioritizing digital infrastructure development, such as the UK's Project Gigabit aiming for nationwide gigabit broadband by 2030 with a £5 billion investment, directly fuel growth for companies like Digital 9 Infrastructure. Conversely, evolving regulations around data localization and foreign investment can introduce complexities and potential limitations on cross-border operations, impacting how assets are acquired and managed across different territories.
What is included in the product
This Digital 9 Infrastructure PESTLE analysis examines the influence of Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors on the sector.
It provides actionable insights for strategic decision-making by highlighting emerging trends and potential challenges.
A concise Digital 9 Infrastructure PESTLE Analysis provides a clear roadmap for navigating complex external factors, alleviating the pain of uncertainty in strategic planning.
Economic factors
The interest rate environment significantly influences the cost of capital for infrastructure projects. For Digital 9 Infrastructure, which utilizes debt financing, an increase in interest rates, such as the Bank of England's base rate reaching 5.25% by August 2023, directly elevates borrowing expenses. This rise in costs can compress profit margins and diminish the appeal of undertaking new projects or refinancing existing debt, impacting the trust's overall financial health and investment strategy.
Inflationary pressures pose a significant challenge for digital infrastructure. Rising costs for essential inputs like energy, hardware, and skilled labor directly increase operational expenses. For instance, the US Consumer Price Index (CPI) for energy services saw a notable increase in early 2024, impacting data center power costs.
While long-term service agreements can offer some insulation, persistent inflation can still chip away at profit margins. The real value of future revenue streams diminishes, potentially leading to lower asset valuations if not adequately managed. Companies that haven't hedged against inflation may see their returns eroded, particularly in sectors with high capital expenditure.
Global economic growth is a primary driver for digital infrastructure demand. As economies expand, so does the appetite for digital services, directly translating into increased needs for data centers, fiber networks, and cloud computing resources. For instance, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) projected global growth to be 3.2% in 2024, a figure that underpins the continued investment in digital transformation across various sectors.
A robust global economy fuels higher data consumption and accelerates digital transformation initiatives. This trend is evident in the projected growth of the global cloud computing market, which was expected to reach over $1 trillion by 2024, showcasing a direct link between economic health and digital infrastructure utilization.
Conversely, economic slowdowns can temper demand for new digital infrastructure projects and potentially impact the utilization rates of existing assets. Businesses facing economic headwinds may scale back their digital transformation budgets, leading to a more cautious approach to infrastructure expansion.
Investment Trends in Digital Infrastructure
Investor appetite for digital infrastructure remains robust, influencing capital availability and valuations for assets like data centers and subsea cables. This sustained interest, particularly from institutional investors, signals confidence in the sector's long-term growth potential, as evidenced by significant deal activity throughout 2024 and into early 2025.
While the overall sector attracts capital, the specific performance and strategic direction of individual companies, such as Digital 9's managed wind-down, can impact their particular investment appeal and valuation metrics.
- Data Center Investment: Global data center investment was projected to exceed $300 billion in 2024, driven by AI and cloud computing demand.
- Subsea Cable Funding: Major subsea cable projects secured billions in funding in late 2024, highlighting ongoing commitment to global connectivity.
- Wireless Infrastructure Growth: Expansion of 5G networks continues to attract substantial investment, with carriers investing tens of billions annually in network upgrades.
- Institutional Capital Allocation: Pension funds and sovereign wealth funds increasingly allocate significant portions of their portfolios to digital infrastructure, seeking stable, long-term returns.
Currency Exchange Rate Volatility
For Digital 9 Infrastructure, operating globally means currency exchange rate volatility is a significant factor. Fluctuations in exchange rates can directly affect the reported revenues, expenses, and the value of its international assets when translated into its reporting currency, likely GBP. For instance, if the Euro weakens against the Pound, Digital 9's Euro-denominated revenues and assets would appear smaller in its financial statements.
This volatility introduces financial risk, making it harder to predict profitability and manage costs across different countries. It also complicates processes like cross-border acquisitions or the sale of international assets, as the final value in GBP can change considerably between the initial agreement and the actual transaction completion due to currency movements.
Consider the impact on its data center operations in Europe. If the average exchange rate for the Euro against the Pound shifts unfavorably, the reported income from these operations could be lower. For example, a hypothetical 5% depreciation of the Euro against the Pound in a given quarter could reduce reported revenue from European assets by a similar margin, even if local currency revenues remain stable.
- Impact on Reported Earnings: A stronger Pound can decrease the reported value of foreign currency earnings, impacting investor perception and profitability metrics.
- Transaction Complexity: Managing cross-border payments and investments becomes more intricate, requiring hedging strategies that add costs and complexity.
- Asset Valuation Shifts: The reported book value of international property and infrastructure assets can fluctuate significantly with currency movements, affecting balance sheet strength.
- Competitive Landscape: Currency advantages or disadvantages can affect the pricing competitiveness of Digital 9's services in different international markets.
Interest rates directly influence Digital 9 Infrastructure's cost of capital, with the Bank of England's base rate at 5.25% in August 2023 impacting borrowing costs. Inflation also raises operational expenses for essential inputs like energy and hardware, as seen with US energy CPI increases in early 2024, potentially eroding profit margins.
Global economic growth, projected at 3.2% by the IMF for 2024, fuels demand for digital infrastructure, supporting the over $1 trillion global cloud computing market expected by 2024. Investor appetite remains strong, with significant deal activity in digital infrastructure throughout 2024 and early 2025.
Currency exchange rate volatility presents a risk, as seen with potential Euro depreciation against the Pound affecting Digital 9's European asset valuations. For example, a hypothetical 5% Euro depreciation could reduce reported revenue from European operations.
| Economic Factor | Impact on Digital 9 Infrastructure | Relevant Data (2024/2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rates | Increases cost of capital, impacting debt financing. | Bank of England base rate at 5.25% (August 2023). |
| Inflation | Raises operational expenses (energy, hardware, labor). | US energy CPI increase (early 2024); potential erosion of real revenue value. |
| Global Economic Growth | Drives demand for digital services and infrastructure. | IMF projected global growth of 3.2% (2024); Global cloud market > $1 trillion (2024). |
| Investor Appetite | Influences capital availability and asset valuations. | Sustained institutional interest; significant deal activity (late 2024-early 2025). |
| Currency Exchange Rates | Affects reported revenues, expenses, and asset values. | Volatility impacts GBP translation of foreign currency assets/revenues. |
Same Document Delivered
Digital 9 Infrastructure PESTLE Analysis
The preview you see here is the exact, fully formatted Digital 9 Infrastructure PESTLE Analysis document you’ll receive after purchase. It offers a comprehensive examination of the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting this critical sector. This detailed report is ready for immediate use, providing valuable insights without any surprises.
Sociological factors
The world's increasing reliance on digital services for everything from remote work and online learning to entertainment and e-commerce is a major driver for digital infrastructure. This trend is fueled by rising internet penetration rates, with over 5.3 billion people online globally as of early 2024, and the widespread adoption of smartphones.
This digital shift necessitates greater data capacity and faster connectivity, as more people and businesses embrace cloud-based applications and streaming services. For instance, global mobile data traffic is projected to grow significantly, reaching an estimated 370 exabytes per month by 2029, up from around 113 exabytes per month in 2023, according to Cisco's Annual Internet Report.
The shift towards remote and hybrid work, accelerated by events in recent years, has fundamentally reshaped how we use data. This isn't just a temporary blip; by 2024, a significant portion of the global workforce is expected to continue with some form of flexible work arrangement, driving sustained demand for robust home internet and secure connections for businesses.
This increased reliance on digital connectivity for daily work means that the quality and capacity of internet infrastructure are no longer optional but essential. Companies are investing heavily in ensuring their employees can work efficiently from anywhere, leading to a surge in demand for reliable broadband and secure VPNs.
The implications for digital infrastructure are clear: there's a pressing need for networks that can handle this distributed traffic seamlessly. This includes upgrading last-mile connectivity to homes and ensuring enterprise networks can securely manage a dispersed workforce, with global spending on IT infrastructure expected to reach over $1.3 trillion in 2024, reflecting this ongoing investment.
Consumer habits are dramatically shifting, with a significant surge in video streaming, online gaming, and social media usage. This trend directly translates into exponential growth in data consumption. For instance, global internet traffic is projected to reach 207 exabytes per month by 2025, a substantial increase from previous years, driven largely by video content.
This continuous and escalating demand places considerable pressure on existing networks and data centers. They are constantly challenged to expand their capacity and enhance performance to keep pace. This need for greater capability directly underpins the necessity for ongoing and substantial infrastructure investment to support these evolving digital behaviors.
Societal Expectations for Seamless Connectivity
Societies now anticipate constant, high-speed internet access, making downtime unacceptable. This fuels demand for infrastructure upgrades and redundancy, shaping investment decisions for companies like Digital 9 Infrastructure. For instance, the global average internet speed continues to climb, with reports in early 2024 indicating speeds well over 100 Mbps in many developed nations, a benchmark that is becoming a baseline expectation.
This pervasive expectation for seamless connectivity directly translates into a need for continuous investment in network expansion and resilience. Providers are pressured to not only keep pace with escalating data consumption but also to build in safeguards against disruptions. By 2025, it's projected that the average global household will have multiple connected devices, each demanding reliable bandwidth, further intensifying this societal pressure.
- Increased investment in network redundancy and fault tolerance
- Prioritization of infrastructure upgrades to meet growing data demands
- Focus on expanding network reach to underserved areas
- Development of strategies to minimize service disruptions
Digital Divide and Inclusion
Bridging the digital divide is a major societal focus, driving significant investment and policy decisions for digital infrastructure. Ensuring everyone has access to fast internet is crucial for economic and social participation.
Companies in the digital infrastructure sector face both opportunities and social obligations when expanding into rural and remote areas. Government subsidies, like the approximately $42.5 billion allocated through the Broadband Equity, Access, and Deployment (BEAD) program in the US, are instrumental in these efforts.
- Equitable Access: Policies aim to ensure all populations, particularly those in underserved rural and remote regions, have reliable high-speed internet access.
- Investment Drivers: Government funding and public-private partnerships are key to overcoming the financial hurdles of connecting less populated areas.
- Social Responsibility: Digital infrastructure providers are increasingly expected to contribute to social inclusion by expanding services to communities that might otherwise be left behind.
- Market Expansion: Connecting these areas opens up new customer bases and revenue streams, albeit with potentially higher upfront costs and longer return on investment periods.
Societal expectations for constant, high-speed internet access are driving significant investment in network redundancy and upgrades. This demand is further amplified by the growing number of connected devices per household, projected to increase by 2025. The societal push to bridge the digital divide is also a major factor, with initiatives like the US BEAD program allocating substantial funds to expand broadband access to underserved areas.
| Societal Expectation | Impact on Digital Infrastructure | Supporting Data/Initiative |
|---|---|---|
| Constant, high-speed connectivity | Need for network redundancy and upgrades | Global average internet speeds exceeding 100 Mbps in developed nations (early 2024) |
| Increased connected devices per household | Pressure on bandwidth capacity | Projected multiple connected devices per household globally by 2025 |
| Bridging the digital divide | Expansion into rural/remote areas | US BEAD Program: $42.5 billion allocated for broadband expansion |
Technological factors
Continuous innovation in fiber optic technology is pushing capacities higher and latency lower. For instance, advancements like Coherent optics are enabling data rates exceeding 1.2 terabits per second on single wavelengths, a significant leap from previous generations.
The ongoing global rollout of 5G networks is a critical driver for digital infrastructure expansion. By the end of 2024, it's projected that over 3 billion people will have access to 5G services, demanding more robust and widespread fiber backhaul to support these faster speeds.
These technological leaps directly necessitate substantial upgrades and expansion of underlying digital networks. The increased data transmission speeds facilitated by fiber and 5G are crucial for supporting emerging applications such as augmented reality, autonomous vehicles, and advanced cloud computing services, requiring significant capital investment in network infrastructure.
The relentless growth of data, fueled by AI, IoT, and widespread cloud adoption, is creating a massive demand for data center space and advanced efficiency solutions. This surge necessitates substantial capital for hyperscale facilities and edge computing infrastructure, focusing on power, cooling, and connectivity.
For instance, the global data center market was valued at approximately $240 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $400 billion by 2028, showcasing the immense investment opportunities and challenges in this sector.
The rapid advancement of Artificial Intelligence, particularly generative AI, is a significant technological factor reshaping the digital infrastructure landscape. These AI applications are creating an unprecedented surge in demand for computational power and data storage, directly influencing how data centers are designed and how much capacity they need to offer.
For instance, the global AI market was projected to reach $200 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow substantially through 2025, driving substantial investment in the underlying infrastructure. This escalating demand necessitates a continuous expansion of data center capacity and a re-evaluation of their technical specifications to accommodate AI workloads.
While AI itself offers avenues to improve network operational efficiency, its voracious appetite for resources is the primary technological catalyst propelling infrastructure expansion. Companies are investing heavily in upgrading their networks and data centers to support AI development and deployment, anticipating continued growth in this area through 2025.
Cybersecurity Innovations and Threats
The escalating sophistication of cyber threats demands ongoing investment in cutting-edge cybersecurity solutions to safeguard essential digital infrastructure. For instance, the global cybersecurity market size was valued at USD 217.93 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 479.17 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 13.8%. This growth underscores the critical need for advanced protection.
Innovations in security protocols, real-time threat detection systems, and robust resilience strategies are paramount for ensuring the integrity of networks and the safety of sensitive data. Companies are increasingly adopting AI-powered security platforms, which saw a 30% increase in adoption for threat detection in 2024. These advancements are vital for defending against evolving attack vectors.
- Increased Investment: Cybersecurity spending is projected to exceed $200 billion annually by 2025, reflecting the growing threat landscape.
- AI in Security: Artificial intelligence and machine learning are becoming integral to identifying and mitigating zero-day threats, with adoption rates climbing.
- Data Protection Focus: Regulations like GDPR and CCPA continue to drive demand for advanced data encryption and privacy-preserving technologies.
- Ransomware Evolution: Ransomware attacks remain a significant concern, with average ransom demands increasing by 15% in late 2024, necessitating stronger preventative measures.
Automation and Network Management Tools
The increasing adoption of automation and advanced network management tools, particularly those powered by artificial intelligence, is a significant technological factor for Digital 9 Infrastructure. These solutions are revolutionizing how complex digital networks are operated, leading to substantial gains in efficiency, reliability, and overall cost-effectiveness. For instance, AI-driven predictive maintenance can anticipate potential hardware failures, reducing downtime and costly emergency repairs.
These technologies are crucial for optimizing network performance. By leveraging real-time data analytics, automation tools can dynamically adjust network traffic, ensuring smoother operations and better user experiences. This proactive approach contrasts with traditional reactive management, which often addresses issues only after they arise.
Key benefits and applications include:
- Enhanced Network Uptime: Predictive analytics identify potential issues before they impact service, aiming for near-continuous availability.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Automation of routine tasks, like configuration and monitoring, frees up IT staff for more strategic work, lowering labor expenses.
- Improved Resource Allocation: AI can optimize bandwidth usage and server load balancing, ensuring efficient utilization of infrastructure assets.
- Faster Issue Resolution: Automated diagnostics and remediation tools can resolve common network problems much quicker than manual intervention.
Advancements in fiber optics, like coherent optics enabling over 1.2 Tbps per wavelength, are continuously boosting network capacity and reducing latency. The global rollout of 5G, expected to reach over 3 billion users by the end of 2024, necessitates substantial fiber backhaul upgrades to support the increased demand for speed and connectivity.
The rapid growth of AI, particularly generative AI, is a major technological driver, increasing demand for computational power and data storage. This surge is pushing data center expansion and upgrades, with the global data center market projected to grow from approximately $240 billion in 2023 to over $400 billion by 2028.
| Technological Factor | Description | Impact on Digital Infrastructure | Key Data/Projections (2024-2025) |
| Fiber Optic Advancements | Higher capacities, lower latency | Necessitates network upgrades | Coherent optics > 1.2 Tbps/wavelength |
| 5G Rollout | Increased mobile data demand | Requires expanded fiber backhaul | >3 billion 5G users by end of 2024 |
| AI and Data Growth | Demand for compute and storage | Drives data center expansion | AI market projected $200B+ in 2023, significant growth through 2025 |
| Cybersecurity Evolution | Sophistication of threats | Requires advanced security solutions | Global cybersecurity market ~$218B in 2024, AI security adoption up 30% in 2024 |
Legal factors
For Digital 9 Infrastructure, navigating the legal landscape around its managed wind-down and asset divestments is paramount. Securing timely regulatory and competition approvals for the sale of its portfolio companies is essential to realizing value effectively.
Delays in these legal processes, which can be complex and time-consuming, directly impact the planned timeline and the ultimate financial returns from these divestments. For instance, a prolonged review by competition authorities could push back the completion of a sale, potentially affecting market conditions and buyer interest.
Global data protection and privacy laws, like the EU's GDPR, create substantial compliance challenges for digital infrastructure providers. These regulations dictate how data centers and network operators must handle, store, and move data across borders, directly shaping their operational strategies. For instance, the increasing complexity and enforcement of these laws mean significant investment in secure infrastructure and data governance practices is essential.
Operating wireless networks and other digital infrastructure necessitates various licenses and access to crucial spectrum. Regulatory bodies worldwide, such as the FCC in the United States and Ofcom in the UK, manage these allocations. For instance, the FCC's recent C-band auction in 2021 generated over $81 billion, highlighting the significant financial implications of spectrum access.
Decisions regarding spectrum allocation, the renewal of existing licenses, and the associated licensing fees directly impact the operational viability and expansion potential of wireless infrastructure. These regulatory actions can influence investment decisions and the pace of network upgrades. For example, spectrum availability and cost are key factors in the rollout of 5G technology, with governments often setting deadlines for license usage to encourage deployment.
Antitrust and Competition Law
Antitrust and competition law are critical considerations for digital infrastructure, especially where a few large companies hold significant market power. Regulators are actively monitoring these sectors to ensure fair play and prevent monopolistic practices. For instance, in 2024, the European Union continued its investigations into potential anti-competitive behavior by major cloud providers, impacting how new players can enter the market and the pricing of essential digital services.
These regulations can directly shape investment strategies and the overall market structure. For example, a dominant player might face restrictions on acquiring smaller competitors or be required to open up their networks to third parties. Such interventions aim to foster innovation and provide consumers with more choices, influencing the profitability and growth potential of digital infrastructure companies.
- Market Dominance Scrutiny: Antitrust authorities worldwide are intensifying their focus on digital infrastructure markets, particularly those dominated by a few key players.
- Impact on Market Entry: Regulations designed to promote competition can lower barriers to entry, allowing new companies to challenge established providers.
- Pricing and Investment Influence: Antitrust actions can lead to mandated price adjustments or force companies to divest assets, directly affecting investment returns and strategic planning.
- Examples in Practice: Ongoing investigations and enforcement actions, such as those seen with major cloud service providers in 2024, highlight the tangible impact of competition law on the digital infrastructure landscape.
International Treaties and Cross-Border Regulations
International treaties and cross-border regulations are critical for subsea fiber optic networks, dictating everything from cable laying rights to data transit protocols. These agreements ensure that infrastructure can span multiple national jurisdictions without legal impediments. For instance, the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) plays a role in setting standards and facilitating cooperation among member states, impacting how Digital 9 Infrastructure operates globally.
Compliance with these intricate legal frameworks is non-negotiable for the smooth operation of global connectivity assets. Navigating differing national laws on data sovereignty, privacy, and cybersecurity adds layers of complexity. The ongoing evolution of international digital trade agreements, such as those discussed within the World Trade Organization (WTO), will continue to shape the operating environment for companies like Digital 9 Infrastructure.
- Cable Laying Rights: International agreements like the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) govern the laying of submarine cables in international waters, ensuring freedom of navigation and access.
- Data Transit Regulations: Cross-border data flow regulations, including the EU's GDPR and similar frameworks emerging globally, impact how data transmitted through subsea cables is handled and protected.
- Cybersecurity Cooperation: International efforts to combat cyber threats necessitate cooperation and adherence to shared security protocols, affecting the resilience of digital infrastructure.
- Dispute Resolution: Mechanisms for resolving disputes between nations or entities regarding subsea infrastructure are often outlined in international treaties, providing a framework for managing potential conflicts.
Legal factors significantly shape Digital 9 Infrastructure's operations, particularly concerning its asset divestments and compliance with global data regulations. Antitrust scrutiny in 2024, for instance, impacted major cloud providers, influencing market entry and pricing for digital services.
Navigating spectrum allocation and licensing is crucial for wireless operations, with regulators like the FCC setting the stage for significant financial implications, as seen in the 2021 C-band auction exceeding $81 billion. International treaties governing subsea cable laying and data transit, like UNCLOS, are vital for global connectivity, with ongoing discussions within the WTO influencing digital trade agreements.
The evolving landscape of data protection laws, such as GDPR, necessitates substantial investment in secure infrastructure and robust data governance practices for companies handling vast amounts of data.
| Legal Factor | Impact on Digital 9 Infrastructure | Relevant Data/Example (2021-2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Antitrust & Competition Law | Influences market entry, pricing, and potential asset divestments. | EU investigations into cloud providers in 2024 highlighted potential market power abuses. |
| Data Protection & Privacy Laws | Dictates data handling, storage, and cross-border movement, requiring significant compliance investment. | GDPR enforcement continues to evolve, with increasing fines for non-compliance. |
| Spectrum Licensing | Affects operational viability and expansion for wireless infrastructure. | FCC C-band auction in 2021 generated over $81 billion, indicating the value of spectrum. |
| International Treaties (Subsea Cables) | Governs cable laying rights and data transit protocols across jurisdictions. | UNCLOS provides a framework for submarine cable deployment in international waters. |
Environmental factors
Data centers are massive energy consumers, and their electricity needs are only growing. This presents a significant environmental hurdle, especially as global demand for digital services escalates. For Digital 9 Infrastructure, managing the carbon footprint of its data center portfolio is becoming increasingly critical.
The company's operations are under growing scrutiny to adopt more sustainable practices. This includes a push towards sourcing renewable energy to power its facilities and implementing advanced, energy-efficient cooling solutions to mitigate environmental impact. For instance, the global data center market was valued at approximately $201.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $373.9 billion by 2029, highlighting the scale of energy involved.
The lifecycle of digital infrastructure, from its creation to eventual decommissioning, inevitably produces electronic waste. As of 2024, global e-waste generation is projected to reach 61.3 million metric tons annually, a significant increase from previous years. This growing volume poses a substantial environmental challenge.
Companies within the Digital 9 are facing mounting pressure from regulators and society to implement more sustainable practices. This is driving a shift towards circular economy principles, which emphasize responsible sourcing of materials, robust recycling programs, and a concerted effort to minimize the generation of e-waste throughout the entire asset lifecycle.
Digital 9 Infrastructure's assets, like subsea cables and exposed wireless networks, face significant risks from extreme weather events driven by climate change. For instance, a 2024 report highlighted that disruptions to subsea cables, often exacerbated by rising sea levels and increased storm intensity, can lead to prolonged outages and substantial repair costs. This vulnerability necessitates proactive investment in climate-resilient infrastructure to ensure continuity of service.
Adapting to these evolving environmental conditions is paramount for Digital 9's long-term operational stability and the protection of its valuable assets. Companies are increasingly allocating capital towards hardening their networks, exploring undergrounding options, and developing advanced monitoring systems to predict and mitigate climate-related impacts. The projected global cost of climate change on infrastructure is in the trillions, underscoring the financial imperative for resilience.
Water Usage for Cooling Data Centers
Data centers are increasingly being scrutinized for their substantial water consumption, primarily for cooling purposes. As global water scarcity becomes a more pressing issue, especially in regions like the American Southwest or parts of Europe, the environmental footprint of these facilities is under the microscope. This puts pressure on companies like Digital 9 Infrastructure to adopt more water-efficient cooling technologies.
The demand for advanced cooling solutions is on the rise, driven by both environmental concerns and the need to manage operational costs. For instance, some estimates suggest that large data centers can consume millions of gallons of water per day. This highlights the critical need for innovative approaches to cooling that minimize water usage.
- Water Consumption: Large data centers can use millions of gallons of water daily for cooling, comparable to the needs of small cities.
- Scarcity Concerns: Growing awareness of water scarcity in arid and semi-arid regions amplifies the environmental impact of data center operations.
- Efficiency Drive: Regulatory pressures and corporate sustainability goals are pushing for the development and adoption of water-efficient cooling technologies, such as liquid cooling or dry cooling systems.
Sustainability Reporting and ESG Standards
The increasing emphasis on sustainability reporting and Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) standards is a significant environmental factor. Investors, regulators, and the public are actively seeking transparent and comprehensive ESG disclosures. For Digital 9 Infrastructure, this translates into a necessity to clearly articulate its environmental stewardship to maintain investor confidence and align with evolving market expectations. For instance, in 2024, the global sustainable investment market reached an estimated $37.4 trillion, highlighting the financial clout behind ESG principles.
Companies are under pressure to demonstrate their commitment to environmental responsibility, which includes reducing carbon footprints and promoting resource efficiency. Digital 9 Infrastructure's operations, particularly its data centers, have a direct impact on energy consumption and waste generation. Adhering to stringent ESG standards can lead to operational efficiencies and cost savings, while also mitigating reputational risks. The EU's Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), which came into full effect in early 2024 for large companies, mandates detailed reporting on sustainability matters, setting a precedent for global standards.
- Investor Demand: Over 70% of institutional investors consider ESG factors in their investment decisions as of 2024.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Governments worldwide are implementing stricter regulations on corporate environmental performance and reporting.
- Market Expectations: Companies with strong ESG performance often enjoy higher valuations and better access to capital.
- Operational Impact: Implementing sustainable practices can lead to reduced energy costs and improved resource management for infrastructure companies.
The environmental impact of digital infrastructure is a growing concern. Data centers, a core asset for Digital 9 Infrastructure, are significant energy and water consumers, requiring efficient cooling solutions. Global e-waste generation, projected to reach 61.3 million metric tons in 2024, necessitates a focus on circular economy principles and robust recycling programs.
Climate change poses direct risks to physical assets like subsea cables and wireless networks, with extreme weather events causing disruptions and increasing repair costs. Adapting to these changes involves investing in climate-resilient infrastructure and advanced monitoring systems. The financial implications are substantial, with global costs of climate change on infrastructure estimated in the trillions.
| Factor | Description | 2024/2025 Data Point |
| Energy Consumption | Data centers require vast amounts of electricity. | Global data center market projected to reach $373.9 billion by 2029. |
| E-Waste | Disposal of electronic equipment creates environmental challenges. | Global e-waste generation projected at 61.3 million metric tons annually in 2024. |
| Water Usage | Cooling systems in data centers consume significant water resources. | Large data centers can consume millions of gallons of water daily. |
| Climate Change Impact | Extreme weather events threaten physical infrastructure. | Projected global cost of climate change on infrastructure is in the trillions. |
| ESG Reporting | Increasing investor and regulatory focus on environmental performance. | Global sustainable investment market estimated at $37.4 trillion in 2024. |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our Digital 9 Infrastructure PESTLE Analysis is underpinned by a robust data framework, drawing from official government reports, international economic forums, and leading technology research firms. This ensures comprehensive coverage of regulatory landscapes, market dynamics, and emerging technological trends.
