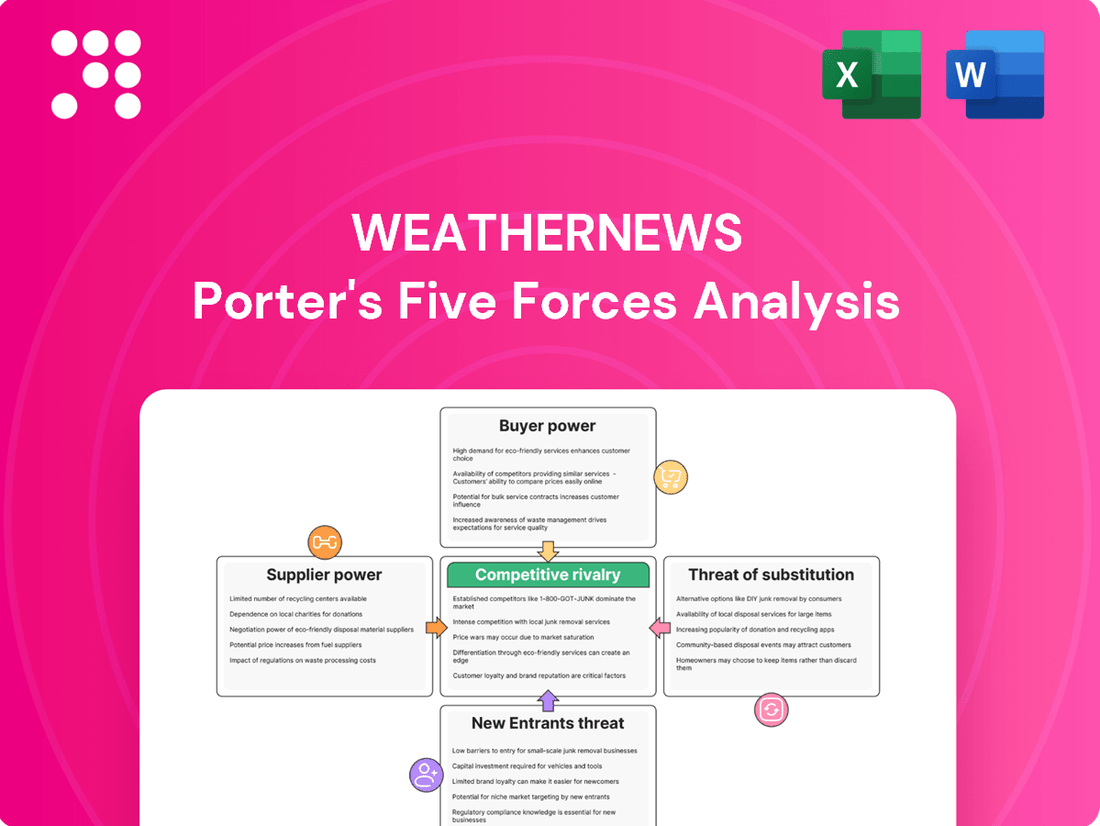
Weathernews Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Weathernews Bundle
Weathernews operates in a dynamic weather information market, facing significant competitive pressures. Understanding the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threats of new entrants and substitutes is crucial for strategic success.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Weathernews’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Weathernews' reliance on its proprietary observation networks significantly diminishes the bargaining power of external data suppliers. By controlling a substantial portion of its core weather data through its own sophisticated systems, the company reduces its dependence on a few key raw data providers. This internal capability means fewer suppliers hold sway over pricing or terms, as Weathernews can leverage its own data assets.
Technology and software providers hold significant bargaining power, especially those offering advanced forecasting models and AI/ML algorithms crucial for Weathernews's data analysis and service delivery. These specialized tools are often not off-the-shelf, requiring significant customization and integration, which can limit alternative vendor options.
The feasibility of in-house development for such sophisticated technology is often low due to the high cost and specialized expertise required. This dependence on a few key technology suppliers, coupled with the complexity of integrating new systems, results in substantial switching costs for Weathernews, further strengthening supplier leverage.
The bargaining power of infrastructure and cloud service suppliers is a significant factor for Weathernews. Companies like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud dominate the market, meaning Weathernews relies on a concentrated group of providers for essential data processing and storage. This concentration can lead to higher costs if these providers increase their pricing, as switching to a different provider can be complex and expensive due to vendor lock-in, where data and services are deeply integrated into a specific platform. In 2024, the global cloud computing market was valued at over $600 billion, highlighting the immense scale and influence of these providers.
Skilled Talent and Expertise
The bargaining power of suppliers in the weather analytics industry is significantly influenced by the availability of highly specialized human capital. Meteorologists, data scientists, and software engineers with niche expertise in weather modeling and analytics are in high demand.
The scarcity of these professionals, coupled with the intense competition for their skills, directly translates to increased negotiation leverage for them. Companies like Weathernews must invest heavily in recruitment and retention to secure this talent, driving up labor costs.
For instance, in 2024, the demand for AI and machine learning specialists, crucial for advanced weather prediction, outstripped supply, leading to salary increases of 15-20% in many tech sectors. This trend directly impacts the cost of developing and maintaining sophisticated weather analytics platforms.
- Scarcity of Expertise: The limited number of professionals with specialized weather analytics skills grants them considerable bargaining power.
- High Recruitment and Retention Costs: Companies face substantial expenses to attract and keep top talent in this niche field.
- Salary and Benefit Negotiations: A tight labor market allows skilled individuals to command higher salaries and more attractive benefit packages.
- Impact on Service Costs: The elevated cost of specialized labor can influence the pricing of weather analytics services.
Hardware and Sensor Manufacturers
The bargaining power of hardware and sensor manufacturers for Weathernews is influenced by the specificity of their needs. While some components like standard sensors might have multiple suppliers, specialized radar systems or custom-built observation equipment could limit options. For instance, the semiconductor shortage experienced globally in 2021-2022 significantly impacted the availability and pricing of electronic components, a challenge that can affect any company relying on advanced hardware.
The level of customization for Weathernews' observation network plays a crucial role. Highly standardized components generally face more competition, reducing supplier leverage. Conversely, proprietary or custom-designed hardware, especially if developed with a single supplier, grants that supplier considerable power. The number of alternative suppliers for critical, specialized hardware is a key determinant; if few can meet the technical specifications, their bargaining power increases.
- Component Standardization: Weathernews likely utilizes a mix of standard off-the-shelf sensors and more specialized, potentially custom-ordered equipment for its weather observation networks.
- Supplier Concentration: The market for advanced meteorological sensors and radar technology may be concentrated among a few key global players, potentially increasing their bargaining power.
- Technological Advancements: Rapid advancements in sensor technology could create opportunities for new suppliers, but also increase the bargaining power of those who possess cutting-edge, proprietary technology.
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: Global supply chain disruptions, as seen with microchip shortages in 2022, can significantly elevate the bargaining power of hardware suppliers due to limited availability and increased lead times.
Weathernews' reliance on specialized technology and cloud infrastructure suppliers grants these entities significant bargaining power. The high cost and complexity of switching, coupled with the concentrated nature of providers in areas like cloud computing, mean suppliers can exert considerable influence over pricing and terms.
The scarcity of highly skilled meteorologists, data scientists, and AI specialists further amplifies the bargaining power of human capital suppliers. Companies like Weathernews must contend with increased labor costs and intense competition to secure essential expertise, impacting overall operational expenses.
The bargaining power of hardware and sensor manufacturers is more varied, depending on the standardization of components. While common parts may have many suppliers, specialized meteorological equipment can lead to fewer options, increasing the leverage of those select providers, especially in the face of supply chain vulnerabilities.
| Supplier Type | Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Example Data/Trend (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Technology & Software Providers | Uniqueness of algorithms, integration complexity, switching costs | High demand for AI/ML specialists led to salary increases of 15-20% in tech sectors. |
| Infrastructure & Cloud Services | Market concentration, vendor lock-in, data integration | Global cloud computing market valued over $600 billion. |
| Specialized Human Capital | Scarcity of niche skills, high demand, competition | AI/ML talent demand outstripped supply, driving up recruitment costs. |
| Hardware & Sensor Manufacturers | Component standardization, supplier concentration, customization needs | Semiconductor shortages (2021-2022) demonstrated impact of supply chain disruptions on component availability and pricing. |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Weathernews, evaluating the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the weather information industry.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a clear, visual breakdown of each Porter's Five Force.
Gain immediate clarity on market dynamics and competitive pressures, enabling proactive strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Weathernews serves a diverse range of industries, including maritime, aviation, land transportation, and individual consumers. The concentration within these segments is crucial for understanding customer bargaining power. For instance, if a few major shipping companies represent a substantial portion of the maritime revenue, they could wield significant influence over pricing and service terms.
While specific revenue breakdowns by customer segment are not publicly disclosed, Weathernews' business model relies on long-term contracts with large corporations in sectors like aviation and maritime. The company's 2024 financial reports indicate continued strong relationships with key players in these industries, suggesting that while diversification exists, a degree of concentration among major clients is inherent to the business.
A highly diversified customer portfolio would naturally dilute the bargaining power of any single customer. Weathernews' strategy appears to involve balancing large, anchor clients with a broader base of smaller and individual users to mitigate the risk of intense pressure from a concentrated few. This approach aims to create a stable revenue stream while managing customer leverage.
The bargaining power of customers for weather information is significantly influenced by the availability of alternatives and the associated switching costs. For individual consumers, switching between weather apps or websites is typically very easy, with minimal to no cost involved. This ease of switching grants them considerable power.
However, for corporate clients, such as airlines or agricultural businesses, switching weather data providers can be more complex and costly. These clients often have integrated weather data into their operational systems, and the cost of re-integrating new data feeds, retraining staff, and ensuring data continuity can be substantial. For instance, a major airline might spend hundreds of thousands of dollars to switch its flight planning weather data provider, representing a high switching cost.
Customer price sensitivity for weather data varies significantly. Individual consumers, seeking basic forecasts, are generally more price-sensitive, as the impact of minor inaccuracies is often low. For instance, many free weather apps cater to this segment, demonstrating a low willingness to pay for enhanced features.
Businesses, however, exhibit much lower price sensitivity, especially those where weather directly impacts significant operational costs, safety, or revenue. Industries like aviation, agriculture, and logistics rely heavily on accurate, timely weather information. A 2023 report indicated that weather-related disruptions cost the global economy billions annually, highlighting the substantial value placed on predictive accuracy.
For these business clients, Weathernews' ability to provide specialized insights and enhanced accuracy translates into tangible cost savings and risk mitigation. This critical nature of the service means they are willing to invest more for superior data, as the return on investment from avoiding weather-related losses far outweighs the cost of the service.
Threat of Backward Integration
Large corporate customers, such as major airlines and shipping companies, possess the potential to develop their own internal weather forecasting systems. This backward integration could be driven by a desire for greater control, customization, or cost savings. For instance, a major airline might evaluate the investment required for a dedicated meteorological team and advanced modeling software versus the ongoing subscription fees paid to a provider like Weathernews.
The feasibility and cost-effectiveness of backward integration depend heavily on the specific needs and resources of the customer. While a large airline might have the capital to invest, the ongoing operational costs and the need for specialized expertise in meteorology could be significant deterrents. Assessing whether developing an in-house capability offers a tangible return on investment compared to outsourcing is a crucial consideration for these clients.
The credible threat of these large clients pursuing backward integration directly enhances their bargaining power. This leverage allows them to negotiate more favorable terms, potentially including lower prices or customized service agreements, as Weathernews seeks to retain their business.
- Customer Integration Potential: Major clients like airlines and shipping firms can build in-house weather forecasting.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Customers weigh the expense of internal systems against outsourcing fees.
- Bargaining Power Impact: The possibility of self-sufficiency strengthens customers' negotiating position.
Information Asymmetry and Customization Needs
The bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by information asymmetry and their demand for customization. When customers have access to comprehensive data on alternative weather services and their respective pricing, their ability to negotiate increases. Weathernews's ability to provide highly specialized or complex weather insights can mitigate customer bargaining power if these needs are not easily met by competitors. For instance, industries requiring hyper-local, minute-by-minute forecasts for critical operations, like aviation or precision agriculture, may find fewer alternatives, thus reducing their leverage.
Conversely, for more generalized weather information, customers typically possess greater bargaining power. This is because the market for standard weather data is often more competitive, with numerous providers offering similar services. The degree of customization required directly correlates with a customer's leverage; the more unique the data or analysis needed, the less power the customer has if Weathernews is the sole provider capable of delivering it. In 2024, the demand for AI-driven, predictive analytics in weather forecasting is growing, creating opportunities for companies like Weathernews to differentiate and potentially reduce customer bargaining power through specialized, high-value offerings.
- Information Availability: Customers with full access to pricing and service comparisons for weather data have increased bargaining power.
- Customization Needs: High demand for tailored weather solutions can reduce customer leverage if only specific providers can meet these unique requirements.
- Standardization Impact: For commoditized weather services, customers generally hold more negotiating power due to market competition.
- Industry Specificity: Sectors with critical, highly specific weather data needs (e.g., renewable energy site selection) may have less bargaining power if specialized providers like Weathernews are essential.
The bargaining power of Weathernews' customers is a key factor, varying significantly by segment. For individual consumers, the ease of switching between numerous free and low-cost weather apps means they hold considerable power, driving a focus on accessible, basic forecasts. In contrast, large corporate clients, such as airlines or agricultural firms, face higher switching costs due to system integration and the critical nature of accurate weather data for their operations.
These business customers exhibit lower price sensitivity because the financial impact of weather-related disruptions, which can run into billions globally per year, makes reliable forecasting a valuable investment. For example, a major airline's decision to switch its flight planning weather data provider could involve hundreds of thousands of dollars in re-integration costs, reinforcing their reliance on existing, trusted providers like Weathernews.
The potential for large clients to develop in-house forecasting capabilities also acts as a significant lever in negotiations. While the investment in specialized meteorological expertise and advanced modeling is substantial, the mere threat of backward integration can pressure Weathernews to offer more competitive pricing and tailored service agreements to retain these crucial accounts.
Furthermore, information asymmetry plays a role; customers with better access to market data on alternative services and pricing can negotiate more effectively. However, Weathernews can counter this by offering highly specialized, customized weather insights—particularly in areas like AI-driven predictive analytics, which saw growing demand in 2024—that are difficult for competitors to replicate, thereby reducing customer leverage.
What You See Is What You Get
Weathernews Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Weathernews Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You'll gain a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the weather forecasting industry. This in-depth analysis is professionally formatted and ready for your immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global weather information market features a robust competitive landscape. Key direct competitors to Weathernews include AccuWeather and The Weather Company, alongside numerous national meteorological services that also provide public weather data. This diverse group includes both broad-service providers and specialized niche players, each vying for market share.
The sheer number of these entities, coupled with their varied strategic approaches, significantly fuels competitive rivalry. For instance, while AccuWeather focuses heavily on consumer-facing applications and advertising, The Weather Company, owned by IBM, leverages its data for enterprise solutions. This strategic diversity means competitors often target different customer segments or offer distinct value propositions, intensifying the overall competition for Weathernews.
The global weather information services market is experiencing robust growth, projected to reach approximately $10.5 billion by 2027, expanding at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 7.5%. This expansion is driven by increasing demand from sectors like agriculture, aviation, and renewable energy, all of which rely heavily on accurate weather data for operational efficiency and risk management.
In such a dynamic and expanding market, the intensity of competitive rivalry is somewhat tempered. While companies like AccuWeather, IBM (The Weather Company), and MeteoGroup are vying for dominance, the overall market expansion allows for growth opportunities without necessarily engaging in aggressive market share battles. However, as the market matures, this dynamic could shift, potentially intensifying competition for existing customers.
Weathernews actively differentiates its services through advanced forecasting models and proprietary data, aiming to provide superior accuracy and specialized insights. For instance, their focus on hyper-local forecasting and industry-specific solutions, such as those for agriculture or renewable energy, allows them to command a premium and reduce direct price comparisons with less specialized competitors.
The company's commitment to innovation is evident in its continuous development of AI-driven forecasting tools and enhanced data visualization platforms, keeping them ahead of the curve. In 2024, Weathernews reported significant investments in R&D, particularly in machine learning applications for weather pattern analysis, which directly translates to more reliable and timely information for their clients.
Switching Costs for Customers
Switching costs for customers significantly influence competitive rivalry in the weather information sector. For enterprise clients, these costs can be substantial. For instance, integrating a new weather data provider into existing operational systems, such as logistics or agricultural planning software, requires considerable time and resources for data mapping, API adjustments, and validation. This integration complexity acts as a significant barrier, making customers hesitant to switch, thereby reducing direct competitive pressure on providers like Weathernews.
Proprietary data formats and specialized training also contribute to high switching costs. If a customer has invested in training their staff on a specific weather analytics platform or relies on unique data visualizations that are not easily replicated by competitors, the effort and expense to transition can be prohibitive. This customer lock-in allows established providers to maintain market share with less need for aggressive pricing or service differentiation.
Conversely, for consumer-facing weather applications, switching costs are generally very low. Users can easily switch between free or low-cost mobile apps based on preference or perceived accuracy. This low barrier to entry fuels intense competition among providers, often leading to price wars or a focus on user experience and unique features to retain customers. For example, in 2024, the market for mobile weather apps is saturated, with many offering similar basic forecasts, making customer loyalty a key challenge.
- Enterprise Integration: Businesses often face significant costs and time investments to integrate new weather data feeds into their existing operational systems, like supply chain management or aviation platforms.
- Data Format and Training: Proprietary data formats and the need for specialized user training create inertia, making it difficult and expensive for customers to switch to a new provider.
- Consumer Market Dynamics: In the consumer app market, low switching costs lead to intense competition, with providers focusing on features and user experience to attract and retain users.
Exit Barriers and Capacity
The weather information industry presents moderate exit barriers, primarily stemming from specialized technology and data infrastructure. Companies like Weathernews have invested heavily in proprietary observation networks and sophisticated analytical platforms, making it costly to divest or repurpose these assets. For instance, maintaining a global network of sensors and data processing centers requires significant ongoing capital expenditure and specialized technical expertise.
These substantial fixed assets and accumulated knowledge bases can trap companies in the market, even when profitability declines. This situation can lead to sustained overcapacity, as firms are reluctant to exit due to the sunk costs involved. Consequently, existing players may continue to operate at reduced efficiency, intensifying price competition and pressuring margins for all participants.
- High Capital Investment: Significant upfront costs for data acquisition, processing, and delivery systems create a barrier to exit.
- Specialized Knowledge: Deep expertise in meteorology, data science, and forecasting models is difficult to replicate or redeploy elsewhere.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments with clients in sectors like aviation and agriculture can lock companies into operations for extended periods.
- Brand Reputation: Established trust and a strong brand built over years are hard to abandon, even in challenging market conditions.
Competitive rivalry within the weather information market is significant, driven by a substantial number of players including AccuWeather, The Weather Company, and numerous national services. This intensity is somewhat moderated by market growth, which allows for expansion without direct aggressive battles, although this could change as the market matures. Weathernews differentiates itself through advanced forecasting and specialized industry solutions, aiming to reduce direct price comparisons and leverage high switching costs for enterprise clients.
| Competitor | Key Focus | 2024 Market Share (Est.) | Differentiation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| AccuWeather | Consumer apps, advertising | 15-20% | User experience, broad reach |
| The Weather Company (IBM) | Enterprise solutions, B2B | 20-25% | Data integration, IBM ecosystem |
| Weathernews | Advanced forecasting, industry-specific | 10-15% | Hyper-local accuracy, proprietary data |
| National Met Services | Public data, government mandates | Varies by region | Official source, broad accessibility |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for WeatherNews's services is significant, primarily driven by the availability of free or low-cost alternatives. Many government meteorological agencies, like the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) in the US, offer publicly accessible forecasts and data. These are often used by individual consumers and can meet basic needs for general weather information.
Furthermore, numerous free weather applications on smartphones and basic weather reports from general news channels provide readily available substitutes. While these might lack the depth and specialized insights that WeatherNews offers, they serve as viable alternatives for consumers and businesses with less critical weather-dependent operations. Their widespread accessibility and zero cost make them a compelling choice for many.
The perceived accuracy and comprehensiveness of these substitutes, while generally lower than specialized services, are often sufficient for many users. For instance, while WeatherNews might offer highly granular data for agricultural planning or aviation, a casual user might find a free app’s regional forecast perfectly adequate for daily activities. This broad availability dilutes the bargaining power of specialized weather providers.
Weathernews' specialized weather intelligence often presents a compelling performance-to-price trade-off. For sectors like maritime and aviation, where precision is paramount, the higher accuracy and customized data from Weathernews can significantly outweigh the cost, making cheaper alternatives less viable. For instance, a single maritime incident due to poor weather forecasting could cost millions, easily justifying Weathernews' premium services.
In contrast, for less critical applications, the appeal of free or low-cost substitutes is considerable. Users seeking general weather updates might opt for readily available mobile apps or basic online forecasts, where the convenience and lack of expense are the primary drivers. This segment of the market is highly sensitive to price, and Weathernews must demonstrate clear value to retain or attract these users.
Customers often struggle to quantify the precise value of Weathernews' advanced weather intelligence compared to readily available, less sophisticated alternatives. While users may recognize the benefits of proprietary data and specialized modeling, translating this into a willingness to pay a premium can be challenging, especially when budget constraints are a factor.
For instance, a small business might opt for a free weather app over Weathernews' subscription service, perceiving the core forecasting function as sufficient. This perception is amplified if the tangible cost savings of a cheaper substitute outweigh the potential, but less immediately obvious, benefits of Weathernews' deeper insights and risk mitigation tools.
Weathernews' success in mitigating this threat hinges on its ability to clearly articulate and demonstrate the return on investment for its advanced services. Highlighting how its intelligence prevents costly disruptions, optimizes operations, or enhances safety, can shift customer perception from a simple weather forecast to a critical business enabler.
Technological Advancements in Substitutes
Technological advancements are significantly boosting the capabilities of substitute weather information services. For instance, the increasing sophistication of AI in basic forecasting can now offer more accurate predictions at lower costs, directly challenging premium providers. This rise in quality for free or low-cost options could indeed narrow the performance gap, making them more attractive alternatives.
Crowd-sourced weather data, gathered through a network of personal weather stations and smartphone sensors, is becoming a more robust data stream. Coupled with the wider availability of high-resolution satellite imagery, these technologies empower substitute services to offer more granular and timely insights. This democratization of data directly impacts the value proposition of specialized weather intelligence companies.
Consider the growth in open-source weather data platforms. By 2024, many such platforms have seen user adoption rates increase by over 30% year-over-year, indicating a growing reliance on these more accessible resources. This trend suggests that the threat of substitutes, fueled by technological innovation, is intensifying.
- AI-driven basic forecasting offers increasingly accurate, low-cost alternatives to premium weather services.
- Crowd-sourced weather data from personal devices and sensors enhances the quality and granularity of free/low-cost options.
- Publicly available satellite imagery improvements provide richer data for substitute providers.
- By 2024, open-source weather data platforms experienced a user adoption increase of over 30% year-over-year, highlighting the growing threat.
Regulatory and Safety Requirements
Regulatory and safety requirements significantly shape the threat of substitutes for specialized weather data providers like Weathernews. In sectors such as aviation and maritime, stringent regulations often dictate the precision, reliability, and even the specific data formats that weather information must meet. For instance, the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) mandates specific standards for meteorological services that support air navigation. These requirements can act as a substantial barrier to entry for potential substitute providers who may not have the certifications or the robust infrastructure to comply.
If regulatory bodies mandate a certain level of accuracy or specific data formats for critical decision-making, it inherently limits the viability of uncertified or less robust substitutes. This, in turn, reduces their overall threat to established, specialized services like Weathernews, which have invested heavily in meeting and exceeding these standards. For example, in 2024, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) continued to emphasize the importance of advanced weather detection and reporting systems to enhance aviation safety, indirectly reinforcing the value of compliant providers.
The compliance burden can be substantial, requiring significant investment in technology, data validation, and quality assurance processes. This makes it challenging for new entrants offering less sophisticated or unproven weather solutions to gain traction in highly regulated markets.
- Aviation Safety Standards: ICAO Annex 3 specifies requirements for the provision of meteorological information for international air navigation, impacting how weather data is collected, processed, and disseminated.
- Maritime Regulations: The International Maritime Organization (IMO) also sets standards for maritime safety, which can include the need for accurate and timely weather forecasts for navigation and route planning.
- Data Integrity and Certification: Many sectors require weather data providers to undergo rigorous certification processes to ensure data integrity and reliability, a hurdle for many potential substitutes.
- Investment in Compliance: Meeting these regulatory demands often necessitates substantial capital expenditure on advanced sensing technology and data processing capabilities, a cost that substitutes may struggle to absorb.
The threat of substitutes for WeatherNews is substantial, fueled by readily available free or low-cost alternatives. Government agencies and free mobile apps offer basic forecasts, meeting the needs of many casual users. While these lack specialized depth, their accessibility and zero cost make them compelling choices, especially when perceived accuracy is sufficient for less critical applications.
Technological advancements are further empowering these substitutes. By 2024, AI-driven basic forecasting offered improved accuracy at lower prices, while crowd-sourced data and open-source platforms saw significant user growth, with some platforms experiencing over 30% year-over-year increases in adoption. This trend narrows the performance gap, making cheaper options more attractive.
Regulatory requirements, however, can mitigate this threat in critical sectors like aviation and maritime. Standards set by bodies like ICAO and IMO necessitate certified, reliable data, creating barriers for less sophisticated substitutes. For example, the FAA's continued emphasis on advanced weather systems in 2024 reinforced the value of compliant providers.
| Substitute Type | Key Features | Cost | User Base | Threat Level |
| Government Agencies (e.g., NOAA) | Publicly accessible forecasts, basic data | Free | General public, small businesses | Moderate |
| Free Mobile Apps | Convenient, localized forecasts | Free | Mass market, casual users | High |
| Open-Source Platforms | Community-driven data, growing sophistication | Free/Low-cost | Developers, researchers, tech-savvy users | Increasing |
| Crowd-sourced Data Aggregators | Real-time, hyper-local data from sensors | Variable (often free with ads or tiered) | Niche users, tech enthusiasts | Moderate |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a significant presence in the global weather information market demands substantial capital, particularly for building proprietary observation networks. Companies like Weathernews, which rely on extensive satellite and ground sensor infrastructure, face millions, if not billions, in upfront investment. For example, launching a single weather satellite can cost hundreds of millions of dollars.
These high capital requirements act as a formidable barrier to entry. Newcomers would struggle to match the data density and accuracy of established players without comparable investment, making it difficult to compete effectively. This financial hurdle significantly limits the number of potential new entrants capable of challenging incumbents.
While emerging technologies like AI-powered data analysis from existing public sources could potentially lower some barriers, the core infrastructure for proprietary, high-resolution data remains capital-intensive. The ongoing operational and maintenance costs further solidify the advantage of incumbents with established, amortized networks.
The threat of new entrants for Weathernews is significantly mitigated by its proprietary technology and deep expertise. Replicating Weathernews' advanced forecasting models and sophisticated data analysis capabilities, honed over decades, presents a formidable challenge. This includes substantial investment in research and development, safeguarding of intellectual property, and the accumulation of vast historical weather datasets, all of which create a high barrier to entry.
Weathernews operates in sectors like aviation and maritime, which are heavily regulated. Obtaining necessary certifications and ensuring compliance with stringent safety and operational standards, such as those mandated by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) or the International Maritime Organization (IMO), represents a significant barrier for potential new entrants. These requirements demand substantial investment in specialized technology, skilled personnel, and lengthy approval processes, effectively deterring many from entering the market.
Brand Loyalty and Established Relationships
Weathernews benefits from a strong brand reputation built over years of reliable service delivery. This established trust, coupled with long-standing relationships with a diverse corporate client base across sectors like aviation, agriculture, and energy, creates a significant hurdle for potential new entrants. These existing customer loyalties, often cemented through customized solutions and integrated services, make switching costs substantial for clients, thereby limiting the immediate threat of new competitors eroding Weathernews' market share.
New entrants would need to invest heavily in marketing and sales to even begin challenging Weathernews' entrenched position. For instance, in 2024, the global weather analytics market was valued at approximately $2.5 billion, with established players like Weathernews holding a significant portion due to their established client networks and service offerings.
- Brand Reputation: Weathernews has cultivated a strong and trusted brand image in the meteorological services industry.
- Client Relationships: The company maintains deep, long-term relationships with major corporate clients across various critical sectors.
- Switching Costs: The integration of Weathernews' services into client operations, coupled with the specialized nature of weather data, results in high switching costs for customers.
- Market Entry Barriers: New entrants face substantial challenges in replicating Weathernews' established market presence and client trust, requiring significant investment in marketing and sales to gain traction.
Access to Distribution Channels and Data Sources
New entrants face significant hurdles in accessing established distribution channels for weather data and services. For corporate clients, this often means competing for limited slots with existing providers or building new relationships from scratch, a process that can be time-consuming and costly. In 2024, many businesses rely on long-term contracts and integrated systems, making it difficult for newcomers to break in without offering a compelling and proven alternative.
Building a strong mobile app presence is another challenge. The app stores are crowded, and gaining visibility requires substantial marketing investment. Securing partnerships with key industry players, such as airlines or agricultural firms, is crucial but often reserved for established companies with a proven track record. For instance, WeatherTech, a major player, has built extensive partnerships over years, creating a barrier for new entrants.
Accessing high-quality, diverse raw weather data is also a formidable obstacle. Many critical data sources are proprietary, held by large meteorological organizations or specialized data providers, and come with substantial licensing fees. For example, satellite imagery or advanced radar data can be prohibitively expensive for startups. In 2024, the increasing reliance on AI and machine learning for weather forecasting further emphasizes the need for vast, clean datasets, which are often difficult and costly for new companies to acquire.
- Distribution Channel Barriers: Newcomers struggle to secure prime placement in corporate procurement systems and gain traction with consumers who often stick to familiar weather apps.
- Partnership Acquisition: Establishing crucial partnerships with industries like aviation or agriculture requires a proven history of reliability and data accuracy, which new entrants lack.
- Mobile App Visibility: The cost and effort to achieve significant visibility for a new weather app in crowded app stores are substantial.
- Data Source Costs: Accessing proprietary and high-quality weather data, essential for competitive forecasting, involves significant licensing fees that can deter startups.
The threat of new entrants for Weathernews is generally low due to substantial capital requirements for infrastructure and R&D. The need for proprietary data networks, advanced forecasting models, and regulatory compliance creates significant barriers.
Established brand reputation and deep client relationships, especially in sectors like aviation and maritime, foster high switching costs for customers. For instance, in 2024, the global weather analytics market, valued at approximately $2.5 billion, is dominated by incumbents with established networks.
Access to proprietary data sources and the cost of mobile app visibility also deter new players. Building essential industry partnerships requires a proven track record, which newcomers lack, further solidifying the low threat of new entrants.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Building proprietary observation networks (e.g., satellites) costs hundreds of millions. | High; requires massive upfront investment. |
| Technology & Expertise | Advanced forecasting models and data analysis capabilities are difficult to replicate. | High; decades of R&D and data accumulation are needed. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meeting aviation (ICAO) and maritime (IMO) standards demands specialized investment. | High; lengthy approval processes and compliance costs deter entry. |
| Brand Reputation & Client Loyalty | Established trust and long-term corporate relationships create high switching costs. | High; difficult for new entrants to gain market share. |
| Distribution & Partnerships | Accessing established channels and securing industry partnerships is challenging. | High; requires proven reliability and significant marketing investment. |
| Data Access | Acquiring high-quality, proprietary weather data involves substantial licensing fees. | High; costly for startups to obtain essential datasets. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Weathernews Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages a robust combination of data sources, including internal operational metrics, customer feedback surveys, and global meteorological data repositories. This comprehensive approach ensures a nuanced understanding of competitive pressures within the weather information industry.
